When we come to the gynecologist, with complaints or for prevention, we are always asked to lie down on a chair for examination, so that the doctor takes smears for analysis. A so-called flora smear is absolutely always taken. The result, if the laboratory is nearby, can be in 10-15 minutes. I somehow got a paid appointment with a doctor, and during my stay in his office, they also analyzed my smear. A flora smear shows the number of leukocytes, squamous epithelium, mucus, as well as the presence of fungi and Trichomonas. If there are no fungi or trichomonas, but the number of leukocytes is increased, the doctor will prescribe a local broad-spectrum antibacterial drug. That is, one that is guaranteed to defeat any microorganisms. And it doesn’t matter which microorganisms caused the inflammation. The medicine will "kill" them all.
But sometimes this stroke alone is not enough. You need to find out the exact set of pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms, their quantity, and also determine which antibacterial medicine is best to treat it. Then a tank is taken to culture the cervical canal for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics (ab).
Cultures are usually prescribed if a local antibacterial drug does not relieve inflammation, and especially often in pregnant women.
Why is it taken from expectant mothers?
Some microorganisms (for example, candida albicans) provoke infection of the membranes in expectant mothers, resulting in infection of the fetus and (or) premature rupture of the amniotic sac with loss of water. And during childbirth or during a caesarean section, these microorganisms can provoke the development of endometritis, and sometimes even sepsis - blood poisoning.
What happens if the culture is bad in a woman who is not pregnant? An infection in the body is always bad. If there are symptoms of inflammation (pathological discharge, itching, hyperemia - redness of the labia), then you need to be treated. If this is not done, the infection may spread to the bladder (cystitis will occur) or even the kidneys - then there will be pyelonephritis, a very serious disease.
Interpretation of results
The culture results are given to the patient in 3-5 days.
The data received is deciphered by a doctor. You should not try to interpret the quantitative values of various microorganisms on your own. Some of them can normally inhabit the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, which does not require treatment. In healthy patients, beneficial flora predominates in the smear, which consists of lactobacilli in an amount of at least 107
. Escherichia coli and enterococci may also be present, but they are not actively growing and are determined by the number
102
.
An unfavorable diagnostic result is indicated by the detection of the following microorganisms in a smear:
- Escherichia coli;
- Enterococci;
- Yeast-like fungi;
- Staphylococcus;
- Proteus;
- Trichomonas;
- Gonococci;
- Gardnerellas;
- Leptothrix and others.
Particular attention is paid to patients whose smear contains diphtheroids. They indicate vaginal dysbiosis and require immediate treatment
Effective drugs are selected for each type of microorganism colony individually.
Bacterial culture is an informative analysis that allows you to determine the causative agent of the disease and its sensitivity to medications. This analysis is most often taken in gynecology and urology. This research method allows you to diagnose various inflammatory processes and diseases and prescribe effective treatment.
The female genital organs contain beneficial bacteria and microorganisms to maintain the necessary balance and acidic environment. They act as a barrier to various viruses and microorganisms. Due to various factors, pathogenic microorganisms become more numerous than beneficial microflora, resulting in an inflammatory process.
Bacteriological culture (bacteriological culture) is a method for diagnosing pathologies caused by bacteria. The main purpose of bacteriological culture is to identify harmful bacteria above the permissible limit, causing various diseases and inflammatory processes.
However, it should be noted that a small amount of harmful bacteria may be present in the vagina, which is associated with female physiology. The doctor takes a sample from the mucous membrane of the genital organs, and then places it in a special nutrient medium, where the necessary conditions are provided.
Bacterial culture from the vagina helps determine the composition of the microflora. If pathogenic microorganisms are present in it, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment.
Separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal
Many women are interested in what RDV or separate diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity and CD is in gynecology. This technique is carried out for several purposes:
- Perform diagnostics. RDV allows you to take biological material for laboratory research in pathologies such as cancer, sarcoma and others.
- Treatment. The method is used to remove various tumors in the cavity of the reproductive organ and cervical canal.
Among the indications for separate diagnostic curettage in gynecology are hyperplasia of the female genital organs, uterine bleeding, endometritis, fibroids, tumors, polyps, fetal freezing, uterine synechiae and other conditions. In pregnant women, this study is carried out with extreme caution.
RDV is performed under local or general anesthesia, which depends on the scope of the intended intervention. The session lasts, as a rule, no more than half an hour. First, a scraping is taken from the cervical canal, then from the cavity of the reproductive organ. The samples are placed in different tubes and sent to the laboratory for further testing.
How are the results of bacteriological analysis interpreted?
Based on the results of the bacteriological analysis, a special conclusion is drawn up, drawn up on a form. It displays, first of all, information about the condition of the cervical canal: the microorganisms inhabiting this cavity are listed. If the result is positive (normal), there are no fungal organisms in the cervical canal, but lacto- and bifidobacteria are present in sufficient quantities. There must be at least 107 of them. When E. coli is detected, the norm is determined by the established standard indicator. Their presence is allowed in quantities not exceeding 102 units.
The presence of single (individual) enterococci in the cavity organ is also considered normal. Deviations (pathologies) are the presence of the following microorganisms of bacteriological type:
- Exceeding the normal amount of Escherichia coli and individual enterococci;
- The presence of yeast fungi (especially those containing mycelium);
- Staphylococcus (any type, including aureus and epidermal);
- Citrobacter;
- Protea;
- Gonococcus;
- Trichomonas;
- Gardnerellas;
- Leptothrix.
You can learn more about microorganisms such as staphylococcus from this video:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=3Zw3VpEcFJY
Tank. culture using conventional techniques may not show the presence of ureplasma, mycoplasma and chlamydia in the uterine cavity. These microorganisms develop at the intracellular level. To detect them, specialists conduct research using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR). In addition to the listed data, the results of bacteriological analyzes display the presence of bacteria and their quantity. Based on the results of bacterial culture, leading experts determine the condition of the cervical part of the uterine body, as well as the cervical canal. Inflammatory processes can be caused by various reasons, for example, decreased immunity, hormonal imbalance, etc.
