Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH, thyrotropin) is a hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gland and is the main regulator of the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. Hormonal imbalance can cause a number of serious physical or mental pathologies. The study is recommended to be carried out regularly every year, since many diseases have a long, latent course. However, many of them are detected at a stage when drug therapy is no longer effective.
Important: if it is necessary to monitor the effectiveness of the chosen treatment tactics, a repeat analysis is carried out at least 2 months after its completion. This fact is due to the fact that the TSH analysis shows the situation in the pituitary gland - thyroid gland system over the last 4 - 6 weeks.
Research method: immunochemiluminescence. Duration: 1 day, excluding the day of taking the biomaterial. Price: 450 rubles.
The concept of TSH and factors influencing the level of its concentration
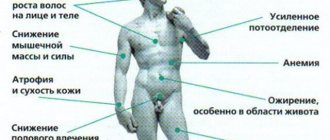
The thyroid gland is an important component of the human endocrine system, which affects metabolic processes in the body and stimulates the proper functioning of all organs. If the production of necessary hormones by the pituitary gland is reduced, lethargy and indifference appear, unhealthy drowsiness and excessive sweating, libido decreases and joints hurt, cramps appear and the heart rhythm is disturbed, hair loss begins and dry skin appears. All these unpleasant symptoms are a direct consequence of the fact that the body has a deficiency of such an important element as thyroid-stimulating hormone.
The main function of the thyroid gland is the production of hormones that help maintain the normal course of many processes in the body. Any fluctuation in the amount of hormones from the normal state towards a decrease or increase is fraught with extremely serious consequences. Therefore, it is so important to identify a dangerous change in the amount of TSH in the body in time and take proactive measures. A blood test for thyroid hormones can show the level of their content. What is TSH? And when is it necessary to take a test to determine its level?
As mentioned above, TSH is called thyroid-stimulating hormone. Otherwise called thyrotropin or thyrotropin. It is responsible for regulating the functioning of the thyroid gland, and its main function is to influence the synthesis of the extremely important growth hormones T3 (triiodotyranine) and T4 (thyroxine). Their area of responsibility is managing energy production and controlling the metabolism of fats and proteins. TSH is also responsible for regulating iodine levels and enhancing lipolysis - the breakdown of fats entering the body into individual fatty acids. To determine whether deviations in the content of this hormone have appeared, it is necessary to donate blood for thyroid hormones. TSH may change under the influence of releasing factors secreted by neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus.
The TSH level changes depending on what time of day the test is taken. This hormone reaches its peak content at night in the range of 2-4 hours or in the morning in the range from 6 to 8, the lowest content in the evening - from 17 to 19 hours. If the patient is awake at night, then a disturbance occurs in the process of TSH secretion. Pregnancy and lactation affect the decrease in hormone levels, and this is the norm. Some medications can have the same effect.
Where can I take this test?
It is worth noting that it is not possible to prepare and take a blood test for TSH in every clinic. The fact is that the expensive reagents that are necessary to conduct such a study do not allow all clinics to carry out such a procedure. But today, in almost every Russian city there will certainly be a laboratory or some kind of representative office of a large center where it will be possible to quickly and at affordable prices determine the level of one or another thyroid hormone.
We looked at what preparation is for taking a TSH test.
When is research necessary?
Doctors - an endocrinologist and a therapist - can prescribe a blood test for thyroid hormones. They assign this analysis to the following categories of persons:
- if hypothyroidism or thyroid goiter is suspected;
- in case of infertility and problems with potency;
- when the patient is undergoing hormone replacement therapy;
- if you have heart problems;
- with myopathy (muscle damage);
- at low body temperature;
- with intense hair loss;
- with loss of menstruation;
- for long-term depression and other cases of hormonal imbalances.
It is important to know how to donate blood for thyroid hormones. This procedure is very important, although there is nothing particularly difficult about donating blood. But, since too many factors can influence the results of a TSH test and distort their results, proper preparation for donating blood for thyroid hormones is very important. If the doctor has prescribed a blood test to check your TSH level and has not told you how to prepare for it, you should ask him about the details of the preparatory period. Otherwise, distorted results will not allow the doctor to make a correct diagnosis, and the prescribed treatment will be ineffective.
