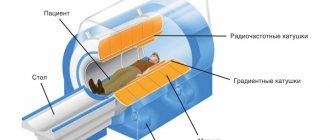
Many women have gone through the procedure of abortion. But they and those who have not yet encountered such a procedure do not fully understand what the process of complete rehabilitation after an abortive cleansing is. But the health of the woman’s reproductive system depends on how the restoration of the reproductive organ proceeds. Bleeding is a physiological consequence of curettage, which can cause some anxiety in a woman. How long does it take to bleed after cleaning the uterus and when is there a reason to worry?
In what cases is curettage performed?
The internal cavity of the uterus is lined with a layer of endometrium. If fertilization of the egg does not occur, every month this layer is naturally rejected and uterine bleeding occurs - menstruation. This is how the uterus periodically cleanses itself, preparing for a new potential conception. For some reasons, situations arise when the inner shell needs to be cleaned. For this purpose, a surgical method is used - curettage.
If your doctor has prescribed a cleaning, you should be aware that this is a surgical procedure and will require a long recovery period.
Cleansing the uterus is used as a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure, which is carried out for the following pathologies:
- Thinning or thickening of the inner layer of the uterus.
- Spontaneous termination of pregnancy.
- Disruption in the menstrual cycle.
- Endometriosis.
- Incomplete completion of abortion using vacuum aspiration.
- Biopsy.
- Diseases of the cervix.
- Inflammatory pathologies.
- Presence or suspicion of a neoplasm of any nature.
How is endometrial curettage performed?
Anesthesia: Intravenous anesthesia is preferred.
Duration of the operation: Total time of the entire procedure: approximately 20 minutes.
After registration in the hospital and the necessary preparation, the health worker invites the patient to the operating room.
The woman is placed on a gynecological chair for intrauterine operations.
The external genitalia and vagina are disinfected with an iodine-containing agent. Urine is drained by a catheter. Blood pressure is measured and pulse is counted.
Pain relief is given (short-term general intravenous anesthesia).
Uterine curette - a surgical instrument for curettage of the endometrium
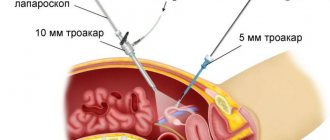
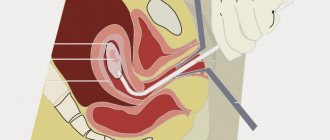
The vagina is expanded with a gynecological “mirror”. The cervix is fixed with special instruments. The cervical canal is gradually “opened” by Hegar dilators. Then, using a uterine curette No. 1-2, curettage (curettage) of the surface of the cervical canal is performed.
Curettage of the cervical canal
The resulting scraping of the cervical mucosa is placed in a separate bottle with formaldehyde.
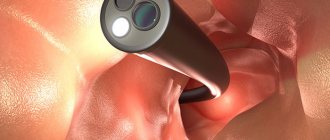
Then, a survey diagnostic hysteroscopy is performed using a hysteroscope device.
Hysteroscopy. Endometrial hyperplasia: thickened endometrium in the form of folds
After visual assessment of the mucous membranes of the uterus. Curette No. 4 is inserted into the uterine cavity and curettage of the uterine walls is performed: consistent, careful scraping of the functional layer of the endometrium from all internal surfaces of the uterus and the area of the uterine angles.
Endometrial scraping
The thoroughness of endometrial removal is assessed by hysteroscopy.
All tissue collected from the walls of the uterine body is placed in a second bottle with a preservative.
After completion of curettage and control hysteroscopy, the endoscopic device and surgical instruments are removed. The vagina is cleaned with a dry cotton swab to remove any remaining blood and tissue. The cervix is treated with iodine tincture. The vaginal specula are removed.
An ice pack is placed on the patient's lower abdomen. If necessary (in case of decreased uterine tone), an injection of oxytocin is given, which contracts the uterus.
Both containers with samples of the endocervix and endometrium are labeled and sent to the histology laboratory.
What should the discharge be like after curettage?
