A PCR smear allows you to determine the presence of an infectious agent in the human body. Most often, human secretions are examined for chlamydia and other pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases transmitted through sexual contact. The diagnostic accuracy is quite high, however, sometimes there are errors in determining the DNA of the pathogen. We will look at what this is connected with in the article.
What is this analysis?
The PCR method is used not only in medicine. It is used in archaeology, genetics, and criminology. The developer of this type of diagnostics is the American chemist Kary Mullis, a Nobel Prize laureate. By the way, he received the most prestigious international award for the discovery of the PCR method.
Thanks to the polymerase chain reaction, scientists have the opportunity to determine DNA similarity, establish paternity and family ties. And yet, the main purpose of a smear using the PCR method is considered to be the diagnosis of infectious diseases in humans.
The polymerase chain reaction is a highly accurate method of molecular genetic research, which allows one to identify viral, genetic and hereditary pathologies. The advantage of this technique is the possibility of identifying pathogenic agents not only at the acute or chronic stage of the disease, but also during the incubation period, that is, before the first symptoms of the pathology appear.
A PCR smear never gives a false positive answer. This is what distinguishes this diagnostic method from others. If there is no infection in the body, the patient will not receive a positive result - there is no doubt about that. Today, a polymerase chain reaction test is performed to determine the type of pathogen and its quantity.
Smear for bacteriological culture in women
The analysis involves inoculating women's secretions onto nutrient media.
After the formation of colonies of microorganisms, the laboratory technician can determine the type of pathogen.
The results of the study take several days to prepare, which presents some inconvenience for the doctor and the patient.
What infections in women can be detected by doing a bacterial culture test?
Bacteriological culture is carried out only to identify bacterial microflora.
There is virtually no chance of error.
Viruses or fungi cannot be identified using this method.
Advantages of PCR
None of the research methods is capable of finding the pathogen directly in the gene contained in the materials under study. PCR is the most accurate and reliable test for sexually transmitted diseases and latent viruses in the body. Unlike other diagnostic methods, polymer chain reaction analysis has a number of advantages:
- it is aimed at detecting the infectious agent;
- is universal because it allows you to detect several types of infectious agents at once;
- in this case, it is sufficient to use only one biological sample from the patient;
- has hypersensitivity, due to which the probability of possible cross-reactions is zero.
Compared to the bacteriological culture method, a PCR smear is considered the most reliable and fastest diagnostic method. The laboratory diagnostic procedure itself does not take more than four hours. It takes at least seven days to obtain the result of bacterial culture. The essence of this method is as follows: a sample of biomaterial is placed in a favorable environment and the activity of pathogens, if any, is observed throughout the entire period of the study.
Research stages
Analysis of a woman’s vaginal secretion is carried out in an equipped laboratory.
First, the smear is stained using the Gram method..
Methylene blue is used for staining. This process facilitates the fastest separation of bacteria into species.
The next step is for the laboratory technician to count each cell type .
The number of leukocytes and the degree of purity of vaginal secretion are assessed.
In a public clinic, the duration of studying the material can be up to seven days; in paid institutions, the analysis result can be obtained the very next day.
What infections is PCR suitable for detecting?
PCR smear analysis can reveal any number of infectious pathogens in the body, including “hidden” viruses that do not show any symptoms for a long time. This diagnostic method is used when it is necessary to confirm or refute the presence of the patient:
- viral hepatitis;
- ureaplasmosis;
- chlamydia of the genital tract;
- human papillomavirus;
- herpes;
- malignant cells;
- mycoplasmosis;
- vaginosis;
- mononucleosis;
- trichomoniasis;
- HIV infections.
Blood, saliva, sputum, and urine are used as test material for PCR analysis. Before the scraping procedure, the patient needs to prepare for it. The attending physician will inform the patient about how to prepare before the PCR smear test. As a rule, specialists conduct appropriate consultations with patients. For example, blood is donated on an empty stomach, and it is not advisable to carry out hygienic procedures immediately before scraping the cervix.
When to get examined?
