Methods to detect the disease at an early stage
To be able to determine whether a person’s tumor is benign or malignant, special samples of blood, urine and other fluids are needed. This is how tumor markers are determined. Each type has its own degree of reliability, for this reason the doctor may prescribe several types of tests. What a blood test for tumor markers shows can only be determined by a specialist in this field.
Tumor markers are a collection of chemicals. They can be formed both by healthy cells in the body and by those that already have pathology. With the help of such tests, you can detect a terrible disease already in the initial stages.
They can be released by the tissues themselves, as well as by tumors that are located next to them.
Substances are of different types. This directly depends on their structure.
- Antigens.
- Blood plasma proteins.
- Substances that affect tumor decay.
- Enzymes that are formed during the metabolic process.
The only difference is their specificity. They are distinguished by composition. In other words, different substances indicate different types of tumors.
Why are tumor markers needed?
Tumor markers are represented by proteins, enzymes and antigens produced by cancer cells. The tumor produces one tumor marker or a number of them. NSE analysis allows you to see the tumor, monitor it and the result of treatment, and assess further prospects for recovery.
Tumor markers are detected by examining urine and blood. Markers are released into organic fluids due to tumor growth and development. There are two types of markers with features. The first marker is specific and works for a specific case, and the second works with a group of tumor markers.
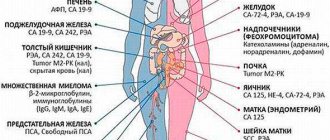
Any marker indicates a specific type of tumor. For example, CA 15-3 indicates breast cancer. This feature helps determine the type of tumor and location.
Neuron-specific enolase is a glycolytic enzyme. Its molecular weight is 80 kDa. Neuron-specific enolase includes λ-λ and α-λ isoforms of gamma enolase.
What is a tumor marker and how is it useful?
One of the leading diseases of our century is cancer. Moreover, the age of patients is becoming younger every year. Therefore, experts are constantly working on the effectiveness of methods for recognizing these ailments at the earliest stages. These methods include analysis of the NSE tumor marker.
Tumor markers are specific substances that are found in every body. But their number depends on the presence of cancer. And this tumor marker, neurospecific enolase, is one of the variations of enolase. This enzyme is inherent in every cell of the body. Takes direct part in the process of glucose oxidation. An individual tissue contains its own individual isoform.
NSE is an enolase, and it is part of the cells of organs of neuroendocrine origin. Due to its specific structure, this particular isoform can be found in cells where the level of chloride ions is significantly increased. This antigen belongs to the list of tumor markers that have the highest organ specificity.
In other words, the NSE tumor marker is a glycolytic enzyme. It serves as a specific litmus test for neuroendocrine tumors. The peripheral nervous system and the brain contain this structure.
The essence of this research process is that the synthesis of the enzyme increases significantly if tumor cells of a neuroendocrine nature are present. This also leads to increased activity in the blood plasma. Glycolysis is activated, and the mutated cells improve their nutrition. This is what has a beneficial effect on the growth of tumors and allows them to metastasize to both surrounding and distant organs. This makes it possible to assume the presence of oncological pathology of these organs.
Enolase contains three unchanged elements.
| Alpha enolase | component of a wide variety of living tissues |
| Beta subunit | it consists of striated muscle tissue and cardiac muscle |
| Gamma subunit | neuron-specific enolase, in large volumes constitutes nervous tissue and neoplasms that originate from mutated nerve cells |
The NSE test acts as a marker of tumors of neuroendocrine origin, namely:
- thyroid carcinoma;
- neuroblastoma;
- pheochromocytomas;
- small cell lung cancer;
- pancreatic carcinoma.
Carefully! The level of enolase also increases due to various diseases of the nervous system (this includes tumors), various brain damage (ischemic or traumatic).
Also, the NSE tumor marker can be elevated in different ways.
- A high concentration of NSE characterizes various oncological pathologies (leukemia, neuroblastoma, bronchial and lung cancer).
- An average increase in indicators is typical for non-oncological lung diseases.
