Hysteroscopy – what is it?
This is the name of a type of endoscopic examination that is used in the field of gynecology. A special tube with a mini video camera is inserted into the uterine cavity. Due to this, the image is transmitted to the monitor and any pathological changes, deformations of tissues and organs can be clearly seen. The resulting picture can be assessed by specialists and the appropriate treatment can be selected.
See also Recovery after hysteroscopy of the uterus. Polyp removal.
See also Hysteroscopy of the uterus - what is it?
Another feature of the method is the ability to immediately carry out some simple operations - cauterize identified erosions, remove small tumors and polyps. However, the procedure is quite painful and is therefore performed under anesthesia. During hysteroscopy, tissue is collected for histological analysis, foreign objects are removed, and septa and adhesions are destroyed. During surgery, inflammatory processes are detected.
Curettage during hysteroscopy
If a patient has serious pathological problems in the reproductive organs, LDV (therapeutic and diagnostic curettage) is prescribed. During the operation, the uterine cavity is immediately examined and the necessary surgical removal is performed. During the process, the doctor uses a camera to monitor all actions. In order for the female body to be able to recover faster, the procedure is carried out approximately 4 days before the onset of menstruation.
Properly performed curettage helps to avoid complications and allows you to start planning a pregnancy within 1-2 months. The woman should contact her doctor, who will decide whether to conduct an additional examination. A competent specialist will help you determine the time when ovulation will occur.
Possible complications
Any interference in the functioning of the human body can lead to negative consequences. Complications are also possible after hysteroscopy. Incorrectly performed manipulations can lead to the following consequences:
- addition of infection;
- the appearance of bleeding;
- inflammation in the pelvic organs;
- cervical injuries;
- allergy to anesthesia - the gas used during the operation;
- vaginal cramps.
Before performing the procedure, the doctor must warn the patient what complication awaits her if the operation is unsuccessful and how this may affect a future pregnancy. Such consequences are rare; modern equipment allows all manipulations to be carried out at a high level.
Unpleasant consequences are bleeding. This is the norm after such a procedure, because the blood vessels are injured. The discharge should end after 2, maximum 5 days. If you continue for more than this period, you should consult a doctor. Particular attention should be paid to your health if there is an unpleasant odor from the discharge or a change in its color, for example, to a black tint.
After hysteroscopy, the lower abdomen may hurt, radiating to the lower back. The duration of such sensations sometimes extends to 10 days. If the pain increases from a more moderate degree to severe, you should complain to a doctor. You also need to consult a specialist if the nagging pain does not go away after the specified period.
Another negative consequence is general malaise and weakness. This may be a consequence of anesthesia or emotional depression. The addition of chills, fever, or migraine is a good reason to consult a doctor.
Indications and contraindications for hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is usually used as a diagnostic method, but can also be used to treat pathologies of the reproductive system. Main indications:
- myomatous uterine nodes;
- polyps;
- irregular and painful menstruation;
- malignant process in the endometrium;
- hyperplasia;
- various vaginal discharge;
- uterine bleeding associated with hyperplastic processes;
- diseases of the appendages;
- biopsy;
- diagnosis of the causes of infertility;
- complicated pregnancy (ectopic);
- the presence of synechiae in the uterus after surgery or inflammatory processes;
- foreign bodies in the cavity;
- complications after childbirth;
- frozen pregnancy or dead embryo;
- intrauterine septums that cause infertility;
- removing the spiral;
- suspicion of a malignant tumor;
- sterilization;
- frequent pain in the lower abdomen;
- removal of fetal remains after abortion.
The operation is traumatic, so after the intervention it takes some time for the endometrium to recover and be able to firmly hold the fertilized egg.
Contraindications
Hysteroscopy is not performed in the presence of oncological processes in the female genital organs, stenosis, severe uterine bleeding, or during pregnancy. The method is not used for chronic inflammation, acute respiratory viral infections, respiratory infections and diseases of the cardiovascular system. To identify contraindications before hysteroscopic surgery, a full examination is prescribed, including biochemical analysis and consultation with other doctors.
What is the danger of pregnancy after the study?
Pregnancy itself, in the form of the process of bearing a fetus in the uterus, is not a dangerous condition for the female body, even if a hysteroscopy has recently been performed. Gynecologists say that, first of all, it is dangerous for the fetus, which is forced to remain in the uterus, which is not ready to fully retain the fertilized egg.
