A smear from the urethra in men (scraping for flora) is an unpleasant, but at the same time necessary manipulation. This procedure makes it possible to determine the presence of urological and sexually transmitted diseases. A smear on the flora is taken from men if there are any unpleasant sensations in the pelvic area. During a routine examination, such a procedure is also carried out, but given that you can’t force guys to go to a consultation unnecessarily, tests are taken only when there is a need to assess the overall picture of the applicant’s health.
Diseases that the study can identify
Examination of the contents of the urethra in men by taking a smear determines the presence of bacteria and other pathogenic microorganisms, which are the main cause of the development of:
- Prostatitis (acute and chronic) - inflammation of the prostate tissue, what kind of disease it is, read here.
- Urethritis is inflammation of the walls of the urethra; the disease is described in detail here.
- Chlamydia is an infection transmitted from a sick partner to a healthy one during sex unprotected by barrier contraceptives.
- Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease caused by gonococci.
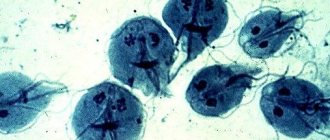
- Trichomoniasis. The causative agent is Trichomonas vaginalis, which affects the mucous membranes of the urethra and organs of the reproductive system.
- Malignant and benign neoplasms.
- Urolithiasis.
Using a smear, you can also find pathogens of hidden infections, that is, those that do not manifest obvious symptoms.
Evaluation of the study result
The analysis obtained is deciphered only in the laboratory and only by a certified specialist. The accuracy of the diagnosis and the result of treatment depend on the reliability of the presented results.
An increase in the number of leukocytes in the analysis is not always an indicator of a pathological process. Moreover, when analyzing flora, the presence of leukocytes (up to 5 in the field of view) is the norm. If a larger number is detected, then this characterizes the presence of an inflammatory process both in the urethra itself and in the prostate gland or the presence of a tumor process. If more than 100 leukocytes are found, this may indicate that the patient has gonorrhea or trichomoniasis. The pathogen is clarified using additional tests.
The presence of red blood cells in large quantities indicates the presence of acute inflammation and a tumor process, but does not exclude injury to the urethra during sampling.
Normally, the presence of epithelial cells up to 10 is allowed. If there are a large number of them, then this indicates a pathological process in the urethra. This indicator is important in a cumulative assessment with leukocytes and reflects the activity of the inflammatory process. An excess of epithelial cells indicates a chronic process, which can be either a consequence of a sluggish infection and tumor pathology, or a previous injury.
A small amount of mucus in a smear is not a pathology, but a large amount of it can mean the presence of an infection, namely:
- Trichomonas;
- candida;
- diplococci;
- chlamydia;
- cocci.
If the inflammatory process worsens, smear analysis will show a large amount of mucus and leukocytes.
The presence of single cocci is not a pathology. If more than 5 different microorganisms are identified, this indicates the presence of dysbacteriosis, which is caused by infection. Gonococci and Trichomonas indicate the presence of infections of the same name, and fungal infection is explained by the causative agent of the genus Candida.
A microflora smear in men is an indicator not only of the absence of infections of the genitourinary system, but also of a person’s general health.
Pathology identified at an early stage allows it to be eliminated even before signs of the disease appear.
What is standard analysis?
Deciphering the standard analysis, based on the results of which one can conclude about the presence or absence of pathology, includes the following indicators:
- Leukocytes (Le). Cells that protect the body from the effects of various infectious agents. Normally there should be up to 5 of them in the field of view. A large number indicates the presence of inflammation in the urethra, prostate or testes.
- Red blood cells (Er). These cells carry oxygen. Normally there should be up to 3 in the field of view. Their increase in combination with leukocytosis indicates inflammation of a traumatic nature or inflammation of the mucous membrane of the urethra, and does not exclude the possibility of injury when taking material from the urethra.
- Eosinophils (Eo). Their presence in more than 10% of the total cellular composition in the analysis indicates allergic inflammation in the urethra.
- Slime. May reflect both inflammatory phenomena and the process of excitation.
- Lipoid grains. Evidence of prostatic secretion. May be due to chronic inflammation of the prostate or an imbalance in sexual activity.
- Sperm. This indicates improper functioning of the muscles of the vas deferens.
- Epithelium. The presence of more than 10 cells indicates the presence of pathology in the urethra. Their combination with leukocytosis reflects an acute inflammatory process, and the norm of leukocytes against the background of an increased amount of epithelium indicates a chronic course of the process.