As a result, concentration studies of this antigen are most often used to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy for small cell lung carcinoma.
Taking tests
Before taking the test, it is recommended to visit an oncologist to determine which marker needs to be taken. All types are not worth taking. This could result in a loss of money. It is better to take a number of tumor markers that show specificity in relation to the organ that detects the risk of tumor development.
The material for research is blood from a vein. In some cases, fluid from the spinal cord may be used. There is no need to undergo preparation immediately before collecting material. Blood donation is carried out on an empty stomach in the morning.
Twelve hours before blood collection, fatty and spicy foods are excluded from the diet to reduce the load on the digestive system. It is permissible to consume only non-carbonated water.
It is worth giving up cigarettes and alcohol. The ban applies to physical and emotional stress. It is worth warning your doctor if you are taking medications. The test norm is considered to be 16.3 ng/mg, regardless of gender and age.
To obtain accurate results, it is recommended to find out the date of the tests in advance in order to take them directly on the required day. The check is carried out after the required number of samples has been accumulated. The blood is frozen until testing. It is worth finding out the date of the inspection.
The analysis process is carried out over a number of days, but sometimes the period is reduced.
Sometimes the analysis result shows values that are not related to oncology:
- Pulmonary tuberculosis.
- Ischemic disease.
- Dementia.
- Kidney and liver failure.
- Poor blood circulation to the brain.
In case of trauma, an increased level of NSE indicates an unfavorable outcome, since a large number of red blood cells and tissues are destroyed. Cells are also destroyed under the influence of medications.
Neuron-specific enolase (NSE)
Neuron-specific enolase (NSE) is an isoform of the enolase enzyme necessary for glycolysis. It is a marker of tumors of neuroendocrine origin.
Synonyms Russian
NSE, NSE.
English synonyms
Neuron-specific enolase, NSE, γ-enolase, γ-phosphopyruvate-hydratase.
Research method
Electrochemiluminescent immunoassay (ECLIA).
Determination range: 0.05 - 370 ng/ml.
Units
ng/ml (nanograms per milliliter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Eliminate fatty foods from your diet the day before the test.
- Do not eat for 8 hours before the test; you can drink clean still water.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress for 30 minutes before the test.
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
Neuron-specific enolase is one of the structural varieties of the enolase enzyme, which is required for glycolysis and is therefore present in all cells of the body. The isoforms of this enzyme are tissue specific. Neuron-specific enolase, NSE, is an isoform characteristic of neurons, differs in some structural features necessary for the normal functioning of this enzyme at elevated concentrations of chlorine ions. In addition to the cytoplasm of neurons, NSE is also found in cells of neuroendocrine origin, such as chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla, parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland and some others. However, increased synthesis of this enzyme occurs in tumor cells, which ensures a high rate of glycolysis, active growth of the tumor and its spread to surrounding tissues. Increased NSE is often observed in small cell lung cancer, as well as in medullary thyroid cancer, pheochromocytoma, neuroendocrine tumors of the intestine and pancreas, and neuroblastoma.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an anaplastic process and has neuroendocrine properties. For example, this type of cancer is characterized by the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), antidiuretic hormone (ADH), and neuron-specific enolase. Such features determine the clinical picture of the disease and can also be used for its diagnosis. The clinical picture of SCLC may be dominated by constitutional symptoms (fever, loss of weight and appetite), symptoms of lung tissue damage (shortness of breath, cough, hemoptysis), symptoms of organ damage during metastasis (pathological fracture with metastases in the spinal column) and paraneoplastic syndromes. As a rule, SCLC has a central location and compresses adjacent mediastinal structures. In 10% of cases, a large tumor presses on the superior vena cava, which is accompanied by impaired venous outflow from the jugular veins and is manifested by headache, changes in complexion, and can also cause thrombosis of the deep veins of the brain (superior vena cava syndrome). SCLC is often accompanied by the syndrome of inappropriate ADH production, in which excess ADH leads to fluid retention and hyponatremia. Another paraneoplastic syndrome typical of SCLC is the syndrome of ectopic ACTH production (Cushing's syndrome). It is characterized by redistribution of fat mass (moon face, abdominal obesity), loss of muscle and connective tissue (pink stretch marks), osteoporosis and hirsutism. A common neurological paraneoplastic syndrome is Lambert-Eaton syndrome, in which blocking antibodies to the calcium channels of neurons are detected, which leads to disruption of the conduction of nerve impulses and is accompanied by severe weakness of proximal muscle groups. A high level of NSE is an unfavorable prognostic factor and is associated with an insufficient response of SCLC to chemotherapy, rapid disease progression and a high probability of death. Therefore, measurement of NSE concentration can be used to predict SCLC. A decrease in NSE levels during treatment is associated with slower tumor progression, which makes it possible to use this tumor marker to evaluate the results of treatment.