According to statistics, those patients who became pregnant almost immediately after hysteroscopy often experience abnormalities in the development of pregnancy of varying severity:
- regression of pregnancy, which is also known as frozen pregnancy, which occurs against the background of low-grade inflammation during pregnancy and hormonal imbalances;
- fetoplacental insufficiency caused by hormonal disorders or inflammatory processes;
- polyhydramnios, which threatens the normal development and birth of a child;
- fetal hypoxia;
- infection of amniotic fluid and fetus;
- placenta previa and abnormal position of the fetus in the uterus.
Almost all of the listed pregnancy complications end in stillbirth or premature birth with the birth of a baby with complex pathologies. This is why gynecologists recommend not to rush into conception. If it does happen, it is important to register with the antenatal clinic as early as possible and be regularly examined by a gynecologist and related specialists.
Since no doctor excludes the possibility that an infection could enter the uterus during hysteroscopy, in the first trimester of pregnancy the woman will have to undergo an extensive examination and take medications as prescribed by the doctor (multivitamins, hormones, etc.). If the pregnancy could not be maintained, the woman will have to undergo long-term rehabilitation. It will help prepare the body so that the next time pregnancy develops without pathologies.
Preparation for hysteroscopy
Long preparation is required before hysteroscopy. The examination is usually carried out on the fourth day after the start of menstruation. Before this time you need to do:
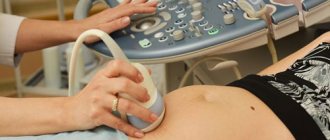
- Ultrasound of the pelvis;
- chest x-ray;
- colposcopy;
- electrocardiogram;
- take general blood and urine tests, a smear from the vagina and cervix.
Blood must be taken for clotting and biochemistry. A few days before hysteroscopy, you need to start following a diet. All foods and drinks that cause gas formation are removed from the diet:
- all types of cabbage;
- legumes;
- baked goods;
- sweet;
- bakery products;
- kvass;
- lemonades;
- soda;
- alcohol.
On the eve of hysteroscopy, you can only eat foods that are easily digestible; when the operation is scheduled for the morning, you can no longer eat in the evening. Drinking is allowed, but liquids without gases. On the day of hysteroscopy, you should not drink or eat.
The evening before the examination, an enema is given to cleanse the intestines. The procedure is repeated in the morning. Then you need to shave your pubic hair, in the perineal area and take a shower.
Douching or inserting suppositories is prohibited unless recommended by a gynecologist. Do not use alkali-based intimate hygiene products or have sexual intercourse.
Hysteroscopy is performed in a hospital setting, so you need to take a robe, towel, slippers, dental accessories and intimate hygiene products with you to the hospital. If the diagnostics show nothing serious, the doctors will let you go home after a couple of hours.
How to prepare for conception after hysteroscopy?
When the operation to remove endometrial formation is already behind the patient, you can start planning a pregnancy:
- To get tested for hormone levels, you must first visit an endocrinologist. With formations in the uterus, a malfunction often occurs, which also does not contribute to conception.
- Get an ultrasound to rule out recurrence of the polyp.
- Sometimes diagnostic hysteroscopy is prescribed for a detailed examination of the endometrium after removal of the formation.
- Get checked for genital infections. If something is discovered, get treatment.
Carrying out hysteroscopy
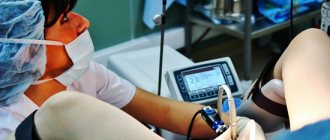
A woman sits in a gynecological chair for an examination. The most commonly used drugs are internal painkillers, which also act as a sleeping pill. A woman in a dream does not feel any manipulations being carried out. She wakes up after the procedure is over. This method of pain relief is the safest and most effective.
After the woman falls asleep, the uterine cervix is fixed with mirrors and then the hysteroscope is inserted. If necessary, the cervical canal is expanded with other instruments. The hysteroscope slowly moves to the desired location - into the uterine cavity. An examination of its walls begins to identify pathological growths and deformations.
During the procedure, a physiological solution is constantly poured into the cavity, washing away the removed fragments and ensuring maximum visibility. Sometimes insertion of a resectoscope is required. Using this device, polyps, other small tumors, septa, submucosal nodes and cauterization of tissue in specific areas are removed.
