Get tested for cortisol
Every person is exposed to stress almost every day - the daily bustle of the city, early rises, fatigue, lack of sleep, malnutrition and many other factors play a big role here.
A stressful state triggers a complex chemical process in the body, which results in the production of the hormone cortisol by the adrenal cortex. With its help, the body's forces are mobilized so that a person can survive stress not only on an emotional, but also on a physical level.
Its special role in the body is difficult to overestimate, since it is cortisol that is responsible for concentration and stimulates the functioning of the brain and heart muscle.
In a normal state of the body, in children and adolescents under the age of 16 years, the level of cortisol in the blood does not, as a rule, exceed 85-580 nmol/l.
Adult women have a reading from 138 to 685 nmol/l.
A lack of cortisol or an excess of it can indicate a number of health problems.
An exception in women may be pregnancy, due to which the level of cortisol may increase 3-5 times, which will be the absolute norm in this case. The body of the expectant mother, devoting all her strength to the growth and development of the child, is constantly in a state of stress, just like the pregnant woman herself, constantly worrying about the condition of the baby in the womb.
However, if there is no pregnancy and the hormone level is elevated, this may indicate the development of diseases such as cirrhosis of the liver, polycystic ovary syndrome, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, depression, as well as various metabolic disorders (proteins, fats and carbohydrates), in which cortisol is directly involved.
Recently, doctors found that an increased concentration of cortisol in a woman’s blood is one of the key signs of the presence of HIV infection in the body. When undergoing a medical examination, taking a hormone test is an integral part of it.
A decrease in the level of cortisol in the blood often occurs in those representatives of the fairer sex who are often addicted to strict diets and lose excess weight too intensively.
Low levels of the hormone can also indicate the approach of menopause, various hormonal disorders, and the presence of hepatitis in the body.
It is possible to take a test for cortisol in the blood of women at any convenient time at the CMD Center for Molecular Diagnostics. A couple of days before coming to the laboratory, a woman should stop taking oral contraceptives, alcohol, smoking, and reduce the consumption of coffee and tea. It is best to donate blood for analysis in the morning on an empty stomach.
You will receive the results of the study the very next day.
Read more about preparing for analysis at www.cmd-online.ru
How does cortisol work in the body?
To understand the importance of this element for human life, you need to clearly understand what functions it performs in the body.
Cortisol is secreted by the adrenal glands in response to the release of adrenaline into the blood. At the same time, it softens the manifestations of adrenaline stress. In other words, it equalizes blood pressure that has risen as a result of stress, normalizes the heartbeat and general hormonal levels. In addition to the main function of protecting the body from the effects of adrenaline, cortisol has a number of others. Thus, this hormone is involved in the process of assimilation of sugar from food received and transferring it to cells.
The hormone has a suppressive effect on inflammatory mediators, thus preventing inflammatory processes in a variety of organs.
Cortisol helps cells regulate levels of minerals and other beneficial trace elements.
The microelement is able to remove excess lipids from the body, which affects a person’s overall well-being and weight. To be clear, an obese person has very little cortisol in their blood.
But if there is a lot of hormone in the blood, it exceeds the norm, then this also leads to very dangerous conditions. The only acceptable cause for a significant increase in cortisol in the blood is severe stress or pregnancy.
In other cases, a violation of the microelement level leads to heart attacks and strokes.
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate DHA-S DHEA-S
DHA-S (DHEA-S) is a male sex hormone synthesized in the adrenal cortex. Determined to diagnose the origin of hyperandrogenism (excess of male sex hormones) in women.
Preparation for DHA-S analysis
: On the eve of the study, it is necessary to exclude medications that affect the level of DHEA-S in plasma, physical activity, smoking, administration and intake of glucose.