Effect of drugs
Some medications can also affect your total TSH levels. The thyroid gland is associated with the functioning of many organ systems, disruption of which can affect the secretion of the hormone. We will consider in more detail the reasons for deviations from the norms in one direction or another below. The amount of TSH in the test is usually measured in units per volume (mU/L). The analysis is prescribed by an endocrinologist or therapist. Indications for its delivery are usually as follows:
- The study is prescribed in case of suspected thyroid goiter or hypothyroidism.
- Against the background of male or female infertility, and in addition, with problems with potency.
- In the event that the patient is undergoing a course of hormone replacement therapy.
- For various patient problems with the heart.
- In case of myopathy (muscle damage).
- Against the background of the development of hypothermia (when the temperature is low).
- For alopecia, amenorrhea and prolonged depression.
- In case of delayed mental and sexual development in children.
Next, we will find out how to prepare for passing the analysis in question.
Rules for preparing for analysis
The correctness of the diagnosis also depends on what tests are performed on the thyroid gland. For a more accurate clinical picture, together with an analysis of the level of TSH concentration, a test of the T3 and T4 hormones is prescribed. Their content in the patient’s blood is inversely proportional to the TSH level - if these hormones reach a certain high level of concentration in the blood, then this acts depressingly on the production of TSH; if the amount of T3 and T4 decreases, then the TSH level increases accordingly. Indicators T3 and T4 enable the endocrinologist to more widely see and correctly assess hormonal levels.
So, in order to take the TSH level test, you should be well prepared. On the recommendation of the attending physician, you will need to first undergo certain procedures. Before donating blood for thyroid hormones, the patient must fulfill certain conditions. Three days before blood sampling, he needs:
- do not smoke or drink any alcoholic beverages;
- exclude heavy physical activity;
- ensure yourself a calm emotional state;
- eliminate hypothermia and overheating of the body;
- do not take medications that have not been approved by the endocrinologist, primarily this applies to hormonal and iodine-containing drugs, as well as various vitamin complexes.
12 hours before donating blood for thyroid hormones, you must refuse food and take tests with an empty stomach. You are allowed to drink only one glass of water in the morning. No matter how difficult it may be to complete these activities, it must be done. These are the rules for taking a test for thyroid hormones, and their implementation is entirely in the patient’s interests. The patient himself is most interested in ensuring that the diagnosis is correct and that the prescribed treatment is effective. For this important reason, all doctor’s instructions must be followed strictly.
Normal TSH in the analysis
It has been established that the TSH content in the blood of patients of different ages is different. When selecting normal values, the doctor takes into account the patient’s age, as well as the presence and duration of pregnancy. The standard units of measurement are µIU/ml, in which all values will be given below.
The normal value for newborn babies up to 4 months is in the range from 0.7 to 11. The values are similar for full-term and premature babies.
At the age of 4 months to 1 year, the norm is 0.7 - 8.5, then up to 7 years from 0.7 to 6.
Acceptable values for children from 7 to 12 years old are in the range of 0.6 - 5.
Puberty for a teenager is accompanied by significant hormonal changes. Thus, the value of thyrotropin from 12 to 20 years should be in the range from 0.5 to 4.4.
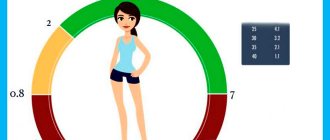
For people over 20 years of age, standard values range from 0.3 to 4.2. After 60 years, there is a slight increase in the concentration of thyrotropin. This is due to a physiological decrease in the amount of T3 and T4.
Articles about TSH norms and interpretations: in women and children, incl. in pregnant women, in men
Normal and deviation after removal of the thyroid gland
After surgical removal of the thyroid gland, the secretion of T3 and T4 stops, and the pituitary gland tries to maximize their content by excessively producing thyrotropin for this purpose. To compensate for the lack of T3 and T4, drugs based on them are prescribed for life.
The normal level of thyrotropin after surgery is from 0.3 to 4.0 mU/ml.