Sometimes after hysteroscopy, curettage of the uterus is performed, which is no different from the usual procedure. The biomaterial obtained during the procedure is sent for histology.
Uterine hysteroscopy and pregnancy are first discussed with a gynecologist. In some cases, examination or surgery is combined with laparoscopy. This may be necessary for infertility that has arisen for unknown reasons, endometriosis, polycystic disease, uterine fibroids and endometrial diseases.
An effective diagnostic method
Hysteroscopy is a gynecological procedure in which a special device (hysteroscope) is inserted into the uterus. The video camera at its end allows you to examine the internal area of the cervix and, if necessary, remove polyps and neoplasms. The tool allows you to take material for further research.
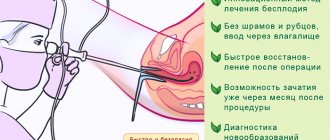
This surgical intervention does not harm the body because it is performed without incisions or punctures through a natural opening. To avoid discomfort, a painkiller is administered.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is used to examine the female reproductive system. It is performed under local anesthesia in a gynecological office. In turn, invasive hysteroscopy is similar to surgery. It is performed in a hospital setting under general anesthesia. Its purpose is to carry out medical manipulations: remove a polyp, another tumor, take a piece of tissue for examination; in some cases, these 2 types of procedures are combined.
The procedure is successful in cases of infertility. Pregnancy occurs after hysteroscopy in most cases. Although this manipulation is not performed specifically to get rid of infertility.
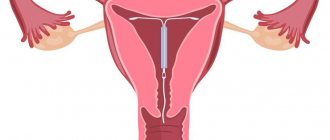
Hysteroscopy - examination of the uterine cavity using a hysteroscope
Recovery of the body after hysteroscopy
After hysteroscopy, intimate relationships are prohibited for at least two weeks to avoid infection. You cannot use tampons or douche, take hot baths, go to the sauna, or swim in open water. In the first month, sports and heavy physical activity are excluded. The urge to urinate cannot be ignored.
Daily shower and temperature measurement are recommended. Its increase may indicate an infection. It is necessary to use only pads, wash with baby soap or intimate gels. It is better not to take painkillers if the pain can be tolerated - such drugs make the blood thinner. Stick to the same diet to avoid stool upset.
Immediately after surgery, doctors give antibiotics to prevent a surge in bacterial growth. Antispasmodics help relieve pain. To restore hormonal balance, medications are prescribed (selection is individual) to prevent relapse of the disease. At the same time, they prevent conception, since pregnancy after hysteroscopy in the first months is undesirable. For these purposes, you can additionally use oral contraceptives.
Herbal remedies are prescribed as adjuncts in the form of decoctions, infusions or ready-made pharmaceutical preparations. You cannot select them yourself - serious complications may arise.
If you plan to become pregnant after hysteroscopy of an endometrial polyp, you will be able to conceive a child in a couple of months. It should be taken into account that for three days after the operation, the damaged tissues will remain inflamed, which is accompanied by a slight increase in temperature. Then the damaged area heals, a crust appears on it, which falls off on its own.
Primary healing occurs after a week, complete healing occurs after 14 days. The recovery time of the body directly depends on the manipulations performed. After electrocoagulation, regeneration occurs within ten days and 2 times less time after other surgical interventions.
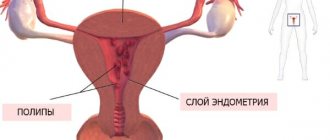
What are endometrial polyps?
Polyps are a true tumor process, the formation of tissue from the mucous membrane of an organ with its own blood flow. Initially they are considered benign, but over time they can change and become malignant. Therefore, any polyp is considered a life-threatening pathology. Especially if there is rapid growth, reproduction and complications as a result of its presence. They can appear in any hollow organ from the nasopharynx to the uterus and rectum.
Unlike other tumors, these formations are small in size and in the uterus can reach 8-10 cm. Such a polyp no longer fits in the cavity of the organ and falls out through the cervical canal into the vaginal area. A gynecologist will detect it with the naked eye during an examination. However, there are formations that form in the canal itself and ultrasound is needed to clarify the localization. Polyps up to 10-15 mm are usually found.