The purpose of cultivating microorganisms and its significance for diagnosis
In addition to water, air, soil, which contain various microorganisms in varying concentrations, including those that bring disease (pathogenic), many branches of medical science are interested in microbes living on the skin and mucous membranes of the human body, which can be represented by:
- Permanent inhabitants who do not pose any danger to humans, that is, the normal microflora of the body, without which we simply cannot live. For example, the disappearance of bacteria living in the intestines and participating in the digestion process leads to dysbiosis, which is not easy to treat. The same thing happens with the disappearance of vaginal microflora. It is immediately populated by opportunistic microorganisms, gardnerella, for example, which causes bacterial vaginosis (gardnerellosis);
- Opportunistic pathogenic flora, which causes harm only in large quantities under certain conditions (immunodeficiency). The above-mentioned gardnerella is a representative of this type of microorganism;
- The presence of pathogenic microbes that are not present in a healthy body. They are alien to the human body, where they enter accidentally through contact with another (sick) person and cause the development of an infectious process, sometimes quite severe or even fatal. For example, an encounter with the pathogens of syphilis - no matter what, it is treated at first, but (God forbid!) it will unleash cholera, plague, smallpox, etc.
Fortunately, many of them have been defeated and are currently kept under seal in special laboratories, but humanity must be prepared at any moment for the invasion of an invisible enemy capable of destroying entire nations. Bacteriological culture in such cases plays, perhaps, the main role in identifying the microorganism, that is, determining the genus, species, type, etc. (toxiconomic position), which is very important for the diagnosis of infectious processes, including sexually transmitted diseases.
Thus, sowing methods, like nutrient media, are different, however, they have the same goal: to obtain a pure culture without foreign impurities in the form of microbes of other classes that live everywhere: in water, in the air, on surfaces, on humans and inside it.
Determination of bacterial culture
Bacteriological culture means a special microbiological study that is carried out in a laboratory. The test sample is taken from biological material, which is sifted at a certain temperature. The purpose of such a study is to identify the presence of microorganisms and determine their quantity. Subsequently, the doctor prescribes treatment based on the data obtained.
Bacteriological analysis is widely used in oncology, gynecology, otolaryngology, surgery, urology and other fields.
The indication for bacteriological examination is an inflammatory process in human organs and systems and suspicion of sepsis.
The following bacteriological material can be taken for research:
- Sputum.
- Mucus from the throat.
- Mucus from the urethra.
- I'm peeing.
- Sperm.
- Breast milk.
- Contents of the cyst.
- Cerebrospinal fluid.
- Bile.
- Blood.
- Material separated from a wound.
- Contents of inflammatory foci.
- Cal.
- Mucus from the nasopharynx.
The following microorganisms are sown from each listed biological material:
- Mucus from the urogenital tract is examined for gonococcus, trichomonas, Candida fungi, ureaplasma, Neisseria gonorrhoeae fungi, mycoplasma, Trichomonas vaginalis fungi, listeria. The condition of the bacterial flora will also be checked here.
- The blood is examined for sterility.
- The mucus of the throat and nose is checked for Listeria, Haemophilus influenzae, hemolytic streptococci, meningococcus, Corynobacter diphtheria, pneumococcus, Staphylococcus aureus.
- Wound discharge, purulent discharge, and biopunctate are examined for Pseudomonas aeruginosa and pseudomonas.
- Feces are checked for Yersinia, salmonella, typhoid bacteria, opportunistic intestinal infections, and foodborne illnesses. The stool is also examined for intestinal dysbiosis.
- A smear, breast milk, urine, scraping, bile, sperm, joint fluid are checked for bacterial flora.
What is bacterial culture for microflora?
This is a laboratory study of biological material by sowing it on a nutrient medium. The analysis is necessary for the timely identification of pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms and determination of a productive treatment regimen. The gynecologist collects biological material from the vagina, cervix (for women), the urologist - from the external opening of the urethra (for men). The resulting sample is applied to a sterile glass, dried and sent to the laboratory for further examination under a microscope. The doctor collects biomaterial from areas of pathology.
Bacteriological seeding is considered a cultural method. To determine the reaction of pathogenic flora to drugs, biological material is placed in a climate favorable for potential pathogens. Selective media are used for growing intestinal bacteria; thioglycolate and Sabouraud are considered universal. Sowing helps to perform a qualitative and quantitative analysis of the composition of the flora, since microorganisms are painted in different colors. In this way, the information content of the method increases, speeding up the diagnosis. Other examples:
- Clotted horse serum helps identify the types of bacteria that cause diphtheria.
- Bile salts identify pathogenic pathogens that cause acute intestinal disorders.
- Differential diagnostic media are necessary to decipher the bacterial culture.
- Carp in the oven - recipes with photos. Preparing baked stuffed fish
- How to grow eyelashes at home
- Salicylic-zinc acne paste - reviews. Instructions for use of salicylic-zinc paste for acne
What is it needed for
The therapeutic goal of bacterial flora testing is to promptly detect increased activity and spread of a pathogenic infection in the body, select medications that can completely destroy the pathogenic flora, and restore the patient’s health. Bacteriological analysis is often carried out in the following areas of modern medicine:
- Gynecology. Based on the results of the study, the composition of the vaginal microflora, the presence of leukocytes, red blood cells in the discharge, and the nature of pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases are determined.
- Otolaryngology. In case of frequent runny nose and recurrent sore throat, a smear on the flora is performed from the nose and back wall of the pharynx, tonsils to determine the nature of the pathogen and an antibiotic to destroy it.
- Oncology. A smear for oncocytology determines the inflammatory process, the presence of cancer cells and their number, the presence of malignant tumors and other changes in the structure of the cells of the mucous membrane of the woman’s genital organs.
- Traumatology, surgery. To exclude suppuration and abscesses, the contents of the wound surface are examined under a microscope. Once microbes are identified, it is easier to select an antibiotic to treat them.