Other types of lung cancer are collectively called non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). This group of diseases, unlike SCLC, does not have neuroendocrine properties, and it is not typical for it to produce excessive amounts of NSE. Therefore, NSE can be used to differentiate SCLC from NSCLC. This laboratory indicator is especially useful when routine diagnostic methods cannot be performed due to the severity of the disease or comorbidity.
Adrenal medulla cells, thyroid parafollicular cells, and gastrointestinal neuroendocrine cells share a common neural crest origin. Tumors from these cells are characterized by increased secretion of specific hormones (adrenaline in pheochromocytoma, calcitonin in medullary thyroid cancer), as well as excessive production of neuron-specific markers, including NSE. Therefore, NSE measurement can be used in the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma, medullary thyroid cancer, gastrinoma and insulinoma, as well as carcinoid tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. The common origin of these cells also explains the phenomenon of the combination of several tumors of different locations in the same patient. Three multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndromes have been described: MEN I, MEN IIA and MEN IIB. They are genetically determined and inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. MEN I includes tumors of the parathyroid glands, endocrine pancreas (gastrinoma, insulinoma, glucagonoma) and adenohypophysis (prolactinoma). The disease is caused by a mutation in the menin protein gene. Common symptoms in MEN I are hypercalcemia and nephrolithiasis. MEN IIA and MEN IIB syndromes are caused by mutations of the RET proto-oncogene. MEN IIA includes medullary thyroid cancer, bilateral pheochromocytomas, and parathyroid tumors. MEN IIB is characterized by a combination of medullary thyroid cancer, bilateral pheochromocytomas, and multiple ganglioneuromas. Medullary cancer is found in almost 100% of MEN II cases and is characterized by an early onset of the disease, an aggressive course and high mortality. The clinical picture of MEN II is caused by an excess of specific hormones. A frequent manifestation of hypercalcitoninemia accompanying advanced medullary cancer is long-lasting diarrhea. MEN II is usually diagnosed based on family history using molecular genetic tests before signs of the disease appear. In addition, the NSE test can be used in the diagnosis of manifest MEN syndromes.
While the most common adrenal medulla cell tumor in adults is pheochromocytoma, the most common tumor in children is neuroblastoma, a malignant tumor also derived from neural crest neuroblasts and capable of producing catecholamines and NSE (most patients are less than 2 years old at diagnosis) . The clinical picture is caused by compression of the tumor on adjacent structures and an excess of adrenaline and dopamine. A frequent combination of neuroblastoma and opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome has been noted. A high level of NSE in neuroblastoma is an unfavorable prognostic sign.
Normally, NSE is present in large quantities in neurons of the central and peripheral nervous system. Its concentration increases significantly when nerve tissue is damaged as a result of mechanical brain injury or hypoxia. Elevated NSE levels are associated with the size of the brain contusion lesion and the presence of subarachnoid hemorrhage. In addition, it is an unfavorable prognostic factor in a patient with traumatic brain injury. This indicator can be used together with instrumental methods when deciding whether to terminate medical care. NSE concentration increases in ischemic stroke, and a high rate of its increase is associated with an unfavorable prognosis of the disease. This clinical and laboratory indicator can also be used to assess the degree of brain damage during anoxia caused by cardiac arrest.