Many representatives of the fair sex neglect regular examinations by a gynecologist and testing for sexually transmitted infections, believing that if there are no symptoms, then there is nothing to worry about. This approach cannot be called correct.
Most STIs occur without any symptoms or are characterized by scant clinical symptoms, which are often attributed to fatigue, hypothermia, inappropriate hygiene products and other unimportant reasons.
At the same time, untreated chronic inflammatory processes can lead to many problems: cycle disorders, decreased libido, discomfort during sexual intercourse, infertility, and miscarriage. Some STIs, such as human papillomavirus, even cause warts and increase the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Regular examinations are needed not only for those who are promiscuous, because you can become infected with an STI from a regular partner, during casual one-time sexual intercourse, and also, in some cases, through household means.
Tests are required in the following cases:
- For an active sexual life (regardless of the number of partners and contraceptive methods) - 1-2 times a year.
- If you have unprotected sexual intercourse (classical, oral and other types) with a casual partner, you must undergo a full range of examinations as soon as possible. Some of the tests should be repeated 1, 3 and 6 months after the first visit to the doctor.
- Before starting a new relationship and when getting married. Checking the reproductive system and getting tested for STIs is not an indicator of mistrust, but a sign of concern for one’s own health and the health and well-being of a partner.
- At the stage of planning a child, both the expectant mother and the father must be tested for sexually transmitted infections.
Be sure to go to the doctor and get tested if you have complaints: itching, burning, pathological discharge, unpleasant odor, urination problems, pain during sexual intercourse, inability to conceive or bear a child.
Also, a test for STIs is needed to monitor the treatment of sexually transmitted infections and before planned major operations (especially surgical interventions on the heart, lungs, abdominal organs, organ and bone marrow transplants).
Samples for research
The material for PCR analysis can be almost any human biological fluid. Foreign DNA of pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate into any environment. Most often, blood and its individual components (plasma or serum) are used as a sample for research. The liquid tissue may contain RNA from viral hepatitis, herpes simplex, cytomegalovirus, and HIV.
Biological fluids have wide indications for testing. These include:
- prostate juice;
- sperm;
- vaginal secretion;
- spinal (cerebrospinal fluid);
- amniotic;
- bronchoalveolar lavage;
- joint fluid;
- saliva.
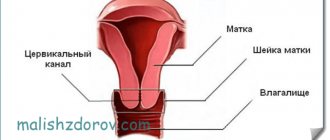
To diagnose sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, trichomoniasis, gardnerellosis, herpetic forms, etc., epithelial scrapings from the mucous membranes are taken from patients. For men, a PCR swab is taken from the urethra, and for women, from the vagina or cervix.
A separate category is biopsy samples. Most often, biopsy samples are examined to determine the nature of the neoplasm and confirm its malignancy. Biopsies of the stomach and duodenum are required to identify the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its quantitative load.
Urine as a biomaterial is used for infectious lesions of the urinary system. In men, a PCR smear is often replaced by a urine test, since the urethra in the stronger sex is a universal element of the genitourinary tract.
To diagnose tuberculosis and obstructive pulmonary diseases, sputum is examined. The material can be collected in a sterile vial (15-20 ml) or a swab taken from the throat. PCR analysis is also used to identify complicated forms of mycoplasmosis and chlamydia - in the absence of treatment and other unfavorable factors, these types of infections can affect the human respiratory system.
What are hidden infections
The list of such studies is different for each woman.
The doctor chooses what tests she needs to undergo based on the results of the examination and the survey:
- having casual sex with partners infected with STDs
- for existing symptoms and complaints made by the patient
- based on the results of a smear analysis for flora
Investigations are indicated for latent infections when:
- analysis of the smear results revealed signs of inflammation, but microorganisms in the discharge were not diagnosed
- the woman has no signs of pathology or symptoms characteristic of an STI are mild
- if a sexually transmitted disease is diagnosed. As a rule, such patients may often have other sexually transmitted infections, the symptoms of which are absent or manifest similar signs.