In the first days, the patient has a high level of TSH after removal of the thyroid gland, which is a variant of the physiological norm. However, subsequently its value should return to normal values. It is important to properly prepare for collecting biomaterial, since many medications lead to false-positive results.
Low thyrotropin values after surgery indicate an overdose of hormonal drugs or pathologies in the pituitary-hypothalamic region of the brain.
Read further: All about the test for antibodies to TSH receptors
How to submit?
In order to maximally help the doctor see the true picture of the hormonal processes occurring in the body, each patient should know how to properly test thyroid hormones. When a person initially knows the entire procedure algorithm, he will try to accurately follow all instructions and will not do anything that could distort his performance. Therefore, it is advisable for the doctor to explain the entire procedure to the patient, explaining in detail how to donate blood for thyroid hormones.
All studies are completed according to a certain scheme. They need to be taken in the morning, from 8 to 11, after the TSH level has passed its peak and began to decline. According to experts, this test cannot be taken in a hurry, only after running to the delivery point and while still in an excited state. Before donating blood, you need to calm down and be in complete peace for 20-30 minutes so that the analysis is reliable. Only after this should blood sampling from the patient begin. In this case, blood is donated for thyroid hormones on an empty stomach. The method by which the level of TSH in the blood is determined is called chemiluminescent immunoassay on microparticles. With this method, blood serum is examined.
Blood is collected for analysis by taking it from the cubital vein on the right or left arm. The frequency of the test procedure is set by the doctor depending on the degree of complexity of the disease. Typically, if a patient has any abnormalities in the performance of its functions by the thyroid gland, such tests are performed twice a year.
How is the examination carried out?
The examination is carried out in a standard manner. From a patient who is in a sitting position, blood is taken from a vein (usually the forearm), after treating the injection site with a disinfectant. In this case, there are no specific accompanying manipulations on the part of the laboratory assistant.
At the end of the procedure, cotton wool or a bandage is applied to the injection site, which should be removed after the bleeding has stopped. With normal clotting, bleeding stops within 5-10 minutes.
The analysis of the obtained material also does not require any specific specifics and can be carried out on the day of blood sampling. In this case, it all depends on the clinic or hospital, which can conduct laboratory tests on its own or send blood for analysis to another laboratory.
What to consider?
It is recommended to do this at the same time each time, under the guidance of the same doctor and in the same laboratory. If the analysis is carried out in another laboratory, then the results will be difficult to compare, because each medical institution has its own methods and protocols, uses different reagents and equipment, and has its own scale for interpreting and evaluating the results. World practice shows that women over fifty are at serious risk for thyroid diseases, so every woman who has crossed this threshold and is interested in maintaining her health should donate blood for TSH once a year for prevention and monitoring of processes. Those women who are not deprived of reproductive functions can take the test on any day of the menstrual cycle.
Norms for TSH levels are calculated for each gender separately, and are also divided into groups depending on age. The results obtained can only be assessed and correctly deciphered by a qualified specialist.
How much does such an analysis cost?
The cost of a blood test for the hormone in question in private research laboratories and medical centers can range from seven hundred to eight hundred rubles, if we are talking about Moscow. In St. Petersburg and other regions, the cost will be slightly lower and range from four hundred to six hundred rubles. It usually takes only one business day to prepare the results.
It should be remembered that it is simply impossible to accurately determine the causes of thyroid dysfunction using only a TSH test. Most likely, this will require additional studies to determine the hormones triiodothyronine and thyroxine.
It so happens that representatives of the fairer sex are more sensitive to changes in thyroid hormones, and therefore they are diagnosed with hypothyroidism much more often than men. One of the most common causes of this disease is pregnancy, which occurs with various complications. As for representatives of the stronger sex, this deviation very often occurs completely asymptomatically, so it makes sense to take blood tests for the TSH hormone for prevention purposes.
Interpretation of blood test parameters for TSH
The correct interpretation of a blood test for thyroid hormones is performed in a medical institution. It is based on a comparison of the study results with normal indicators, which are established for different groups of patients depending on their gender and age, as well as the laboratory test method used. This takes into account how intensively the thyroid gland processes blood into hormones. The norm is compared with the analysis indicators and a qualified conclusion or prognosis is made regarding the course of the disease. On the form of the established sample, where the data obtained by the laboratory method are entered, the standard values are already entered, and the patient himself can see whether his result fits within the framework allocated by the standard or goes beyond it in one direction or another.