Several types of formations occur in the uterine cavity:
- Glandular - jelly-like soft growths. They often appear against the background of a hormonal system failure in young women. They may be false if they are formed from the functional layer of the endometrium. Such formations are nothing more than an accumulation of surface cells that can come out with menstruation.
- Fibrous ones have their roots in the basal endometrium of the uterus. Dense because they contain mostly connective tissue. Formed before menopause as a result of age-related hormonal changes.
- The mixed type combines fibrous and glandular tissue. Such polyps are found more often during reproductive age in women who have given birth.
- Adenomatous formations are both types 1 and 3, the glandular tissue of which has modified cells. It has the highest risk of malignancy.
- Placental and chorionic polyps are growths from the remains of a child's place. The former arise due to incomplete cleansing of the uterus during childbirth, the latter after termination of pregnancy in the early stages.
- Decidual - the growth of a special uterine membrane, which appears only when the baby is pregnant. Such a polyp comes out with the child.
The reasons that lead to the formation of formations are the following:
- Hereditary predisposition to tumor processes;
- Injuries resulting from operations, childbirth;
- Infections and inflammations;
- Endocrine problems;
- Autoimmune conditions.
Symptoms occur with formations of 1 cm or more or with polyposis:
- Stomach ache;
- Blood after sex, physical activity;
- Copious mucous discharge;
- Long and heavy menstruation.
Attention! Polyps are a sign of problems in the body, so they often have companions in the form of other disorders.
How does hysteroscopy help cope with infertility?
Pregnancy may not occur for many reasons, most often hormonal disorders are to blame. The imbalance does not ensure the safety of the fetus, and conception fails. Other common causes of infertility include:
- Obstruction of the fallopian tubes. This may appear due to adhesions, fusion of the entrance to the canal.
- Abnormal structure of the uterus. It can be bicornuate, infantile, or have septa.
- Hyperplastic changes in the mucosa. The fertilized egg does not attach to the deformed endometrium.
- Adhesions in the uterine cavity. Because of them, the egg cannot penetrate inside and gain a foothold.
Before planning a pregnancy after hysteroscopy, you need to eliminate the listed obstacles, except for a bicornuate or infantile uterus. Polyps often prevent you from conceiving a child. These are small neoplasms inside the uterus, usually arising against the background of hormonal imbalance. Polyps sometimes act like a spiral. Especially if the education is large. Therefore, all polyps identified during diagnosis are removed.
The septums are easily destroyed, polyps and adhesions are removed, and the fallopian tubes are cleaned. To eliminate clogging, air is injected into the channels. If hyperplasia is detected, the uterus is curetted, but the mucous membrane is removed. In this case, complete restoration of the endometrium will require a longer time. If we take into account reviews of those who became pregnant after hysteroscopy, then this often happened without problems, after 2-3 months.
What is hysteroscopy and its effectiveness for conception?
The procedure refers to endoscopic operations. To carry it out, a special device is used - a hysteroscope, which is inserted through the natural genital tract: the vagina, the cervix and the cavity itself. No incisions are made to perform microsurgery. Examination of the female reproductive organ is carried out using a flexible and thin tube, at the end of which there is a miniature camera. It transmits an enlarged image to the monitor screen and the doctor can assess the patient’s condition.
Hysteroscopy is a microsurgical operation performed with a hysteroscope that allows you to diagnose and remove pathology, including those that can affect conception.
The procedure may be prescribed if:
- postpartum complications;
- infertility;
- menstrual cycle disorders;
- abnormalities in the development of the uterus;
- incorrectly performed abortion;
- suspected inflammation of the endometrium (inner layer of the uterine mucosa), adhesions in the uterine cavity;
- polyps;
- ingrown intrauterine device.
It is most often used to assess abnormal uterine bleeding, in the diagnosis and treatment of infertility, to clarify the pathology of the uterine cavity, in cases of recurrent miscarriage and before IVF.
Klyucharov I.V., 1FGBOU HE Kazan State Medical University of the Ministry of Health of Russia
https://lib.medvestnik.ru/articles/Bezopasnost-i-perenosimost-hirurgicheskoi-gisteroskopii-po-Betokki-v-jenskoi-konsultacii.html
The study is carried out on days 5–7 of the menstrual cycle. The procedure is quite painful, so it is performed under general anesthesia. After the anesthesia takes effect (the woman falls asleep), the doctor fixes the cervix with mirrors and dilates the cervical canal. During the examination, the cavity of the uterine organ is washed with saline solution, which helps to enlarge it and provides better visibility. The doctor examines the mouth of the fallopian tubes, the walls of the cavity, and the cervical canal. After diagnosis, the data is analyzed, based on it, a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed.