In newborns, especially premature infants, the concentration of DHEA-S in plasma is increased, then sharply decreases during the first week of life. Several years before puberty and during this period, the plasma concentration of DHEA-S increases. Further, with age, there is a progressive decline in DHEA-S in men and women. No specific circadian rhythm has been identified for this hormone. During pregnancy, its concentration in plasma decreases.
Alcoholism, taking 75 g of glucose, and severe illnesses cause a decrease in DHEA-S. Physical activity, fasting, smoking – increase.
Reasons for increased DHA-S levels:
adrenal hyperandrogenism (adrenal hyperplasia, tumors, Cushing's disease)
Reasons for low DHA-S levels:
17-ketosteroids are metabolic products of male sex hormones. This analysis allows you to evaluate the total level of all male hormones per day. This is an advantage over individual hormone blood tests, which measure individual hormone levels over time and are thus less sensitive. Daily urine on 17-KS allows you to catch any fluctuations in any male hormones during the day. This method would be more informative than a blood test for hormones if everything was collected and prepared for analysis correctly. In modern conditions, if the laboratory determines 17-hydroxyprogesterone in the blood, it is better to donate blood.
In newborns and children aged 15 years, the content of 17-KS in urine is lower than in adults. With age, excretion of 17-KS increases. After 30-40 years, a gradual decrease in the concentration of 17-KS in urine is observed. Men excrete 17-CS higher than women. During pregnancy, excretion increases. Peak excretion occurs in the morning, and minimal excretion occurs at night. In winter, the content of 17-KS in urine is higher than in summer.
3 days before collection and on the day of collection, coloring foods (yellow, orange, red) are excluded from food: carrots, beets, red apples, citrus fruits (all including juices, salads, sauces, soups, etc.), vitamins. Otherwise, the indicator will be overestimated. On the eve of the study, physical activity, smoking, and stress are excluded.
On the day of collection, the first morning portion of urine is not collected. Next, the whole day, all night and the first morning portion of the next day (at the same time, just the day before, i.e. so that exactly 24 hours pass between two morning portions) are collected in one large container. Next, the volume of daily urine is carefully measured with a measuring cup (the accuracy of the analysis depends on the accuracy of the volume) and written down on a piece of paper along with your full name. The contents of the container are mixed and poured into a small jar, like a regular urine test. The 17-KS level will be recalculated to the total daily volume indicated on the piece of paper.
Beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin. Chorionic gonadotropin is synthesized by the cells of the chorion - the membrane of the embryo. Its determination in the blood or urine means the presence of chorionic tissue in the body: pregnancy, remnants of membranes after the end of pregnancy, a tumor of chorionic tissue (hydatidiform mole, chorionic carcinoma). Judge the well-being of pregnancy, embryo viability, etc. hCG cannot be directly assessed, because it is secreted not by the cells of the embryo, but by the membranes, which can continue to grow even after the pregnancy has died out. HCG consists of two subunits; it is the beta subunit that is specific, and it is on its determination that the diagnosis of pregnancy is based. However, it also has more than half the same composition as LH of the pituitary gland.
Exceeding the norm for a given stage of pregnancy:
- hydatidiform mole, chorionic carcinoma
- multiple pregnancy
Decrease, insufficient dynamics of hCG growth:
- threatened abortion
- ectopic pregnancy
- placental insufficiency
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of use
- Copyright holders
- Adenoma
- Uncategorized
- Gynecology
- Thrush
- About blood
- Psoriasis
- Cellulite
- Ovaries
Hormones, how and when to take them, preparation for the study.
Progesterone - this hormone is released on days 19-21 of the cycle, on an empty stomach.
Testosterone - this hormone can be tested any day.
Estradiol - on the eve of the test, avoid physical activity (sports training) and smoking. In women, the analysis is performed on days 2-5 of the menstrual cycle, unless other dates are indicated by the attending physician.