If an inflammatory process in the pelvic organs is suspected, doctors prescribe a flora culture. Among the disadvantages of laboratory testing is the long wait for results from 3-5 days to several weeks, depending on the pathogenic agent . To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). After or simultaneously, it is recommended to conduct an antibiogram to determine the resistance of microorganisms to certain antibacterial drugs. Essentially, this is a test for sensitivity to antibiotics.
Indications
Performing a flora culture is an important component of a comprehensive diagnosis and speeds up the final diagnosis. The main types of the studied methodology:
- urogenital bacterial culture;
- sowing for flora from an open wound;
- bacterial culture from the nose, ear, pharynx, eye;
- culture of urine, milk, bile, sperm, feces;
- bacterial culture for staphylococci, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, chlamydia.
Culture for flora is carried out in urology and gynecology when infectious and inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs are suspected, for example, colpitis, pelvioperitonitis, endometritis, adnexitis. In oncology, such a study checks for the presence of cancer cells; in otolaryngology, it detects infections of the oropharynx and nasal passages. Based on the results of laboratory research, the following pests can be identified:
- nonspecific microbes: Escherichia coli, enterobacteria, Klebsiella, hemophilic microorganisms;
- anaerobic microbes: pyogenic cocci, trichomonas, chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, gonococci;
- staphylococcal infection;
- yeast-like fungi.
Biomaterial
To sow the flora, it is allowed to take any biological fluid from a man or a woman. Biomaterial for all categories of patients can be:
- mucus from the nasopharynx;
- vaginal discharge;
- stool sample;
- discharge from the cervical canal, urethra;
- sputum from the lungs;
- contents of cysts, purulent sinuses, etc.;
- blood;
- urine;
- sperm (ejaculate);
- contents of wounds and other foci of skin pathology.
Sowing result
At the end of the study, the laboratory technician must receive two assessments from the test sample:
- Qualitative (whether there is a suspected pathogen in the biological material being studied).
- Quantitative (what concentration was detected).
Qualitative assessment is deciphered using degrees of growth. There are only four of them.
- First degree: slight growth on a fairly liquid medium, no growth at all in a solid medium.
- Second degree: growth occurs on a dense medium (about 10 colonies).
- Third degree: growth on a dense medium (10-100 colonies) is also assessed.
- Fourth degree: more than 100 colonies.
When considering opportunistic flora, the first two degrees are not considered diseases. Most likely, this is ordinary contamination of biological material. The third and fourth degrees make it possible to identify the cause of the disease.
If the analysis shows a pathogenic flora, then all four listed degrees are taken into account.
Quantitative assessment is accepted conditionally and is determined in CFU. The characteristic means a community of bacterial cells that have been able to grow into a colony.
Colonies and CFU/ml are related as follows:
- 103/ml is considered 1 colony;
- 104/ml takes 1-5 colonies;
- 105/ml is a sufficient growth of 5-15 colonies;
- 106/ml is considered to have more than 15 colonies.
Quantification is just as important. It helps to determine the degree of contamination and monitor the treatment performed.
There are approximate deadlines for the readiness of sowing results:
- Flora: 4-7 days.
- Mucus from the nasopharynx: 5-7 days.
- Feces: 4-7 days.
- Urogenital material: 4-7 days.
- Blood to determine sterility: 10 days. However, here we can say a preliminary result after just three days.
Bacterial culture is a very important procedure that provides good information about the causative agent of human disease. If it was prescribed by a doctor, then the test must be completed.
Common Terminology in Cytology Response
In the process of gynecological examination and obtaining cytological analysis answers, the following terminology is used:
- CBO - condition of the cervix without deviations from the norm.
- Cytogram of inflammation - cervicitis is present (inflammatory process of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal).
- Leukocyte infiltration - an increase in the concentration of white cells, presumably vaginosis, exocervitis or endocervitis is present.
- Koilocytes are cells characteristic of the flow of HPV (human papillomavirus).
- Proliferation refers to the process by which cells divide at an accelerated rate. A similar reaction is characteristic of intrauterine inflammation.
- Leukoplakia - the material contains signs of pathology. Despite intracellular changes, there is no development of cancer.
- Metaplasia is the process of replacing cells of one type with another. It is not a pathology if a woman underwent treatment for non-cancer uterine changes during menopause. The process accompanies the body condition of patients who have been in menopause for more than 6 years.
- Dysplasia is a directly precancerous phenomenon.
If the answer received raises doubts in the doctor’s mind, the specialist will prescribe an even more thorough examination to clarify the clinical situation. A woman takes a smear to clarify the nature of the flora, and undergoes an analysis to determine sexually transmitted diseases.
When a sample of material contains atypical cells, laboratory technicians use the following abbreviations:
- ASC-US - for unknown reasons, a change in the structure of the squamous epithelium occurs. It is often detected in middle-aged women during the premenopausal period, since it is characterized by hormonal instability.
- AGC - change in the structure of cylindrical cells (occurs with vaginosis, characteristic of other inflammatory disorders). The cause-and-effect relationship is clarified through additional diagnostic measures.
- L-SIL - the presence of a small number of degenerated cells of non-malignant origin. The patient will have to undergo a colposcopy procedure, supplemented by a biopsy.
- ASC-H - intracellular changes indicating the presence of precancerous pathology or an already begun tumor process.
- HSIL - smear contains flat cells, serves as a precancerous condition. Immediate therapeutic measures are carried out, thereby preventing the process of degeneration of the pathology into cancer.
- AIS - detection of cylindrical cancer cells. The patient is urgently treated. If the presence of degenerated cells is laboratory proven, this fact must be recorded in the analysis response, specifying the type of changes.
When the transcript of the analysis response does not contain specific markings, the smear indicates the normal state of the female body. When establishing the nature of the disorder, the doctor focuses on the results of different types of diagnostics.