The hysteroscope is inserted through the natural genital tract: the vagina, cervix and the uterine cavity itself.
If necessary, surgical procedures are performed. For this purpose, a hysteroscope is used for performing operations - a resectoscope. It consists of two parts: an optical system and a set of special tools. It is used to remove polyps, submucous fibroids (fibroids up to 3–4 cm), and intrauterine adhesions. If the doctor sees changed areas of the mucous membrane, he can take a biopsy of the damaged area and also cauterize it.
A resectoscope is an endoscopic instrument that is used in gynecology to remove pathologies in the uterine cavity under visual control.
Before the operation, you must undergo the following tests:
- Clinical blood test, as well as for hepatitis and HIV infection;
- fluorography;
- ECG - with interpretation and doctor’s report;
- smear from the cervical canal for cytology;
- vaginal smear to check the cleanliness and condition of the microflora. If grade III or IV cleanliness is detected, the patient must undergo sanitation of this area.
Doctors say that with the help of hysteroscopy it is possible to get rid of pathology both in the uterine cavity and in the cervical canal without undergoing serious surgical interventions.
This makes it possible for a woman to subsequently conceive and bear a baby. However, there is no 100% guarantee that pregnancy will occur after hysteroscopy. The fact is that this does not depend on the procedure itself, but on the pathology that will be detected during the study. Hysteroscopy allows you to remove some formations that prevent pregnancy. These could be adhesions, polyps, or abnormalities in the structure of the uterus.
According to statistics, about 20% of women who underwent hysteroscopy became pregnant after about a month. Another 20% - after 2-3 months, 30% - after six months, 15% - after a year. Only 15% were unable to get pregnant.
After the procedure, sometimes you feel a nagging pain of a spastic nature in the lower abdomen. Unpleasant sensations usually last about 3-4 days. To eliminate pain, the doctor may prescribe antispasmodic drugs: No-shpu, Drotaverine, Papaverine, Spazmalgon.
Medicines help relieve spasms of smooth muscles, improve blood flow to the uterus, dilate pelvic vessels, and also relieve pain.
Antispasmodic drugs after hysteroscopy - gallery
No-Spa helps relieve spasms of smooth muscles, improves blood supply to internal organs
Drotaverine eliminates spastic pain, improves oxygen supply to tissues, promotes relaxation of smooth muscles
Spasmalgon is a combination drug with a pronounced antispasmodic and analgesic effect.
Papaverine exhibits a slight sedative effect, reduces smooth muscle tone, causes a vasodilator and antispasmodic effect
In addition, spotting and spotting may occur. This is considered normal, since the device touches the walls of the uterus and slightly injures them. The discharge usually lasts no more than 4–5 days.
To prevent inflammatory processes, a woman is prescribed antibacterial agents.
Contraindications and negative consequences
The procedure is contraindicated when:
- suspected cancer;
- acute inflammatory processes of the genital organs;
- pregnancy;
- severe uterine bleeding;
- heart and kidney failure;
- diseases in the acute stage.
As with any operation, this procedure can have negative consequences:
- severe bleeding - occurs when removing endometrial polyps or fibrous nodes, as well as when surgery is performed incorrectly;
- trauma to the walls of the uterus can cause the formation of adhesions;
- the development of endometritis is inflammation of the inner mucous layer of the uterus due to infection.
Agostini et al. Over the course of 10 years, more than 20,116 hysteroscopies were studied, and 30 (0.15%) cases of infectious complications were identified, of which 18 (0.09%) were endometritis and 12 (0.06%) were urinary tract infections.
Bagdasaryan A.R., Federal State Budgetary Institution Scientific Center of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Perinatology named after. Academician V.I. Kulakov Ministry of Health of Russia, Moscow
https://lib.medvestnik.ru/articles/Oslojneniya-diagnosticheskoi-i-operativnoi-gisteroskopii.html
Video: what is hysteroscopy? When is it used?
