Ultrasound examination is often used to monitor the condition of the embryo at all stages of pregnancy. This diagnostic method is simple, accessible to everyone, and absolutely safe for the health of the mother and her unborn child. How far after conception an embryo is visible on an ultrasound depends on many factors, since each pregnancy is different.
When can pregnancy be confirmed using an ultrasound?
There is no point in running for an ultrasound the day after unprotected sex. The size of the egg, even a fertilized one, does not allow it to be seen with ultrasound imaging. How long does it take to see the fertilized egg and determine its size? You can see the embryo when the fertilized egg is at least 1 cm. If there is a delay in menstrual bleeding for a week, by this time the gestation process has approximately reached 6 weeks. By this period, when diagnosed with a high-precision device, the fertilized egg is already visible. It is not yet possible to determine the presence of a heartbeat in the embryo and examine its structure.
Due to the peculiarity of ultrasound diagnostics in the early period of gestation, namely the need to insert a transducer into the vagina, such an examination is carried out strictly according to indications. The grounds are suspicion of ectopic implantation of the fertilized egg, hydatidiform mole.
There may be other considerations based on which the gynecologist suggests this procedure to the woman.
When is a qualified, experienced specialist using a good device that provides high-quality visualization able to recognize the signs of pregnancy? After 3 weeks. Ultrasound diagnoses the ectopic location and implantation of the ovum after 2 weeks (transvaginally) and on the 20th day after conception (through the peritoneum). To help with ultrasound diagnostic data, a blood test is usually prescribed. HCG levels allow us to judge the implantation of the embryo. At 7-8 weeks (from about 10 days of delay), a good ultrasound diagnostician determines pregnancy with almost 100% certainty.
Why doesn’t an ultrasound “show” pregnancy?
If all the signs of gestation are present, the level of gonadotropin indicates successful implantation of the embryo, and ultrasound data does not show a fertilized egg and does not confirm the fact of pregnancy in a particular patient, this does not mean that the pregnancy did not take place. The reasons that an embryo is not visible on ultrasound may be the following:
- a transabdominal sensor was used;
- low accuracy of equipment;
- incorrect calculation of gestational age, ultrasound diagnostics are carried out too early, the fertilized egg is not visualized;
- gynecological pathology (corpus luteum cyst, for example).
For the expectant mother in this situation, the main thing is not to panic. You need to repeat the hCG test (its readings should double in 2 days - this is an indicator of a normally developing pregnancy) and re-visit the ultrasound room in a week.
The use of a transvaginal sensor is much more informative for identifying a normally located embryo than a transabdominal examination
What do yolk sac pathologies indicate?
Ultrasound diagnostics can show disturbances in the development of the sac. Pathologies vary; the organ may not be visualized at all on ultrasound; it may grow to an abnormally large size.
The preservation of the sac after 12 weeks is an unfavorable sign and can lead to miscarriage. Sometimes it happens that the yolk organ is clearly visible on an ultrasound, but the fetus itself is not visualized and there is no heartbeat.
This phenomenon is called anembryony; it occurs when the embryo dies at the blastocyst stage or does not develop at all.
What justifies the need for early ultrasound diagnostics?
If the hCG result is 1000-2000 mU per liter, ultrasound can be effective. This study will help the obstetrician-gynecologist recognize possible early pregnancy problems and its normal state. It could be:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- confirmation of the fact of embryo implantation;
- finding out the reasons for delayed menstruation in the absence of pregnancy;
- establishing the gestational age (the shorter it is, the more accurate the data);
- determination of pregnancy fertility (not always possible);
- establishing the threat of failure.
Ultrasound diagnostics in the early period is carried out only in exceptional cases, but it is still better to wait 5-8 weeks. At this time, the embryo is visible and the speed of its development can already be determined.
If an ultrasound was performed early, the size of the corpus luteum is suspected of pregnancy. If menstruation is delayed and the size of the corpus luteum is at least 16 mm, we can talk about pregnancy, although the fertilized egg is not yet visible.