Preparation for analysis
For maximum information content, it is recommended two days before collecting the material to refuse:
- sexual intercourse and use of vaginal methods of contraception;
- douching, administration of vaginal creams and suppositories.
It is advisable to carry out a smear at least two weeks after discontinuation of antibacterial drugs due to the high risk of false negative results during antimicrobial therapy.
It is also recommended to postpone the collection of material for 2-3 days if a colposcopy was performed the day before.
The period of menstruation and two days after its end are considered contraindications for this study.
Features of the structure of the female reproductive system
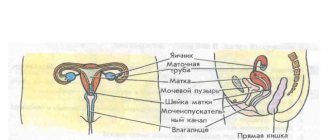
In a woman, the cervical canal plays an important role during pregnancy and childbirth. Its average length is usually 3-4 cm.
Fungi and microbes live in the female vagina. The uterine cavity is sterile. Certain cells are responsible for the production of natural mucus. The amount of female sex hormones can have a direct impact on the quality and properties of this mucus. At the beginning and end of menstruation, a viscous acidic environment is characteristic. At this time, it completely blocks the cervical canal. Those microbes that enter an acidic environment die, and sperm completely lose their motility, as well as their ability to fertilize. In the case of maximum estrogen levels, the mucus acquires an alkaline liquid environment. In the middle of the cycle, sperm together with eggs give birth to a new life. After conception, progesterone is produced.
The female vagina is lined with such epithelium, which is first renewed, then matures, and is rejected at the end of the cycle. The next population of cells will appear every 4-5 days. The composition of these cells will depend on several factors, namely:
- menstruation phase;
- menstrual cycle.
How to donate a sowing tank
In fact, the question of how to donate a sowing tank is quite relevant. And this is not surprising. The quality of the result directly depends on the correctness of the collection of research material. So how to properly pass bacterial culture?
How to prepare for bacterial sowing? When collecting material, you should adhere to the following rules:
- the utensils used for collection must be sterile;
- the collection should be carried out before starting antibiotic treatment;
- delivery of the material to the laboratory must be prompt, otherwise the microorganisms will simply die (feces, for example, must be delivered warm);
- when collecting urine, an average portion of urine taken after morning hygiene procedures should be used (urine delivery to the laboratory must be carried out within 2 hours);
- When taking a swab from the nose and throat, you should not brush your teeth, drink, eat, or rinse your nose and mouth with disinfectant solutions;
- feces must be collected into a sterile container using a sterile spatula (delivery to the laboratory must be carried out within 5 hours);
- blood may be drawn before starting antibiotics;
- sputum is collected in the morning on an empty stomach during a coughing attack with mucus in a sterile container (before collection, you should brush your teeth; the material should be delivered to the laboratory within an hour);
- discharge from the genital organs in women is made no earlier than 14 days after menstruation and no earlier than a month after stopping antibiotics (you cannot urinate for 2 hours before collecting material), men cannot urinate for 4-6 hours before taking a sample;
- It is also worth noting that tank sowing in children is no different from “adult” methods. The material for the culture tank can be taken from any mucous membranes of the child, as well as any biological fluids can be collected for him.
When is tank sowing prescribed and how to understand the answers?
Name of microorganism and its quantity
Patients do not prescribe bacteriological analysis to themselves; this is done by the doctor if he has suspicions that the problems of a patient presenting various complaints are associated with the penetration of a pathogenic pathogen into the body or with the increased reproduction of microorganisms that constantly live with a person, but exhibit pathogenic properties only in certain conditions. Having passed the test and after some time received an answer, a person gets lost and sometimes gets scared when he sees incomprehensible words and symbols, therefore, to prevent this from happening, I would like to give a brief explanation on this issue:
- The first point of conclusion, as a rule, is the name of the pathogen in Latin, for example, Escherichia coli. This is E. coli, it is a natural inhabitant of the intestines and in acceptable quantities does not cause any harm;
- The next point is the concentration of the microorganism. E. coli – abundant growth (1x10^6 or more) norm – less than 1x10^4;
- Next – pathogenicity: the flora is opportunistic.
When examining biological material for the presence of pathogenic microorganisms, the answer can be negative or positive (“bad tank culture”), since the human body is only a temporary shelter for them, and not a natural habitat.
Sometimes, depending on what material is to be inoculated, you can see the number of microorganisms expressed in colony-forming units per ml (one living cell will grow a whole colony) - CFU/ml. For example, urine culture for bacteriological examination under normal conditions gives up to 103 CFU/ml of all identified bacterial cells, in doubtful cases (repeat the analysis!) - 103 - 104 CFU/ml, in case of an inflammatory process of infectious origin - 105 or higher CFU/ml. About the last two options in colloquial speech, sometimes they are simply expressed: “Bad tank sowing.”
How to “find control” against a pathogenic microorganism?
Simultaneously with the inoculation of the material in such situations, the microflora is inoculated for sensitivity to antibiotics, which will give a clear answer to the doctor - which antibacterial drugs and in what doses will “scare” the “uninvited guest”. There is also a decryption here, for example:
- The type of microorganism, for example, is the same E. coli in the amount of 1x10^6;
- The name of the antibiotic with the designation (S) indicates the sensitivity of the pathogen to this drug;
- The type of antibiotics that do not act on the microorganism is indicated by the symbol (R).
Bacteriological analysis is of particular value in determining sensitivity to antibiotics, since the main problem in the fight against chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, etc. remains the selection of effective treatment that does not harm the body and does not impact the patient’s pocket.
Table: Alternative example of tank culture results identifying effective antibiotics
Uterine fibroids symptoms
In general, uterine fibroids are a benign tumor that arises in the muscular layer of the uterus, the myometrium. Characteristic manifestations of fibroids are pain in the lower abdomen, intermenstrual bleeding, heavy and prolonged periods and pain during bowel movements.
When should you visit a doctor?