LH - 3 days before taking blood, you must avoid sports training. 1 hour before blood collection - smoking. Immediately before taking blood, you need to calm down. Blood is drawn on an empty stomach, sitting or lying down. The analysis is done on days 2-5 of the menstrual cycle, unless other dates are indicated by the attending physician. In the case of irregular ovulation cycles, blood should be drawn to measure the LH level every day between 8 and 18 days before the expected menstruation to determine the ovulation of the cycle.
FSH - on the eve of the test, exclude physical activity (sports training) and smoking. In women of reproductive age (from approximately 12-13 years of age and before the onset of menopause), the test is performed on the 2-5th day of the menstrual cycle, unless other dates are indicated by the attending physician.
Prolactin - exclude sexual intercourse and heat exposure (sauna) 1 day before, smoking 1 hour before. Since prolactin levels are greatly influenced by stressful situations, it is advisable to exclude factors that influence the research results: physical stress (running, climbing stairs), emotional arousal. Therefore, before the procedure, you should rest for 10-15 minutes in the waiting room and calm down.
Cortisol - on the eve of the test, it is necessary to avoid physical activity (sports training) and smoking. It is also necessary to exclude the use of drugs such as synthetic analogues of glucocorticoids, estrogens, opiates, and oral contraceptives.
T 3 general - 1 month before the test it is necessary to avoid taking thyroid hormones, unless otherwise prescribed by an endocrinologist. 2 - 3 days before the study, do not take medications containing iodine. Blood collection should be carried out before X-ray contrast studies. On the eve of the study, it is necessary to exclude sports training and stress. Blood is taken on an empty stomach. Immediately before blood collection, the patient should be at rest.
T4-total - 2 - 3 days before the study, do not take iodine-containing drugs and, 1 month before - thyroid hormones, unless there are special instructions from an endocrinologist. Blood collection should be carried out before examinations, using radiocontrast agents. On the eve of the study, it is necessary to exclude physical activity and stress. Immediately before taking blood, the patient should be at rest for at least 30 minutes. Blood is taken on an empty stomach.
TSH - the level of this hormone must be checked on an empty stomach to exclude thyroid dysfunction. On the eve of the study, it is necessary to exclude physical activity (sports training), drinking alcohol and smoking.
AT TSH - No specific preparation for the study is required. Available on any day of the menstrual cycle.
DEA sulfate - No preparation required for the test
17-OH progesterone - in women, blood is usually taken for testing on the 3rd - 5th day of the cycle).
STG. 3 days before taking blood it is necessary to avoid sports training, 24 hours before taking blood, avoid drinking alcohol, 1 hour before taking blood - smoking. It is better to donate blood in the morning, after an overnight period of fasting. The study is carried out on an empty stomach (12 hours after the last meal). The patient should be completely at rest for 30 minutes before blood is drawn.
Rules for conducting hormonal tests
Establishing the basal level of any hormone does not require strict preparation. The minimum set of conditions here include donating blood on an empty stomach between 8 and 9 am. Some hormones are analyzed using this method. However, most hormones are influenced by external and internal factors occurring in the body
It is important to take into account the day of the cycle on which hormones are given. Because daily dynamics often have clinical significance when diagnosing pathology
General rules for preparing for hormone tests:
- It is advisable to refrain from eating heavy foods (fatty, fried, spicy, salty, highly seasoned) 8–12 hours the day before.
- A day, or better yet, a few days before visiting the laboratory, you need to give up physical overload, intense sports, and emotional turmoil.
- In advance of the examination, about a week in advance, you will need to stop taking medications, especially hormonal medications, antidepressants and other serious medications. You must inform your doctor about such courses of treatment.
- During the day you will need to exclude intimate contacts.
Blood is donated in the morning between 8 and 10 o’clock, always on the days of the cycle on which the doctor has prescribed hormones. A small volume of blood is collected from the ulnar vein. The reliability of the readings is affected by alcohol and smoking, therefore, before taking a test for hormonal levels, you should also refrain from this. You should come to the laboratory in advance to allow your body to calm down and normalize your pulse and blood pressure.
