The second trimester ultrasound is considered the most important of the three routine ultrasound examinations. It provides complete information about the development of the fetus, allows you to identify anomalies, and determine disorders in the course of pregnancy. Expectant mothers always look forward to this examination to make sure that everything is fine with the baby, and as a bonus, to find out the gender of the baby.
One of the most touching moments
When and why is ultrasound performed in the 2nd trimester?
Many mothers wonder: when to do a second scheduled ultrasound? They say that for some the doctor prescribes a test at 19 weeks, and for others at 20. Indeed, the timing may vary in each individual case. At what week a woman will be sent for an ultrasound examination depends on the mother’s health condition and fetal development parameters identified during the first ultrasound screening.
The Russian Ministry of Health has established a rather vague framework regarding at what stage of pregnancy the second ultrasound is performed. According to the department's order, it is done between 18 and 21 weeks.
Timing of routine ultrasound
How often you can do an ultrasound during pregnancy is determined by your doctor. Much depends on the presence/absence of complications of the “interesting situation”. If the pregnancy is progressing normally, then ultrasound diagnostics are performed once per trimester.
Research in the middle of pregnancy is especially important: it allows you to more or less accurately determine whether everything is normal with the baby. When is the second ultrasound done? The duration of the study is 20 – 24 weeks. By this period, the organs and system are fully formed, which allows you to get a reliable picture. In which week is it better to undergo examination in each specific case, you need to check with the doctor observing the pregnancy. Everything is determined individually and taking into account previous results.
Is it possible to do it earlier?
Many expectant mothers are interested in the question of whether it is possible to undergo an ultrasound examination earlier than prescribed in the 2nd trimester. The dates are shifted to the 16th week if there are indications. If high risks of developing fetal anomalies are identified during the first screening in the second trimester, not just an ultrasound scan is performed, but perinatal screening. This is a comprehensive analysis, including ultrasound and biochemical blood test (triple test). It is recommended to undergo the procedure before the 20th week:
- if the results of the first study are questionable;
- with hormonal disorders;
- if the expectant mother is over 35 years old;
- if the family has a child with genetic pathologies;
- if the patient took drugs prohibited during pregnancy.
With the help of screening ultrasound, it is possible to detect profound disability in utero, the absence of limbs, and determine that after birth the baby will need an expensive operation, or even it will be completely impossible to maintain his life without medications. The timing of repeated perinatal screening was not chosen by chance. Closer to the 20th week, it is already possible to identify various hereditary anomalies and it is not too late to have an abortion if diagnostic methods indicate the presence of serious abnormalities in the baby.
Additional ultrasound
If a routine ultrasound shows that the norm is violated, the norm is clarified at the end of the trimester - at 25-26 weeks. You need to undergo additional research only on the recommendation of the supervising doctor. A repeat procedure is prescribed in the second trimester in special cases.
- Additional scans are necessary if there is a suspicion that the pregnancy has stalled. Timely detection of fetal death and subsequent measures will help preserve the patient’s reproductive function.
- The indication for a repeat visit to the ultrasound center is the risk of premature birth. After confirming the high probability of early delivery, doctors determine measures that will help delay the baby's appearance until the right moment. It is not always possible to prolong pregnancy. But the possibilities of modern medicine increase the chances of life for premature babies.
- Diagnosis is needed when a pregnant woman has serious health problems. The procedure helps prevent pregnancy complications and reduce risks for mother and baby.
What can be seen on the second ultrasound
Ultrasound of pregnancy in the 2nd trimester allows monitoring the activity of the child’s body, after which it is assessed whether the data obtained correspond to the acceptable limits of the norm. The work of an ultrasound diagnostic specialist includes the following areas:
- measuring the baby's heart rate;
- identifying indicators of development, location of internal organs and parts of the child’s body (head size, chest circumference, abdomen, limbs);
- determining the position that the baby occupies in the stomach, as well as the height and weight of the child;
- determining the number of embryos (although rare, there are cases when only at the second ultrasound parents find out that they are expecting more than one child);
- assessment of placenta previa and degree of maturity;
- examination of the anatomical structure of the baby’s body, including the main organs: brain, heart, liver, stomach, spleen, bladder, lungs, genitals;
- determination of the development of the skull (in particular, the facial bones), spine and chest;
- measuring the volume and quality of amniotic fluid in which the fetus’s intrauterine life takes place;
- assessment of the condition of the umbilical cord;
- detection of pathologies in the cervix and cervical canal, diagnosis of tone.