Uterine fibroids often develop in young girls, including those who have not given birth and are not sexually active, as well as in adult women aged 25 years or more. Since it is impossible to predict the appearance of fibroids, all women, starting from the moment their periods appear, should regularly visit a gynecologist and undergo all necessary examinations, including ultrasound.
Treatment of uterine fibroids
If a fibroid is detected, we begin to monitor it. Signs of active tumor growth are an indication for the prescription of medications, including drugs that cause a reversible condition similar to menopause. Since the growth of fibroids depends on female sex hormones, it stops during artificial menopause.
Consequences of an advanced disease
In advanced cases, the myomatous node can become necrotic and cause septic conditions, a fatal condition. But even in the absence of such serious complications, fibroids can significantly worsen the quality of life, for example, causing infertility.
Prevention of female diseases
Gynecologists insist that to reduce the risk of developing various pathologies of the cervix and cervical canal, a woman must follow simple rules of prevention. These include the following recommendations:
- Regular visits to the gynecologist.
- Carrying out cytological studies.
- Timely treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases.
- We must try to prevent artificial termination of pregnancy. For this purpose, contraceptive methods such as condoms, cervical cap, pills, etc. are used.
- It is important to respect the culture of sexual life.
- If the menstrual cycle is disrupted, it is imperative to look for the reasons.
- Compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene.
- If any complaints regarding women's health occur, it is important to immediately contact a gynecologist.
These simple rules will help you stay healthy and prevent dangerous diseases such as cancer. Every girl should remember the importance of preventive examinations with a gynecologist.
If there are no complaints, a visit to the doctor should be made once a year. If there are any problems, the doctor himself selects a schedule for visiting the hospital. Under no circumstances should inspections be skipped. It is necessary to take the prescribed tests and strictly follow the specialist’s recommendations. Take care of yourself and be happy.
Reasons for the development of cervical ectopia
Cervical ectopia (the term “ectopia” has long replaced the outdated term “erosion”) can have different origins. These are ectopia of the cervical epithelium, pseudo-erosion of the cervix, erosion of the cervix, endocervicosis
. In the practice of a gynecologist, there are ectopias that are traumatic in nature, but much more often specialists have to deal with ectopias of infectious origin. Most often, the development of cervical ectopia is caused by viral infections (mainly human papillomavirus, HPV), and less often by bacteria.
Treatment of ectopia
The main difficulty in treating diseases of this group is timely diagnosis: unfortunately, despite the abundance of information about the importance of regular visits to the gynecologist, many patients still skip annual preventive examinations, seeking medical help only in the later stages of the disease
Prevalence of cervical ectopia
The problem of cervical ectopia is extremely common: one or another disease from this group is found in every second woman who goes to the gynecologist with complaints of discomfort, pain during sexual intercourse, bloody discharge during sexual intercourse (the so-called contact discharge). The latter already indicates that the process is neglected. If the cause of ectopia is an infectious process, then the woman is worried about the discharge.
What tests need to be taken?
If cervical ectopia is suspected, a PCR test is performed to detect the human papillomavirus, as well as bacterial culture to detect staphylococcus, streptococcus, e. coli and other bacteria that can cause inflammation of the cervix - endocervicitis. Patients are also checked for the presence of cytomegalovirus infection and herpes virus. All these tests can be performed in the Zdorovye network of clinics, as well as transvaginal ultrasound. It is advisable for patients with ectopia to undergo extended colposcopy with various tests to exclude malignant changes in the cervix.
Consequences of HPV
When HPV of high oncogenic risk is detected, patients are necessarily prescribed treatment to prevent the development of cancer. However, cervical cancer is not the only problem associated with ectopia: patients often complain of decreased fertility and libido (sex drive), so cervical diseases must be treated regardless of the presence or absence of a risk of developing cancer due to ectopia. If necessary, doctors at clinics in the Zdorovye network perform cauterization of ectopia using electrocoagulation and pharmaceuticals.
When to take it
Another question that I want to draw attention to is when you need to rush to the doctor. Usually a woman feels that not the most pleasant changes have occurred in her reproductive system. For example, discharge, itching, burning appeared. There is no need to delay your visit to a specialist. By the way, genital tract infections are not the only reason why the study is being conducted.
There are others on the list:
- frequent inflammatory processes in the genital organs;
- The smear showed an increased number of leukocytes and coccal bacteria.
A routine examination of a woman during pregnancy is not complete without this analysis. For those women who monitor their health, I recommend testing as a preventive measure. I'll tell you frankly, sometimes we don't even suspect that we carry parasitic microorganisms within us.
And their presence can lead to serious consequences in the future. Understanding how important the professionalism and experience of specialists is in this matter, I advise you to visit the Invitro medical center. Here, by the way, they don’t delay the results.
And this is very important, if you have a bad culture, you need surgical treatment. You can also contact the professionals from the Hemotest laboratory. If you are interested in the price of the analysis, then it is quite affordable, since this type of research is quite popular.
Basic recommendations
Planned curettage of the cervical canal is prescribed a few days before the start of the menstrual cycle. In this case, the operation coincides with the physiological period of rejection of the uterine epithelium. Intravenous anesthesia is used to perform diagnostic curettage.
After the operation (for 2-3 weeks), the patient must maintain hygiene, avoiding hypothermia and excluding heavy physical exertion. You are not allowed to visit the solarium or gym during this period. Swimming in the pool, sea and bath is contraindicated. Showering is allowed. Similar rules must be followed in the postoperative period, since the genital tract has not healed. Upon completion of the course of treatment, a repeat cytology smear is prescribed.
An alternative method to curettage is hysteroscopy. To perform this, you will need a hysteroscope. With its help, a specialist examines the uterus. Diseases of the female genital organs occur for the following reasons:
Regular visits to the gynecologist will help to promptly identify any pathological change.
How to prepare for a cervical smear?
Proper preparation for a painless procedure ensures reliable results. The doctor writes a referral to the patient and talks about the nuances that need to be taken into account before taking the test.
A gynecologist takes tests on a pregnant woman. Sexual contact is avoided for several days before the procedure. Do not take medications or contraceptives.
