Ultrasound of the pleural cavity is used if diseases in this structure and adjacent tissues are suspected. In pulmonology, ultrasound examination belongs to the auxiliary diagnostic methods: ultrasound is not able to penetrate deep into the lungs. But sonography, compared to x-rays, is better at showing the surface layers of organs inside the chest.
What is the pleural cavity?
The pleura is an elastic thin membrane that covers the outside of the lungs and is formed by connective serous tissue. The pleural cavity is a gap-shaped space between the connective membrane and the lungs. It is filled with pleural fluid and is involved in the functioning of the respiratory system.
Reference! The fluid produced by the pleura prevents air from entering the chest cavity, reducing friction between the sternum and lungs.
The volume of the lungs can change due to the pleural cavity.
What conclusions does the specialist make based on the results of such an ultrasound?
This diagnostic method can detect the following diseases:
- pneumonia,
- pleurisy,
- adhesive process,
- metastases in the lungs and pleura,
- fibroma,
- lipoma,
- pleural effusion (accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity as a consequence of inflammation),
- blood or purulent clots in the pleural cavity, exudate (damage to the pleura),
- tumors (benign and malignant), inflammatory processes,
- pulmonary infarction,
- pulmonary hemorrhage.
When is an ultrasound performed?
This type of ultrasound examination plays an important role in the timely detection and treatment of diseases of the bronchopulmonary system, as well as in assessing their condition. In addition, ultrasound of the pleura and lungs is performed to accompany the biopsy for additional control.
The difference between this type of diagnosis and other types of ultrasound is that it is not prescribed for prevention - it is used only after the patient complains of certain symptoms , for example:
- chest pain;
- difficulty and pain during breathing;
- prolonged persistent cough, usually dry;
- presence of blood in sputum;
- large volume of sputum and its presence for a long time;
- dyspnea.
In addition, ultrasound of the slit-like space between the layers of the pleura is also prescribed in the case of a number of medical indications:
- chest and lung injuries;
- diagnosis of “pleurisy”, especially in the presence of a quiet percussion sound in this disease;
- during breathing, lung lag was detected;
- any suspicion of tumors or neoplasms;
- high occupational risk of bronchopulmonary diseases;
- initial stages of tuberculosis;
- fibrosis;
- sarcoidosis;
- inflammatory diseases;
- bronchitis and other lesions of the respiratory system.
Pathologies found during examination
Pleural effusion is the accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity. Effusion is a watery formation, and therefore it is invisible during ultrasound, but the pleura clearly shows the boundaries of fluid accumulation, which are noticed when the patient breathes.
Determining the fluid accumulated in the pleural cavity is important for the diagnostic result. During research, the sonography method is not always effective, because there are no substances in the transudate that help to detect it.
Because of this, such a transudate is called anechoic. The amount of this fluid is used to judge the severity of hypothyroidism or cirrhotic lesions in the liver. The accumulation of proteins in the exudate gives a chance to notice it during an ultrasound examination.
Specifics of purulent pleurisy during ultrasound examination. Doctors call the concentration of pus discharge in the pleural cavity pyothorax, empyema, pleurisy. Ultrasound examination in this case shows sharp and round angles between the chest wall and the accumulation of purulent discharge. Do not forget that such signs are characteristic of both pleural effusion and pulmonary abscess. In this case, empyema is diagnosed by its medium or low echogenicity, and the pleura has a slight thickening.- Pleural metastases. With ultrasound examination, metastases in the pleural cavity are similar in structure to pleural effusions. A large number of metastases are visually detected when examining the diaphragm or pleura above the ribs. Metastases are usually divided into low-echoic and medium-echoic. Externally, these formations resemble round and semicircular polyps. As a rule, metastases indicate that the patient has cancer of the bronchi or lungs.
- Pneumothorax. Pneumothorax is a pathological condition characterized by the presence of air in the pleural cavity. Very important when diagnosing pneumothorax is the immobility of the lung during the act of breathing, which can be seen in dynamics. But people with asthma or patients with pulmonary emphysema may also have a similar symptom, so the specialist needs to be careful when collecting anamnesis so as not to confuse these diseases.
- Tuberculosis. With this disease, the specialist conducting the ultrasound examination can observe hamartochondromas (spherical formations with clear, smooth edges). At some stages, these formations may have capsules - protective shells in which they are closed.
Also, with tuberculosis, a high acoustic density is created, which is formed by small-celled areas of calcifications. The first stage of tuberculosis can be detected by palpating the lymph nodes in the aorta area. To the touch they will look like oval formations containing liquid. In the last stages of tuberculosis, the echogenicity of the nodes increases.
What are they watching?
During the examination of the bronchopulmonary system and the pleural cavity, the doctor will definitely assess the condition of the organs and determine such indicators as:
- the volume of the pleural cavity and the fluid present in it;
- the position of the cavity shell, as well as its thickness;
- properties of the liquid, including its concentration;
- location of neoplasms, presence of fluid accumulations;
- echogenicity and condition of the pleural layers.