Hidden infections carry a certain danger, even if they have not declared themselves at all:
- have a negative impact on the structure of the urogenital tract, as a result of which the activity of the organs of the genitourinary system is disrupted
- the risk of infertility increases
- a sick patient spreads the disease, especially to her sexual partner
How to submit biological fluids for PCR: general rules
The method of preparation depends on what kind of biomaterial needs to be submitted for research:
- If a saliva sample is required for analysis, the procedure is performed on an empty stomach. You should not take medications several hours before the test. In addition, it is undesirable to drink a lot of liquid, especially hot liquid, so as not to disturb the natural composition of the microflora of the oral cavity.
- Urine for PCR must be collected in the morning. To do this, you need to prepare a sterile container and wash thoroughly. The material should not contain foreign impurities, so men need to pull back the foreskin during urination, and women need to cover the vagina with a cotton swab.
- Three days before sperm donation, a man must abstain from sexual intercourse. During the preparation period, it is not advisable to visit the sauna, take a hot bath, drink alcohol, or consume spicy foods. You should not urinate before collecting biomaterial, so it is advisable to limit your fluid intake the day before the analysis.
- Blood, as already noted, must be donated in the morning, on an empty stomach. 2-3 days before the analysis, it is advisable to give up fatty foods, alcohol and potent medications.
How to take it and how long it will take to get the result ready
How to take it and how long before the result is ready
Most clinic visitors feel a slight fear before taking tests. The procedure is completely safe and painless, the number of complications during its implementation tends to zero.
Collection for laboratory diagnostics is carried out by appointment, because you need to prepare for a doctor’s visit. The easiest way to prepare is for a blood test; there are no restrictions here.
Blood donation is carried out on an empty stomach, the material is taken from a vein in a volume of up to 10 ml. A PCR smear is made from the mucous membranes of the cervix (from the cervical canal), urethra and vagina.
Each slide is marked depending on the department from which the material was taken, with the Latin letters C, V, U and sent to the laboratory. How long it takes to prepare the result largely depends on the laboratory and its workload. On average, the period is two days. In emergency cases, the turnaround time can be reduced to several hours.
Indications for scraping in women
If a sexually transmitted disease is suspected, the doctor may prescribe a PCR smear for the woman. In laboratories that belong to budget clinics, such tests are usually not performed. Before choosing a place for research, you need to make sure that the necessary diagnostics are carried out there.
Most sexually transmitted diseases may not manifest themselves for several months, so the absence of symptoms is not a guarantee that the girl is not infected. Being a carrier of the infection and not realizing the disease, a woman can not only infect her partner, but also miss time for successful treatment. Sexually transmitted diseases can lead to infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease and other complications.
A PCR smear for infection is prescribed to a woman if there has been contact with an unfamiliar partner. If the sexually transmitted status of the latter is unknown, then there is a risk of infection. Taking a smear for PCR is advisable if:
- a woman doubts the “purity” of her new partner, since a condom was not used during sexual intercourse;
- the woman had several sexual partners during the year;
- the patient was previously diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease;
- pregnancy has occurred.
Screening for sexually transmitted infections is mandatory for expectant mothers, since some of them, even if they occur latently and do not make themselves felt, can pose a serious danger to the life and health of the fetus.
PCR smear for STIs
How to properly take a smear for STIs (chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma)? The causative agents of sexually transmitted infections are hidden - they do not manifest themselves in other tests and are very difficult to detect. How is discharge collected for laboratory diagnostics?
To obtain the accuracy of the analysis during the study, it is necessary to take a smear correctly:
- A PCR swab from the urethra is taken from men;
- in women, a smear for STIs is taken from vaginal secretions, urinary tract or cervix;
- you can’t take a smear during women’s periods;
- after an intensive course of antibiotics, you should wait 3 weeks, then get tested;
- before collecting mucus from the genitals, you should not urinate (at least three hours must pass after the last bowel movement);
- It is unacceptable to use scented detergents to wash the genitals before taking tests;
- a more reliable result can be obtained by collecting secretions before critical days or immediately after their completion;
- It is unacceptable to use vaginal suppositories or douching on the day of collection of discharge.
