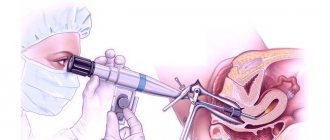
You can also remove a large endometrial polyp using flexible hysteroscope scissors. To do this, the hysteroscope is brought to the base of the polyp, and the leg of the polyp is cut off with scissors inserted into the operating channel of the hysteroscope under visual control. After that, forceps are inserted into the operating channel of the hysteroscope, they fix the polyp under visual control and remove it from the uterine cavity.
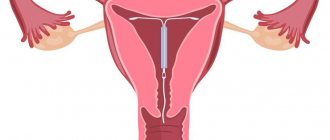
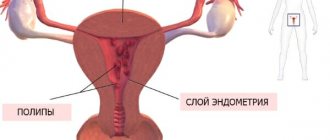
Pathological formations of the mucous membrane, protruding above its surface and connected to it by a leg or its base, are single or multiple formations of irregular round or oval shape. The base of the polyps may be thick, but its diameter is always smaller than the body of the polyp.
The surface of the polyps is smooth or folded. In most cases, polyps differ in color from the surrounding mucosa. They are usually pale pink, with a grayish or yellowish tint and are much lighter than the surrounding endometrium, which makes it possible to distinguish polyps from mucosal folds. Often on the surface of the polyp, against the general pale background of its surface, a vascular pattern is clearly visible. Uneven development of the vascular network can cause nutritional disturbances in individual areas of the polyp, which hysteroscopically manifests itself in the form of dark purple or bluish-purple spots.
When using the flushing method of hysteroscopy, it can be noted that polyps under the influence of fluid flow can move relative to their base and also change their shape.
In the diagnosis and treatment of endometrial polyps, hysteroscopy plays a special role, as it allows not only to clarify the localization of these pathological formations, but also to carry out their targeted removal. In addition, which is especially important, it also allows you to control the completeness and thoroughness of polyp removal.
Duration of sick leave after surgery - how many days
The patient is sent for MSE after 4 months. from the day of illness onset. In medical practice, all types of surgical interventions are divided into two groups:
- Lungs;
- Moderate;
- Heavy.
Light operations are those after which the sick patient gets up independently the next day and can be discharged from the hospital on the 3rd or 5th day. In some cases, sick leave may be issued for 15 days, and on the 16th day it is necessary to begin performing work duties. Moderate-severe operations are operations after which the hospital stay can be prolonged, and recovery requires up to 30 days.
Major operations are cases when a person after surgery may require long-term assistance from qualified personnel to rise to his feet. In this case, the duration of the illness may drag on for several months. Such operations include:
What affects the duration of sick leave?
A woman cannot independently influence the duration of sick leave. The decision on the need for opening is made only by the doctor based on examination and examination data.
In an attempt to get a ballot, some people resort to tricks and invent symptoms that actually do not exist. With the help of ultrasound, MRI, tests and other diagnostic procedures, the doctor can reliably determine the presence of symptoms and make a decision on whether to open sick leave or deny it.
The duration of sick leave is determined:
- the need for hospitalization;
- the presence of complications and the risk of their development;
- complexity of the operation;
- volume of intervention.
Grounds for extending a certificate of incapacity for work
Complications of surgery may include:
- bleeding;
- the addition of a secondary infection, with the subsequent development of inflammation;
- temperature increase;
- severe pain syndrome;
- failure of the postoperative scar (its divergence or suppuration).
How many days should it be extended?
The period for which a doctor can single-handedly issue a certificate of incapacity for work is 15 days. Next, the patient is sent to a medical commission to justify the extension of the certificate of incapacity for work.
If he is in a hospital, then during medical rounds the examination is carried out by expert doctors; if he is undergoing outpatient treatment and was discharged with an open sick leave, then the attending specialist makes an appointment during the working hours of the VC (medical commission), where the examination is also carried out by experts, based on its results a decision is made conclusion on the possibility of extension.
Hysteroresectoscopy of the uterus.
What is this
All this is carried out with the aim of eliminating contraindications to surgery. Also, the doctor explains in detail what the hysteroresectoscopy operation is, what it is in gynecology, and what specific indications for it are performed for this patient.
In cases where hysteroresectoscopy is recommended for nulliparous women, she is additionally prescribed drugs that soften the cervix a week before the operation. This is carried out in order to improve patency to expand the cervical canal, and reduce its trauma, since in nulliparous women the cervical canal is tightly closed. At the same time, endometrial hysteroresectoscopy itself is no different from that of a woman who has given birth.