When receiving a response, the form usually indicates one of three quantitative options for the hormone level:
- Norm.
- Hyperfunction of the gland (excess).
- Hypofunction of the gland (decreased).
When interpreting the normal or pathological value of a particular hormone, it is necessary to take into account the patient’s gender and age. To conduct hormonal analysis in women, you need to take into account the day of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, testing for hormonal levels in women in the reproductive period is carried out on specific days of the menstrual cycle. Some hormones need to be tested during menstruation. Pregnancy greatly affects the hormonal levels of the female population. During the period of gestation, pronounced hormonal changes occur.
Hormones have a systemic effect on the body, so the regulation of their production is extremely difficult. The concentration of hormones in the bloodstream can also be influenced by such factors as the individual properties of the patient’s body, the seasonal time of year, and the climatic features of the region of residence. And in addition, taking specific medications.
If, according to the results of an analysis of hormone levels, there are pronounced deviations from normal in one direction or another. Then, depending on the specific hormone, an extensive examination is prescribed, including a series of studies aimed at identifying a specific pathological process. In doubtful situations, the doctor can send for a repeat hormonal analysis in the same laboratory to check the consistency of the information. Also taking into account the day of the cycle when it is better to take hormones. If the indicator is good and there are no symptoms, then everything is fine with the body or the cause is not hormones. Correct diagnosis, which is made in accordance with the days of the cycle and based on an accurate interpretation of laboratory data, will allow medical professionals to make timely adjustments to the hormonal balance.
Normal indicators and interpretation of tests
There are several ways to determine the amount of cortisol. Typically, blood or urine is taken for analysis. An additional research technique is an ACTH test. This refers to adrenocorticotropic hormone, which actually stimulates the production of the substance discussed in this article. This test is required to determine the type of adrenal insufficiency. Thus, its normal level indicates the primary form of the disease, and a reduced level indicates a secondary one.
The level of cortisol in a blood test varies depending on gender and age:
- in children under 10 years of age – 29-149 nmol/l;
- from 14 – 55-695;
- until 16 – 29-857.
Further, the level stabilizes within 138-636 nmol/l. And for women:
- in the morning the norm is from 140 to 621;
- in the evening – 49-290.
For men, acceptable indicators are:
- at the beginning of the day – 171-535 nmol/l;
- at the end - 65-325.
In pregnant women, standard values sometimes increase up to 5 times. This does not pose any danger. In order to get tested, you should visit an endocrinologist. In the case of women, a gynecologist can also write a referral. Cortisol in urine is indicated in mcg/day. The norm for all genders is from 80 to 120.
How to prepare for donating blood for hormone testing
It is imperative to prepare for the collection of material for hormones in advance, since many factors can significantly distort the picture. It is best for the endocrinologist (he is the one who refers you for this study) to give clear and detailed recommendations for preparing for the examination, which begins 2 weeks before the blood is donated.
14 days before the test, you must completely stop taking hormonal medications. If this is impossible for health reasons, you must inform the endocrinologist and laboratory worker about this.
Physical activity is prohibited 3 days before donating blood. They always increase the level of stress hormone, and therefore do not allow you to see the real picture.
24 hours before sampling, you must completely stop drinking alcohol, fatty foods and smoking. You will also need to protect yourself as best as possible from stressful situations that will cause a “hormone surge.”
8 hours before donating blood, you should refuse to eat and drink only clean, still water in any quantity.
How will the analysis be carried out?
The patient's condition will be assessed by an experienced doctor, who will prescribe a test or a series of tests for hormones. If certain pathologies are suspected, a blood test for cortisol is prescribed. The doctor decides which biological fluid to donate - urine or blood.
The material is taken into special sterile containers if blood is to be donated from a vein. This is done in the laboratory by experienced specialists.
If you have to donate urine, you should collect the daily amount yourself. After sleep, the first portion of urine is not collected, unless otherwise specified by the doctor!