Based on the results of fetometry, which is carried out during a prenatal ultrasound examination, the specialist diagnoses the disease and makes a conclusion. It tells you whether the pregnancy is progressing well, and also specifies the date of the upcoming birth.
Fetal examination
Using ultrasound diagnostics in the second trimester, the fetus is first examined, and then the auxiliary structures. The existing norm will help you understand that the baby is developing normally; the norms are compared with the results obtained and conclusions are drawn.
Ultrasound in the second trimester of pregnancy is carried out according to a strict schedule. First, the parameters of the fetus are deciphered (fetometry), then the body parts and organs of the baby are examined. This allows you to understand whether there are any anomalies and whether the child is developing according to the gestational age. During the procedure, be sure to study:
- Fetometric indicators. Not one parameter is informative, but several at once: abdominal circumference, head size, length of the femur. If the obtained indicators and the norm diverge, the norms of other measurements help the ultrasound specialist make the correct diagnosis. For example, the length of the humerus is additionally measured, the fronto-occipital size and chest circumference are assessed. After this, it can be concluded whether a slight deviation in the indicators signals pathology or is an individual feature.
- Brain structures. Be sure to evaluate the cerebellum, cerebral hemispheres, cistern, visual thalamus, and lateral ventricles. Deviations in the parameters of brain structures may be a separate pathology or indicate gene abnormalities.
- The front part of the skull. The profile is studied, the nasal bone and eye sockets are assessed. Smooth features and bone abnormalities indicate chromosomal defects (for example, Down syndrome).
- Internal organs. Ultrasound allows you to evaluate the correct location of organs and their function. They study the kidneys, intestines, liver, gall bladder. Viewing the heart and assessing the heartbeat is mandatory. An ultrasound scans the baby's spine longitudinally and transversely. The study allows us to identify abnormalities in the development of organs, diagnose tumors, and identify congenital heart defects. The formed organs of the genitourinary system make it possible to find out the sex of the baby.
Interpretation of ultrasound in the 2nd trimester, norms
Ultrasound interpretation is performed after screening. This procedure includes work on comparing the data obtained with a table containing ultrasound standards in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. This work should be carried out by the attending gynecologist. Only he will be able to summarize everything that was revealed during the ultrasound examination and tell the mother whether there is any reason for concern.
It is best to go to see a doctor immediately after the procedure to get a transcript of the ultrasound protocol. Most likely, by this time the gynecologist will already have the results of a biochemical blood test, which, together with an ultrasound examination, will show a complete picture of the health status of the mother and child.
Biparietal size (BPR)
At each routine examination, using ultrasound, the diagnostician looks at the biparietal size of the fetal head or BPR. This indicator is obtained by measuring the distance between the temporal lobes of the embryo. The purpose of the BDP is very specific - determining the duration of pregnancy. In addition, by the distance between the temples, the doctor determines whether there are any deviations in the baby’s growth.
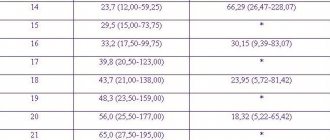
At 20 weeks, the biparental size should be within the normal range - 43-53 cm.
If the indicator is lower, then this may be a sign of intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR).
Fronto-occipital size (FOR)
The LZR is calculated based on the distance between the frontal and occipital bones of the child’s head. The fronto-occipital size of the skull in ultrasound diagnostics is always paired with the biparient size. These two parameters, as mentioned earlier, provide information about the gestational age and whether the baby is developing safely. The norm for LZR at the second screening is 56-68 mm.
Intrauterine retention of the fetus, which is diagnosed by reduced BPR and LZR, is most often diagnosed in women who abuse smoking and alcoholic beverages or have experienced extreme stress. However, it is worth noting that poor performance is not always a consequence of the unlucky behavior of the expectant mother. Quite often they can be caused by late ovulation and implantation of the embryo. And in some cases, the cause is a hereditary trait that is passed on to the baby from the parents. Ultimately, medical malpractice may occur. A doctor who receives unsatisfactory test results will give a referral for additional examination.