If a few days before the scheduled date of delivery, vaginal examinations were carried out using a speculum, then it is advisable to postpone the procedure. It is forbidden to do douching, which distorts the vaginal microflora. To maintain hygiene, use regular boiled water without using detergents.
Before visiting the treatment room, wash only in the evening . 1-2 hours before the appointment, refrain from urinating. The procedure does not cause discomfort or pain to the patient.
The meaning of the cervical canal
The cervical canal is a kind of bridge from the cervix to the vagina.
Doctors call it the pharynx. During menstruation, blood clots pass through it, and through it the sperm moves to the egg. The average channel width is 7-8 mm. These values may vary depending on age-related changes, the presence of urinary tract infections, and the woman’s hormonal status. Pregnancy adds its own adjustments to the usual life of the cervical canal. In the expectant mother, the length of the cervical canal reaches 3.5 - 4 cm, provided that the length of the cervix is at least 2 cm. Both ends of the pharynx must be closed. Based on their condition and degree of openness, the doctor determines the approach of labor. It is in this area of the female reproductive system that a plug is formed, which throughout the entire 9 months separates the placenta and the baby from the effects of harmful environmental factors. A few weeks before giving birth, the plug comes off. From now on, mothers listen more carefully to their well-being. As soon as the baby begins to move along the birth canal, the pharynx expands to almost 10 cm.
If the period is still very short, the cervical canal acquires a bluish color, signaling that there is pregnancy.
What is CD stenosis
In gynecology, there is such a thing as stenosis of the cervical canal. This condition implies an acquired or congenital pathology, accompanied by narrowing or complete obstruction of the cervical canal.
Causes
Among the reasons for the narrowing of the endocervix, the following provoking factors should be mentioned:
- Chronic inflammatory process in this area.
- Injuries to the central circulation during childbirth or gynecological procedures.
- Decrease in the level of female hormones during menopause.
- The presence of neoplasms in this area.
These are just some of the reasons that can cause pathology. Sometimes a congenital form of stenosis occurs in girls.
Symptoms
Cervical canal stenosis in women of childbearing age is accompanied by a decrease in the amount of monthly bleeding. Some patients experience pain in the lower abdomen and general malaise. In the middle of the cycle, slight spotting with an unpleasant odor may occur.
Sexual intercourse is often accompanied by painful sensations. If the canal is overgrown, large quantities of blood accumulate in the uterus, this is often perceived as neoplasms in it. In addition, there are difficulties with conception.
Possible complications
The main danger of cervical canal stenosis in gynecology is considered to be female reproductive failure. This occurs due to the inability of sperm to pass through the cervix. If pregnancy occurs, there is a high risk of fetal death or spontaneous abortion.
Treatment methods
Treatment of stenosis in gynecology is indicated for girls with obstruction of menstruation and the impossibility of conceiving a baby. If the pathology is not accompanied by visible symptoms, the doctor often chooses observational tactics. In this case, a woman must undergo a routine ultrasound scan at least twice a year. Treatment of stenosis is carried out using several methods. Among them are:
- Bougienage of the Central Committee. The narrowing is eliminated using a special medical instrument - a bougie. Therapy is carried out over several weeks with periodic replacement of the bougie with a larger diameter instrument.
- Surgery. Laser or radio wave therapy is used here. Only in severe cases is full-fledged surgical intervention used.
The prognosis for a patient with cervical canal stenosis depends on the disease that provoked the narrowing.
Timely treatment helps to cope with the problem and prevent various complications.
Endometriosis symptoms
Another extremely common gynecological problem is endometriosis, a condition clinically manifested by chronic nagging pain in the lower abdomen. The pain may be constant. Endometriosis is also characterized by the presence of brown spotting discharge before and after menstruation. Menstrual bleeding itself becomes heavy and painful due to endometriosis.
Causes of endometriosis development
Endometriosis is a consequence of varicose veins of the small pelvis, poor circulation in the pelvis. This is why endometriosis is often detected in professional athletes, young and practically healthy women: intense physical activity can provoke circulatory problems, which, in turn, lead to endometriosis.
Diagnosis of endometriosis at the Zdorovye clinic
To diagnose endometriosis, the Zdorovye network of clinics performs an ultrasound examination, in which the doctor, as a rule, detects an enlarged uterus with characteristic growths.
How to prevent endometriosis?
You can prevent the development of endometriosis by limiting physical activity and avoiding activities that require excessive effort. Such prevention is especially important for women whose relatives suffer from endometriosis: it has been proven that predisposition to this disease is inherited.
To treat endometriosis, the Zdorovye clinic network uses drugs that relax the uterus. If endometriosis develops against the background of inflammation, we also treat the cause of the inflammation, and in the later stages of endometriosis we use hormonal drugs. However, it is better to organize treatment in such a way that there is no need to prescribe hormonal drugs.
Consequences of untreated endometriosis
Untreated endometriosis can cause infertility or uterine fibroids. The latter is a fairly common complication of the nodular form of endometriosis, but can also develop as an independent disease.
Endocervical cysts
Similar neoplasms in gynecology occur in many patients who have already given birth, after 35-45 years. Most often cysts are benign. In nulliparous girls, such formations are extremely rare.
The causes of the cyst are the accumulation of mucus, which, under the influence of any provoking factors, cannot come out.
Why does pathology develop?
More often, the problem develops against the background of injuries to the mucous layer. Factors that provoke a cyst may be the following:
- Birth of a child. During childbirth, damage to the endocervix often occurs, which causes formations to appear in this area.
- Ectopia or erosion. Here, the outflow of mucus is disrupted due to blockage of the canal by dead cells during the healing of erosion.
- Endometriosis. Pathology occurs due to the entry of mucosal cells into the cervical canal.
- Inflammatory diseases in the area of the internal genital organs.
As already mentioned, endocervical cysts are extremely rare in children and nulliparous women.