Planning pregnancy after hysteroscopy
If the operation was only diagnostic in nature, then the recovery period is reduced. Planning pregnancy after hysteroscopy is possible after the next menstruation. However, they should not be confused with discharge that may appear after the procedure. After curettage of the uterus, it is recommended to wait 2-3 months for pregnancy; after major operations, it takes up to six months.
After hysteroscopy, antibiotics and hormonal agents are necessarily prescribed. They speed up healing, prevent the development of infection and help the body recover faster. After hysteroscopy, there is a pause in intimate relationships for a month.
Then you can return to a full sexual life, but only using protection. It is advisable to give the body up to three months to fully recover. However, you can plan a pregnancy 6-10 weeks after surgery. Most often, successful conception occurs after six months.
You can plan a pregnancy after hysteroscopy if the operation was performed in the 2nd phase of the cycle. This does not affect ovulation, but the question is whether pregnancy will be successful. If during the procedure the endometrial layer was even slightly damaged, then you need to wait until it is completely restored so as not to later lose the fertilized egg. For the same reason, long-term protection after surgery is recommended.
If tumors were discovered during hysteroscopy, then tissue particles are immediately taken for analysis - to determine the malignancy of the formation or to assess the risk of degeneration into cancer. If the response is unfavorable, the woman is referred to an oncologist. Then planning a pregnancy after hysteroscopy depends on the removal of the tumor and its nature.
After the operation, a woman must monitor her menstruation and be tested for sexually transmitted diseases, inflammation, and infections. All this must be cured before conception. If you are planning a pregnancy after hysteroscopy using IVF, this can only be done after six months. When the egg is implanted, the woman should be constantly examined.
When can you plan a pregnancy?
So, when can you get pregnant after hysteroscopy? This question worries all women who have undergone such a procedure.
The period when you can plan a pregnancy depends on the indication for which the procedure was performed. If it was done to clarify the diagnosis or exclude other diseases, no traumatic manipulations were performed - pregnancy occurs almost immediately and no special preparation is required for it. The optimal period for pregnancy after diagnostic hysteroscopy is considered to be an interval of 3–5 months.
If adhesions were removed or the endometrium was scraped, pregnancy cannot occur quickly. Getting pregnant becomes possible only after a full-fledged endometrium is formed. How long this will take depends on the woman’s body. On average, with hormonal therapy, the endometrium grows within six months. If after the procedure adhesions form again, the period increases for several more months until they are removed again.
Pregnancy can be planned when a normal endometrium is formed
There is no point in trying to get pregnant quickly after such a procedure. It is necessary to wait for a complete recovery and carefully prepare for pregnancy so that it proceeds physiologically and is not complicated in any way.
Possible consequences of hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy refers to surgical operations, but unlike abdominal ones, it is less traumatic. However, some complications may occur:
- the appearance of adhesions due to damage to the mucosa;
- perforation of the uterine wall;
- penetration of germs and infections into the genital organs;
- development of purulent processes;
- the appearance of uterine bleeding.
In the latter case, stopping is sometimes impossible and the organ has to be removed completely. However, such consequences appear very rarely. The cause of complications is the incorrect use of antibacterial agents, insufficient treatment with antiseptic drugs, and lack of experience on the part of the surgeon.
All of the above are extremely rare, and to prevent negative consequences, absorbable and hormonal anti-adhesive therapy is done. During the operation, an anesthesiologist is on duty in the office; the procedure is monitored visually from the very beginning. When pregnancy is planned after hysteroscopy: reviews indicate that there are no complications. Conception occurs quickly and without problems.
Hysteroscopy is a modern and low-traumatic way to cope with infertility. Often the cause is factors that are easily removed through the procedure. As a result, pregnancy after hysteroscopy can occur within three months.
- The test is positive, but the ultrasound does not show pregnancy
- Pregnancy after laparoscopy: when is conception possible?
- Recovery after hysteroscopy of the uterus. Polyp removal.
- Laparoscopy is a new method of diagnosis and surgery
- Laparoscopy of ovarian cyst
Why is hysteroscopy with laparoscopy prescribed?
Hysteroscopy and laparoscopy are endoscopic methods of examination and treatment. In gynecological practice, both methods are often combined. This is used to establish the most accurate diagnosis and carry out the most radical treatment. In most cases, laparoscopy is performed first, and then hysteroscopy, but it all depends on the clinical situation and the expected pathology.