The procedure is prescribed approximately on the fifth to ninth day of the menstrual cycle, this is due to the smallest height of the endometrium, reduced during this period by its vascularization (blood supply), which prevents the risk of bleeding and improves visualization.
How is rehabilitation after hysteroscopy of the uterus?
» Hysteroscopy » Purpose of hysteroscopy in the postoperative period
March 10, 2020 Hysteroscopy
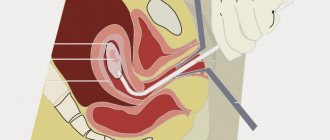
Hysteroscopy is a therapeutic and diagnostic endoscopic procedure that allows you to examine the cervical canal, its cavity and the openings of the fallopian tubes with an ultra-thin optical instrument (hysteroscope).
The hysteroscope is inserted through the vagina, first it enters the cervical canal, and then into the cavity of this organ. Thanks to this, you can assess the condition of the uterus, which is visible on the monitor.
Examination using hysteroscopy is a high-tech modern method.
Thanks to hysteroscopy, it is possible to identify various pathological neoplasms in the uterine cavity, as well as in the cervical canal (polyps of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal, endometrial polyps, various malignant neoplasms, endometrial hyperplasia, submucosal nodes of uterine fibroids).
By using this remarkable method, various diseases are diagnosed in the early stages, so that effective and timely treatment can begin.
In addition, hysteroscopy carefully monitors each stage of the surgical treatment inside the cervical canal itself and the uterine cavity.
Purpose of hysteroscopy in the postoperative period
After other types of surgery (during hysteroscopy), such discharge can last from two to four weeks. In addition, patients often complain of moderate pain in the lower abdomen and perineum. Usually these symptoms disappear on their own after a couple of days.
If the pain syndrome is more pronounced, then you can take regular painkillers, for example, Ibuprofen.
If the pain intensifies, bleeding or unusual discharge from the genital tract appears, you should immediately seek medical help. To prevent the development of complications after surgery, for the time recommended by your doctor, you should avoid:
- sex;
- use of tampons;
- taking a bath;
- douching.
- visits to saunas and baths;
After hysteroscopy, the patient will be able to become pregnant in the future.
Hysteroscopy will relieve her of endometrial polyps, which often make pregnancy impossible.
Prevention of inflammatory processes
To prevent the occurrence of an inflammatory process, the doctor, at his discretion, can prescribe and give the patient a five- to seven-day course of antibiotics. This is especially true for patients who have had their intrauterine septums cut (the latter have been the cause of multiple spontaneous abortions in the past) and extensive intrauterine synechiae. In other cases, antibiotics are rarely prescribed.
Observation of patients after hysteroscopy has been performed depends on the extent of the operation performed, the initial state of the woman’s internal genital organs and the nature of the pathology that was found in the uterus.
If during hysteroscopy a diagnostic curettage was performed or a simple operation was performed (polyps of endometrial tissue, a small myoma submucosal node were removed), then there is no need for a special postoperative regimen. In this case, the patient is discharged home on the same day (or the next day after surgery).
When a woman undergoes hysteroscopy with dissection of intrauterine adhesions (synechias), the doctor inserts an intrauterine contraceptive (IUC) into her uterine cavity for two months. It is better to do this to reduce the risk of developing recurrent adhesions (and this risk after surgery is more than 50%). If for a certain reason an IUD cannot be inserted, then a special silicone balloon or Foley catheter is inserted into the patient’s uterus for a week. If these devices are introduced, a course of antibiotics is required.
After hysteroscopy, heavy bleeding began, are you worried about acute abdominal pain and high body temperature? Contact your doctor immediately to prevent the negative consequences of hysteroscopic intervention.
Hysteroscopy and its consequences
In this case, purely diagnostic manipulations can be carried out without preliminary dilation of the cervix with a hysteroscope having a thickness of no more than 3 mm.
The use of a hysteroscope, which has an operating canal in its structure for inserting surgical instruments, requires significant dilatation of the cervical canal (up to 9-10 mm). Depending on the type of equipment used, surgical intervention can be carried out in the following ways: resection - in this case, the growth or neoplasm is cut off using so-called “scissors” or cutting instruments of a different shape; electroresection - provides a fairly large set of tools (loops, rollers, balls), the action of which is based on the electrical evaporation of tissue, which allows for the targeted removal of pathological formations; laser resection with coagulation - a significant advantage of such instruments is tissue coagulation after resection, which significantly reduces the risk of bleeding.