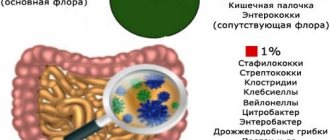
- The presence of microorganisms indicates an infectious process. In this case, epidermal staphylococcus, saprophytic staphylococcus, Staphylococcus aureus (no more than 5% of cases), viridans streptococcus, fecal streptococcus, Escherichia coli, Proteus, Corynobacter (up to 25%) may be normal. Pathogenic are gonococci, trichomonas, chlamydia, candida.
Throughout life, the composition of a person's microflora can change. But the presence of a large amount of one of the microorganisms is a sign of an inflammatory process. When taking a microflora analysis, the experience and level of professionalism of the laboratory staff and the availability of the necessary reagents are very important. In some cases, when the results obtained are ambiguous, additional research is resorted to. .
Indications for prescribing a urological smear
Analysis of a smear from the urethra is prescribed to men during preventive examinations, when obvious or hidden signs of inflammatory processes are detected, and if it is known that the sexual partner is a carrier of STD pathogens.
The obvious need for a smear is indicated by:
- The appearance of atypical discharge from the urethra - with pus, ichor, and an unpleasant odor.
- Pain, burning and other uncomfortable sensations that appear directly during urination or immediately after its completion.
- Increased frequency of urination and the appearance of false urges to empty the bladder.
- A rash of any kind in the anus, on the genitals, scrotum, perineum, itching, redness and swelling.
- Long-term lack of conception in the partner.
If the symptoms listed above occur, a urethral smear should be taken as soon as possible. Timely treatment prevents the disease from becoming chronic and developing complications.
The doctor deciphers the smear analysis. It is impossible to interpret the results as accurately as possible on your own, since the indicators can be affected by age, concomitant pathologies, and improper preparation for collecting contents.
For STDs, a urological smear showing pathogenic microorganisms is the basis for prescribing appropriate therapy. However, you will additionally need to take urine and blood tests and biochemistry.
If prostatitis, diseases of the urinary organs, or neoplasms are suspected, instrumental diagnostics are also performed - ultrasound of the pelvic organs, CT or MRI.
What to do if there are few leukocytes in the smear
A large number of immune cells indicates a well-functioning immune system.
If the level of leukocytes is low, then this is no longer good.
A low level of white blood cells indicates a deterioration in the immune system.
This means that there are diseases from which the immune system is suppressed.
There are three reasons for a decrease in white blood cell levels:
- redistribution of white blood cells
- a small amount of material from which white blood cells are built
- disruption of brain structures that are responsible for the production of leukocytes
According to statistics, an infectious process leads to a reduced content of leukocytes in the smear and in the blood, which, with two-week leukopenia, is one hundred percent indicative of inflammation.
If there are few leukocytes, then the body weakly fights the infectious process.
For example, HIV infection causes a significant decrease in the level of white blood cells.
To establish an immune response, it is necessary to treat immunosuppressive conditions and increase the level of immunity with immunostimulants and vitamin-mineral complexes.
If the smears have an increased level of leukocytes, then it is necessary to additionally do a general blood and urine test.
If these tests show an excess, then you need to look for the cause of the inflammatory process in the organs of the genitourinary system.
Be examined, take the necessary tests and get advice from a specialist.
Then the doctor, if necessary, prescribes effective treatment.
Types of analysis
After collection, the contents from the urethra are sent for 2 types of research:
- The first is a general smear, the purpose of which is to determine the microflora. Shows the quantitative content of bacteria, leukocytes, intracellular and fungal microorganisms. The general smear often does not show the type of specific bacterium, since when examining a slide under a microscope, they all look approximately the same. A probe is used to collect the contents, it is inserted into the urethra and then the contents are applied to a glass slide and stained, thus obtaining a smear.
- The second is a study for hidden infections, performed using the PCR method. When carrying out a polymerase chain reaction, even the smallest amount of DNA of infectious agents in the test material is detected. PCR is divided into qualitative and quantitative analysis. In the first option, only the general result of the smear is written on the form - positive if infectious microorganisms are detected and negative if they are absent. Quantitative analysis shows the type of microorganism and its quantity in the smear.
POPULAR WITH READERS: Urethroscopy – procedure, rehabilitation, reviews
A smear culture is also carried out to determine sensitivity to antibiotics, which allows you to select the most effective antibiotic therapy.
Treatment for elevated leukocytes in a smear
To treat high levels of leukocytes in urine, it is necessary to determine the pathogen that caused such indicators in smears and decide on a strategy for treatment measures.