What is the research used for?
- For diagnosing small cell lung cancer (SCLC), making its prognosis and monitoring its treatment.
- For the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma.
- For the diagnosis of medullary thyroid cancer.
- For the diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumors of the gastrointestinal tract.
- For the diagnosis and prognosis of neuroblastoma.
- To make a prognosis for traumatic and hypoxic brain damage.
When is the study scheduled?
- For symptoms of SCLC: unmotivated weakness, weight loss, cough and hemoptysis, shortness of breath, pathological fractures and characteristic paraneoplastic syndromes, especially in a smoking patient.
- When planning chemotherapy and assessing its results, as well as when making a prognosis for SCLC.
- For symptoms of pheochromocytoma in adults: arterial hypertension (diastolic), especially during a crisis course of the disease, accompanied by a throbbing headache, rapid heartbeat, increased sweating, and anxiety.
- For symptoms of medullary thyroid cancer: thickening in the neck, painless regional lymphadenitis, prolonged diarrhea.
- For hyperinsulinemia, hypergastrinemia, hyperglucagonemia.
- For symptoms of neuroblastoma in children: pain in the bones, abdominal pain, lameness, nausea, loss of appetite and weight, hemorrhages on the skin around the eyes, diarrhea.
- With a hereditary predisposition to multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes.
- For brain injuries and cerebral coma, ischemic stroke and cerebral anoxia.
- When making a prognosis of the disease in a patient with traumatic and hypoxic brain damage.
What do the results mean?
The isolated use of research for the purposes of screening and diagnosing cancer is unacceptable. The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. Diagnosis of any disease is based on a comprehensive examination using various methods, not just laboratory ones, and is carried out exclusively by a doctor.
Reference values: 0 - 16.3 ng/ml.
Reasons for increased levels of neuron-specific enolase:
- stroke,
- cerebral edema,
- neuroblastoma,
- small cell lung cancer,
- medullary thyroid cancer,
- pheochromocytoma,
- neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas (insulinoma, gastrinoma, glucagonoma),
- multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome,
- chronic renal failure,
- benign lung diseases,
- pulmonary tuberculosis,
- systemic scleroderma,
- advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
A decrease in the level of neuron-specific enolase is not diagnostically significant.
What can influence the result?
Normally, the majority of NSE comes from red blood cells, so any destruction of red blood cells (due to drugs or injury) is accompanied by an increase in NSE levels.
Important Notes
The NSE test cannot be used as a screening test to detect early stage tumors.
Also recommended
- Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
- Fragments of cytokeratin 19 CYFRA 21-1
- Serum calcitonin
- Free metanephrine and free normetanephrine in urine
- Total metanephrine and total normetanephrine in urine
- Insulin
- Gastrin
Who orders the study?
Oncologist, general practitioner, neurosurgeon, anesthesiologist-resuscitator, geneticist.
Literature
- Bharti A, Ma PC, Salgia R. Biomarker discovery in lung cancer – promises and challenges of clinical proteomics. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2007 May-Jun;26(3):451-66.
- James A. Bonner, Jeff A. Sloan, Kendrith M. Rowland, Jr., et al. Significance of Neuron-specific Enolase Levels before and during Therapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2000;6:597-601.
- Jaume Trape et al. Increased plasma concentrations of tumor markers in the absence of neoplasia. Clin Chem Lab Med 2011;49(10):1605–1620.
- Chernecky CC Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures / S.S. Chernecky, V.J. Berger; 5th ed. – Saunder Elsevier, 2008.
- Brodeur GM, Pritchard J, Berthold F, Carlsen NL, Castel V, Castelberry RP, De Bernardi B, Evans AE, Favrot M, Hedborg F, et al. Revisions of the international criteria for neuroblastoma diagnosis, staging, and response to treatment. J Clin Oncol. 1993 Aug;11(8):1466-77. Review.
- Daubin C et al. Serum neuron-specific enolase as a predictor of outcome in comatose cardiac-arrest survivors: a prospective cohort study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2011 Aug 8;11:48.