What period does ultrasound show and its accuracy?
The age of the fetus is determined by obstetric and embryonic methods. The first one is counted from the 1st day of the last menstrual bleeding, the second one counts the gestational time from the day of conception (this date is considered the day of ovulation). The embryonic period is 2 weeks shorter than the obstetric period. During the ultrasound procedure, the obstetric method of reference is considered the basis. The procedure itself is not a computational mechanism for calculating gestational age. It consists in determining the degree of fetal development and correlating the data with the obstetric period. The accuracy of ultrasound (in determining the number of weeks of pregnancy) directly depends on the gestational age itself:
- up to 12 weeks – accuracy is 1-2 days;
- from 12 to 28 weeks – the error is a week in both directions;
- after 28 weeks the error increases.
After 12 weeks, the accuracy of determining the gestational age decreases significantly
The timing of the ultrasound does not coincide with the obstetric one: reasons
A deviation of 14 days in both directions is not considered a pathology; obstetric practice allows this. For example, if the ultrasound timing exceeds obstetric calculations in the initial period of gestation, the reason may be an error in determining the obstetric timing due to the fact that almost immediately after fertilization there was slight bleeding, which the woman mistook for menstruation. The second reason may be the large size of the fetus.
When researching, it is necessary to take into account the baby’s heredity. Large parents may have large children, short miniature couples may have small children. Also, the fetus on ultrasound may be smaller in size than it should be according to the estimated term, if the doctor recorded the embryonic period. This is where the natural reasons end.
The fetus may develop inconsistently with hypoxia or other pathologies. To clarify the condition of the child in the womb, the doctor prescribes Doppler testing. For a woman, this procedure is no different from the studies she has already undergone, but it allows the diagnosis to be clarified.
Objectives of follow-up surveys
The third ultrasound of the fetus is prescribed from the thirty-second to the thirty-fourth week of pregnancy and is necessary in order to determine the position of the child, assess its size and weight, and study the condition of the placenta, as well as amniotic fluid. The last ultrasound (normally) is performed before birth and is not mandatory. It is necessary in cases where the doctor needs to decide on the type of birth, and reveals the location of the umbilical cord (so that the fetus is not entwined with it), the approximate weight at birth and the breech position of the baby.
What to do if the size of the fetus does not correspond to the obstetric period?
Consult your doctor. He will conduct an examination, determine the height of the uterus and measure the abdominal circumference, evaluate the mother's condition and suggest either hospitalization or re-examination in a week. There is no need to refuse hospitalization and repeated examination, because not only the condition of the expectant mother, but also the life of her child depends on this. The hospital may conduct additional examinations that will either show that everything is normal or help prescribe adequate treatment.
Ultrasound diagnostics is an art. Much depends on the qualifications of the doctor. A good specialist using precision equipment is able to determine pregnancy with a vaginal sensor for a period of 3 weeks or more (using the obstetric method). But actually, at how many weeks a doctor can confirm a pregnancy depends on the individual case.
- Types of ultrasound diagnostics
- Why is the fertilized egg not visible during the examination?
- Anomalies of prenatal development
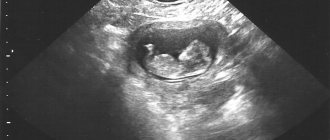
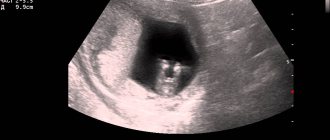
The fertilized egg is visible on ultrasound in the sixth week after conception; the size of the embryo is approximately 1 cm. In accordance with the standards of the World Health Organization, the first study should be carried out at 10-14 weeks of pregnancy. But few parents want to wait that long. Everyone wants to make sure that the pregnancy is intrauterine and the unborn baby is developing normally.
Immediately after discovering pregnancy, every woman should contact an antenatal clinic for registration. Doctors will monitor her throughout the pregnancy, monitor the development of the fertilized egg in the early stages of pregnancy, anticipating possible risks.