But independent comparison of indicators and unqualified interpretation of a blood test for thyroid hormones should not replace consultation with a specialist. Therefore, only an endocrinologist can evaluate and draw conclusions based on the results of the analysis. Moreover, deviations from the norm can be either in the direction of increasing or decreasing hormone levels. Any deviations have their own nature, which is unknown to a non-specialist. A certain combination of deviations may indicate different diseases and this can only be seen by someone who has extensive practical experience, much less makes a diagnosis.
We have already found out what tests are done for the thyroid gland. Now let's look at the decryption. Standard (reference) indicators are compared with those obtained as a result of the analysis. The TSH norms for age groups are as follows:
- for newly born children - 1.1-17 mU/l;
- for ages up to 2.5 months - 0.6-10 mU/l;
- 2.5-14 months - 0.4-7 mU/l;
- 14 months - 5 years - 0.4-6 mU/l;
- 5-14 years - 0.4-5 mU/l;
- children over 14 years old and adults - 0.4-4 mU/l.
It is noticeable that with increasing age, the normal TSH level becomes lower and this trend continues throughout life. For this reason, an endocrinologist should do the decoding for each age, this is especially important in old age. The decoding is made taking into account the individual characteristics of a person - his gender, age, general health, body weight, diseases he suffered in the past, taking medications or vitamin preparations, and so on.
Appointment for analysis
Indications for testing TSH levels
The analysis can be prescribed to patients in various cases. Most often, a doctor’s prescription is made for the development of diseases such as:
- Depression
- Decreased libido
- Impotence
- Alopecia, which is characterized by hair loss for no apparent reason
- Myopathies, etc.
Very often, a TSH test is prescribed for a variety of diseases, since it can be used to assess the condition of the thyroid gland. Indications for the procedure are cardiac arrhythmia, female infertility, enlarged thyroid gland, etc. In some cases, patients' body temperature drops below 35 degrees and lasts for several days. To establish the causes of the pathology, the patient is prescribed a TSH test.
The analysis can be prescribed not only to make a diagnosis, but also to monitor the treatment of pathological processes.
If a patient has symptoms of hyperthyroidism, which is characterized by an excess of thyroid hormones and iodine, then he needs to be tested for TSH. It is also prescribed for iodine and hormone deficiency - hypothyroidism.
The analysis can be prescribed not only to adult patients, but also to young children. It is prescribed to newborn children if thyroid dysfunction is diagnosed. There is often a need for it if children are diagnosed with delayed sexual and mental development. There are many diseases for which patients are prescribed a thyroid-stimulating hormone test. In most cases, they are associated with the functioning of the thyroid gland.
Preparation and procedure
Proper preparation means reliable research results
To ensure the reliability of the results, the patient must correctly go through the preparatory stage:
- First of all, he must stop smoking.
- A person is strictly prohibited from drinking alcohol before the procedure.
- Even if you are an athlete, you need to avoid excessive physical activity.
- In order to ensure correct results of the thyroid-stimulating hormone test, you need to stop eating fatty and spicy foods a few days before.
- The patient should try not to be exposed to nervous shocks and stressful situations. This is explained by the fact that a person’s psycho-emotional state also affects the results.
- If patients are taking hormonal medications or medications that suppress hormones, they must be discontinued 14 days before the test. Stopping medications should only be done if advised by the attending physician. Otherwise, medication should be continued.
- Before taking the test, the patient must take vitamin complexes and medications that contain iodine as carefully as possible. This is explained by the influence of iodine on the performance of the thyroid gland, which leads to distortion of the analysis results.
- Before the test itself, the patient is strictly prohibited from eating breakfast. It is best to drink still water and go for analysis. In some cases, you can have breakfast with light foods.
- After eating, the test should be taken no earlier than 3 hours later.
Today you can take a blood test for thyroid-stimulating hormone both in a budget clinic and in a paid hospital. The maximum concentration of TSH is observed in the morning, so it is necessary to take a blood test during this period.