Is the collection procedure painful? You should not be afraid of a smear for diagnosis - the biomaterial is taken with a medical probe in a small volume without damaging the surface of the mucous membrane. After collection, the secretions are placed in a transport liquid for storage.
Important! Taking mucus from the urethra can cause discomfort for some time - a burning sensation when urine is released.
Smear procedure
A gynecologist takes scrapings from women. The procedure for taking a scraping for polymerase chain reaction is no different from a regular gynecological examination for vaginal flora. The procedure for taking a PCR smear for chlamydia, trichomoniasis, human papillomavirus, gonorrhea and other sexually transmitted infections follows the standard procedure:
- The patient prepares for the procedure and takes a seat on the gynecological chair.
- To collect the material, the gynecologist puts on disposable sterile gloves and examines the external genitalia.
- Next, a special dilator is inserted into the woman’s vagina, which allows the internal epithelium to be examined using a mirror.
- To collect biomaterial, a special brush is used, which does not have absorbent properties and is not capable of damaging the mucous membranes. It is used to take scrapings from the cervical canal and vaginal walls. An ordinary cotton swab is not suitable for this purpose.
- The used medical device containing vaginal secretions is inserted into a tube, capped and sent to the laboratory.
The scraping procedure is usually painless, but sometimes patients experience discomfort due to contact of the sensitive mucous membrane with gynecological instruments. Pain during the collection of biomaterial may indicate an ongoing inflammatory process.
Methodology for taking tests for infections in women
A smear from the urogenital tract is taken by a doctor.
A sterile spatula or cotton swab is used to collect biomaterial.
During the examination of the patient in the gynecological chair, smears are taken for microflora, for bacterial culture or PCR diagnostics.
The research method is chosen by the doctor.
Blood is drawn from a vein, preferably on an empty stomach in the morning.
Biomaterial is taken for serological reactions, ELISA or PCR.
Urine for testing for infection is collected in a sterile jar to prevent foreign microflora from entering the biomaterial.
The study is carried out using the PCR method, but bacterial culture cannot be ruled out.
Preparing women for a smear test
- You cannot have an intimate relationship before the procedure - at least two days must pass after the last contact.
- If a woman is being treated with antibiotics or using vaginal suppositories, the course of therapy must be completed three weeks before taking the PCR smear. Otherwise, the analysis result may be false.
- A smear is not taken during menstruation.
- Immediately before collecting biomaterial, you should not douche or use antibacterial soap.
- Before the procedure, you cannot visit the toilet; you can urinate for the last time three hours before the procedure.
How can a woman prepare for tests for infections?
No type of female smear test can guarantee a 100% result.
In any case, there is a high risk of obtaining false positive or false negative results.
Often the reason for this is improper preparation for testing, or violation of the rules for taking and transporting biomaterial.
To obtain reliable results, several conditions must be met.
Before being tested for infections, a woman will need to:
- Avoid sex for at least a couple of days.
- Do not visit the toilet before taking a smear, so as not to wash away pathogenic microflora with urine, at least for 2-3 hours.
- Avoid vaginal procedures using antibiotics and antiseptics on the eve of a visit to the gynecologist.
- Do not take antibacterial drugs orally or use topical treatment for at least seven days.
Features of preparation and conduct of the procedure in men
As already mentioned, a PCR smear in men is taken from the urethra. To obtain the necessary biomaterial, the urologist uses a special thin probe and inserts it to a depth of 3-4 cm. The process of taking a PCR smear for ureaplasma, gonorrhea and other common pathogens can bring pain and significant discomfort. But you'll have to be patient. Often in men, a PCR smear causes a burning sensation and itching, so before inserting a probe in order to reduce discomfort, patients are recommended to massage the urethra. The step-by-step scraping procedure looks like this:
- The man removes his genitals from clothing.
- Before inserting the probe into the urethra, the doctor puts on disposable gloves and visually inspects the skin and mucous membranes for rashes.
- Then, using an instrument, the urologist takes a PCR swab from the urethra. The probe is inserted 3-4 cm into the depth of the urethra and scrolled several times.