It is necessary to correctly diagnose the disease in order to determine the causes of the increased level of leukocytes in smears, and to select effective medications.
To ensure that the treatment is as effective as possible.
Treatment is often prescribed with antibiotics, and they have many side effects, especially when strong drugs are prescribed unreasonably.
If an infection gets into the urethra by accident, after an examination or after an incorrect placement of a catheter, with violations of antiseptic rules, then such patients are treated for about a week.
Irrigation and douching of the urethra with antiseptic solutions.
When the source of infection is eliminated, leukocyturia is also eliminated.
Contraindications for the procedure
You cannot take a smear from the urethra in men with a body temperature of 38 degrees or higher. This prohibition is due to the fact that the results of the study are likely to be incorrect. A smear is prescribed after a persistent decrease in temperature.
The study is also contraindicated for men with severe mental illness and alcohol intake.
Taking a smear may be difficult if the urethra is severely narrowed due to a tumor or anatomical features. For such pathologies, alternative diagnostic methods are selected.
Although you need to know that the most reliable results can only be obtained by analyzing a smear.
Types of probes used
There are many urological probes used to collect material from the genitourinary organs. Some of them are used only when material needs to be taken from the woman’s genitals.
A urethral swab is taken from men using:
- Universal probe type A. Consists of a handle and a working part made of viscose-microcellulose material in the form of a brush. In addition to the classic design, universal probes can have a reduced working part, which, in turn, reduces the trauma of taking a smear from the urethra.
- Volkmann spoon (type B). This is a double-sided spoon-shaped probe with rounded ends. The “spoons” have different sizes, which allows you to take biomaterial from the urethra in men, and from the vagina and cervical canal in women.
- Eyre spatula (type E). This is a spatula-shaped device with a perforated or rough spatula.
You can also use a special probe with a cotton swab at the end to collect material from the canal.
Urological probes for smears can be disposable or reusable. Most clinics use disposable ones, as they provide highly sterile manipulation.
How to take a smear from the urethra in men
The procedure for taking a smear is as follows:
- The patient stands with his trousers and underwear slightly lowered.
- The specialist taking the smear cleans the outlet of the urethra with a napkin, and then inserts a sterile instrument (brush, probe, cotton swab). If the patient does not experience heavy discharge, then he is asked to massage the penis a little from top to bottom.
- The collected material is placed on glass slides and marked. If a man is suspected of having a trichomonas infection, then saline solution is immediately added to the biomaterial. During research, this will help to identify mobile pathogens.
- The slides are sent to the laboratory, where they are dried and then examined under a microscope.
- If necessary, the laboratory assistant stains the biomaterial with methylene blue or aniline dyes (Gram stain).
If there is very little material on the tampon or probe, the doctor massages the prostate through the rectum, its contents are washed out of the urethra with prostatic juice, and a smear is immediately taken.
The material along with the instrument is placed in a sterile container and sent to the laboratory. Smears are made from it onto glasses with staining, studied under a microscope, or cultured on nutrient media, then the grown colonies of microbes are studied, or molecular genetic analysis is carried out.
| Indicators | Urethra | Vagina | Cervical (cervical) canal |
| Leukocytes | 0-5 | 0-10 | 0-5 |
| Epithelium | 5-10 | 5-10 | 5-10 |
| Slime | missing or small amount | small quantity is acceptable | small quantity is acceptable |
| Gonococci | – | – | – |
| Trichomonas | – | – | – |
| Fungi of the genus Candida (yeast bacterium) | – | – | – |
| Microflora | – | lactobacilli or bacilli in large quantities | – |
| Key cells | – | – | – |
- Trichomonas. In the absence of disease, flat microorganisms that are sexually transmitted are absent in the smear.
- Epithelium. Should be present in the range from 5 to 10. If the indicator exceeds the norm, the man has an inflammatory process of the urethra.
- In the absence of pathology in the smear, mucus is observed in a minimal amount.
- Leukocytes. These immune cells are necessarily contained in a smear from the urethra. The normal value varies from 0 to 5. If the number is increased by at least one division, we are talking about an infection that needs to be treated with medications - cystitis or prostatitis.
- Candida fungi. Absent under normal conditions.
- Gonococci. The presence of these microorganisms indicates gonorrhea in a man. A healthy person does not have them.
Preparation for manipulation
According to the rules, a doctor cannot take a urological smear immediately upon the patient’s first visit.
You need to carefully prepare for the manipulation:
- Avoid taking medications at least 2 days in advance. This is especially true for drugs for topical use - ointments and antiseptics in the form of a spray. If medications cannot be discontinued for health reasons, the doctor must be informed about this.