Proper preparation for a TSH test can not only ensure the reliability of the results, but also help the doctor make the correct diagnosis, which is very important for absolutely all patients.
Analysis transcript
TSH norm and reasons for deviation
Many patients are interested in the results of the analysis, but they cannot understand what certain numbers mean. Each age category of patients has its own TSH norm:
- In newborns, thyroid-stimulating hormone should be 0.6-10 units. per liter of blood.
- If the child’s age is from 2.5 months to 2 years, then he should have a TSH of 4-7 units.
- Children aged 2-5 years normally have 4-6 units of thyroid-stimulating hormone,
- Children over 14 years of age and adult patients – 0.4-4 units.
All these indicators are the norm. If, as a result of the tests, you see different numbers, this indicates the presence of disorders that need to be treated.
When taking a test for thyroid-stimulating hormone, deviations can be both smaller and larger. This indicates a decrease or increase in the level of TSH in the human body. If the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone is elevated, this may indicate that the patient has had his gallbladder removed. With pituitary tumors in humans, exactly the same clinical picture is observed. An increase in TSH may indicate a pathology of the thyroid gland, which is characterized by a decrease in the amount of hormones produced.
Useful video - TSH blood test.
Read: How to donate blood for hCG: preparation, procedure and norm by week of pregnancy
If the pituitary gland is insensitive to thyroid hormones at the genetic level, then this will be reflected in the form of an increase in TSH levels. This pathological condition can also occur when iodine-containing foods are consumed in large quantities. A decrease in TSH levels can be observed in females during pregnancy with the development of gestosis. The same clinical picture is observed with insufficient adrenal function, acute and subacute Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
An elevated TSH level indicates low activity of the thyroid gland. The cause of this pathological condition in most cases is somatic diseases. In case of mental disorders of the patient, a similar clinical picture may be observed. High numbers show the results of the analysis if the patient has a pituitary adenoma, which is a benign tumor. If a person is poisoned by lead, he or she develops an intoxication syndrome, which is reflected in the test results.
When TSH levels increase, it is not always possible to judge the presence of a serious disease.
Very often, an increase in the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone is observed in pregnant women. If the patient takes certain medications, this may lead to an increase in TSH levels. After undergoing surgery on the thyroid gland, such deviations can also be observed. An increase or decrease in TSH levels does not always indicate pathological processes in a patient. Very often, such analysis results can be a consequence of a person’s lifestyle.
TSH is elevated
If hormonal levels are elevated, this may indicate the presence of certain diseases, namely:
- somatic and mental disorders;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- thyroiditis;
- hormonal immunity to the thyroid group of hormones;
- hypothyroidism;
- anomalies in the pituitary gland - adenoma, tumor and others;
- syndrome of unregulated secretion of thyrotropins;
- ectopic secretion due to tumors in the lungs or mammary glands;
- proeclampsia is a complicated form of gestosis during pregnancy;
- inflammatory pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- great physical activity;
- lack of iodine in the body;
- bad genetics and others.
The fact that the level of TSH concentration is increased is indicated by such signs as:
- dryness and dehydration of the skin;
- severe hair loss;
- intolerance to cold;
- menstrual irregularities;
- high fatigue.
TSH is reduced
If a blood test reveals low TSH, this may indicate the following problems:
- The presence of stressful conditions and mental disorders.
- The development of thyrotoxicosis, that is, poisoning with thyroid hormones of various etiologies (this happens due to illiterate use of hormonal drugs, against the background of toxic goiter, autoimmune thyroiditis, and so on).
- In case of injury or necrosis of the pituitary gland (after childbirth, including).
- A reduced level of TSH is also observed as a result of strict diets and fasting, and also as a result of the use of certain medications (we are talking about anabolic steroids, corticosteroids, cytostatics, etc.).
It’s now clear how to properly take a TSH test.
TSH is low
Reduced hormone levels indicate the presence of the following problems:
- severe disorders - mental and stress;
- poisoning by the thyroid group of hormones - thyrotoxicosis, can be caused by the fact that hormonal drugs were taken incorrectly, or the development of Graves' disease;
- necrosis of the pituitary gland or severe trauma.