Ultrasound is one of the most accurate studies that allows you to determine pregnancy, monitor the development of the fetus, and diagnose embryo pathologies. Thanks to this examination, many lives of both children and their mothers have been saved.
Introduction
Ultrasound (ultrasound) is a study that is very often used to monitor the condition of the baby at any stage of pregnancy, even when only an embryo is visible on ultrasound.
This is due not only to the information content, but also to the ease of diagnosis, accessibility and safety of the technique. During pregnancy, ultrasound is used in several cases:
- When it is necessary to confirm the fact of pregnancy.
- The time has come to measure the size and weight of the baby, assess their compliance with accepted standards for each period.
- If it is necessary to assess the viability of the child.
- Identify developmental abnormalities.
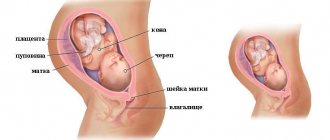
- When you need to determine the size of the placenta, its maturity, and indicate the place of attachment.
- Determine the amount and properties of amniotic fluid.
- If you want to determine the sex of the baby.
According to modern rules, every pregnant woman undergoes an ultrasound examination and is observed by a gynecologist. Many people think that they need to go for an ultrasound when the embryo is visible.
However, usually the very first examination is carried out from the tenth to the fourteenth week, the second is prescribed from the twentieth to the twenty-fourth, and the third from the thirty-second to thirty-fourth week. If something happens during pregnancy, or the doctor suspects the development of any pathology, then additional examinations are prescribed.
The procedure can be carried out in two ways: with an abdominal sensor (when the abdomen is examined, onto which a special gel is applied) or vaginal (through the vagina) . The second method is used if the fetus is not visible on a standard examination.
Types of ultrasound diagnostics
Transvaginal and transabdominal examinations are considered particularly effective in the early weeks of pregnancy. This ultrasound allows you to examine the location of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. The study can also determine ectopic pregnancy.
It is not always possible to see the membranes of the fetus using ultrasound, even at 5 weeks. Even if the embryo is not visible, an experienced specialist should notice the thickening of the uterine walls characteristic of pregnancy. The procedure is repeated after 1-2 weeks as prescribed by the doctor.
Information about the prenatal development of a child can be obtained using the following types of ultrasound diagnostics:
- 3D and 4D studies;
- dopplerography;
- cardiotocography.
Diagnostics using three-dimensional images allows you to examine the baby, his face, arms, legs - that part of the body that he wants to turn around. This ultrasound is performed in later stages of pregnancy, when the child’s body is more or less (depending on the number of weeks) formed. This is a color study, most often the baby is shown in golden color.
A Doppler study allows you to evaluate the fetal circulatory system, as well as examine the uterus and placenta. Such an ultrasound can be prescribed by a doctor at any stage of pregnancy. It makes it possible to confirm or refute a defect of the cardiac system, exclude a frozen pregnancy, and check the functioning of the fetal heart. At a later stage, Doppler ultrasound may indicate a lack of oxygen.
Cardiotocography (CGT) determines the level of oxygen starvation of the fetus and records the calm heartbeat of the child under the influence of changes occurring in the uterus. If necessary, an examination is prescribed by the observing gynecologist.
Return to contents
Why is a yolk sac needed?
At the earliest stages of development, when the embryo is just forming, the yolk sac performs a variety of functions, without which normal development is impossible.
From the 18th day of the beginning of a new life, the first embryonic red blood cells (erythroblasts) are formed in the wall of the yolk sac and capillaries begin to grow, from which the entire circulatory system of the fetus is later formed.
Interesting: How long after giving birth does a cat begin to walk?
From the 28th day, the walls of the yolk sac produce the first germ cells, which a little later will move to the gonads of the embryo.
It is important to note that at this time the eggs of the future girl are laid.
If at this stage the mother is ill or has experienced severe stress, the laying of eggs will not occur correctly and in the future the adult woman will suffer from infertility.