- 3 days before taking a smear, avoid sex, including anal intercourse and masturbation.
- The evening before the test, take a shower. You can't wash your face in the morning. However, you can wash the genitals without soap and gel if the discharge is too abundant and has a strong odor.
- 1-2 days before the smear, it is advisable to exclude smoked foods, too spicy and salty foods, and alcohol from the diet.
- On the day of the study, you should empty your bladder no later than 3 hours before the scheduled procedure. Urine washes away pathogenic microorganisms from the walls of the canal and they may not be detected in a smear taken immediately after urination. Within 2-3 hours, bacteria and other microorganisms accumulate, which makes it possible to accurately determine their quantity in the discharge.
Compliance with all recommendations at the preparatory stage minimizes the risk of obtaining false positive results, which means that treatment will be selected correctly and in a timely manner.
POPULAR WITH READERS: How a prostate tour is performed, indications and contraindications for surgery
Often men think about taking a urethral smear after accidental sexual intercourse with an unfamiliar partner. In such a situation, it makes no sense to take a test immediately after sex; most likely, it will not show the real picture. The causative agents of STDs can be identified by smear after an incubation period, which sometimes lasts up to a month.
The optimal timing for taking a general smear to identify a specific pathogen depends on the type of microorganism:
- Gripper (gonorrhea) is detected by a smear 3-14 days after sexual intercourse.
- It is better to be tested for chlamydia 2-3 weeks after the suspected infection.
- Mycoplasma and ureaplasma are determined by smear on average after 14 days.
- The bacteria that causes trichomoniasis develop within 3-14 days.
- For HIV infection, syphilis, and cytomegalovirus, it makes sense to take a smear 1-1.5 months after possible infection.
- It is advisable to take a smear for genital herpes after 1-3 weeks.
- The causative agents of hepatitis C and B are detected in tests after 30 days.
However, PCR testing detects pathogenic microorganisms much earlier - 2-4 days after infection.
Elevated leukocytes in the smear: where and from which doctor to treat
If the reason for the increase in the level of leukocytes in smears is urological, then men are treated by a urologist.
If you have an STI, then see a dermatovenerologist and urologist.
You need to get treatment where these doctors see you.
In a hospital, clinic or hospital.
The doctor himself will determine what treatment a man needs and prescribe outpatient or inpatient treatment.
Algorithm for the procedure
The method of taking biomaterial is not particularly difficult, but it must be carried out in a medical office under sterile conditions.
Stages of collecting a smear from the urethra in men:
- The patient is asked to remove the genitals from clothing.
- The doctor or nurse cleans it with sterile saline solution.
- The organ must be positioned so that the canal is straightened.
- A probe is inserted into the canal to a depth of 2 to 5 cm.
- After insertion, the instrument must be carefully rotated in a circle, this will allow you to take the maximum possible amount of the separated substance.
- The probe is removed and the contents of the smear are applied to a glass slide.
If PCR is planned, then after taking a general smear, the patient should be sent to urinate, but not completely, that is, a little urine should remain in the bladder.
Then the man comes back to the office, where the health worker, using a probe with a special brush at the end, takes a scraping from the urethra.
That is, after inserting the instrument, they do not make rotational movements, but rather scrape them along the wall from top to bottom.
The resulting discharge is placed in a special sterile sealed container. The slides and containers are sent to the laboratory.
How is biomaterial collected?
It is very important to wash thoroughly the night before.
The sampling technique is not difficult. It is carried out by a urologist or venereologist, mainly in the morning.
During the procedure, the specialist uses special instruments - a Volkmann spoon or a bacteriological loop. In some cases, a sterile swab is inserted.
The smear is performed at a depth of 4–5 cm in the urethra. After inserting the probe into the urethra, the doctor turns the handle of the instrument in a circle. Rotational movements allow you to collect the maximum amount of material from the walls. After this, the probe is removed.
The collected material is distributed on a sterile glass slide or on a special nutrient medium for cultural research. The smear is sent to the laboratory for careful examination.
Read also: Blood by PCR
Should you be afraid of pain?
Taking a smear from healthy men is not accompanied by pain, only a feeling of slight discomfort is possible. But if the canal walls are inflamed, which may be caused by urethritis or sexually transmitted diseases, the procedure causes discomfort.
The discomfort is associated with the fact that the walls of the canal are irritated in the acute phase of the disease, and the impact of a foreign object further increases this irritation.