Symptoms
There is a belief that cancer does not show symptoms, but this is not true. A number of signs when the doctor will send you for testing:
- Lung cancer – shortness of breath, coughing up blood, unexplained weight loss.
- The presence of neuroblastoma in children is the presence of pain in bone tissue, fever, weight loss.
- Pheochromocytoma – high blood pressure, nervous system excitement, pale skin, blurred vision.
- Thyroid cancer - stomach upset, lump in the neck.
If you discover health problems, you should urgently consult a doctor to rule out the appearance of a tumor.
In the first days of treatment, NSE tumor markers will be elevated. This indicates a positive response of the body to treatment.
If the indicators remain elevated, the situation indicates the ineffectiveness of treatment.
Diagnosis
Neuron-specific enolase testing is prescribed to detect small cell and neuroendocrine cancers and monitor the effectiveness of treatment. The NSE tumor marker has poor sensitivity, so the result may be inaccurate. It is recommended to use enolase in combination with CEA. Since the behavior of NSE and CEA in the blood when small cell lung cancer is present in the body is contradictory, it is worthwhile to determine the blood of these two cancer markers simultaneously.
Research methodology
The main method for determining test results is electrochemiluminescent immunoassay (Eclia). Blood serum is used as the biomaterial being studied. The amount of the analyte is determined by the relative increase or decrease in chemiluminescence.
Bronchial cancer. NSE is the main tumor marker for small cell lung cancer. An increase is detected in 50–70% of cases of diagnosing bronchial cancer. There is no correlation with the location of metastases, but there is a good correlation with the clinical phase of this pathology (progression).
Analysis of the result obtained
Analysis of the tumor marker analysis has features that the doctor will talk about in detail. It is worth contacting the doctor immediately after receiving the results so that the interpretation is correct.
It is worth noting that the normal NSE indicator is from 0 to 16 ng/ml. A slight increase (20 ng/ml) indicates a benign process. Indicators above 25 ng/ml indicate damage to malignant neoplasms.
You should know why the NSE index increased. Having important information, it will be possible to consult a doctor in time. Reasons for increased enolase:
- Pathology of the nervous system.
- Damage to part of the brain.
- Cancer disease.
- Benign education.
Non-compliance with the norm
It happens that this non-malignant formation increases the indicators. Somatic diseases and inflammatory processes can provoke a jump in enolase. Then, after treatment, the doctor prescribes a repeat test for neuron-specific enolase.
If malignant tumors are detected after a specific period of time, the procedure is scheduled again. If the indicators are elevated, additional examinations are prescribed to identify a connection with tumors. But it is also possible that during the study, enolase will be normal.
Tumor markers in children
Detection of oncology can be difficult, since the child cannot always explain his feelings. Therefore, treatment sometimes begins late, when it no longer brings results. They are more likely to develop neuroblastoma, which appears before the age of five.
Tumor markers in children and adults can detect cancer at an early stage or exclude the disease. The child's blood is collected venously. Blood collection is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach, so the baby should be fed 8 hours before the test. Spicy and fatty foods should be avoided 12 hours before the procedure. You cannot take medications. If refusal is not possible, you should consult a doctor.
The above preparation methods are the same for adults and children.
Reliability of analysis for tumor markers
Not all tumors provoke an increase in the concentration of cancer markers, especially at the initial stage of the disease. Most often, the test is prescribed for early detection of cancer and evaluation of anti-cancer treatment.
Reasons for the unreliability of tumor markers:
- The composition of biologically active compounds includes not only normal, but also atypical cells;
- A positive test result often indicates chronic diseases of non-tumor origin;
- In some cases, the concentration of tumor markers in the blood does not increase, especially at the initial stage of cancer;
- In some patients, cancer does not change the cellular composition of the blood;
- An increased concentration of cancer markers may indicate nosological types of cancer.
The reliability of the results is affected by the following features of cancer markers:
- Degree of sensitivity. Many protein substances have low susceptibility, and therefore it is often not possible to detect the disease at the initial stage;
- Specificity of cancer marker. Substances may indicate one type of cancer or different types of cancer pathologies.