Also, low TSH is observed in those who are fasting or on extremely strict diets, or taking large quantities of steroid drugs, corticosteroids, and cytostatics. An even lower level of TSH may be associated with rare pathologies - Itsenko, Grevs, Plamer syndromes, as well as encephalitis and meningococcal infection.
If you enter the “lower gray zone”, where the hormone level is 0.1-0.4 mU/l, an additional study is usually carried out on the concentration of the hormones T3 and T4 in the blood - thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
If you fall into the “upper gray zone,” which corresponds to elevated levels in the range of 5-10 mU/l, it is proposed to do a TRH test, which uses thyrotropin-releasing hormone.
During pregnancy, TSH levels are tested several times, because this must be constantly monitored so that the health of neither the expectant mother nor her unborn child is harmed. You should be especially careful during the first trimester of pregnancy, because at this time the formation of all vital organs and systems in a woman’s body takes place.
TSH – hormone value
The role and functions of thyroid-stimulating hormone
TSH is an abbreviation for thyroid-stimulating hormone, which is produced by the pituitary gland. With its help, the thyroid gland is stimulated to secrete thyroid hormones.
The formation of thyroid-stimulating hormone is carried out by the pituitary gland. This is a gland that is located in the brain. TSH affects the thyroid gland and causes it to produce the hormones T4 and T3.
With the help of these hormones, the full functionality of systems such as:
- Sexual
- Cardiovascular
- Gastrointestinal tract
With the normal functioning of these hormones, a complete metabolism in the human body is ensured. Also, these hormones are involved in various mental processes.
When the hormones T3 and T4 reach a certain limit, TSH production is suppressed.
If the production of these hormones decreases, this leads to an increase in the concentration of thyrotropin. According to this scheme, the hormones T3 and T4 and TSH interconnectedly regulate each other. That is why patients very often, along with a TSH analysis, are prescribed an analysis to determine the amount of T3 and T4 hormones. Thanks to the results obtained, endocrinologists and therapists have the opportunity to learn about the patient’s hormonal background and identify certain diseases.
Indications for testing
The doctor prescribes an examination for TSH, a sensitive thyroid-stimulating hormone, the norm of which in women varies widely, if the following pathologies are present or suspected:
- Latent hypothyroidism.
- Toxic goiter.
- Amenorrhea.
- Endemic goiter.
- Thyrotoxicosis.
- Formation of nodules in the thyroid gland.
- Diffuse goiter.
- Increased levels of prolactin in the blood.
- Frequent changes in body temperature.
- Neoplasms of the thyroid gland.
- Disorders of certain muscle groups.
Diffuse toxic goiter is one of the main indications for analysis of thyroid-stimulating hormone levels
Interesting: In addition, a TSH test can be prescribed: when planning pregnancy, during pregnancy, in the postpartum and postoperative periods, for the purpose of dynamic monitoring, as well as when correcting body weight.
Why does thyroid-stimulating hormone increase?
High TSH levels in children and adults may indicate a number of diseases:
- hypothyroidism is a long-term lack of thyroid hormones. The last stage of the pathology in children is accompanied by cretinism, and in adults – by myxedema (severe swelling of the mucous membranes). The high prevalence (20 cases per 1000 people) is often accompanied by late detection. The situation is explained by the low specificity of symptoms at an early stage. At the same time, the level of TSH in hypothyroidism increases sharply, and the values of T3 and T4 decrease in proportion to the severity of the pathology;
- Pituitary adenoma is a tumor of glandular tissue of unknown etiology. Pathology accounts for one sixth of all cases of brain tumors. The danger is a long asymptomatic course. Therefore, often at the detection stage, drug therapy does not give the required effect, surgical removal is required;
- autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto's thyroiditis) is a chronic inflammation of the thyroid tissue. The more pronounced the inflammation, the greater the deficiency of T3 and T4. The prevalence among children does not exceed 1.5%, and among adults – 11%. Women get sick 4-8 times more often than men. Adequate and timely medical care leads to a favorable prognosis;
- with the syndrome of uncontrolled secretion of thyrotropin, there is a lack of inhibitory mechanisms for its synthesis by the pituitary gland. Moreover, its increase does not depend on the content of thyroid hormones in the blood;
- oncology of the thyroid or breast gland, as well as lungs;
- various mental disorders;
- primary adrenal insufficiency;
- juvenile hypothyroidism;
- thyrotropinomas;
- lead intoxication;
- severe somatic pathologies.