LJ Magazine
Secondly, I have not been sure for a long time that any life is good.
Life is certainly worth living. If you have, for what? If you have a favorite creature.
It doesn’t matter who is a man, a woman, a child, a dog, a fish in an aquarium or a geranium on the window.
Or you have a wonderful job, you have found your calling, and you feel that you are not living in vain.
Or your job is disgusting, but it is highly paid, so in your spare time you can afford to fulfill your every whim; take your soul away, as they say. Or you don’t have any of this, but you are young, relatively healthy, and there is a chance that you will have all of this together or separately. Well, if you are forty, you have nothing and not even a hint that something will appear, and, going to work, you grind your teeth with anger, because they pay pennies, and in general, by your calling, you should be in a completely different place and doing completely different things?
And what is life? Haze of Maya.
Technique for removing endometrial polyposis
After the diagnostic stage of hysteroscopy and detection of endometrial polyps, small polyps are removed by curettage with a sharp curette. When scraping, the curette is held freely, grasping it with your fingers, like a pen or bow. Having inserted the curette to the fundus of the uterus, withdraw it back to the internal os, pressing on the wall of the uterus and scraping the endometrium. Repeated movements remove the mucous membrane from the fundus, anterior, posterior and lateral walls of the uterine cavity. The scraping from the uterus is removed with a curette, removing it from the uterus from time to time, but not with every movement towards the uterine pharynx. If polyps are detected in the mucous membrane of the body and cervix, separate curettage is performed. First, the mucous membrane of the cervical canal is scraped without going beyond the internal os, then the mucous is scraped from the walls of the uterine cavity.
After completion of curettage and removal of scrapings from the uterine cavity, a control hysteroscopy is performed.
Having inserted the hysteroscope into the uterine cavity, a sequential examination of the walls of its cavity is carried out, especially carefully in places where polyps are detected. After making sure that the polyps have been removed, the procedure is stopped.
If remaining polyps or their parts are detected in the uterine cavity, targeted curettage is performed again, followed by control hysteroscopy.
If a large endometrial polyp is detected, if necessary, additional dilation of the cervical canal is performed to No. 13-15 with Hegar dilators. After additional expansion of the cervical canal, forceps are inserted into the uterine cavity to remove the polyp, grasp the polyp with them, turning the forceps around its axis in one direction, unscrew the polyp and remove it from the uterine cavity. During control hysteroscopy, the site of attachment of the polyp is carefully examined; if remnants of the base of the polyp are detected, they are removed with a curette.
Removal of endometrial polyps is carried out in the first phase of the menstrual cycle.
I developed a decidual polyp during pregnancy (I wrote in the next thread). Its peculiarity is that it arose against the background of hormonal changes in the body and was characterized by the fact that it was completely penetrated by blood vessels, and bled at the slightest impact. They couldn’t even see him right away and understand the reason; they immediately put him in storage with the threat of “false abruption of the placenta.” Then, when it turned out that it was a polyp, a controversial issue arose, since it was necessary to determine its “nature,” so to speak, in order to rule out oncology. I was sent to oncology, where the soldier-butcher doctor (I can’t call it anything else) climbed in and looked at me so much that I started bleeding heavily, she started yelling, like, what’s your pregnancy like, what are you thinking about, she spoke in such a tone, as if in front of her was a 14-year-old walking schoolgirl, who had gotten pregnant from someone unknown... (although at that time I was well over 20, the pregnancy was long-awaited for my husband and I). In her words, or more precisely, I urgently need to do a cleansing, because the polyp is bleeding, what if it is malignant, you need to do a biopsy, but a biopsy during pregnancy (especially in the first trimester) cannot be done, allegedly, bleeding will open, there will be a miscarriage, and God forbid something else happens to me, but the bleeding will - it will open to anyone, because during a simple examination I bled a lot, and even more so this polyp consisted of blood vessels. With these words, to put it mildly, they intimidated me to the point of shaking and tears, I came out - I couldn’t remember myself, my brain was torn, I needed to decide something urgently... In the end, I went to two doctors (this time independently of the LCD), both calmed me down and said, that it is advisable to do a biopsy, of course, better (to exclude oncology), but there is nothing wrong with it, even during pregnancy. And if the polyp is not malignant, then it is better not to touch it during pregnancy, and remove it after childbirth, if necessary. And they were shocked that, first of all, the oncologist, in an orderly, rude tone, told me to do the cleaning, saying that there was nothing to save anyway... As a result, they gave me a biopsy, there was no bleeding, literally in 3 minutes they took a piece for analysis, then it was sent to Moscow. A week later they sent me the results (of course, I was nervous while waiting), but the results were “happy.” The doctor then explained in simple Russian that this polyp, which appeared during pregnancy, is just a clot of blood vessels (hormonal levels have changed, the amount of blood increases, its composition changes, etc.). And in essence, it should also disappear after childbirth. As a result, I safely gave birth to a heroic son, and the polyp actually “resolved” on its own…. And even after 8 years, I still want to come to that oncologist-gynecologist with my son and “bark something literary and artistic”)))
At the stage of preparation for endoscopic surgery, it is important to know: after removing polyps in the uterus, how long will you stay in the hospital and what restrictions will there be in everyday life? The attending physician of the Clinic will definitely answer
answer all questions and give the necessary recommendations, which will become an effective prevention of the complicated course of the postoperative period.