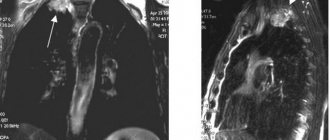
Appendix 1. Chest ultrasound with examples of pleural effusion.
The image above shows the effusion:
- A: none;
- B: small;
- C: moderate,
- D: big.
- double arrows indicate pleural effusion measurement;
- thick arrows indicate aperture;
- X: lung;
- * pleural effusion.
Lung cancer on ultrasound
Air tissue reflects 99% of ultrasound waves, only tumors are visible immediately under the visceral pleura.
Central lung cancer is often associated with atelectasis or recurrent pneumonitis.
When there is atelectasis, consolidation, pleural effusion, the ultrasound beam penetrates into deeper zones.
In patients with lung cancer, the presence of pleural effusion suggests stage T4 disease.
In rare cases, the causes of effusion are different - impaired lymphatic drainage, atelectasis, hypoproteinemia.
Aspiration of fluid, cytological and biochemical analysis will help make an accurate diagnosis.
Rupture of the pleural line and lack of sliding may indicate invasion of the chest wall.
The bulk of the tumor receives nutrition through neoangiogenesis from the bronchial artery.
Neoangiogenesis involves an ugly vascular architecture - chaotically disordered, tortuous.
The spectrum is monophasic with small fluctuations in systole/diastole, variable flow direction.
Large cancerous tumors, larger than 5 cm, often have an area of necrosis in the central zone.
When the area of necrosis is associated with the bronchial tree, hyperechoic gas bubbles appear.
Preparation
Diagnosis of the pleura and lungs using ultrasound does not require any preparatory measures from the patient . However, your doctor may recommend taking medications that help remove mucus from the lungs. These pharmaceutical products may have different names, but their action is based on the work of one of the following active substances:
- acetyl or carbocisteine;
- guaifenesin;
- butamirate;
- ambroxol;
- Bromhexine.
You can use herbal products with thyme, sage, eucalyptus, plantain, anise and ivy.
How do they do it?
Different types of ultrasound are very similar to each other. As a rule, the doctor applies a small amount of gel - a conductor - to the area under study, and then examines it using a sensor. However, to examine the pleural cavity and lungs, a small-diameter probe is used for a detailed study of the intercostal spaces . This method of studying the pleural cavity differs from studies of other organs.
Good visualization can be achieved by placing the sensor in a parallel plane to the ribs, and asking the patient to raise his arms up. Sometimes the patient is asked to stand up.
Reference! Typically, ultrasound examination of the lungs and pleura occurs in a sitting position.
During the procedure, to clarify certain indicators or if a number of complications are suspected (the presence of pathological fluid or pus), the doctor can explain to the patient the need to change the position.
The duration of an ultrasound scan is from 10 to 20 minutes; in each specific case, the time depends on the severity of the detected diseases. If there are no pathologies or suspicions of them, then no one will detain the patient.
Video
The video below will give an idea of the procedure for performing an ultrasound of the pleural cavity using the example of identifying pleural fluid.
Sample for abdominal organs
Liver:
- sizes (increase/decrease relative to the norm);
- measurements of three lobes and oblique-vertical measurements of the right lobe of the liver;
- contour (smooth / uneven);
- capsule (normally not visualized);
- parenchyma (structure, homogeneity);
- the presence of focal compactions;
- diameter of the main vessels (hepatic portal vein, inferior vena cava, abdominal aorta, hepatic veins);
- nature of the vascular bed.
Gallbladder and bile ducts:
- bubble size and shape;
- wall thickness;
- presence of formations (description if available);
- diameter of the main bile duct.
Pancreas:
Spleen:
- size;
- splenic index;
- homogeneity of echostructure.
The stomach and intestines may not appear in the ultrasound report, because these organs are not usually examined.
Ultrasound can only reveal pathological symptoms, such as fluid deposits or a “hollow organ” symptom.
Often this form is accompanied by photographs taken during the examination. I use the information from the document, the doctor compares the data obtained with the normative ones, which allows the specialist to judge the condition of the organs
Price and where to make it?
You can examine the pleura and lungs using ultrasound either for a fee or free of charge.
For free
If you have a compulsory medical insurance policy and a referral for the procedure from your attending physician, then it is better to undergo an ultrasound for free in any city clinic equipped with the appropriate equipment.
Paid
If there is no referral or you don’t want to waste time in queues at municipal clinics, then an ultrasound scan can be done for a fee at any private clinic or medical diagnostic center offering similar services. Comparative average price for ultrasound procedures:
- Moscow (ultrasound of the pleural cavity and lungs) – from 700 to 3500 rubles;
- St. Petersburg - from 400 to 1950 rubles;
- regions – from 600 to 1500 rubles.