A tumor marker test is performed if a tumor is suspected. In this case, after this study, instrumental and hardware diagnostics are carried out.
Testing for tumor markers is carried out repeatedly to monitor changes in the composition of the blood. To improve the quality of calculations, it is recommended to conduct a blood test for tumor markers in one laboratory.
The second category of patients who should undergo a tumor marker test are people with already diagnosed cancer. In this case, doctors use research to observe how the pathological process proceeds, evaluate the effectiveness of therapy and prevent relapse.
Cancer markers in women
Cancer is dangerous for women; the reproductive system may be affected. An oncological marker for the fairer sex is important; women are susceptible to breast and ovarian cancer.
An increase does not always indicate danger. In any person, the marker is present in small quantities. In women, the indicator increases in the following cases: during menstruation, during pregnancy, during exacerbation of inflammatory processes, the formation of cysts and benign formations.
Types of tumor markers
There are a number of tumor markers that allow you to examine the body. The SCC analysis has high reliability. This tumor marker allows you to monitor therapy against cervical cancer. This analysis is also suitable for detecting the initial stage of lung cancer. Neuron-specific enolase assay helps identify neuroblastoma.
Types of tumor markers:
- MSA. Doctors prefer this marker due to its high sensitivity to formations in the chest area. The norm is 11 IU/ml.
- Antigen CA 27-29. An increase in rates is observed with the formation of ovarian cancer.
- HCG tumor markers. Even a slight increase indicates uterine cancer.
- CA 15-3. This is a specific cancer marker that shows metastases in the mammary glands. It can be used to confirm or refute breast cancer and liver cirrhosis. The norm is 22 IU/ml.
- HE-4. Determines ovarian cancer at an early stage, which allows for complete recovery.
- SA-125. An increase indicates that the neoplasm is benign. If the indicator is slightly increased, this indicates menstruation and pregnancy. The norm is 35 IU/ml.
- CA 72-4. This marker helps detect ovarian, lung and stomach cancer. Necessary for monitoring the correctness of therapy.
- AFP. Increases in breast cancer in women. The rate increases in pregnant women due to hormonal changes and preparation for breastfeeding.
The reliability of the test is determined by the woman’s age-related changes. During menopause, metabolism in the body slows down, so it’s worth doing it again.
Tumor markers
In medicine, markers are marks in a patient’s blood that are easily detected phenotypically and linked to certain manifestations of the genome. Tumor markers are biological factors that characterize the presence of clinical pathology and its course. With the help of their analysis, it becomes possible to track the effect of a particular therapy on the course of the disease.
Clinical diagnosticians divide tumor markers into:
- The main ones are markers of increased sensitivity that have high specificity.
- Secondary are markers that clarify the picture when analyzing the presence of previous ones.
- Additional – more often used in analyzing relapses and clarifying the course of the disease.
In addition, tumor markers can provide information about the location of the tumor. Thus, the presence of CA15-3 and CEA markers in the blood indicates the presence of a pathological process in the mammary glands, and CA19-9 indicates a pathology in the intestines. The tumor marker discovered by NSE shows that there are pathologies in the neuroendocrine system. Markers directly highlight tumor formations and tissues adjacent to them.
Effect of chemotherapy
The substance will be within normal limits during a long lull, but with progression it can increase. If the selected method is not suitable, the enolase level will constantly change.
In the first days of chemotherapy, the patient's blood levels will increase sharply. Gradually the level will begin to fall. In case of recurrence of the disease, an increase in the oncological marker is observed.
Carrying out a chemotherapy procedure
Who should be examined and when?
Despite the asymptomatic nature of cancer, everyone does not need to be tested. Only for those whose relatives have experienced the disease. The procedure is carried out 1-2 times a year. People with benign tumors are also recommended to undergo analysis for the content of tumor markers. Others should donate blood once every 2-3 years if there are conditions that can cause cancer.
People who are completely cured should be checked every 3 years. In the first year, you should take the test once every month. In the second, 1 time every 2 months. For the third time, 1 time every 3 months.