The main cases when these two methods are combined are:
- For infertility, especially of unspecified cause. At the same time, a study is carried out to determine the patency of the fallopian tubes.
- For endometriosis, for coagulation (cauterization) of the maximum number of lesions.
- With polycystic disease, it is often combined with infertility.
- For uterine fibroids and simultaneous endometrial pathology, as well as in some other situations.
Hysteroscopy: indications, progress of the operation, recovery - MEDSI
Hysteroscopy
- a method of examining the uterus using a hysteroscope (a type of endoscopic equipment), which allows for diagnostics and therapeutic manipulations (according to indications).
This manipulation comes in several types:
- Diagnostic (to detect pathology)
- Therapeutic (to eliminate the disorder)
- Test (to check the result)
There are two types of hysteroscope: rigid and flexible. It is equipped with a light source, optics, a hysteropump and a video system consisting of a video camera, video monitor and cable. All this allows for accurate diagnosis and, if necessary, surgical intervention.
Hysteroscopy: indications
This procedure allows not only to examine the inside of the uterus, but also to perform minimally invasive surgery. Therefore, the doctor prescribes hysteroscopy in cases such as:
- The presence of anomalies or malformations of the uterus and fallopian tubes (septa, fusions, etc.)
- The development of malignant or benign neoplasms (tumors) is expected
- The appearance of changes in the condition or structure of the endometrium (polyps, hyperplasia, endometriosis)
- The patient has myomatous submucosal nodes
- Possible perforation of the uterus
- Disorders of the monthly cycle, development of postmenopausal bleeding
- Diagnosed with infertility
- To monitor the condition, as well as eliminate various violations that appeared after:
- Performing a medical abortion
- Termination of non-developing pregnancy, miscarriage
- Carrying out a caesarean section
- The appearance of postpartum inflammation
- Unsuccessful attempts at IVF (in vitro fertilization)
- Performing hormonal therapy or surgery
- Installation of intrauterine device
Hysteroscopy allows surgical manipulations to be performed accurately and with minimal disruption of the internal walls of the uterus, which ensures rapid healing. This feature of the procedure is especially important for women who are planning to become pregnant.
Preparation for the procedure
Before prescribing a hysteroscopy, it is necessary to undergo several types of examinations:
- Blood tests:
- General
- Research for diseases:
- Syphilis
- Hepatitis
- HIV
- Biochemical
- Coagulation study
- Determination of blood type, Rh factor (if they have not been clarified earlier)
You should also be examined by a therapist. Additional examination of other organs may be required if there is a suspicion of their pathology in order to avoid risks during the operation.
It is necessary to warn your doctor about taking medications. Before undergoing hysteroscopy, you must stop using blood thinning medications.
Like any other surgical procedure, hysteroscopy has contraindications:
- Excessive bleeding
- Cervical cancer
- Presence of an ectopic pregnancy
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system, kidneys or liver
- Cervical stenosis
- Inflammation of the genital organs
- Acute forms of infectious diseases
Stages of the procedure
When performing hysteroscopy, the following procedure is typical:
- Treatment of cervical tissue in the intimate area with antiseptic agents
- Fixation of the organ neck with mirrors
- A probe is inserted to measure the size of the uterus
- Expansion procedures are carried out using liquid or gas
- After these manipulations, a hysteroscope is inserted into the cavity of this organ, which is moved clockwise
- Inspection of tissues, their structure and shape is carried out
- If necessary, therapeutic or minimally invasive surgical procedures are performed
Depending on the type of intervention that needs to be performed, the hysteroscope can be equipped with:
- Biopsy forceps (taking a tissue sample for further examination)
- Scissors
- Electrodes (providing tissue coagulation)
- Laser (to remove tumors and pathologies or cut the septum, etc.)
The procedure allows for the minimally traumatic elimination of uterine tumors such as:
- Polyps
- Partitions
- Remains of the fruit or its membranes
- Fusion
- Myoma
- Excessive growth of the endometrium
This procedure removes foreign bodies from the uterus, including contraceptives. This manipulation also allows for sterilization.
Hysteroscopy for nulliparous women in some cases helps in the fight against infertility.
For some pathologies, the doctor may prescribe a repeat procedure.