The head of the clinic, the head of the gynecological department No. 2, Ph.D., advises. Zhumanova Ekaterina Nikolaevna.
Initial consultation is free!
Highly qualified medical care FREE under the compulsory medical insurance policy!
Please note that all tests provided to the Clinic must be originals or certified copies.
Complications of hysteroscopy and hysteroresectoscopy: prevention and treatment
retroflexion of the uterus; b) stenosis of the cervical canal; c) endomyometritis; d) uterine cancer; e) infantile uterus; f) excessive efforts when expanding the cervical canal; g) non-compliance with the rules for performing intrauterine interventions. Most often, mechanical perforation of the uterus (complete or incomplete) is observed during probing of the uterine cavity and/or expansion of the cervical canal.
In addition, perforation of the uterus can occur when the resectoscope is inserted “blindly” (with the sharp edge of the ceramic coating of the inner tube).
Under our supervision was patient N., 26 years old, who was admitted to the clinic for artificial termination of pregnancy. First pregnancy, gestational age - 8 weeks. With the expansion of the cervical canal, incomplete perforation of the uterus was performed with the formation of a “false” tract in the myometrium.
Control hysteroscopy revealed that the “false” tract is distinguished by uneven edges (fragments of stratified myometrium) and a bleeding surface, as well as a narrow lumen.
Hospital treatment: how long will it take?
In addition to the surgical technique, the duration of hospital treatment may increase due to the method of pain relief used and the presence of postoperative complications.
Anesthesia options
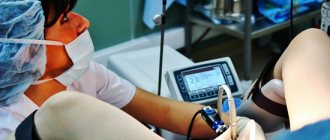
The choice of anesthesia method is the prerogative of the anesthesiologist. In standard cases, an intravenous anesthesia technique is used, when the doctor, before performing a hysteroscopic operation, injects a drug into a venous vessel that provides complete and short-term pain relief for the entire period of the surgical intervention. 2-3 hours after the procedure, the woman is able to leave the medical facility on her own. Local anesthesia is not used for polypectomy.
Risk of complications
During any operation, unpleasant consequences are possible due to the technical features of the procedure or the woman’s health condition. The following complications will force you to stay in the hospital for several days:
- uterine bleeding;
- damage to the uterine wall during the procedure (perforation);
- severe pain associated with the accumulation of fluid in the uterine cavity during cervical spasm (cervical atresia);
- exacerbation of chronic inflammation (endometritis);
- severe anemia in case of heavy blood loss (anemia), which requires blood transfusion or long-term drug therapy.
When using modern surgical techniques in the Clinic with experienced specialists, the risk of complications is minimal, so the time spent in the hospital is limited to the day of surgery.
Rice. Adnexit
With proper preparation for surgery and the use of highly effective treatments (hysteroscopy with laser coagulation), the duration of hospital stay will be no more than 3-5 hours. On the day of surgery and the first week of the postoperative period, the following recommendations must be strictly followed:
- refusal of any physical activity (sports, heavy lifting, long walking);
- mandatory adherence to intimate hygiene;
- use of medications prescribed by a doctor (it is unacceptable to self-medicate and use drugs that affect blood clotting);
- complete refusal of any vaginal interventions (you cannot use tampons, douche, or be sexually active).