What is cortisol
The hormone is necessary for the human body in order to adequately tolerate stress and quickly recover from it. Cortisol received the title of “stress hormone” for the formation of defensive reactions to external threats and stressful situations. It increases heart rate and increases blood pressure.
An increase in the hormone is observed both during emotional stress and during physical overload. At times of stress, the hormone in the body is responsible for the following functions:
maintaining concentration;
improving brain nutrition;
improvement of protein synthesis;
maintaining normal heart function;
maintaining normal vascular function;
accumulation of glycogen in the liver.
The substance also reduces the absorption of calcium by bones, which to some extent increases their elasticity, reducing fragility.
Functions and Features
The hormone cortisol is important for the body because it allows you to cope with stress and hunger normally. It is directly related to other hormones, especially adrenaline.
When danger arises, the body releases adrenaline, which increases the level of the hormone cortisol. A person experiences an increase in blood pressure, heart rate, and vasoconstriction. It is cortisol that limits the effects of adrenaline, controlling and, if necessary, reducing the volume.
Decreased hydrocortisone value
With low cortisol levels, the patient may experience weakness and abdominal pain, decreased blood pressure and rapid loss of body weight. The reduced numbers may indicate that:
- ACTH production is impaired (for example, due to a brain tumor);
- There is a pathology of the adrenal glands: Addison's disease;
- Adrenal hyperplasia;
When cortisol levels are low, the first step is to stimulate the production of ACTH. If this does not help, additional diagnostics are performed. Your doctor may want to check other hormones.
There are several rules that you need to know when preparing for research:
- It is necessary to notify the doctor in advance about taking medications prescribed for continuous use. Before the analysis, the doctor may recommend stopping their use for several days.
- Before taking the test, you need to protect yourself from stress. As noted above, a stressful situation directly affects the production of the hormone.
- It is necessary to reduce physical activity a couple of days before the analysis and up to and including the day of the examination.
- It is advisable to stop smoking a day before going to the clinic.
- You need to avoid drinking alcohol the day before and on the day of the test.
- The analysis is given without breakfast. You must come to the clinic in the morning on an empty stomach. The level of the hormone depends on whether the patient has eaten or not. If your doctor allows it, you can drink a glass of regular still water.
Venous blood is taken for analysis. If the patient donates blood for the first time, the doctor will explain how to properly donate blood from a vein and tell where the laboratory is located.
A woman should know when to take cortisol tests and on what day of the cycle. If the doctor has not said anything else, women take the test on the 3rd to 7th day of the monthly period. Sometimes a specialist decides on which day of the cycle to donate blood.
After receiving the results, you need to go to a specialist again. You cannot diagnose yourself and prescribe treatment on your own.
A blood test for cortisol shows that the amount of the hormone in the blood changes with age. The following table gives the average cortisol value depending on the number of years lived:
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of use
- Copyright holders
- Adenoma
- Uncategorized
- Gynecology
- Thrush
- About blood
- Psoriasis
- Cellulite
- Ovaries
Normal cortisol levels during pregnancy
It is clear that for each person, especially women, the level of the hormone that is considered normal varies greatly. However, scientists were able to average the measurement results for age categories.
In a person under 1 year of age, the level should be from 28 to 966 nmol/l.
Next, the microelement content in the blood begins to increase:
- 1-5 years – the level is 28-718 nmol/l;
- 5-10 years – 28-1049 nmol/l;
- 10-14 years – 60-690 nmol/l;
- 14-16 years 28-856 nmol/l;
- From 16 years and older – 140-640 nmol/l.
The level of trace elements in the blood also fluctuates depending on what time of day the analysis was performed. By the way, for men all daily and age-related fluctuations are much less than for women.
During pregnancy, even if a woman knows how to take a cortisol test correctly and, most importantly, prepares for it, the norm of the microelement in the blood can be exceeded 5 times. In her situation, this is not a signal of the onset of pathology, it is rather the norm. Therefore, when analyzing cortisol in pregnant women, the duration of pregnancy is taken into account to the nearest week.
The level of any trace element in the blood is normalized by influencing the cause of its disturbance. That is, at the first stage of treatment, the cortisol level is adjusted using synthetic hormones. But in the future, the patient undergoes a full diagnosis in order to identify the causes of this situation. And as a result of additional research, a treatment plan is developed.
When is it prescribed?
A cortisol test is prescribed by a doctor after examining the patient and taking a medical history. The attending physician decides on the need for diagnostics to check or monitor the functioning of the pituitary gland and adrenal glands. It is the indicators that will give an idea of the health or the presence of pathologies of the endocrine system.
A cortisol test will be ordered if:
- Depression and constant stress. Prolonged blues can provide insight not only into a person’s mental state, but also into their physical health. If the results turn out to be above normal, treatment should be carried out so that the state of depression does not become a permanent process.
- Persistently elevated blood pressure. This option will only be considered if the drugs prescribed to correct blood pressure have stopped working.
- Suspicion of Itsenko-Cushing's disease. This is a condition characterized by increased production of hydrocortisone. The disease is characterized by muscle weakness with constantly elevated blood pressure and excessive body weight.
- Addison's disease or suspected development of such a disease. It is quite rare, and is characterized by a decrease in the level of hormone generation by the adrenal cortex. In this case, the amount of such a substance in the blood will not be increased, but decreased.
You should not interpret cortisone tests yourself.
To correctly interpret the results obtained, you should consult a doctor. A specialist who deals with such problems is called an endocrinologist. Some cases require repeat testing to rule out or confirm the disease.
Indications for checking hormone levels
You should donate blood for hormones to determine cortisol levels if you have the following disorders:
- absence of pregnancy with a healthy reproductive system,
- miscarriages repeated more than 2 times,
- excessively early puberty in both girls and boys,
- the appearance of acne over the age of 20 years,
- increased bone fragility (may occur due to prolonged insufficient absorption of calcium),
- high blood pressure in the absence of disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system,
- muscle weakness,
- Addison's disease
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease,
- rapid weight loss in the absence of diseases and parasites in the intestines.
The doctor, if he sees the need, refers the patient for a cortisol test, based on the results of which further therapy is prescribed. The hormone is determined in the blood serum. The level of the hormone varies depending on the time of day, as well as the day of the cycle (in women), which is why you should know exactly the optimal time for the analysis.
What is cortisol?
Cortisol is considered to be the most powerful hormone of the adrenal cortex from the glucocorticoid series of hormones.
Its synthesis and concentrations in the blood are determined by the pituitary hormone ACTH, otherwise known as adrenocorticotropic hormone.
In addition to ACTH, stress can stimulate active reproduction and release of this hormone into the blood.
With the exception of stress and adrenocorticotropic hormone, cortisol is subject to circadian rhythms (its concentration peaks in the morning, and by midnight it begins to gradually fall).
The ACTH hormone and its concentrations depend on the hormone corticoliberin, synthesized by the hypothalamus.
All processes of communication between the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal glands or corticotropic hormone-releasing hormone-cortisol are controlled and corrected based on the principles of negative communication.
Interesting! The principle of negative connection from the point of view of the hormonal ratio of the body is represented by a kind of “swing”.
That is, an upward jump in cortisol suppresses the volume of synthesis of its stimulants - corticoliberin and ACTH, and vice versa.
Cortisol cannot dissolve in water, so it enters the blood and is transported through the bloodstream in a form bound to globulins (blood proteins).
Of the total blood cortisol, approximately 75-80% is transported along with transcortin (cortisol-binding globulin), 15% is bound to albumin, and only 10% of cortisol circulates through the bloodstream in free form.
Directly free cortisol is a biologically active compound that can affect body processes:
- Increases overall reactivity during stress, physical activity, and viral diseases.
- Increases blood glucose concentrations, stimulates the production of glucose and glycogen from fats and proteins.
- Activates the process of degradation of fatty tissues of the lower extremities, while simultaneously increasing the rate of their formation in the neck and face.
- Accelerates the degradation of proteins in muscle and connective tissues.
- Suppresses the occurrence of inflammatory processes.
- Increases excitability and psycho-emotional instability.
When changes occur in such processes, this analysis is required.
This is due to the fact that a decreased or increased indicator over a long period of time can lead to noticeable and sometimes irreversible disruptions in the body.
Causes, symptoms and treatment of low cortisol
A lack of cortisol never occurs out of the blue - there are a number of reasons for this. They are often pathological and are directly related to abnormalities in the functioning or structure of the adrenal glands. Hypocortisolism can result from:
- development of Addison's disease;
- congenital anomalies of the adrenal glands (in particular, their pathological growth);
- defects of the hypothalamic-pituitary system;
- hypothyroidism of various etiologies and severity;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs based on corticosteroids.
Low cortisol in the blood can be a consequence of overwork and lack of sleep. But at the same time, the patient himself may not be aware of the deviation, since many symptoms of the pathological condition are often simply ignored by them. However, the longer such an anomaly lasts, the more dangerous the consequences will be!
Clinical manifestations
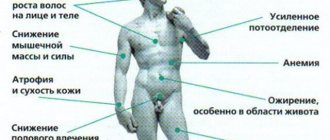
Reduced cortisol is manifested by the following clinical signs:
- constant (chronic) fatigue;
- hypotension;
- decreased or complete loss of appetite;
- sudden weight loss;
- fainting (especially in women);
- nausea and vomiting;
- pain in the abdomen;
- muscle pain;
- weakness even with light physical exertion;
- decreased libido;
- hair loss;
- tendency to depression;
- depressed psycho-emotional state.
As you can see, if cortisol is low, it is no less dangerous than when it is high. To overcome unpleasant symptoms, you should not wait until they go away on their own. Timely seeking medical help is the main key to recovery!
Methods for normalizing a hormonal element
How to normalize the hormone cortisol? First of all, you need to decide on the goal. That is, to understand whether it needs to be raised or lowered.
If we are talking about a deficiency of a hormonal element, the patient is prescribed replacement therapy using glucocorticoids. The dosage and duration of treatment is a purely individual factor, so the therapeutic regimen is developed by the attending physician for each patient separately.
To lower the levels, special drugs are used - cortisol blockers, or anti-catabolics. Among the most accessible and relatively safe drugs, doctors often resort to prescribing:
- Fast protein in the amount of 20-30 g;
- Leucine;
- Clenbuterol;
- Agmatina;
- Anabolic steroids.
A good and highly effective cortisol blocker is ascorbic acid. If you are intolerant, or for any other reason why vitamin C cannot be prescribed, you can resort to the use of fish oil or amino acids.
Foods enriched with proteins and carbohydrates in large quantities also significantly suppress cortisol production. However, you should not take any measures without first consulting a doctor. Self-medication can lead to serious consequences, and this should not be forgotten, no matter what abnormalities in the functioning of the body we are talking about!
News on the topic of cortisol analysis
Read more
DIY cortisol test
Doctors prescribe a blood test to determine the level of the hormone cortisol in many diseases, especially endocrinological ones. Obtaining the results of this procedure takes time - but scientists have managed to turn a smartphone into an express laboratory.
Read more
A blood test will indicate a potential suicide
Contrary to popular belief, the likelihood of committing suicide is increased not only in patients with mental disorders - the risk group is much larger. Scientists propose identifying people who are “on the brink” using a blood test.
Read more
The threat of a heart attack can be determined by one hair
Timely diagnosis of an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases in people prone to them would help save millions of lives on a planetary scale every year. One of the factors that provokes the development of a heart attack is chronic stress. However, until now, scientists have not been able to find a reliable marker that would indicate that stress has reached alarming levels, and a heart attack can happen at any time. Canadian scientists have managed to develop a method that allows one to determine the degree of stress by the level of the hormone cortisol in the hair.
An unfavorable work environment leads to a persistent increase in cortisol levels
Negative job characteristics, such as high demands placed on employees and low levels of social support, are significantly associated with increased blood cortisol levels.
Read more
Information about the stress we have endured is “hidden” in our hair.
For decades, scientists have obtained information about the level of stress a person has endured by studying the level of a specific hormone, cortisol, in the blood. But this method has significant limitations, and scientists from the USA have created a more accurate method.
Read more
Aggression in child psychiatrist patients can be determined by saliva analysis
Aggression is typical not only for adult patients in psychiatric clinics, but also for children suffering, for example, from hyperactivity and attention deficit disorder. Scientists from the USA have created a simple method for determining the degree of aggression in boys.
Read more
Stress increases risk of memory loss in diabetics
British scientists have concluded that stress leads to an increased likelihood of memory loss in patients with diabetes. Subjects who had elevated concentrations of the stress hormone cortisol in their blood performed lower than others on a cognitive skills test.
Read more
Short-term stress impairs memory and learning
Even short-term stress, which manifests itself as irritability and negative reactions to events, can impair memory and other important brain functions, according to a recent analysis.
Low birth weight can cause problems
Low birth weight in babies can lead to low levels of cortisol, also known as the stress hormone, and can lead to serious illness, according to a recent study.
What does elevated cortisol indicate?
When daily urine shows elevated levels of the hormone, this phenomenon is called hypercortisolism. Doctors note that this is not always a pathology - for some people, such indicators are considered normal throughout their lives.
All of these conditions cause increased cortisol production, but this is temporary.
But there are also more serious, pathological reasons for which cortisol increases:
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease;
- oncological diseases;
- neoplasms of the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, bronchi, ovaries, uterus;
- diabetes;
- hyperthyroidism of the thyroid gland.
Deviations upward
If hydrocortisone levels are consistently high, the doctor can determine the presence of one of the following pathologies:
- pituitary adenomas;
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome;
- pathologies in the adrenal glands (cancer, adenoma, hyperpasia);
- obesity;
- pregnancy;
- fever;
- asthma;
- infectious diseases;
- acromegaly;
- ectopic syndrome;
- pathologies in the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism);
- SD (uncompensated type).
Assessing the circadian rhythm of cortisol production
A violation in one of the above processes is a reason for the attending physician to prescribe an analysis of the circadian rhythm of cortisol production. Typically, symptoms of circadian rhythm disorder with increased cortisol levels include:
- Visceral obesity: increased abdominal circumference, which creates the feeling of too thin limbs.
- Thinning of the skin, vulnerability, the appearance of stretch marks with a purple tint.
- Muscle mass decreases, muscles become weak and tired.
- Immunity decreases, fungal diseases often appear.
- Women experience excessive body and facial hair, disruptions in the ovulatory cycle, and infertility.
And low cortisol levels manifest themselves in the following symptoms:
- High levels of potassium, glucose and calcium in the blood.
- Decreased appetite, severe weight loss.
- Reduced blood pressure levels.
An analysis of the circadian rhythm of cortisol production is prescribed by an endocrinologist at the Sensitive LCC in Yeisk, and the same specialist will assess the condition of the adrenal glands and pituitary gland and prescribe effective treatment.
Benign neoplasms in gynecology: surgery Diseases of the parathyroid gland, and surgical treatment Diagnosis of hormonal imbalance Colonoscopy with drug-induced sleep at the Sensitive LCC Polypotomy under local anesthesia New ultrasound machine at the Sensitive LCC: a high level of diagnostics Gynecological operations: what is tubectomy? Types of contact lenses