During curettage of the uterus, the gynecologist removes the functional layer of the reproductive organ. The operation is quite traumatic, and immediately after it is performed, the uterus turns into a bleeding wound. On the first day, discharge after cleansing a frozen pregnancy or for another purpose is very abundant and of high intensity. This condition can be compared to menstruation, when the endometrial layer is naturally shed. In a situation with curettage, this is done with the doctor’s instruments.
It is worth understanding that every woman’s menstrual cycle functions under the direct influence of hormones. It depends on them how long menstruation lasts.
Discharge after surgical abortion is also influenced by hormones, however, there are indicators of the normal duration and nature of bleeding. During the 5-6 days after the operation, there is especially a lot of blood discharge, but there should not be any foul-smelling odor. Then comes bloody discharge, then spotting, and then it stops altogether.
The total duration of cleansing of the reproductive organ should normally not be more than ten days. Do not worry if you experience pain in the uterine area during this period - this is normal.
If curettage was performed before the expected start date of menstruation, then the duration of the discharge will be equal to the number of “critical” days.
So that every representative of the fair sex who has encountered such an unpleasant and traumatic procedure understands what to pay attention to during the rehabilitation period, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the information presented below.
Additional nuances of scraping
Preparation
Since the curettage procedure is an operation, the preparation for it will be appropriate.
Analyzes:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Fluorography.
- Smear.
- Biochemical blood test (HIV, syphilis, blood group).
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the pelvic organs.
- Cardiogram.
Immediately before the operation it is recommended to eat and drink; the procedure must be carried out on an empty stomach.
In the morning before the procedure, you should take a shower, remove hair from the perineal area, and put on clean underwear.
You should also be prepared for the fact that you will have to spend several days in the hospital. Therefore, take with you a robe, slippers, a change of underwear, pajamas and other necessary accessories.
Reference! Ask your doctor in advance what medications you will need and buy them, especially for painkillers, and also ask about the symptoms of possible complications. Remember, you must be prepared for anything.
The main criteria for assessing the condition after surgery
It must be remembered that there are 4 criteria for discharge that help keep the situation under control - color, abundance, duration and consistency.
Color and smell
Proper healing of wounds in the uterus can be determined by the change in color of the marks on the pad.
Brown
The appearance of a brown spot is a sign that the blood is rapidly clotting, and this portends a quick restoration of the reproductive organ.
Yellow
If the cleansing was carried out due to the death of the fetus, disturbances in the body’s reparative processes often occur. In such patients, the discharge has a watery structure with suspicious inclusions, it is quite abundant, and is characterized by a characteristic yellowish tint and a rotten odor. The change in color of the secreted secretion occurs due to the fact that a special inflammatory fluid comes out of the uterus. It consists of formed elements, blood and water.
Yellow marks on the gasket are an alarming signal that indicates the presence of an acute inflammatory process.
This liquid provides an ideal habitat for a large number of microorganisms. During their life, nitrogen-containing compounds are released, which cause a foul odor.
Pink
Pink discharge after endometrial scraping is a clear sign that blood clotting is impaired. Patients who are concerned about pinkish marks on the pad should consult a hematologist with complaints.
Unpleasant aroma
A rotten smell is another very dangerous symptom. It appears due to volatile compounds that bacteria produce during their life.
Abundance
After surgery, the amount of discharge should be the same as during menstruation. The woman will notice that every day the pad can be changed less and less, and by the end of the week the need to use these hygiene products will disappear.
If the blood volume during “critical” days is approximately 180 mg, then after curettage it is allowed to exceed this figure by 1.5 times.
If you need to change the pad too often (less than 3 hours), you should definitely consult a doctor - this condition can cause anemia.
Lack of bleeding is also a cause for concern. The reason for this is either an incorrectly performed operation; or a hematometer; or exacerbation of a gynecological disease; or hormonal imbalance.
Duration
Many women wonder how many days after RDV of the uterine cavity the bleeding continues. Another marker that allows us to judge the success of regeneration processes is the duration of bleeding. Normally, the discharge will last 10 days: on the 7th–8th day there is very little of it, and on the tenth it disappears completely. If this period is exceeded, you should consult a gynecologist for advice.
Consistency
The nature of the discharge should be similar to menstrual. After cleaning, due to the death of the fertilized egg, traces of a brown or bright red color with endometrial particles can be seen on the pad. The discharge after curettage of fibroids has a similar consistency and should also have a normal smell.