Until the sixth week, the yolk sac plays the role of the “primary liver” and produces proteins that are very important for the development of the embryo, such as alpha-fetoprotein.
The yolk sac also takes an active part in metabolic processes, the formation of immunity and collects fetal secretions.
Why is the fertilized egg not visible during the examination?
Expectant mothers often ask the same question: when is a fertilized egg visible on an ultrasound? There are often cases when at 8 or even 12 weeks the fetal heartbeat cannot be heard and is not visible. Don't despair! Ultrasound diagnostics do not always provide 100% information. The result can be influenced by many factors, both technical and human. Doctors recommended conducting several studies to confirm the information received. This is not only an ultrasound, but also laboratory tests and gynecological examinations.
As sad as it is to realize, inaccuracies in ultrasound diagnostics have interrupted the lives of more than one baby, and yet these are isolated cases that do not occur so often. Basically, ultrasound gives a reliable result, but if there is a risk of a frozen or ectopic pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo a more in-depth examination.
If the ultrasound does not detect an embryo in the fertilized egg, it is necessary to conduct a blood test for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin). With positive dynamics, the level of this hormone increases in proportion to the weeks of gestation. The possibility of incorrect calculation of the period cannot be ruled out. Perhaps he is too small to see the fetus on the instruments. Doctors count the gestational age in obstetric weeks, that is, from the first day of menstruation inclusive, so errors in calculations are common. It is worth going to another medical institution and undergoing ultrasound and tests again. Don't rush into agreeing to a cleanse until you've exhausted all your options.
The week at which the embryo is visible on ultrasound, and not just the fertilized egg surrounding it, largely depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the location of the egg in the uterus. Modern equipment plays an important role. Usually the embryo is shown 6-7 weeks after conception.
All sorts of myths about ultrasound:
- Ultrasound negatively affects the intrauterine development of the fetus. There is no evidence to confirm or refute this fact. Scientists and doctors agree that everything should be in moderation. In a normal pregnancy, 3 routine ultrasound examinations are sufficient. Only in case of pathologies or threat of miscarriage can the number of studies be increased. Ultrasound is often not recommended in the early stages of pregnancy, but closer to childbirth you can undergo a 3D examination and get a picture as a keepsake. The fetus has already formed in recent weeks, and ultrasonic waves will not harm it.
- Under the influence of ultrasonic waves, DNA changes. During ultrasound, waves penetrate the object and are repelled from it, which allows the formation of an image. The whole process creates only a mechanical vibration of the tissues inside the mother's womb. Studies on pregnant mice did not reveal any genetic changes caused by ultrasound.
- Unnatural nature of ultrasound. This is a matter of subjective perception. Diagnostics is a voluntary procedure; the desire to undergo it depends only on the parents of the unborn baby.
- Ultrasound is an experiment. There is a deal of truth in it. The study of the prenatal life of the fetus provides a lot of material for scientific work. The knowledge and experience gained allows us to save the lives of mothers and children around the world.
In any case, the consent of the mother is required for ultrasound diagnostics. The main thing is to ensure that the doctor uses modern equipment with low radiation levels.
What to do when an embryo is not visible on an ultrasound at 9 weeks? Repeat it after a week, or preferably after 3. The examination will show what size the fertilized egg is when it is 1 cm or more. Most often, the fetus reaches this size by 6 weeks of gestation. But everything is individual. It happens that an ultrasound can clearly show that a woman is pregnant only at 8-12 weeks.
Many expectant mothers who dream of a son or daughter are concerned with the question: from what week will an ultrasound definitely confirm that she is pregnant? Experts say that from the age of 7 you can take a referral from your gynecologist and undergo diagnostics. If the examination does not show anything, and there are no menstruation, do not be upset, it happens. Sign up again in a month.
Is the procedure safe during the baby's formative stage?
Modern doctors have good help in the form of ultrasound, when they can evaluate the organs at the birth stage and decide how correctly the child is forming. But this applies to the later stages of the baby’s development. In the early stages, the safety of the study is controversial.