When discharged from the hospital on the day of the polypectomy, the doctor will definitely tell you about the risk of possible complications and prescribe drug treatment. If you carefully follow medical recommendations, you can continue rehabilitation therapy at home.
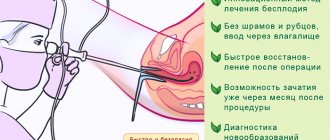
Hysteroscopy is a safe surgical procedure that takes no more than 20-30 minutes, allows you to get rid of the disease without a high risk of complications and creates conditions for discharge from the hospital on the day of the operation.
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Ph.D. Zhumanova Ekaterina Nikolaevna.
Removal of an endometrial polyp is a procedure familiar to almost every fifth woman. As a rule, the hysteroscopy method is used to excise a uterine polyp; it is considered more gentle and less traumatic. This method is also an excellent diagnostic tool that will help determine the nature of the polyp, the presence or absence of cancer cells in its structure. Quite often, women are interested in what consequences arise after removal of a uterine polyp.
How is hysteroresectoscopy performed?
Here two electrodes are used, which are both parts of the same cutting tool.
This method allowed the use of a liquid medium.
And the procedure itself for removing a pathological area with a cutting loop is more productive, since the conditions for dissection or cutting are better and are many times more effective than using a monopolar electrode. When a hysteroresectoscopy operation is performed, a variety of anesthesia can be used, depending on the patient’s concomitant diseases, her current condition, as well as the duration and scope of the operation and even the patient’s personal wishes. It can be intravenous, general (rarely used), endotracheal anesthesia (in case of a long operation), spinal anesthesia (if the operation lasts no more than thirty to forty minutes).
Therefore, how long hysteroresectoscopy lasts and how anesthesia is administered directly depends. Usually, this question is
Hysteroscopy. Sick leave or not.
Girls, good evening.
Like the smart Vasya, I wrote down for myself what to hand over when.
Today I went to take HIV, hepatitis and a smear test for flora at a paid clinic.
They took some blood with some kind of butterfly (the veins were very thin), sniffed ammonia and went for a smear.
And there, lady, MONTHLY (waited for August 20). The doctor takes a swab from the edge and asks where I will do it.
I say which doctor, and she responds: “God forbid from her.” screw it up, screw it up and you’ll redo it.” I'm shocked. She calls the head of the department and makes an agreement with him.
(I did laparo with him). He tells me to call on Monday when the tests are ready. I quickly run to our clinic to take other tests (I’m at work, I asked for time off).
Fortunately, there were no people, but they injected me 3 times, and their fucking test tube was defective and the blood did not flow.
Reviews from women
In most cases, hysteroscopy takes place without any unpleasant consequences.
Unfortunately, recently the number of women suffering from endometrial polyposis has been increasing. They undergo mandatory surgical intervention, the impressions of which they share with friends. Some of them even gave specific recommendations to a particular clinic where they had surgery. Many patients gave positive feedback regarding the treatment of polyps with this method.
Women who have undergone such surgery say that the postoperative period is calm.
What is a hysteroscope
A hysteroscope consists of a very thin tube with a camera inside. This tube is used to safely insert surgical instruments into the uterus. During the procedure, an enlarged image is transmitted directly from the uterus to a monitor. This is what allows diagnostic or surgical intervention to be carried out as clearly and safely as possible.
The characteristics of the postoperative period and the risks of complications depend on which procedure is performed. There are two types of procedures using a hysteroscope:
- diagnostic hysteroscopy of the uterus.,
- surgical hysteroscopy of the uterus.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy – examination of the uterine cavity, cervix and vaginal walls. This procedure is carried out on days 6-10 of the menstrual cycle on an outpatient basis. The procedure does not require anesthesia, and local anesthesia is also not usually used. Diagnostic hysteroscopy takes no more than half an hour and does not require subsequent hospitalization.
- infertility, chronic miscarriage;
- suspicion of neoplasms (cysts, fibroids, polyps);
- suspicion of obstruction of the fallopian tubes;
- abnormalities of the uterus;
- painful and prolonged bleeding during menstruation;
- spotting or breakthrough bleeding in the middle of the cycle;
- pain in the lower abdomen of unclear nature;
- cycle failures;
- spotting during postmenopause;
- IVF planning.
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is the most informative method for studying postoperative and postpartum complications.