Even if curettage was performed for diagnostic purposes, there should be no significant difference in the nature of the discharge, and any pathological changes are a reason for a visit to the gynecologist.
What discharge is considered pathological?
Discharge after cleaning the uterus in normal volumes indicates a good wound healing process. An increase in vaginal secretion is a clear sign that the reproductive organ is difficult to restore.
Separate attention simply needs to be paid to the color: yellow discharge after curettage appears only if a bacterial infection develops. Such a symptom should not be ignored, since the development of the pathological process poses a great threat to a woman’s health. For preventive purposes, doctors prescribe antibiotic therapy after surgery.
The following symptoms should also be a reason to contact a specialist:
- There is no discharge after curettage.
- Significant increase in temperature.
- Pain in the lower abdomen that cannot be controlled by analgesics.
- A large amount of blood.
- Questionable consistency of the secretion.
- Rotten smell from the genitals.
- Significant deterioration in health.
- Mucous greenish discharge.
- The appearance of an unpleasant odor.
- Change in color of discharge - it becomes yellow or green.
- The appearance of clots and mucous discharge streaked with blood.
Undoubtedly, cleaning the uterus is a huge stress for the female body. It is quite natural that body temperature can rise to low-grade levels. The patient will complain of weakness - if this is tolerable, it should not cause concern.
It happens that a woman experiences mild pain - a completely natural process when recovery is accompanied by spasm. To relieve pain, you can take any analgesic.
Every day, your overall health and condition should gradually improve.
The lack of positive dynamics may indicate the presence of associated complications, so the woman will need additional diagnostics.
What complications may arise?
When the operation is performed correctly, complications rarely occur, however, sometimes they do occur. This list includes:
- Uterine bleeding. Occurs infrequently, in a particular risk group are patients with bleeding disorders. Heavy discharge after endometrial curettage should occur within several days after the manipulation, while much later bleeding that occurs poses a great threat to the health and life of the patient.
- Hematometra is an accumulation of blood clots in the reproductive organ. The pathology develops against the background of excessive compression of the cervix, which appears after the operation. Hematometra causes progression of the infectious process. For preventive purposes, gynecologists prescribe injections of antispasmodics.
- Endometritis is an infectious process caused by pathogenic microflora entering the uterus. To avoid complications, gynecologists prescribe antibiotic injections.
- Infertility - given modern methods of performing surgery, there is only a small probability that such a complication will occur.
How is a smear taken for cytology?
The Pap smear is performed in a clinic setting. The woman sits in a gynecological chair. During the procedure itself, the gynecologist takes cells from the cervical canal area, from the vaginal mucosa. In the first case, a special probe is used - endobrush. It is administered after a slight expansion of the uterine canal by using a dilator. An Eyre spatula is used to collect material from the vaginal walls.
When liquid cytology of the cervix is performed, during the manipulation itself the woman may feel minor discomfort and mild pain. Its appearance is due to the expansion of the cervical canal, which is supplied with a large number of nerve endings. The duration of the procedure depends on the experience of the gynecologist, and averages 5-10 minutes. The resulting material is placed in a test tube with a reagent and sent to the laboratory.
The relationship between types of cleaning and discharge
Women often ask their doctor whether the intensity and duration of bleeding depends on the reason for cleaning the uterus.
After removal of the endometrium and fertilized egg due to the death of the embryo, the uterus is cleaned very abundantly. Discharge after abortive curettage performed for short periods will last from 10 to 14 days. If, for medical reasons, the termination of pregnancy was performed in the later stages, bleeding after RDV will be long.
Discharge after diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity is a small amount of blood, which disappears about a week after the manipulation. Normally, by the 10th day there should be no traces of blood on the pad.
Any terms that relate to the duration of cleansing the uterus are very arbitrary. The body of each representative of the fair sex is unique, so it is impossible even for an experienced gynecologist to predict anything. Doctors can only guess the duration of uterine cleansing based on their experience.
What is endometrial hyperplasia - causes and symptoms of the disease
The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus, or more precisely, the mucous layer lining the uterine cavity. It creates the necessary conditions for implantation of the fertilized egg and its normal development.