However, you need to understand that for pathologies of the genitourinary system in men, it is impossible to choose the right therapy without a smear. Therefore, you will have to be patient, especially since an experienced doctor performs the manipulation in just a few seconds.
In private clinics, local anesthesia is offered before the procedure. A special gel is used for anesthesia, which does not affect the analysis results.
After the procedure, it is possible to experience burning and itching in the urethra, as well as pain during emptying of the bladder. Often men, fearing a recurrence of such symptoms, sharply limit fluid intake.
This is fundamentally wrong - concentrated urine irritates the mucous membranes even more. Sufficient intake of water, herbal teas with chamomile, calendula, cranberry or lingonberry juice helps speed up healing.
Severe pain can be relieved by taking a painkiller; a warm sitz bath can also help with this.
After taking a smear, it is not advisable for men to drink alcohol for 2-3 days or eat too spicy, fatty and smoked foods. If all recommendations are followed, unpleasant symptoms disappear within 2-3 days.
POPULAR WITH READERS: Spermogram interpretation, normal
Analysis transcript
A general smear is ready on average after 3 days. The form indicates the number of detected cocci, epithelial cells, mucous inclusions, leukocytes and atypical cells if detected.
It is considered normal if the following is found in the discharge:
- Within 5-10 epithelial cells. A larger amount of epithelium indicates an inflammatory process. Detection of transitional epithelial cells in a smear occurs with prostatitis.
- 4-5 leukocytes per field of view. A deviation above normal is a clear sign of inflammation of the urethra.
- Moderate amount of mucus. Exceeding this indicator is a laboratory sign of an inflammatory reaction.
A normal smear should not contain yeast-like fungi, gardnerella and other pathogens of infectious diseases. A small number of diplococci is acceptable.
Analysis of the contents of the urethra for hidden infections (PCR method) takes about 2 days. Normally, there should be no pathogenic microorganisms.
If they are identified, the study may take a little longer, since it is necessary to establish their quantitative relationship.
An accurate determination of the number of microorganisms that cause sexually transmitted infections allows us to determine whether the acute or chronic phase of the disease is developing. Based on this, medications are selected.
What antibiotics treat leukocytosis in a smear?
Antibiotic therapy is determined by the pathogens that caused the increased content of leukocytes in smears.
For example, chlamydia is treated with antibiotics - modern macrolides (for example, clarithromycin) and fluoroquinolones.
Gonorrhea is treated with ceftriaxone or azithromycin.
Trichomoniasis is treated with metronidazole or tinidazole.
Ureaplasmosis and mycoplasmosis are treated with tetracyclines, macrolides, fluoroquinolones, lincosamines or aminoglycosides.
Viral diseases such as HSV and cytomegalovirus are treated not with antibiotics, but with antiviral drugs.
What to do if you receive a false positive result
False-positive results mean receiving a smear test, the results of which suggest that a man has developed a certain disease, but in fact he does not. This is usually indicated by the absence of characteristic symptoms.
To avoid getting a false positive result, you need to:
- Strictly follow all stages of preparation for manipulation.
- Reduce the likelihood of bacteria from the external environment entering the smear. That is, the procedure must be carried out under aseptic conditions using sterile instruments. The health care worker must wear gloves, and the transportation of glass slides and material for PCR must be carried out in accordance with the rules adopted by the institution.
- Carry out a repeated smear examination after antibiotic therapy in compliance with the time frame.
If the doctor has doubts about the analysis, he can send his patient for re-diagnosis or prescribe a comprehensive examination.
How to reduce the number of white blood cells in smears
An increased level of leukocytes in smears, as we have already noted, is caused by inflammatory reactions.
In addition to fighting infectious agents, it is necessary to change old habits and change lifestyle to reduce the level of leukocyturia:
- quit smoking and abusing alcoholic beverages
- reduce the level of exposure to stressful situations
- perform light physical activity after heavy exercise
- If you are overweight, you need to lose it
- consult with your doctor about the effect of taking medications on the level of leukocytes in smears and urine
Compliance with these conditions will help reduce the elevated white blood cell count.
When to prescribe a repeat smear after antibiotic treatment
Sexually transmitted infections and inflammation, identified as a result of complex diagnostics, including determination of the flora of the urethral contents, indicate the need for antibiotic therapy. The type of antibacterial agent, its dosage and course duration are determined individually.
After completion of treatment, a second general smear is taken no less than 3-5 days later. An earlier sampling of the material may give a positive result, since bacteria can still persist for some time in the epithelial cells. PCR analysis is recommended to be done even later - 3-4 weeks after completion of the course.