The AIUM (American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine) guidelines on the safety of medical ultrasound (2009) provide recommendations for diagnostic safety. It is believed that the period at which embryonic rudiments appear on ultrasound is critical in the development of the brain. Ultrasound waves have a thermal and mechanical effect on tissue. This can cause heating of the developing nerve cells and disrupt their division.
There is also a danger in the period at which the fetus is visible. The local effect of ultrasound on the wall of the uterus can tone it, which contributes to spontaneous miscarriage.
Therefore, recommendations for performing an ultrasound are as follows:
- use the minimum required power;
- reduce the duration of the study;
- do not carry out without medical indications;
- Do not perform in Doppler mode in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Studies in small animals have confirmed the damaging effects of high-power ultrasound on brain and eye structures. It is impossible to conduct such experiments in humans, so a negative effect is only assumed.
How do specialists see an embryo?
Have you taken a test and found out that you are expecting a baby? Unfortunately, tests are sometimes wrong, but an ultrasound examination, starting from 9-12 weeks, will definitely show that you will soon become a mother. A referral for an ultrasound will be given by your gynecologist from the clinic. You can also contact private honey. cent, you will be given a referral for examination.
If you want to know for sure whether you are pregnant or not, ask if they will examine you with a good ultrasound machine in the 1st trimester? It is important that the equipment has high resolution and other additional functions. From 4 to 5 weeks the fetus is so tiny that it is only 1 to 2 mm.
At which obstetric week do doctors begin counting pregnancy? C1 is from the 1st day of a woman’s period. Therefore, there will be a difference of 2 weeks between the actual week of conception and the obstetric one. This is important to know in order to calculate obstetric 9 months. carrying a baby. Yes, and routine ultrasounds are performed, measuring the timing in obstetric weeks.
What does it mean if the yolk sac is not visualized?
Observation of the yolk sac is usually performed during in vitro fertilization to analyze the fertilization process, although evaluation of the yolk sac is an effective way to diagnose early pregnancy. There are different options for pathologies of embryo development.
Based on the size of the yolk sac, one can judge how the pregnancy is developing; if the size of the yolk sac is insufficient, one can speak of a frozen pregnancy, in which cleaning of the uterine cavity is recommended. It is important to do it on time.
Although in this case there are effective methods of hormonal therapy.
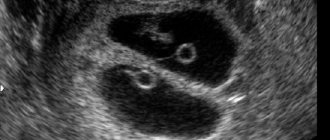
In general, the yolk sac is visualized between 6 and 12 weeks of pregnancy. If during this period the yolk sac is not visualized, then there is a high probability of complications.
Premature reduction (shortening) of the yolk sac will suggest a non-developing pregnancy.
The likelihood of complications during pregnancy increases sharply if the size of the yolk sac is more than 5.5 mm (with a maximum of 6 mm) at 5-10 weeks and less than 2 mm at 8-12 weeks. In the second case, the risk of a non-developing pregnancy is very high.
Embryo examination method
If the baby in your womb is not yet 9 weeks old, then experts recommend doing the examination using several methods:
- Using a transabdominal sensor, moving along the anterior wall of the peritoneum;
- Using a transducer. The examination is carried out through the vagina. This is a transvaginal method. The transvaginal method is considered the best way to carry a baby for a short period of time. The wave frequency used is high and on the screen the doctor sees the condition of the woman’s uterus and fetus.
Is ultrasound safe for the fetus?
Thanks to this method of examination, the doctor can determine at an early stage of development whether the embryo is visible, does it have abnormalities? The doctor will try to carry out the procedure quickly. The examination itself lasts on average 15 minutes.
Now is the early stage of formation of internal organs in the fetus. An experienced doctor will move the sensor faster than usual over the woman's abdomen or uterus. The ultrasound specialist will try not to hold the device for a long time over any internal organ of the baby.