In other words, the mucous membrane “holds” the fertilized egg inside the uterus, provides it with nutrition, and participates in the formation of the placenta.
The endometrium consists of supporting connective tissue (stroma), embedded uterine glands and numerous blood vessels.
All structures of the uterine mucosa develop and function under the “guidance” of sex hormones. In the first half of the menstrual cycle (during the phase of estrogen influence), the uterine glands and the functional layer of the endometrium grow.
In the second - under the influence of progesterone - this growth stops. The endometrial stroma swells and accumulates useful substances. The uterine glands begin to secrete a nutritious mucous secretion. Every month, the endometrium prepares to “accept,” “feed,” and store the fertilized egg in the uterus.
If pregnancy does not occur, the “overripe” functional layer of the endometrium is destroyed and rejected with menstrual blood.
In the next monthly cycle, according to the balanced influence of sex hormones, the uterine mucosa is restored from the basal “germ” plate.
Location of the uterine mucosa - endometrium
When the balanced hormonal influence, or more precisely, estrogen, “breaks down,” the uterine glands multiply beyond measure and the uterine mucosa thickens.
Endometrial hyperplasia is an abnormal benign growth of the uterine lining associated with hyperestrogenic stimulation
The cause of endometrial hyperplasia is a general or local hormonal imbalance: excessive influence of estrogen on the uterine mucosa with insufficient action of progesterone.
Dangerous consequences of hyperplasia:
- Uterine bleeding leading to anemia
- Infertility
- Malignancy
Signs and symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia:
- Spotting bloody discharge from the genitals, not associated with menstruation.
- Menstrual irregularities:
- amenorrhea,
- hyperpolymenorrhea,
- Irregular menstrual cycle.
Diagnostics
- Ultrasound – ultrasound examination of the uterus reveals signs of endometrial hyperplasia by increasing the size of the M-echo.
- Hysteroscopy with separate diagnostic curettage of the endometrium - confirms or refutes the ultrasound diagnosis.
- Histological examination of removed tissues establishes the final diagnosis.
An accurate diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia and determination of its form (typical benign or atypical precancerous) can only be made by histological examination of tissue obtained by curettage of the uterine mucosa. Return to contents
Treatment of complications after cleaning
Discharge that continues for more than 1 month indicates the presence of pathology. This is a very long period of time, so this condition is always a reason for hospitalization. A woman needs to see a doctor urgently, and a specialist will order all tests. As soon as the doctor receives the research results, one of the treatment methods will be chosen:
- Repeated surgery, which is usually indicated for the accumulation of clots or a poorly performed abortion. Discharge after repeated curettage should return to normal in the near future.
- If there is an inflammatory process, the patient is prescribed antibiotics.
- Against the background of severe bleeding, medications are prescribed to promote uterine contraction.
- Hormonal imbalances are corrected with an individually selected treatment regimen. For this purpose, a woman needs to visit an endocrinologist.
- Anemia is treated with proper separate nutrition and consumption of iron-containing vitamins.
Possible danger
Although minor uterine bleeding after curettage is normal, these days a woman should especially carefully monitor her well-being and the nature of the discharge. If problems arise, thanks to attentiveness, you can solve them at the very beginning, preventing dangerous consequences.
In the period after a gynecological procedure, you should pay attention to the following factors:
- duration of bleeding;
- opening of re-bleeding;
- smell and color of discharge.
Normal bleeding after cleaning should not last more than 2 weeks. If the blood continues to flow, this warns of problems in the woman’s body. Due to blood loss, anemia and other dangerous consequences may develop. Longer bleeding sometimes indicates severe hormonal imbalance or postoperative complications.
Normal recovery of the body after gynecological cleansing implies that at first the blood flows heavily, and then gradually decreases. If this happens and then the bleeding resumes, urgent help is needed. This phenomenon indicates the formation of clots in the uterine cavity that have begun to separate.
If vaginal discharge after removal of the endometrial layer in the uterus is not uniform in color or has an unpleasant specific odor, you should consult a doctor. This warns of the development of an infectious disease. The patient requires additional examination and further treatment.