People experiencing the disease for the first time should take a test before surgery to think about the need for chemotherapy and other treatments.
Those undergoing chemotherapy should take a test to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
After 3-5 years of treatment, it is recommended to undergo tests throughout life, once every six months or a year, to identify a possible relapse.
Indications for analysis
The sensitivity of the NSE tumor marker for small cell cancer ranges from 60 to 81%, and the specificity of the analysis in combination with visual signs of the disease reaches 100%. Enolase concentration correlates with both the stage of the disease and the growth rate of bronchogenic neoplasia.
An increase in NSE concentration in seminoma is observed in 68-73% of patients. The sensitivity of the tumor marker for neuroblastoma is slightly lower and amounts to 62%.
Reliability
This analysis is not considered 100% accurate. But today this method is the most reliable. A jump in the enzyme means that there is a problem in the body. But an increased level of enolase does not mean that a malignant formation has appeared.
It is worth clarifying whether the result is false. Afterwards you need to take the test again in 3-4 weeks. If the second time the result is negative, it is false. An increased level indicates the reliability of the result. In this case, you need to consult an oncologist. He will prescribe an additional examination to identify the location of the tumor.
You need to trust tumor markers. Their levels are constantly elevated in the presence of cancer. The study will help detect a neoplasm during the period of formation, when there are no signs.
Changes in indicators without signs of cancer pathology
Increased levels of NSE can be observed in some diseases without signs of malignancy.
A change in the level of neurospecific elonase without signs of a tumor process is observed:
- septic shock;
- inflammatory processes in the lungs, pneumonia;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- benign neoplasms of the central nervous system;
- head injury;
- ischemic stroke;
- cerebral contusion with hemorrhage into the subarachnoid space. In this case, together with the data of additional studies, a decision is made to terminate the provision of medical care.
Elevated tumor marker levels without evidence of cancer in brain injury indicate a poor outcome.
Important! NSE is produced from red blood cells, so with any grass or hemorrhage, or the use of drugs that destroy red blood cells, its levels will differ from normal.
In addition, processing of the blood sample should begin no later than 1 hour after collection. Otherwise the results will be invalid.
Additional detection methods
The following methods are used to diagnose the oncological process:
- Mammography (if breast cancer is suspected).
- Endoscopy.
- MRI.
- Ultrasound.
- X-ray diagnostics.
- Histology.
Mammography
Mammography involves taking an image of the breast using an X-ray. This method helps detect mutated cells before a tumor forms.
Breast mammography
This method is used in the following options:
- The appearance of lumps in the chest.
- Heredity.
- Presence of edema.
Endoscopy
During this examination, an endoscope with a camera is inserted into the body. Such a study helps to detect oncology of the stomach, lungs, and intestines.
MRI
MRI makes it possible to detect a small tumor, establish the presence of metastases and monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
The method helps to find organ pathology:
- brain;
- uterus and its cervix;
- liver;
- kidney;
- pancreas.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound reflects sound waves from body tissues. The method helps detect the following cancer:
- uterus;
- mammary glands;
- thyroid gland.
It is often necessary to order additional examinations to clarify the diagnosis.
X-ray diagnostics
Helps determine the contours of the tumor. This method is suitable for obese people: you do not have to be in the machine, as, for example, with an MRI.
Histology
Histology examines tumor tissue and determines the origin of cancer. There is an opportunity to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment and choose the right one before starting.
Additionally, blood, urine, and cytological studies are collected.
There is also an ELISA method that allows timely detection and prevention of a malignant process in the body. This method takes a lot of time, which is not entirely comfortable, and the cost of the drugs for this study is quite high.
It is possible to do an express test for tumor markers, but it is not carried out in all medical organizations and will require large expenses. The method is not considered reliable, and the doctor will not make a diagnosis based on the final results.
It is worth consulting with a specialist. You cannot self-medicate. An elevated enzyme may also indicate a benign formation.
Tumor markers help prolong the patient’s life, while maintaining the possibility of detecting the recurrence of oncology.