Symptoms
Many gynecological diseases affecting the female genital organs cause similar symptoms. Because of this, you cannot diagnose them yourself. The presence of an endocervical cyst may be indicated by the following manifestations:
- Menstrual irregularities. Failures arise due to the narrowing of the Central Committee.
- Feeling of pressure and fullness in the lower abdomen.
- Discharge with a rusty or red tint after sexual intercourse.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
- Increased temperature (observed in case of infection).
- Inability to get pregnant.
To identify pathology, the patient is prescribed a study of the cervical canal. Normally, the size of the cervix should be 2-3 mm. The cavity of the cervix should be filled with homogeneous mucus.
If the Central Committee is expanded, this indicates the presence of certain problems. If cancer is suspected, a woman is prescribed a special examination.
Treatment
During diagnosis in gynecology, cervicoscopy, cervicometry and ultrasound are used, as well as cervical biopsy and PCR. After detecting small formations that are not harmful to health and do not interfere with conception, doctors choose observational tactics. In this case, the patient must undergo regular preventive examinations. For larger cysts that carry pathogenic flora and interfere with conception, the following treatment methods may be prescribed:
- Radio wave therapy.
- Cryotherapy.
- Laser treatment.
- Scraping.
- Full surgical intervention.
The type of treatment is selected depending on the characteristics of the pathology, the size of the cyst and some other factors.
Diagnosis and treatment
Interpretation of the analysis is included in the specialization of the gynecologist
When examining the collected material, doctors pay special attention to atypical cells. Their moderate amount symbolizes the development of the inflammatory process
Therefore, a smear for cytology is taken at a time when the number of leukocytes does not exceed the permissible value.
The normal smear provides for the absence of atypical cells. Otherwise, the gynecologist makes a diagnosis of “Dysplasia” of the 1st, 2nd or 3rd degree. Malignant cells are observed during the development of cervical cancer. If a specialist has identified grade 1 dysplasia, then the patient must undergo a full examination. With the development of dysplasia of the 2nd and 3rd degrees, colposcopy, biopsy and conization are performed. The latter procedure involves removing the affected area of the cervix using a scalpel or radio knife. Stage 3 dysplasia refers to cancer, the treatment of which is the specialty of a gynecological oncologist. The patient is admitted to an oncology clinic.
Diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the cervical canal involves the use of curettage. The procedure for curettage of the canal is carried out for therapeutic purposes in the following cases:
- hyperplasia;
- polyps;
- bleeding of the uterus;
- removal of fibroids.
The resulting material is sent to the laboratory. Curettage is prescribed by a gynecologist in cases where this technique is the only way to diagnose and treat the female genital organs.
Planned curettage of the cervical canal is prescribed a few days before the start of the menstrual cycle. In this case, the operation coincides with the physiological period of rejection of the uterine epithelium. Intravenous anesthesia is used to perform diagnostic curettage.
After the operation (for 2-3 weeks), the patient must maintain hygiene, avoiding hypothermia and excluding heavy physical exertion. You are not allowed to visit the solarium or gym during this period. Swimming in the pool, sea and bath is contraindicated. Showering is allowed. Similar rules must be followed in the postoperative period, since the genital tract has not healed. Upon completion of the course of treatment, a repeat cytology smear is prescribed.
An alternative method to curettage is hysteroscopy. To perform this, you will need a hysteroscope. With its help, a specialist examines the uterus. Diseases of the female genital organs occur for the following reasons:
- infection;
- hormonal disbalance;
- tumor.
Regular visits to the gynecologist will help to promptly identify any pathological change.
A tank culture from the cervical canal is an informative analysis that allows the doctor to accurately determine the presence of a bacterial infection and the strains of pathological microorganisms that provoked the inflammatory process. This makes it possible to quickly, and most importantly, choose the right drugs for treatment.
Modern medicine has a huge number of techniques in its arsenal, which make it possible to promptly detect the most severe diseases and promptly begin their therapy. Gynecology also has its own diagnostic principles; smear cytology is considered one of the most reliable. A cervical canal procedure involves a swab of the cervix to evaluate the vaginal environment and detect bacteria such as:
- enterobacteria;
- Klebsiella;
- mushrooms, etc.
The collection from the cervical canal is done using a special sterile stick.
The doctor extracts mucus, which is produced by local glands and pieces of desquamated cells of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal. After removing the biomaterial, it is placed in a specially prepared test tube with a nutrient medium for bacteria.
E. coli and other representatives of pathogenic microflora will absorb the beneficial substances they need from the artificially created environment and multiply. This will allow you to accurately determine the type of colony and select a medicine to which a particular strain of microorganisms is sensitive
It is important not to create destructive conditions in the test tube that will lead to the death of microorganisms, otherwise the doctor will not be able to determine the provocateur of the disease and will not cure the woman
After collection, the mucus that is sent for cytological examination is placed in a closed tube and inserted into a thermostat. Next, the nurse or the patient herself delivers it to the laboratory. In laboratory conditions, the test tube is opened and the biomaterial is transferred to another nutrient medium, which is located in a Petri dish. The mucus stays in it for 3-5 days, only after this time can you individually isolate all the representatives of the pathogenic bacteria present in the smear.
How to correctly perform the procedure
So that you understand how safe this procedure is, I will tell you how a smear is taken and what is subsequently done with the material. So, only a sterile brush is used for the procedure. It is sent to the cervical canal, where glands and cells with microorganisms collect.
This procedure is somewhat unpleasant for a woman, but generally safe and not painful. The next stage is related to the direct study of the material. As soon as the specialist has taken the analysis, the contents of the brush are placed in a glass beaker, where the necessary conditions have already been created for the development of microorganisms.
Here the laboratory technician is faced with an important task - not to allow microorganisms to die, otherwise he will not be able to determine which ones are present in the woman’s body. And the flora analysis will be done in vain.
To multiply parasites, the flask is placed in a thermostat; the temperature here is always 37 degrees. The next step is to transfer the contents of the flask to another nutrient medium and place it again in a thermostat for several days. Here the process of reproduction of fungi and bacteria is already in full swing.