- After removing the probe, the doctor makes a smear on a glass slide, which is subsequently sent to the laboratory.
In addition to painful sensations, the scraping procedure causes psychological discomfort in men. Those who visit a urologist regularly do not have such problems. In addition, proper preparation for the PCR smear is important. It consists of meeting the following conditions:
- A few days before the analysis, a man needs to give up intimate relationships.
- The smear is taken in the morning.
- Before the procedure, a man does not need to perform genital hygiene; it is best to take a shower in the evening.
- Three hours before taking a biomaterial sample, you should not go to the toilet.
Just as in women, potent drugs can distort the result of a polymerase chain reaction test.
In what cases do they give directions?
In what cases are referrals given?
This type of research is super sensitive and allows you to quickly obtain results, which has made PCR in gynecology an integral part of diagnostics in gynecology. Urologists also often resort to it to make a diagnosis in men.
A PCR smear in women and men reveals:
- the presence of hidden sexually transmitted infections: chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis, herpes virus, including its oncogenic strains;
- HIV;
- hepatitis viruses A, B, C, D;
- rubella, measles, mumps viruses;
- Ebstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus;
- human papillomavirus;
An obstetrician-gynecologist gives a referral for examination in the following situations:
- pregnancy planning;
- severe pregnancy, history of miscarriages
- acute genitourinary infection during pregnancy or exacerbation of an existing chronic disease;
- unprotected sexual intercourse or having multiple sexual partners in the past 36 months;
- if there is a suspicion of an STI in women, when other examination methods have not revealed any pathological changes;
A smear for DNA testing is taken from the cervical canal, posterior vaginal vault and urethra with a special brush that does not injure the mucous membranes. To get an accurate result, it is important what day of the cycle you came to take a smear for infections. The gynecologist discusses in advance that menstrual bleeding should end at the time of the visit; it is best to take the test in the second half of the menstrual cycle.
After collecting material for STIs from women, which takes an average of three minutes, all collected material is transferred into a test tube and placed in a special apparatus (amplifier). The essence of his work is to find sections of the genetic code of a pathological agent and copy them, further identification, processing of information and issuing ready-made results. It is worth noting that another advantage is the possibility of complex diagnostics: during the test, several pathological agents can be detected.
How are PCR tests interpreted?
In principle, in order to understand the results of a laboratory test for polymerase chain reaction, you do not need to have a medical education. Deciphering the expert opinion is quite simple. The answers given to the patient contain information about the type of infection. If a pathogen is detected, a positive result will be noted in the report. It indicates the presence of DNA or RNA of the virus in the body of the person being studied.
For effective treatment of some diseases, it is necessary to have accurate data on the quantitative load, which means the presence of RNA copies of the pathogen per 1 ml of blood. To a greater extent, determining the quantitative load is important for diseases provoked by opportunistic microflora, since infectious agents are activated and negatively affect the human body only if their number exceeds established thresholds. This PCR analysis is of particular importance for drawing up a treatment plan and monitoring the dynamics of patients infected with viral hepatitis or HIV infection.
Decoding the result
PCR can be qualitative or quantitative. Qualitative shows whether the genetic material of a microorganism has been detected or not. On the response form it looks like this:
- RNA/DNA detected;
- No RNA/DNA detected.
A quantitative research method is possible only if the microorganism is present. Then the answer form states how many copies of RNA or DNA were found in a unit of the material being studied. For example, 1000 copies of DNA per ml were detected. A quantitative result is needed to determine the severity of the disease.
How long to wait for an answer
PCR tests are characterized by maximum accuracy, specificity and sensitivity. A smear for polymerase chain reaction allows you to find out whether there is a specific type of infection in the body of the person being examined, determine its strain and the number of RNA copies. The PCR method makes it possible to detect the pathogen even with a minimal content of viral DNA in the submitted biomaterial samples.