Postoperative period, recovery
Rehabilitation options depend on the type of hysteroscopy that was used. During the diagnostic procedure, there is no need for recovery, so the very next day the patient can carry out her usual activities.
When performing a surgical intervention, it is necessary to undergo antibiotic and antifungal therapy.
In the postoperative period, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Refrain from sexual contact (up to several weeks - it depends on the complexity of the operation)
- Don't use tampons
- Refrain from going to the bathhouse, swimming pool or sauna
- Don't douche
For the first time after hysteroscopy, physical activity should be minimal.
During the recovery period, in 1% of cases, complications such as:
- Trauma to adjacent organs
- Getting infected
- Severe bleeding (usually the bleeding is insignificant and disappears in the first days after the intervention)
If any complications or discomfort occur, you should consult your doctor.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- MEDSI uses the latest equipment equipped with bipolar electrodes, which allows for extremely low trauma
- Hospitalization in a modern comfortable hospital and the procedure is possible on the day of treatment
- Reception is conducted by experienced, highly qualified specialists who have diplomas and certificates in the field of gynecology and are constantly improving their professional level
You can make an appointment for a consultation at a time convenient for you by calling 8 (495) 7-800-500.
Source: https://medsi.ru/articles/gisteroskopiya-pokazaniya-khod-provedeniya-operatsii-vosstanovlenie/
Consequences
Due to the fact that hysteroscopy, despite its relative safety, is a surgical intervention, after it is performed certain consequences may arise that can cause some discomfort to the patient. However, it is necessary to distinguish between consequences that are a normal reaction of the body to medical actions (artificial dilation of the cervix, curettage, etc.) and complications caused by incorrect actions of the doctor, characteristics of the body, or the patient’s failure to comply with postoperative recommendations.
Pain
Pain after the procedure is a completely natural reaction to surgical procedures. As a rule, the pain is spasmodic in nature and is a consequence of increased contractile activity of the muscular layer of the uterus and forced expansion of the cervical canal. Complaints of aching pain in the lumbar region are also common.
The intensity and duration of pain depends on the pain threshold of the individual patient and the goals of hysteroscopy. If hysteroscopy was performed solely for diagnostic purposes, then recovery takes no more than 4-6 hours, and even minor surgical procedures can cause longer-term pain, which can be successfully relieved with anesthetics.
Important! Regardless of the nature of the hysteroscopy performed, pain should not last more than 7 days (optimally 2-3 days).
Intramuscular injection of baralgin will help eliminate pain
Discharge
Slight spotting is normal even after diagnostic hysteroscopy. There should be no heavy discharge even after resection of polypous formations. The appearance of ichor after hysteroscopy, and then mucous discharge, may indicate minor damage to the mucous surface of the cervix or be a consequence of surgical actions to remove tumors or take a tissue sample for a biopsy.
If diagnostic curettage was performed for medical reasons, then the amount of blood after the procedure, as well as the duration of bleeding, should not differ significantly from menstruation and will end within the appropriate time frame, that is, after 4-7 days.
Temperature
The temperature after hysteroscopy should not exceed the threshold of 37º-37.2º. As a rule, a similar reaction of the body to intervention occurs in a fairly large percentage of women and differs from the temperature associated with complications in that it occurs on the same day and repeats in the evening for 2-3 days. Temperature caused by inflammatory processes or other complications is characterized by exceeding a threshold of 37.2º, is not related to the time of day and usually occurs 2-3 days after hysteroscopy.
Is menstruation a contraindication or not?
During menstruation, routine hysteroscopy is not performed. It is usually prescribed on days 5-7 of the cycle to identify neoplasms, fibroids, and polyps (in the first phase of the cycle, the endometrium is thinner, which allows you to see even tiny defects). But foci of inflammation are easier to detect when the endometrial layer is thicker (in the second half of the menstrual cycle, on days 20-24). Hysteroscopy of the uterus with biopsy before IVF is prescribed immediately after the end of menstruation. Two or three weeks are often enough to restore and renew the endometrium, which allows the patient to enter the protocol already in the next cycle.
However, if emergency hysteroscopy is indicated (in case of intense bleeding, suspicion of the presence of a dead fertilized egg or foreign objects in the uterus), it can be performed on any day of the cycle. It doesn’t matter whether you’re menstruating or not.