Surgical hysteroscopy is performed to correct pathologies. Through the hysteroscope tube, the surgeon inserts into the uterine cavity the instruments that are necessary to remove the tumor, curettage the uterine cavity, or collect material for histological examination. The operation using a hysteroscope is performed in the gynecology department of the hospital under general (intravenous) anesthesia. The entire procedure, depending on the complexity, takes from 30 to 60 minutes. After its completion, during the postoperative period, the patient must stay within the hospital walls from two hours to several days to monitor her condition.
Surgical hysteroscopy can be performed immediately after diagnosis, in which case the patient is initially prepared for surgery.
- removal of polyps, fibroids, adhesions, cysts from the uterine cavity;
- removal of adhesions of the uterine tubes in the area of the corners of their junction with the uterus;
- removal of the uterine septum;
- frozen pregnancy;
- incomplete miscarriage;
- endometriosis;
- the need to collect material for histology;
- removal of an ingrown intrauterine device.
Reviews from patients about removal of uterine polyps and consequences
Most women note that they were very afraid of the operation. In the end, the procedure itself and recovery after it went well. Modern anesthesia drugs did not lead to the serious condition that patients fear most. And, accordingly, no complications arose.
In isolated cases, women complain of constant relapses. This rather indicates the doctor’s inattentive approach to the problem, so it is advisable to consult another specialist.
Separately, I would like to say about patients who had a polyp removed without anesthesia. Women report severe pain. Therefore, those who are just about to undergo surgery should discuss the possibility of anesthesia with their doctor.
Phrases like “it’s okay, you’ll be patient” indicate a lack of professionalism. The law establishes that a doctor must anesthetize any manipulation with all available means, if the risk from their use does not pose a serious threat to the life and health of the patient.
Although some say that when removing a polyp from the uterus without anesthesia, they only felt discomfort. Everything is individual and depends on the woman’s pain threshold.
Most of those who underwent surgery were able to get pregnant within 3-5 months.
In isolated cases, patients experienced severe pain during the rehabilitation period.
Features of the procedure
Hysteroscope
Modern endoscopic equipment for this study allows you to visualize the internal state of the uterus. With its help, you can accurately localize pathological structures and remove them directly during manipulation.
Indications for manipulation:
- Diagnosis of benign neoplasms, fibroids, adenomyomas, endometrial polyps, diagnostic search and confirmation of the presence of malignant tumors.
- Bleeding from the uterus, the cause of which has not been established.
- Cleansing the uterine cavity from the remaining parts of the placenta.
- Infertility.
- Control of the treatment performed.
- Hormonal disorders.
Hysteroscopy is not performed in case of acute inflammatory process in the uterus, during pregnancy, acute respiratory infections or acute respiratory viral infections, exacerbation of somatic diseases, and also during critical days.
Surgery is performed both as a diagnostic and as a therapeutic measure.
Before hysteroscopy, an ultrasound examination of the uterus is often performed. An ultrasound scan is necessary to confirm the preliminary diagnosis and determine where the tumor is located. Ultrasound can also be done to monitor the treatment, as it helps to monitor how the endometrium has grown after a certain intervention.
Hysteroscopy, what do we know about it?
—Blood discharge in postmenopause. Suspicion of: - submucosal MM; —adenomyosis; — endometrial cancer; —anomalies of the uterus; - intrauterine synechiae; —presence of fetal egg remnants in the uterine cavity; —presence of a foreign body in the uterine cavity; - perforation of the uterine wall. — Clarification of the location of the IUD or its fragments.
-Infertility. - Miscarriage.
—Control examination of the uterine cavity after previous operations on the uterus, hydatidiform mole, chorionepithelioma. —Evaluation of effectiveness and control during hormone therapy.
— Complicated course of the postpartum period.
CONTRAINDICATIONS TO HYSTEROSCOPYContraindications to diagnostic hysteroscopy are the same as for any intrauterine intervention: - general infectious diseases (influenza, tonsillitis, pneumonia, acute thrombophlebitis, pyelonephritis, etc.); — acute inflammatory diseases of the genital organs; —III–IV degree of purity of vaginal smears; — serious condition of the patient in the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system and parenchymal organs (liver, kidneys); —pregnancy (desired); — common cervical cancer; - profuse uterine bleeding. PREPARATION FOR THE STUDY Hysteroscopy should be considered as a surgical intervention, which, depending on the indications, is carried out both urgently and routinely.