Head and abdominal circumference (OG and coolant)
Head and abdominal circumference are also complementary indicators of child development. First, the doctor measures the OG, which, together with the biparental and fronto-occipital dimensions of the head, can tell a lot about the baby’s health. By mid-pregnancy it should be between 154-186 mm. Deviations from the norm in one direction or another may be a reason for ordering a more detailed study to identify the cause.
If the OG is less than prescribed, this is a probability of developmental defects; if it is more than normal, then the doctor may suspect problems in the condition of the brain. To exclude the presence of hydrocephalus, if too high an indicator of OH is detected, the mother is examined for re-screening.
The abdominal circumference is considered in relation to the head circumference in order to understand how proportionally the baby’s body parts develop.
If the parameter does not correspond to the gestational age, then doctors can focus their attention on the condition of the placenta and umbilical cord. Perhaps they do not supply the fetus with enough nutrients and oxygen.
Bone length
During an ultrasound examination, the doctor thoroughly examines the length and shape of the paired bones of the embryo. This procedure includes the length:
- femoral bones (FB);
- shin bones (SHB);
- forearm bones (FB);
- humerus (humerus);
- nasal bone (DNA).
These measurements are needed to determine genetic pathologies, which include, for example, Patau syndrome or Carnelia de Lange syndrome. Too short limbs may indicate their presence, which will be recorded in the screening report. The length of the nasal bone is of great importance during the first ultrasound, being a guideline in identifying genetic abnormalities, primarily Down syndrome. In the 2nd trimester, DNA may not be present at all in the expert protocol.
By the way, the detection of deviations in bone length should not be taken as a final verdict that the child is doomed to health problems. No one has canceled such aspects as the characteristics of the skeletal apparatus of each person or hereditary factors. Therefore, the final diagnosis will be made only after confirmation of the disease, as well as based on the results of a biochemical blood test, including a test for the level of hCG, estriol and alpha-fetoprotein.
Umbilical cord
The umbilical cord plays a vital role in the life of the fetus, providing it with everything it needs - nutrients and oxygen. This connecting thread between mother and child is a cord, which is formed by three vessels. This should be normal, but if there are deviations, then there are fewer of these vessels. The diagnostician must monitor how many veins and arteries make up the umbilical cord in order to understand whether the baby in the womb has enough nutrition from the outside.
Note that the umbilical cord also performs an auxiliary excretory function. Through it, metabolic products come from the baby, which are then excreted by the mother’s body.
Amniotic fluid
Ultrasound in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, in addition to monitoring the state of development of the child, also includes monitoring of its environment - amniotic fluid. Their quality and quantity are assessed; for this purpose, a unit of measurement is used, such as the amniotic fluid index (AFI).
If the doctor determines that the AFI is less than 2 cm, then oligohydramnios is established, if it is more than 8 cm, polyhydramnios is established. Both diagnoses are a cause for serious concern. Polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios are a sign of fetal malformations, the presence of an infectious process in the womb. In this case, the woman requires urgent treatment.
Uterus
Particular attention is paid to the main female organ – the uterus. During pregnancy, she experiences enormous stress, and it is very important to evaluate the condition of the uterine walls using an ultrasound. First of all, the specialist looks at the presence of tone. Good equipment will definitely show how tense the uterine muscles are. In addition, scars are carefully examined if the woman has had uterine surgery in the past. The doctor looks to see if this suture interferes with the course of pregnancy and if neoplasms appear near it.
The length and patency of the cervix are measured. If the diagnostician notices its shortening, he can diagnose isthmic-cervical insufficiency. This is an alarming sign that the cervix cannot withstand the pressure of the uterus due to the rapidly increasing size of the fetus.
Placenta
Three components are important in assessing the placenta: its presentation, thickness and maturity. Normally, the “baby spot” should be located along the back wall of the uterus. If it is adjacent to the anterior wall or is located too low, doctors may dismiss the possibility of a natural birth and give the woman a caesarean section. Low presentation is diagnosed at a level below 5.5 cm from the internal os of the uterus. This figure may change closer to birth, given that the placenta can rise higher.