The timing of the analysis largely depends on which of the existing polymerase chain reaction methods is used in a particular laboratory. The simplest way to study biological material is considered to be microscopic. Usually this research method does not take much time. Patients have to pay extra for urgency, but if for some reason there is a need for an emergency test, the results can be delivered to the patient within an hour. Those who go to specialized medical institutions equipped with their own laboratory receive test results the fastest. Otherwise, it is necessary to take into account the time that will be spent on delivering the biomaterial.
Diagnosis of hidden infections
Examination for the presence of hidden infections allows you to diagnose pathology in the absence of symptoms.
The main method of testing for hidden infections is PCR.
The analysis allows you to identify the presence of several pathogens simultaneously.
But the limitation of the study is due to the fact that it has a fairly high price.
The cost of identifying one pathogen ranges from 300 rubles and more.
PCR diagnostics is a highly sensitive method and is highly effective.
The peculiarity of the technique is that it facilitates the diagnosis of the disease even when the process is still in the incubation period.
At the same time, the concentration of pathogen DNA is still relatively low and detection of infection by other methods is impossible.
Prices for PCR smear in Moscow
The final cost of the test will depend on what infection the patient needs to be tested for. In Moscow, the following prices are set for laboratory tests using the PCR method:
- sexually transmitted diseases - the analysis is performed on average in 1-2 days, the cost is 300-500 rubles. (for detection of one pathogen);
- the same terms and prices are established for diagnostics using the PCR method of Epstein-Barr virus, human papilloma, herpes, cytomegalovirus infection;
- an examination for hepatitis A, B, C, D, G will cost the patient 650-800 rubles; to clarify the quantitative load, you will have to pay another 2000 rubles. (the study will take 4-5 days to complete);
- confirmation of the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori in a gastric or intestinal biopsy – 400-600 rubles;
- HIV antibodies and antigens—400-500 rubles;
- the amount of HIV RNA in blood samples is more than 10 thousand rubles.
In order to save money, doctors recommend choosing test packages - such studies are cheaper. Discounted services are provided in most network clinics where tests are performed using the PCR method (SM-Clinic, Invitro, ON-Clinic) and multidisciplinary medical centers.
If pathogenic pathogens are found in the smear, there is no need to despair. The main thing is to start therapy as soon as possible. Today there are many drugs, thanks to which even patients with incurable diseases have every chance of a high quality and normal life expectancy. The choice of treatment tactics should be made by a doctor. Self-medication for infectious diseases is unacceptable.
Decoding female tests
Correct interpretation of the flora smear analysis is one of the specialist’s tasks.
Only the doctor who is treating the woman will be able to assess the reliability of the analysis.
Therefore, when interpreting the result, the doctor pays attention to the following indicators:
- Leukocyte count . If a woman’s smear contains a higher number of leukocytes than normal and many epithelial cells, this will indicate the presence of inflammation. If an increased level of leukocytes is detected in the urethra, a conclusion is drawn about the development of inflammation of the urethra; if the number of leukocytes exceeds the norm in the vagina, then this is a sign of vaginitis, in the cervical canal - colpitis. Here we can talk about inflammation caused by both specific microflora and nonspecific types of infection.
- Are there red blood cells? Their presence may indicate damage to microscopic blood vessels.
- For the presence of mucus. If there is a lot of it in the smear, then this signals the development of a pathological process.
A smear is considered normal when:
- Analysis of a woman's smear can show the presence of epithelium. If it is low, then the woman probably has low estrogen levels. With a significant amount of epithelium, the development of an inflammatory process is possible.
- No pathogenic microorganisms were found in it.
- The flora is predominantly rod-shaped.
- Key cells are missing.
- There is a small amount of mucus.
- Opportunistic microorganisms may be present in isolated quantities.
When deciphering the analysis of the urogenital smear being examined, it is imperative to take into account the presence of pathogens in it: trichomonas, chlamydia, gonococcal infection, etc.
If there is a pathogenic microflora, this confirms the presence of an infectious disease that requires immediate treatment.
Smear examination is one of the most common ways to study biomaterial, which has a high diagnostic value.
The analysis allows us to determine the presence of infection even in doubtful cases.