When the number of parasites increases to a volume that can be examined, the laboratory technician performs the following actions:
- determines the types of microorganisms present in the material;
- calculates the number of units within species;
- Conducts antibiotic tests.
Now that you know what the analysis shows, you need to understand how important it is for the health of the mother and child. How many days does the analysis take? About five, the doctor will tell you more precisely.
Indicators of normal microflora
The contents of the cervical canal are not sterile. In any case, the vagina and cervix are inhabited by microorganisms.
If microbes are classified as opportunistic or facultative, then they do not pose any danger.
According to the standard, culture from the cervical canal should reveal many lactobacilli and bifidobacteria - microorganisms beneficial for women's health, representatives of the natural vaginal flora.
The presence of a large number of intestinal inhabitants is undesirable: enterococci, Escherichia coli.
In single quantities, these bacteria do not threaten women's health, but when found in large numbers in cultures from the cervical canal, they are symptoms of inflammation of the genitourinary system.
Even one single bacterium of staphylococcus, gonococcus, trichomonas, leptothrix, found in culture from the cervical canal, indicates infection of the cervix with dangerous pathogens. Such infections pose a particularly great threat to pregnant women.
Normally, bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in the culture from the cervical canal should be at least 10 * 7. Only a specialist can decipher the culture from the cervical canal.
People without medical education will not be able to independently determine whether the microflora is normal or there are deviations.
Each woman has individual indicators, so it is not enough to simply compare the numbers obtained as a result of culture from the cervical canal with the reference interval.
A slight deviation from the norm may be natural for a particular patient. After bacterial culture, the doctor comprehensively analyzes the results of the vaginal smear and culture from the cervical canal.
This is necessary to compare the flora found immediately after taking the biomaterial and the bacteria grown on the nutrient composition.
But there are criteria that definitely do not belong to the norm - pathogenic microbes that are at the stage of intensive development.
Culture from the cervical canal helps to detect not only the presence of pathogenic microbes, but also, no less important, to determine the stage of their development:
- the initial stage is weak growth of microorganisms, which can only take place in a liquid medium;
- second stage – bacteria multiply more actively, are able to master solid media, and form no more than 10 colonies on them;
- the third stage - the number of colonies on solid compounds increases to 100 - this indicates the presence of an inflammatory process;
- the final stage – the number of colonies exceeds 100.
The norm of microorganisms in culture from the cervical canal is disrupted for hormonal, immune, and hygienic reasons.
In addition, deviations in the composition of the microflora are a symptom of female ailments of an infectious nature.
Bacterial culture during pregnancy
Analysis of biomaterial from the cervical canal during pregnancy is often prescribed to expectant mothers, which rightly raises concerns among women - will the collection of biomaterial harm the fetus?
In order not to worry, it is enough to know the anatomy of the pelvis. The cervical canal is closed by a mucous barrier through which no pathogenic bacteria can penetrate.
But the color of the cervical canal changes already in the early stages of pregnancy, which can become an additional symptom of the presence of an embryo in the uterus.
Before childbirth, the mucus leaves the cervical canal, so it is imperative to treat the microflora in order to achieve the desired degree of purity of the smear in the early stages of pregnancy.
In addition, there is a pathology in which the cervix, under the pressure of the growing fetus, begins to open not before childbirth, but starting from the second half of pregnancy - in such cases, improving the vaginal microflora in the later stages will be impossible.
Pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms will penetrate into the prematurely dilated cervix and the inflammatory process of the cervical canal will begin - cervicitis, which poses a direct threat to the gestation of the fetus.
How to take a smear
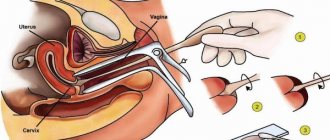
The procedure for taking a smear does not require special equipment or any special conditions. The sampling is performed in a gynecological office on a chair. The analysis time takes no more than three minutes. The session is painless for the patient. In this case, the doctor must use sterile instruments and gloves. Technique:
- The patient lies down on the gynecological chair.
- A special speculum is inserted into the vaginal area to reveal the cervix.
- Biological material is collected from the cervical canal using a cotton swab, brush or spatula.
- A smear is also taken from the urethra and vagina (each test is collected with a separate instrument).
You might be interested in: 15th week of pregnancy
When examining a smear for bacteriological culture, the result will have to wait at least 5 days. This is due to the fact that this is the time it takes for bacteria to grow and identify.
Preparation
Normally, a smear during pregnancy should be taken in the middle of the menstrual cycle. Before submitting biomaterial for cytology, you should follow some doctor’s recommendations. For example, before taking a smear from a woman during pregnancy, a specialist advises patients to avoid sex, the use of vaginal products, douching and contraceptives for several days. During this period, you should also not visit a gynecologist or perform a colposcopy. In this case, a smear during pregnancy for cytology will be as reliable as possible.
Many gynecologists recommend that patients donate biomaterial even if their microflora is healthy. To avoid unpleasant consequences when taking a smear from the cervical canal during pregnancy, you need to pay attention to contraindications.
Before the study
Reviews about smears during pregnancy from experts suggest that for a more transparent picture, a woman should prepare for this procedure. If she ignores the gynecologist’s recommendations, he will receive a distorted result, and this is the path to prescribing incorrect therapy and unpleasant consequences. You should prepare for the analysis several days in advance, or better yet 2 weeks.
To do this, stop using any antibacterial agents. You should also avoid douching. Experts recommend excluding the use of vaginal contraceptive creams and suppositories. A couple of days before the test, you should avoid sexual intercourse. If a few days before the analysis, colposcopy or any other diagnostic procedures were carried out with the introduction of a speculum into the uterine area, then the study should be postponed for several days.
It is important to note that for pregnant women this procedure should be performed by a gynecologist who has sufficient experience. As a rule, the results are ready on the fifth day after collecting the material.