A placenta that is too thick - more than 4.5 cm - may indicate intrauterine defects, the presence of infection or Rh conflict. In this case, the pregnant woman will need drug treatment. Another important indicator is the maturity of the child's place; in the 2nd trimmeter it should be zero. The first degree of maturity indicates premature aging of the placenta.
Face, brain and organs
In the middle of gestation, the baby’s face is clearly visible on the ultrasound equipment monitor. During the 2nd trimester ultrasound, the doctor determines whether the child’s facial features are correctly formed. He notes the presence and condition of the eye sockets, upper and lower jaws, and also carefully examines the face for the presence of pathologies - cleft palate or cleft lip (cleft palate).
The brain, as the main organ of the central nervous system, is examined for the presence of the correct structure and tissues: the outlines of the hemispheres, ventricles and cerebellum. After this, the doctor examines other organs, assessing their formation. If he detects changes in echogenicity during examination and detects pathology, he will report this in the ultrasound report.
Motor activity of the child
By this time, the mother feels the baby’s movements well and can feel his movements from time to time. If a woman is worried about the baby’s overly active actions or, conversely, too sluggish movements, then she can report this to the diagnostician.
During an ultrasound, a specialist will definitely evaluate the child’s motor activity and dispel all the parents’ worries.
Note that if too frequent or too infrequent movements are confirmed, this should alert the pregnant woman and the observing doctor. Perhaps this is how the discomfort that the baby feels in the womb manifests itself.
Determining the sex of the child
The sex of the child is determined already during the first ultrasound screening. However, given the insufficient formation of the genital organs of the embryo, the percentage of error is quite high. In the 2nd trimester, doctors will dot all the i's, even if in the past they made a mistake or simply did not see if it was a boy or a girl. Modern ultrasound equipment makes it possible to determine the gender of the child with a high degree of probability. If at the previous ultrasound the mother was not told who lives in the tummy, then now you can safely trust the doctor’s words and prepare a dowry for the newborn.
Last part of the protocol
At the very end of the ultrasound protocol there will be a diagnostician’s conclusion: whether the measurements taken during the screening process correspond to the obstetric period. In addition, the form will indicate the weight of the fetus, which is automatically calculated by the equipment after analyzing fetometric indicators. At 20-21 weeks it should be between 215-320 grams.
Process
The process of performing an ultrasound in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy is not much different from the examination in the 1st trimester. Many come to the screening with the child’s father so that once again the two of them can enjoy photos and videos of their baby. Especially when the procedure is carried out on equipment that allows you to take pictures in 3D or 4D format.
At this stage, an ultrasound is performed through the abdominal wall, to which the sensor is applied. The woman should lie on her back on the couch with her knees bent.
Preparation and conduct of ultrasound examination
No special preparation is required to perform an ultrasound. Even without following special recommendations, you can get a clear picture, unlike the first trimester, when you need to prepare for the procedure. But still, before the study, it would be useful to listen to the advice:
- two days before going to the hospital, minimize citrus fruits and seafood in your diet;
- give up carbonated drinks one day before;
- eliminate fatty foods and foods with high cholesterol levels from the menu a day;
- three hours before the procedure, eat and no longer snack.
A special cream will help avoid stretch marks
Diagnosis is carried out transabdominally - through the abdominal wall. The patient lies down on the couch. The abdomen is treated with a special gel, and then the specialist moves a sensor over the abdomen. The expectant mother does not experience any discomfort. On the screen she can see the baby's movement and hear his heartbeat. The procedure is not dangerous for the baby.
The expectant mother needs to first find out where to have an ultrasound done. It is better to choose proven diagnostic centers with new equipment. An important point is the interpretation of the ultrasound. The possibility of error can be eliminated if the procedure is carried out by a qualified specialist. You can choose an uzist using reviews on specialized forums or recommendations from friends. There is no need to rush to a decision if the results of the study show pathology. The ultrasound doctor could have made a mistake. To confirm the violation, a series of diagnostic measures should be taken. If you have doubts about the competence of a specialist, you should contact another center.