Some situations should prompt a woman to consult a doctor without delay. You should think about emergency medical care if you have the following symptoms:
- bleeding after cleaning is profuse and intense, the pad lasts no more than 1 hour;
- large blood clots come out;
- the discharge did not stop within a month after the intervention;
- there is an unpleasant repulsive odor;
- cutting sensations appeared in the abdomen;
- body temperature increased to 38°C;
- dizziness and severe weakness occurred.
Important information: Why does the nipple bleed when pressed and what to do when the mammary glands bleed
Dangerous complications may be indicated by the fact that the bleeding stopped abruptly. The volume of blood released should gradually decrease. Otherwise, one may suspect the formation of clots in the uterine cavity, which have blocked the flow of blood.
How to prevent complications from occurring
Complications during the rehabilitation period arise against the background of decreased immune defense, as well as hormonal imbalances. To protect yourself as much as possible from a long recovery period, you must follow simple rules:
- Do not leave the hospital for at least 24 hours after cleaning.
- For 7 days after curettage, observe bed rest.
- Avoid excessive physical activity.
- Protect yourself from stressful situations.
- Don't freeze.
- Follow all recommendations of the gynecologist.
- Use therapy aimed at maintaining the body's protective resources.
- Promptly undergo repeated ultrasounds to assess repair processes.
Women who are periodically observed by a gynecologist after surgery are maximally protected from complications. Therefore, it is so important not to ignore the need to visit doctors. Patients who went to the hospital for a consultation may not have to worry about their health in the future.
Curettage of the uterus is an unpleasant but necessary operation, which is sometimes impossible to do without. The procedure, which is performed by highly qualified specialists, very rarely causes complications that require appropriate treatment. However, discharge after cleansing is a natural and completely normal process that cannot be avoided.
The task of every woman is to control the nature, color and duration of the discharge. Many people do not know what to do if their health changes for the worse during the recovery period. In such a situation, there is only one way out - to seek help from specialists. Only a doctor can give a real assessment of the state of women’s health, as well as prescribe adequate therapy.
Doctors' recommendations for recovery
General recommendations:
- Abstinence from sexual activity for at least 30 days to avoid infectious diseases and complications associated with them. In addition, during this period it is not desirable for male prostaglandins to enter the uterus, which cause its contraction.
- Over the next 6 months, it is advisable to use a condom to prevent pregnancy.
- For two months you should not take a bath, visit a pool or swim in bodies of water.
- During menstruation, you should not use tampons so that infection does not enter the uterine cavity and the inflammatory process does not begin.
- For six months, you should limit physical activity as much as possible.
Attention! It is not recommended to use any other means of contraception other than condoms for 6 months after curettage.
Recommendations for taking medications:
- If you are prescribed antibiotics, take them strictly according to the regimen recommended by your doctor. This applies to the time of administration, dosage and name of the antibiotic.
- It is very undesirable to drink alcohol during the recovery period. And while taking antibiotics, this is completely unacceptable.
- In addition to antibiotics, painkillers and enzymes are prescribed without fail; the latter are used to prevent adhesions.
During the recovery period, it is necessary to undergo several courses of physiotherapeutic procedures.
Recommended physiotherapeutic procedures:
- EHF therapy (irradiation with electromagnetic waves). This procedure helps increase the body's resistance and is a prevention of endometritis.
- UT - ultrasound therapy is used to prevent the formation of adhesions.
- Infrared rays are used to reduce and prevent inflammatory processes.
In order to restore menstruation, gynecologists sometimes recommend the use of oral contraceptives, but only those prescribed by the doctor. The dosage regimen is also strictly specified.
Some experts recommend undergoing so-called sorption therapy after curettage.
Its essence is as follows. In a hospital setting, a special composition with absorbent and antiseptic properties is introduced into the uterine cavity. The composition is administered using a special catheter.
Reference! The curettage (scraping) procedure is a significant stress for the woman’s body, as the endometrium is artificially removed. And this leads to a malfunction of the pituitary gland, hypothalamus and ovaries, which seriously affects the functioning of the endocrine system, and in particular the menstrual cycle.
How to restore the cycle after curettage and how to restore the body is described in the video: