The growth of a polyp from the epithelium in the uterine cavity is a common occurrence in women, regardless of age.
It is usually benign in nature, but as the uterine mucosa grows and hyperplasia, it may well turn into a malignant form. This increases the risk of developing oncology, endometrial cancer or infertility.
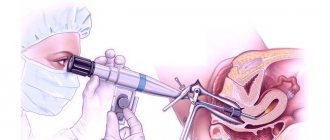
Hysteroscopy is a new modern procedure that allows you to scan the entire uterine cavity, promptly identify polypous areas of tissue, and remove them at the initial stage in order to avoid the development of a tumor and completely unpleasant consequences in the future.
What are polyps in the uterus?
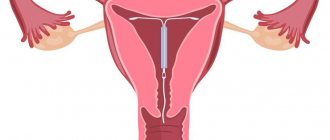
A polyp is a small wart-like growth up to 3 cm in length. Under the influence of a number of provoking factors, it begins to grow from the endometrial mucosa in the uterine cavity and initially has a benign course. Gradually creating favorable conditions does not prevent the degeneration into cancer.
Localization of the polyp is possible both inside and on the surface of the cervical cavity.
The neoplasm is removed through surgery, although at the initial stage and according to the diagnostic results, it is possible to eradicate the polyp using medications and folk methods.
Main stages of endometrial treatment
Growths in the uterus are a pathology that requires complex and long-term therapy. In each case, the sequence and availability of actions may vary.
Diagnostics
The beginning of any treatment is a correct diagnosis. To identify polyps on the surface of the endometrium, 2 instrumental techniques are sufficient:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs, and the transvaginal type will be more informative. Modern equipment finds formations of several mm if the procedure is carried out in the first 3 days after menstruation, otherwise the growing endometrium will hide the polyps.
- Diagnostic or office hysteroscopy is the most accurate way to identify growths in the uterus. Carry out only after ultrasound in a similar time frame. Requires preparation in the form of a set of tests for infections and other parameters.
Additionally, a blood test will be required to check the level of sex hormones, because in most cases, imbalance and endometrial polyps are combined with each other.
Observation and drug correction
Formations in the uterine cavity measuring 5-10 mm are not removed. The patient is monitored by a gynecologist, and the main task is to eliminate the causes of the pathology. For this purpose, the following means are used:
- Hormonal drugs, if there is an imbalance, polycystic ovaries and other diseases that occur against the background of endocrine disorders;
- Antibiotics are necessary for polyps inside the uterus, because the formations are often accompanied by infectious inflammation. These can be either tablets or vaginal suppositories.
It is impossible to say exactly what medications will be prescribed; much depends on the patient’s health condition. Sometimes doctors skip this step because urgent removal of polyps from the endometrium is required.
Hysteroresectoscopy
This is what is called hysteroscopy to remove growths in the uterus. This is a full-fledged surgical operation, which is performed using gentle modern methods. The devices are delivered into the organ cavity through the vagina and cervix, which is fixed with a dilator. Then they provide pressure inside the uterus with incoming and outgoing fluid. For this purpose, special solutions are used to allow electrical appliances to operate normally. The polyp is cut off or annealed with electric current. Laser removal of tumors is available in a few clinics. In standard cases, when there are no accompanying severe complications in the form of large fibroids or extensive polyposis, hysteroscopy is performed on an outpatient basis. For pain relief, intravenous injections of short-term general anesthesia are used. After waking up, the woman rests for several hours under the supervision of an anesthesiologist. Since modern anesthetics do not cause noticeable side effects, the patient will be able to go home on her own the same day.
Severe cases are operated on as an inpatient unit under full anesthesia followed by a stay in the hospital. A woman over 40 with numerous formations can have the uterus amputated completely, then the intervention will be open through an incision in the peritoneum.
Attention! In many public clinics, blind endometrial curettage is still used to get rid of endometrial formations. Therefore, when prescribing an intervention, it is necessary to clarify how it will be carried out.
Causes of polyps
The impetus for the growth of a growth on the endometrial mucosa in the uterus can be the following provoking factors:
- hormonal imbalance, when the amount of estrogen begins to prevail over all other hormones, thereby stimulating the growth of pathological cells from the epithelial uterine layer;
- gynecological diseases: hyperplasia, endometritis, adenomyosis, mastopathy, polycystic ovary syndrome;
- diseases caused by inflammation: adnexitis, colpitis, vaginitis;
- frequent abortions;
- installation of an intrauterine device;
- curettage against the background of excessive mechanical trauma to the delicate endometrial mucosa.
In particular, the risk group includes women suffering from:
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypertension;
- obesity;
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- diseases of the nervous and endocrine systems.
The cause of polyposis may well be constant stress, starvation, and strict diets.
Types of polyps in the uterus
A polyp on the cervix appears either as a single specimen or in a small group. It has a porous structure and resembles a dark purple cylindrical growth.
Depending on the cause and nature of growth, three types of polyps are distinguished:
- adenomatous as the most dangerous growths with the ability to progress and degenerate into a malignant tumor;
- glandular with growth from the iron tissue of the uterus, more often detected in young women (up to 25 years);
- fibrous , which may be caused by proliferation or hyperplasia of the connective tissue of the uterus against the background of the localization of another type of neoplasm.
Procedure
Before the instruments are placed into the uterus, the woman is given cervical relaxing injections and anesthesia. Anesthesia when removing endometrial polyps using hysteroscopy is usually short-term - 20-30 minutes. Only in complicated cases is full surgical anesthesia used.
The following actions:
- A cervical dilator is installed;
- A tube is inserted - a hollow tube with a diameter of 65 mm for diagnostics and 80 mm for hysteroresectoscopy;
- An optical instrument and surgical instruments are delivered through it;
- The organ cavity is first filled with special solutions to straighten out the folds. Fluid is pumped in and out continuously to maintain a safe pressure inside the uterus;
- Using a video camera, a polyp is found;
- The formation is removed by excision, laser, radio wave scalpel or electrode;
- Clean and seal the wound under the base of the growth;
- The polyp will come out with fluid;
- The uterus is washed with antiseptics;
- Remove the tools step by step;
- The removed lesion is sent for cytology.
Symptoms of polyps
With the appearance of a small single polyp, there are practically no symptoms. Only a random scheduled visit to a gynecologist can identify the problem at an early stage.
Most often, women turn to doctors when the inflammatory course in the uterine cavity goes too far, becomes chronic and protracted, and of course, all the signs of polyposis are evident:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen that intensifies before the onset of menstruation;
- discomfort during intimacy;
- discharge of white clots, flakes from the vagina or bloody (brown) discharge that is in no way related to menstruation;
- the appearance of scanty spotting menstruation or prolonged periods with periodic occurrence of uterine bleeding.
Symptoms will only intensify with even minor contact or mechanical impact:
- The uterine mucosa becomes hyperemic and irritated.
- Gradually, the polyp will begin to grow , blocking the entrance to the cervical canal of the uterine cavity. Women experience prolonged menstruation.
- Over time, the epithelial layer will begin to degenerate into pathological tissue. As a result, the process will become malignant, the formation of pathogenic cancer cells. This condition can provoke a miscarriage in women if they still manage to get pregnant. Or the pregnancy will be complicated, and the polyp, as it grows, will ultimately lead to the placenta descending, insufficiency of the isthmus and cervix.
The risk group includes older women during menopause, when heavy bleeding or spotting appears. Such signs can no longer be ignored and you need to consult a doctor.
On a note! The very first signs of hypoplasia or metaplasia should alert you. Especially when women over 48 years of age experience a prolonged absence of menstruation, or vice versa, the appearance of heavy bleeding.
Is anesthesia dangerous during the procedure?
The danger of anesthesia is often greatly exaggerated. Modern medicine has modern drugs that make it possible to carry out interventions using sedatives and anesthetics without any risk to the patient’s health. Most drugs are approved for use for concomitant diseases that were previously contraindications to the use of anesthesia.
Most complications that appear after the use of sedation and anesthetics are in one way or another associated with violation of recommendations for preparation for the procedure or during the rehabilitation period. In order for the operation to be successful and to avoid complications as a result, it is enough for the patient to strictly follow the instructions given by the anesthesiologist and gynecologist.
Is it necessary to remove polyps in the uterus?
Polyps in the uterus pose a certain danger to women’s health, because there is a high probability of developing cancer, so of course, it is necessary to remove the growths as quickly as possible.
In addition, polyposis leads to heavy uterine bleeding, inability to get pregnant or complications during pregnancy.
IMPORTANT! Polyps increase the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy and pose a threat of miscarriage, because placental abruption can occur at any time. If doctors insist on abortion, then women should probably agree. In addition, the condition becomes no less dangerous for the fetus.
To avoid such complications, it means that doctors eradicate polyps immediately after their discovery, regardless of the stage of development.
The main indications for the operation are:
- achieving polyps larger than 10 mm;
- the age category of women after 42 years, when hormonal levels become extremely unstable.
The adenomatous form of polyps is especially dangerous, prone to malignancy and degeneration into malignant cancer at any time.
Treatment options
Treatment of polyps in the uterus is complex.
At the initial stage, in order to avoid surgery, which is still a gross intervention in the already injured uterine cavity, medications are prescribed:
- antispasmodics for severe nagging pain (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Analgin);
- topical antiseptics for douching (Septoderm, potassium permanganate) to suppress foci of disease and wash out infection.
Today, the most effective methods for removing growths in the uterine cavity are:
- scraping;
- cryodestruction;
- laser coagulation;
- polypectomy;
- curettage as an emergency measure in the event of heavy bleeding against the background of polyposis, which doctors resort to when it is impossible to remove the growth in another way.
On a note! Heavy, unstoppable bleeding is a sign of impaired hemostasis or the cyclic functionality of blood factors necessary for timely stopping of bleeding. To stop life-threatening bleeding, doctors sometimes take emergency measures by introducing a curettage (carriage) to eliminate the lesion.
But hormonal therapy is not able to get rid of the tumor completely, but it can stop the polyposis process and the growth of the tumor in size.
If it makes sense, doctors prescribe hormones in long courses if necessary to achieve stable remission.
Even surgical methods do not guarantee complete removal of the focal affected tissue.
Sometimes doctors have to prescribe chemicals to women after surgery, i.e. It is proposed to undergo a course of chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Scraping
Previously, curettage of the uterus to remove polyps to avoid relapses was performed on almost every woman.
But today this is an ineffective and traumatic method. The procedure is carried out blindly, which means there is no guarantee of complete removal or separation of the polyp stalk.
There is a high probability of leaving particles of damaged tissue in the uterus, which can subsequently begin to revive again and lead to relapses.
Today, curettage is recognized by many doctors as an absolutely useless procedure, although it is often performed in conjunction with a newer and more effective technique - hysteroscopy.
This allows manipulations to be carried out more efficiently. Thanks to the inserted hysteroscope, the doctor will be able to visually examine and assess the condition of the cavity in full. Next, the polyp will be torn off along with the stem and cauterization will be performed.
Or a curette is used as an instrument inserted to dilate the cervix, then a metal loop is made, the polyp is torn off from the wall of the uterus and brought out.
Samples of the collected tissue were sent to the laboratory for further study.
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is one of the modern techniques that allows you to completely remove a polyp, thereby avoiding possible complications after surgery.
The essence of the technique is to use a hysteroscope - a thin, bendable tube with a miniature video camera at the end.
Introducing it into the uterine cavity allows doctors to completely visualize the growths from all sides, assess their size, shape, and degree of distribution.
The duration of the procedure takes no more than 30 minutes.
In addition, the device makes it possible to immediately carry out a procedure to remove a polyp, i.e. unscrewing the stem, visualizing all manipulations on the computer monitor, then neutralizing the affected area, cauterizing with antiseptics.
Thus, the pathological tissue is removed in full and the risks of re-formation on the uterine mucosa are minimized.
Benefits of the procedure
Hysteroscopy has earned recognition among doctors and is often used in practice to remove polyps in women.
Main advantages:
- possibility of carrying out without anesthesia;
- low-impact nature of the cervix and cervical canal;
- thorough diagnosis of the uterine cavity;
- identification of almost any gynecological pathology, regardless of the degree or stage of the lesion;
- elimination of endometrial hyperplasia and uterine parenchyma at an early stage;
- the procedure takes 30-40 minutes and patients do not require hospital treatment;
- rapid rehabilitation after surgery;
- reducing the likelihood of complications and relapses later.
This is a gentle and effective technique that allows you to examine the uterine cavity layer by layer, carry out the procedure painlessly, minimize possible bleeding and shorten the recovery period.
It is the hysteroscope, by insertion into the uterine cavity, that makes it possible to identify growths of even the smallest size, when women have practically no symptoms.
Also, glandular fibrous polyps, which are fraught with the development of cancer, thereby suppressing the infectious focus in time by carefully unscrewing the leg of the polyp with special forceps and bringing it out, reducing the risk of developing oncology.
All actions are reflected on the monitor, so the doctor’s manipulations are carried out smoothly and quickly, leaving smoother walls in the uterine cavity.
Removal method
The technique is carried out on an outpatient basis and does not require preliminary preparation or the use of other treatment methods.
The essence of the procedure:
- the patient sits on the gynecological chair;
- anesthesia is administered, which lasts 1.5 hours by administering a solution intravenously;
- The cervical canal expands specially. tools;
- a hysteroscope tube with a video camera at the end and illumination is inserted to visualize the cervical canal and tubal orifices, namely gas in a small amount to completely open the cavity and straighten the walls of the mucous membrane;
- a smear is taken for subsequent examination, and a piece of affected tissue is also taken for subsequent examination;
- a curettage carriage is inserted, the leg of the polyp is unscrewed; surgical scissors;
- curettage is performed;
- pathological fluid is pumped out of the uterine cavity.
The woman can be transferred to the general ward for several hours after the manipulations, taking into account her general well-being.
Preparing for surgery
Before preparing for hysteroscopy, the doctor will have a diagnostic conversation with the patients.
It is important to identify the presence of contraindications, existing symptoms, and individual intolerance to injected honey. drugs.
In particular, it is prescribed:
- blood test for syphilis, AIDS, Rh factor;
- taking a smear to detect infection or determining the degree of cleanliness of the vagina and taking material for antibodies, hepatitis using markers;
- a general blood and urine test to refute or document the development of the inflammatory course.
Additionally, a woman must pass:
- fluorography;
- Ultrasound;
- consultation with a therapist, who issues a conclusion on the need for hysteroscopy.
No preparatory procedures are carried out before the operation. Enough the day before:
- do not overeat;
- limit fluid and water intake to avoid the appearance of negative symptoms after the administration of anesthesia;
- avoid sexual intercourse for 4-5 days;
- do not douche for 7 days, do not use vaginal suppositories and take pills the day before.
It is advisable to give a cleansing enema in the evening to empty the intestines and have a light breakfast, avoiding foods that can cause fermentation and gas formation. The procedure is carried out in the morning and mainly on an empty stomach.
Recommendations after therapy
Scraping is a tough procedure and, of course, does not go away without a trace. The operation is similar to a mini-abortion, when, after all, pain in the lower abdomen is possible, and blood discharge leaves the vagina.
As recommendations, women should be advised when unpleasant signs appear:
- take an analgesic antispasmodic (no-spa);
- carry out douching for 3-4 days until the bleeding stops and the cervix returns to its normal tone
IMPORTANT! It is unacceptable to visit a hot bath, sauna, or steam bath, or lift weights for 3-4 days. It is worth giving up intimacy for a while, in particular, inserting tampons into the vagina containing aspirin, which can lead to blood thinning.
Doctors have a very mixed opinion about carrying out hormonal therapy in case of imbalance. The main thing is to understand how effective and advisable their use is. On the one hand, of course, the endometrium needs restoration.
Therefore, hormone treatment is most often prescribed in the case of removal of glandular adenomatous polyposis or endometrial hyperplasia, i.e. in severe advanced cases.
Doctors advise some women to place intrauterine devices with Levonorgestrel, which can restore endometrial function, improve hormonal levels and even promote conception.
Removal of polyps with laser
Laser removal of polyposis has long been very popular.
It is the laser, as a gentle method, that does not lead to tissue scarring and preserves reproductive functions, which is important for women planning childbearing.
The method prevents relapses and allows women not to undergo treatment in a hospital. The procedure takes no more than 3 hours.
But the result is the rapid elimination of polyps, sealing of blood vessels, and the absence of leaving scars in the uterine cavity, which, of course, greatly increases the chances of conceiving in the future.
Types of hysteroscopy
This broad concept includes different methods of implementation. Therefore, the word “hysteroscopy” alone cannot describe what will be done in a particular case.
By difficulty:
- A standard removal procedure, which is performed on an outpatient basis without anesthesia, under local anesthetics or short-term general anesthesia. Suitable for a few small uterine polyps that are not burdened by concomitant pathologies;
- Complex cases, when the formation is quite large, the area affected by polyposis is extensive, or there are additional problems in the form of fibroids or endometriosis, require an removal procedure under general anesthesia in a hospital setting. This may include working with patients who have general health problems, such as poor blood clotting.
By purpose:
- Diagnostic hysteroscopy is performed to examine the endometrium of the uterus, as well as to take a biopsy sample for histology;
- The treatment procedure is carried out to eliminate formations;
Attention! Sometimes diagnostic procedures end with the removal of the polyp.
By type of equipment used:
- Mechanical hysteroscopy, when the formation is removed by excision or unscrewing using forceps and other surgical instruments.
- Electrocoagulation, if an electrode in the form of a loop is used to separate the body of the polyp. The tissues melt under the influence of current.
- Laser removal allows the formation to evaporate quickly and without scars.
- Radiosurgery is comparable in effectiveness to the previous method; for removal, a special instrument is used that evaporates tissue with radio waves.
Mechanical treatment is often completed by treating the wound with an electrocoagulator to avoid bleeding.
Consequences of polyp removal
No special consequences were identified after laser therapy or hysteroscopy. But everything depends on the skillful hands and manipulations of the doctor during operations.
In some cases there may be:
- bleeding from the vagina;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- modification of the menstrual cycle and the nature of discharge;
- slight increase in temperature in case of infection of the endometrium;
- the appearance of discomfort and pain after sexual intercourse;
- long absence of menstruation up to 3-4 months;
- the appearance of uterine perforation due to blind curettage or hysteroscopy;
- accumulation of blood clots in the uterine body.
Rarely, if the growth is not completely removed, adenomatous growth is possible again, as a precancerous process.
In fact, if the polypous lesion begins to recur, complications and unpleasant signs appear, there is a high probability of the polyps spreading again.
With a correctly chosen technique and a competently performed operation, negative consequences are excluded. The process of regeneration of damaged cells and tissues will proceed quickly.
If unpleasant symptoms appear, then you should not ignore the following:
- discharge of serous, purulent discharge from the uterus with an unpleasant odor;
- increased temperature that does not subside for more than 3 days;
- the occurrence of acute, burning pain in the lower abdomen;
- the appearance of heavy bleeding, which may indicate poor quality of manipulation by the doctor.
In these cases, it is possible to prescribe a course of treatment with antibiotics, antispasmodics, antiseptics, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Complications resulting from hysteroscopy
Surgery has a number of theoretically possible negative consequences. After removal of a polyp from the uterine cavity, the following may occur:
- Bleeding, the appearance of which is often associated with a woman’s failure to comply with the rules of the rehabilitation period.
- Infection as a result of the operation is almost impossible. During the procedure, the uterus is treated with antiseptic solutions, all instruments are sterile, and after the operation a course of antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
- Embolism is the entry of air into the vessels, which can cause the death of the patient. This happens as a result of preparing the uterus for the procedure, when carbon dioxide is introduced into the cavity to straighten the walls. The professionalism of a doctor will not lead to such consequences. As a rule, liquids are more often used for removal for this purpose.
- Acute allergic reaction to anesthetics. Before the operation, the anesthesiologist must conduct special tests that can be used to determine a safe anesthesia drug. In addition, the condition of the patient’s cardiovascular and respiratory systems is taken into account.
- Damage to the cervix during insertion of the hysteroscope tip.
- Perforation of the uterine wall, that is, a hole as a result of manipulation. This is very dangerous for a woman's life. Therefore, correct setup of the equipment, monitoring of the progress of actions and the experience of the surgeon are important.
- Non-infectious inflammation and adhesions can result in infertility. Preventive observation during the rehabilitation period will prevent this.
- Relapse of pathology. Its likelihood increases with incomplete removal of the polyp, so the professionalism of the doctor plays an important role here too.
- Oncology as a result of incomplete removal of a formation containing cancer cells. Therefore, after surgery, all polyps are sent for histology to study their structure and composition. If a dangerous diagnosis is confirmed, a decision may be made to repeat hysteroscopy or amputation of the uterus.
Attention! The listed complications after surgery are observed in isolated cases; the occurrence of many of them depends on the experience of the surgeon, so you need to carefully consider the choice of a doctor.
Period after surgery
A big role is given to compliance with medical recommendations after surgery.
It is important to maintain personal hygiene, keep the uterine cavity clean and not expose it to injury, mechanical stress, or friction at first.
Attention! Self-medication and the use of folk remedies after removal of polyps are excluded. Although the benefits of douching with boron uterus for the rapid restoration of the mucous epithelium are known. But all actions must be previously agreed with a doctor. Improper home treatment can only make the situation worse.
Observation
Visits to the gynecologist after surgery for examination should be regular.
First, once every 2 weeks, then once every 3-4 months.
It may be necessary to adjust the restorative treatment course.
It will be necessary to take medications to relax muscles or relieve spasms in the cervix.
Also take a course of anti-inflammatory drugs as needed.
Hormonal treatment
Hormonal therapy is prescribed after removal of a glandular-fibrous polyp, also to correct hormonal levels, which usually fail and are weakened after surgical manipulations.
It is important to restore hormonal status and normalize the cyclicity of menstruation.
Applicable gestagenic, hormonal drugs orally:
- Yarina;
- Regulon;
- Janine;
- Duphaston;
- Norkolut.
Yarina
Janine
Regulon
Duphaston Norkolut
offers women over 35 years of age to put on the Mirena spiral for up to 5 years, which does not lead to side effects and is a completely effective hormonal drug.
The intervention does not have the best effect on the uterine cavity, so it is important for women to follow all the doctor’s recommendations and instructions.
When carrying out hormonal therapy for up to 6 months, it is important to further undergo a final examination and tests.
Antibacterial treatment
Treatment with antibiotics is carried out more often for prophylactic purposes, in order to prevent possible infectious complications after surgery to remove polyps.
Antibiotics are prescribed for courses of up to 10 days. But therapy is carried out only according to indications in a number of clinical cases when the development of an inflammatory process and infection of the genitourinary tract is observed.
It happens that curettage and inept manipulations by a doctor lead to the development of an inflammatory focus, when in order to relieve inflammation it is necessary to take medications in order to avoid, thus preventing relapses in the future.
Folk remedies after hysteroscopy
Many alternative medicine recipes help not only cure endometrial polyps, but also serve as a means of preventing relapses. For example, the hog uterus can restore the balance of hormones and relieve inflammation. Using sage and red brush gives the same effect. A combination works better: in the first half of the cycle one plant, and in the second half another.
Celandine has a good effect against various tumors and formations. It can be drunk in the form of infusions and decoctions, as well as douched. Today it is available to buy ready-made candles with plant extract at the pharmacy.
Attention! Folk remedies for uterine endometrial polyps are best used after completion of drug treatment and rehabilitation. The reaction of substances can be unpredictable.
Possible complications after surgery
Complications more often occur after curettage, i.e. blind polyp removal. Not removed particles of the affected tissue begin to be reborn from the epithelium of the uterine mucosa again.
Women appear:
- leucorrhoea;
- pain and heaviness in the lower abdomen;
- high temperature.
A genitourinary tract infection can lead to:
- uterine perforation;
- accumulation of blood clots in the uterine body;
- tissue scarring;
- the appearance of adhesions after curettage
The most dangerous complication may be the recurrent course of polyposis, which can degenerate into a malignant form and into a cancerous process.
Of course, this is rare in medical practice and much depends on the women themselves and compliance with all recommendations after the operation.
If severe pain or spasms appear in the cervical canal of the uterus, then you need to see a gynecologist again. This can only indicate that it is necessary to perform repeated curettage and cauterize the uterine cavity with a laser.
Basic recovery recommendations
After a successful hysteroscopy, a woman remains in the hospital for 2-3 days, after which she is sent home for further recovery.
Among the main recommendations are:
- Continue antibiotic therapy to prevent infection.
- Regular measurement of body temperature.
- Maintain careful hygiene of the genitals after using the toilet (regular washing with soap).
- If the pain persists, take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (normally, the pain is moderate and lasts up to 3-5 days).
- Controlling urinary regularity.
- Eliminate heavy lifting.
- Sexual rest for up to 30 days.
During rehabilitation it is important:
- Eat a balanced diet to prevent constipation.
- Avoid swimming in open water, visiting solariums, hot saunas or steam baths.
If all recommendations are followed, recovery occurs quickly and, after 3 months, the woman can lead her usual lifestyle.
Is it possible to get pregnant after polyp removal?
Damage to the endometrium, of course, prevents the implantation of the fertilized egg.
But doctors say that fertilization of the egg is possible. However, for 0.6 months while the patient is being treated after surgery to remove the polyp node, it is recommended to use contraceptive barrier drugs to allow the uterus to fully recover and return childbearing abilities to its previous state.
You need to plan a pregnancy no earlier than 3-4 months and only after complete restoration of hormonal levels, healing of all affected lesions in the uterine cavity, and normalization of the thickness of the endometrium.
What is not recommended to do after surgery?
It is important for women to monitor their health during the postoperative period and not neglect the doctor’s recommendations.
In order for the recovery period to pass quickly and unnoticed, you need to:
- refuse to visit a hot bath, steam bath, sauna for 3-4 days;
- do not douche or insert tampons;
- eliminate for a time (up to 1 week) sexual contacts and gross interference with the uterus;
- Do not take medications for 1 week that can thin the blood and lead to bleeding;
- refuse strenuous physical training;
- adjust diet and sleep.
Preparation
Preparation for hysteroscopy is similar to other surgical interventions in gynecology. First, an examination and, if necessary, certain treatment are carried out. The following tests are performed:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Coagulogram.
- Blood type and Rh factor.
- Vaginal smear for flora.
- ECG.
- Test for STIs.
- Tests for HIV and parenteral hepatitis.
Hysteroscopy is planned at the beginning of the menstrual cycle (before day 10), since endometrial tumors are clearly visible during this period.
Immediately before surgery, it is recommended to follow these rules:
- Two days before hysteroscopy, avoid sexual contact.
- On the day of the operation, take a shower and then put on underwear made from natural fabrics.
- Remove jewelry and contact lenses.
- Immediately before entering the operating room, empty your bladder.
- Do not eat for at least 6 hours before anesthesia.
special instructions
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that allows you to eliminate endometrial hyperplasia in the shortest possible time and without pain, suppress the affected areas and remove polyps in full. Relapses occur extremely rarely in women.
But you should not ignore observations after surgery or refuse timely treatment of other diseases in the uterine cavity. The first period should be expected closer to 8 weeks after polyp removal.
Although it is worth understanding that surgical intervention can affect a woman’s well-being and hormonal levels in different ways.
The first menstruation may begin with increased discomfort and pain, and may occur in a special way and not as usual.
The main thing is to prevent negative consequences. If unpleasant symptoms appear, you should see a doctor and get advice on what to do next.
Secretion after a diagnostic procedure
Diagnosis of the uterus and fallopian tubes using hysteroscopy, as a rule, does not imply that the woman has intense discharge during the recovery period. By and large, a woman sometimes experiences active pink or bloody discharge on the first day. Bloody discharge after hysteroscopy in small quantities is also possible. Then spotting may continue for several more days, and this is not a deviation, since during the examination mechanical damage to the upper layer of the endometrium could occur. Some time after the daub is over, mucous secretion may increase somewhat. This indicates the final restoration of the integrity of damaged areas of the endometrium.