After the doctor has deciphered the smear and the doctor has some doubts about sexually transmitted pathologies, he is obliged to offer the woman additional examinations, including a blood test for hidden infections, which often accompany some sexually transmitted diseases.
PCR: what is it? Diagnosis of infectious diseases using polymerase chain reaction
7656 10 October
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. At the end of the article, see the dictionary.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
was invented in 1983 by Kary Mullis (American scientist).
He subsequently received the Nobel Prize for this invention. Currently, PCR diagnostics is one of the most accurate and sensitive methods for diagnosing infectious diseases. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
is an experimental method of molecular biology, a method for significantly increasing small concentrations of certain nucleic acid (DNA) fragments in biological material (sample). The PCR method is based on the repeated doubling of a certain section of DNA using enzymes under artificial conditions (in vitro). As a result, quantities of DNA sufficient for visual detection are produced. In this case, only the section that satisfies the specified conditions is copied, and only if it is present in the sample under study. In addition to simply increasing the number of DNA copies (this process is called amplification), PCR allows for many other manipulations with genetic material (introduction of mutations, splicing of DNA fragments), and is widely used in biological and medical practice, for example, for diagnosing diseases (hereditary, infectious) , to establish paternity, to clone genes, introduce mutations, and isolate new genes.
Specificity and Application
PCR is a molecular diagnostic method that has become the “gold standard” for a number of infections, time-tested and thoroughly clinically tested. The PCR method allows you to determine the presence of a disease pathogen, even if only a few DNA molecules of the pathogen are present in the sample.
PCR allows you to diagnose the presence of long-growing pathogens without resorting to labor-intensive microbiological methods, which is especially important in gynecology and urology when diagnosing urogenital sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Also, this method is used to diagnose viral infections such as hepatitis, HIV, etc. The sensitivity of the method significantly exceeds that of immunochemical and microbiological methods, and the principle of the method allows one to diagnose the presence of infections with significant antigenic variability. The specificity of PCR when using PCR technology even for all viral, chlamydial, mycoplasma, ureaplasma and most other bacterial infections reaches 100%. The PCR method allows you to detect even single cells of bacteria or viruses. PCR diagnostics detects the presence of pathogens of infectious diseases in cases where this cannot be done by other methods (immunological, bacteriological, microscopic). The PCR method is especially effective for diagnosing difficult-to-cultivate, unculturable and latent forms of microorganisms, which are often encountered in latent and chronic infections, since this method avoids the difficulties associated with growing such microorganisms in laboratory conditions. The use of PCR diagnostics is also very effective against pathogens with high antigenic variability and intracellular parasites. The PCR method makes it possible to identify pathogens not only in clinical material obtained from a patient, but also in material obtained from environmental objects (water, soil, etc.). In urological and gynecological practice - to detect chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, gonorrhea, herpes, gardnerellosis, mycoplasma infection, HPV - human papillomavirus; in pulmonology - for differential diagnosis of viral and bacterial pneumonia, tuberculosis; in gastroenterology - to identify helicobacteriosis; in the clinic of infectious diseases - as an express method for diagnosing salmonellosis, diphtheria, viral hepatitis B, C and G; in hematology - to detect cytomegalovirus infection, oncoviruses. The specificity of PCR is based on the formation of complementary complexes between the template and primers - short synthetic oligonucleotides 18 - 30 letters long. Each of the primers is comparable (complementary) to one of the strands of the double-stranded template, framing the beginning and end of the amplified region. After combining (hybridization) of the template with the primer (annealing), the latter serves as a primer for DNA polymerase in the synthesis of the complementary strand of the template.
Carrying out PCR
To carry out PCR in the simplest case, the following components are required:
- DNA template containing the DNA section that needs to be amplified;
- two primers complementary to the ends of the desired fragment;
- thermostable DNA polymerase;
- deoxynucleotide triphosphates (A, G, C, T);
- Mg2+ ions necessary for the operation of the polymerase;
- buffer solution.
PCR is carried out in a thermal cycler - a device that provides periodic cooling and heating of test tubes, usually with an accuracy of at least 0.1°C.