During the entire pregnancy, a woman will be prescribed at least 3 scheduled ultrasounds, and some will have repeat ones. According to statistics, on average, this is 9 times during the period of gestation. The specialist does screenings from the monitor screen. In addition, the woman donates blood for tests.
"Advice. Don’t worry, the doctor will check whether your baby is normal or not? He decides on additional ultrasound examinations.”
When will the ultrasound clearly show the embryo?
If the egg contains a viable embryo, the doctor confirms that the woman is pregnant and the condition of the fetus is stable. For each woman, even 1st, 2nd and subsequent pregnancies proceed in their own rhythm. In one, the fetus develops faster, in the other slower. Future mothers are wondering, how many weeks does it take for an embryo to become visible on an ultrasound from a dot and then a pea? Scans done through the vagina can diagnose pregnancy earlier than those done through the peritoneum. Average indicators are taken as the norm. It is believed that the fetus should be audible and visualized on the screen already at 6 or 7 obstetric weeks. If the specialist does not notice anything, he will make a diagnosis of anembryonia. Gynecologists advise the woman not to be upset, but to come for an examination in another 7 days. If your cycle before pregnancy was irregular, then perhaps the embryo was behind in development and therefore the specialist did not notice it. See what the baby looks like on day 21 of gestation:
It is important to know when an embryo is clearly visible on an ultrasound? What will they look at on an ultrasound?
If you are now 9 or 10 weeks pregnant and feel great, there is no threat of miscarriage, then an ultrasound is not necessary. It will be assigned only at your request. At this time it is impossible to say exactly the sex of the fetus. You can only determine whether the placenta is well attached to the wall of the uterus and that you are definitely pregnant. Additional examination is relevant if you have undergone IVF.
What is the point of ultrasound at this stage of embryo development:
1) Determine precisely that the fertilized egg is tightly attached to the uterus; 2) Find out how viable the fetus is; 3) Confirm that the pregnancy is normal and not ectopic; 4) Find out 1 baby or several in the uterus; 5) Determine where exactly the placenta is attached in the uterus; 6) Find out whether the fertilized egg is of the correct shape and has grown sufficiently;
Find out whether this is a real pregnancy or a tumor in the uterus?
Find out at what stage of gestation the expectant mother is. About the embryo
After conception, the embryo looks like a round shell with a tail. It grows in the womb and changes. From 5 to 7 weeks it is already like the letter “C”. Another 7 days will pass and the ultrasound specialist will determine that the embryo has a head and arms.
A normal fertilized egg looks like an oval and is dark gray. During this period, the gynecologist will be interested in 2 main indicators of the embryo: SVD or what is the diameter of the fertilized egg if measured along the contour passing inside; KTR or the size from the coccyx to the crown.
What is the yolk sac, how and when is it formed?
The yolk sac is the embryonic provisional organ of most vertebrates, including humans. A provisional organ is a temporary organ that performs the functions of tissue structures that have not yet had time to take shape in the embryo. Provisional organs also include the chorion, amnion, allantois, and serous membrane.
Until the 6th week of gestation, the sac is quite large. It is larger than the amniotic cavity and germinal disc. At 12-13 weeks it begins to decrease. This is explained by the fact that the embryo has already formed organs that can take over the functions of a pharmacist. By the end of the first trimester, it stops working and is completely reduced. The remains of the sac develop into a small cyst at the base of the umbilical cord.
During pregnancy, the yolk sac is formed for the purpose of normal development of the embryo until the placental membrane begins to fully function. The formation occurs from an endoblastic vesicle (a derivative of the endoblast), and the existence of the organ is not long-lasting, only the first three months of gestation.
The yellow sac looks like a closed circle, which is located inside the chorionic cavity. Due to the fact that the main purpose of the internal organ is to feed the fetus, it is larger in size than the embryo itself. Diagnosis of the yellow sac is made using ultrasound, and the further gestational period depends on what parameters are determined. The most important parameter during this period will be the presence of a yellow sac on the ultrasound monitor screen.