How to prepare
Preparation for the second study is somewhat different from the previous one, since this time you do not need to follow a strict diet and drinking regime. There are no dietary restrictions, but experts still do not recommend overeating or drinking a lot before the procedure, so that nothing distracts the mother from admiring her baby, and the doctor from the scrupulous work of assessing his development.
You need to take a diaper, towel and shoe covers with you. You should check in advance whether they are included in the cost of the ultrasound. Many paid clinics do not require you to carry these items with you.
Peculiarities
Previously, a second ultrasound was not prescribed to all women, but only to those who were in the so-called risk group. It includes those who are over 35 years old, who have a history of infectious diseases, miscarriage, and genetic pathologies in the fetus identified in the past. Now the second scheduled screening period is assigned to all pregnant women, who must undergo it without fail.
Many mothers involuntarily wonder what they look at on an ultrasound in the 2nd trimester. The study confirms what was recorded as a result of the first screening, and also shows how much the baby has grown and strengthened since then, and whether factors have appeared that could negatively affect his condition.
The peculiarity of ultrasound in the 2nd trimester is that it does not have a strict framework. The Ministry of Health recommends sending pregnant women for the procedure from 18 to 21 weeks, but the gynecologist can revise the period and schedule screening for 17 or 22 weeks.
After IVF pregnancy
All pregnant women as a result of in vitro fertilization will undergo examination in the 2nd trimester. Only, unlike those mothers whose pregnancy took place naturally and was not overshadowed by threats of miscarriage, for women with IVF this will not be the second screening. After all, as you know, almost the entire artificial insemination procedure is carried out under constant ultrasound control. In such patients, special attention is paid to Doppler studies - assessing blood flow in the vessels of the uterus and placenta.
Pregnancy with twins or triplets
During pregnancy with twins or triplets, the timing and procedure for performing ultrasound are the same as for singleton gestation. The only difference is that the procedure itself will take a little more time, because the specialist must carefully study the development parameters of two or even three babies. The indicators of each of them will be recorded in the examination protocol.
Reliability of screening results
Sometimes it happens that according to the preliminary results of screening in the 2nd trimester, a woman is at risk for possible defects. Do not panic ahead of time, it happens that the results of the examination are false positive. The final result is influenced by many factors: age 35 years and older, the woman’s overweight (obesity contributes to changes in hormonal blood parameters), bad habits, past or present, taking medications or the unfavorable influence of the woman’s environment.
In each individual case, the doctor individually assesses the reliability of the tests and the presence of associated factors. If, nevertheless, a sufficiently high degree of risk of possible deviations is determined, then the expectant mother will be prescribed auxiliary studies:
- blood sampling for certain, specific hormones, in addition to the main ones;
- taking amniotic fluid to study its contents, a manipulation called amniocentesis;
- obtaining blood for analysis from the baby's umbilical cord artery - cordocentesis;
- histological examination of chorionic villi.
In addition to testing blood from a woman’s vein, other studies are invasive and quite difficult, but they most reliably refute or confirm the doctor’s conclusion, which he makes based on the results of screening in the 2nd trimester.
Is a second ultrasound harmful?
Nowadays, few people argue about whether ultrasound examination harms the mother and child, almost unanimously agreeing that such a procedure has much more advantages. Nevertheless, there are opponents of such screening.
As medical practice shows, the preservation and successful course of pregnancy in most cases depends on competent, accurate and timely diagnosis.
It allows you to prescribe the necessary treatment and improve the condition of the fetus even before it is born. Therefore, the second ultrasound during pregnancy is a very important and mandatory procedure.
When to do the next ultrasound
The expectant mother will need to undergo the next ultrasound in the third trimester. The period of implementation is quite limited - from 32 to 34 weeks. This is a very important study - the last one before giving birth and meeting the baby. Based on the screening results, it will be clear how the child will be born and whether he will need additional medical care.
When examining a woman who is eight months pregnant, the diagnostician examines the fetus for the presence of late-onset malformations. An ultrasound examination determines the position of the child, the quantity and quality of amniotic fluid, growth indicators, motor activity, the condition of internal organs and the maturity of the placenta.