To avoid evaporation of the reaction mixture, add high-boiling oil, such as Vaseline, to the test tube. The addition of specific enzymes can increase the yield of the PCR reaction. Reaction progress
Typically, PCR involves 20-35 cycles, each of which consists of three stages. The double-stranded DNA template is heated to 94 - 96°C (or 98°C if a particularly thermostable polymerase is used) for 0.5 - 2 minutes to separate the DNA strands. This stage is called denaturation - the hydrogen bonds between the two chains are destroyed. Sometimes, before the first cycle, the reaction mixture is preheated for 2 to 5 minutes to completely denature the matrix and primers.
Once the strands have separated, the temperature is lowered to allow the primers to bind to the single-stranded template. This stage is called annealing. The annealing temperature depends on the primers and is usually chosen 4 - 5°C below their melting temperature. Stage time - 0.5 - 2 minutes.
DNA polymerase replicates the template strand using a primer as a primer.
This is the elongation stage. The elongation temperature depends on the polymerase. Commonly used polymerases are most active at 72°C. The elongation time depends on both the type of DNA polymerase and the length of the amplified fragment. Typically, the elongation time is taken to be one minute per thousand base pairs. After all cycles are completed, an additional final elongation step is often performed to complete all single-stranded fragments. This stage lasts 10 - 15 minutes. Preparing material for research and transporting it to the laboratory
For successful analysis, it is important to correctly collect material from the patient and properly prepare it. It is known that in laboratory diagnostics the majority of errors (up to 70%) are made precisely at the sample preparation stage. To collect blood in the INVITRO laboratory, vacuum systems are currently used, which, on the one hand, minimally injure the patient, and on the other, allow the material to be collected in such a way that it does not come into contact with either personnel or the environment. This avoids contamination (contamination) of the material and ensures the objectivity of the PCR analysis.
Dictionary
DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid – is a biological polymer, one of two types of nucleic acids that ensure storage, transmission from generation to generation and implementation of the genetic program for the development and functioning of living organisms. The main role of DNA in cells is the long-term storage of information about the structure of RNA and proteins.
RNA-ribonucleic acid is a biological polymer similar in its chemical structure to DNA. The RNA molecule is built from the same monomeric units - nucleotides - as DNA. In nature, RNA usually exists as a single strand. In some viruses, RNA is the carrier of genetic information. In the cell it plays an important role in the transfer of information from DNA to protein. RNA is synthesized on a DNA template. This process is called transcription. There are areas in DNA that contain information responsible for the synthesis of three types of RNA, which differ in the functions they perform: messenger or messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and transport RNA (tRNA). All three types of RNA are involved in protein synthesis in one way or another. However, information on protein synthesis is contained only in mRNA.
Nucleotides are the basic repeating unit in nucleic acid molecules, the product of a chemical combination of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (pentose) and one or more phosphate groups. Nucleotides present in nucleic acids contain one phosphate group. They are named according to the nitrogenous base they contain - adenine (A), containing adenine, guanine (G) - guanine, cytosine (C) - cytosine, thymine (T) - thymine, uracil (U) - uracil. DNA contains 4 types of nucleotides - A, T, G, C, RNA also contains 4 types - A, U, G, C. The sugar in all DNA nucleotides is deoxyribose, RNA - ribose. When nucleic acids are formed, nucleotides bind to form a sugar-phosphate backbone of the molecule, on one side of which there are bases.
Primer is short DNA used to replicate the template strand.
Each of the primers is complementary to one of the strands of the double-stranded template, framing the beginning and end of the amplified region. Literature
- Glick B., Pasternak J. Molecular biotechnology. Principles and Application. Per. from English - M.: Mir, 2002. - 589 p., illus. ISBN 5-03-003328-9
- Shchelkunov S.N. Genetic engineering - Novosibirsk: Sibirsk. Univ. publishing house, 2004. - 496 pp.; ill. ISBN 5-94087-098-8
- Patrushev L.I. Artificial genetic systems - M.: Nauka, 2005 - In 2 volumes - ISBN 5-02-033278-X
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.