Main article: Causes and consequences of increased thyrotropin in blood test results
The influence of TSH levels on a woman’s reproductive system
During pregnancy, it is necessary to monitor TSH levels
What is thyroid-stimulating hormone responsible for in women and what are the consequences of disturbances in its synthesis in the pituitary gland? The properties of TSH are such that it affects the production of sex hormones that ensure the development of eggs. Gonadotropic hormones regulate the onset and course of menstruation and determine the duration of the cycle.
There are two types of changes in the amount of TSH in a woman’s body:
- Insufficient concentration of pituitary thyroid-stimulating hormone. In this case, the development of secondary hypothyroidism is typical. With a lack of T4 and T3, the body experiences a lack of TESG (testosterone estrogen binding globulin), which depends on them.
At the same time, the concentration of testosterone increases, and this is the male sex hormone. As a result, the less active estriol is activated instead of estradiol. The following happens:
- the menstrual cycle lengthens;
- the follicle in the ovary grows more slowly;
- the endometrium in the uterus does not develop enough;
- menstruation is very weak;
- discharge is either scanty or abundant;
- possible absence of menstruation (amenorrhea), as a consequence of the cessation of ovulation;
- uterine bleeding appears without connection with the menstrual cycle;
- development of functional infertility.
TSH affects the menstrual cycle indirectly through other hormones.
- Excessive concentration of TSH in cancer of the pituitary gland. An increase in the production of thyrotropin leads to phenomena characteristic of hyperthyroidism:
- the interval between menstruation becomes short;
- menstruation is irregular;
- gonadotropic hormones are synthesized in insufficient quantities;
- cessation of menstruation (amenorrhea);
- menstrual flow is very scanty and painful;
- During menstruation, pathological general weakness is observed;
- Infertility is diagnosed due to hormonal deficiency.
Both deficiency and excess of TSH in a woman’s body leads to persistent menstrual irregularities and infertility.
The influence of TSH on the sexual development of girls
Photo. These girls have normal TSH
Thyroid-stimulating hormone tsh is normal in women, due to age and physiological characteristics. A gradual increase in concentration is observed after reproductive functions fade away.
With the development of the genital organs in a girl, disturbances in the hypothalamic-pituitary system can lead to pathological abnormalities. Both increased and decreased concentrations of TSH in the body are dangerous.
The thyroid-stimulating hormone norm for women after 50 is higher than for young women, which is explained by the decline of sexual functions.
- Low TSH concentration . This leads to testosterone being activated, so the girl’s body does not produce enough follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). The synthesis of such an important hormone as luteinizing hormone (LH) also suffers. All this leads to the following consequences:
- there is a developmental lag compared to peers;
- menstruation appears later than physiologically determined periods;
- there is no sexual attraction to the opposite sex;
- underdeveloped mammary glands;
- poorly developed labia and clitoris;
- the figure resembles that of a boy.
The video in this article demonstrates the characteristic appearance of a girl with TSH deficiency. A delay in the development of sexual characteristics can lead to problems with socialization.
- High TSH concentration . When the concentration of thyretropin in a girl's blood is increased, this can accelerate her sexual development. In this case, premature physiological maturation occurs, with significant deviations from the norm. This is due to the fact that a high concentration of TSH stimulates the production of estrogen, luteinizing and follicle-stimulating. As a result, this happens:
- breasts increase in size from the age of 8;
- early appearance of pubic hair;
- The first menstruation appears much earlier than among peers.
It is important to regularly examine girls for TSH levels in the blood in order to prescribe treatment and prevent pathological disorders in sexual development.
Causes of low thyrotropin levels
A smaller deviation from the norm is observed in diffuse toxic goiter, which is an autoimmune pathology. The condition is characterized by excessive secretion of thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism), which accumulate and exhibit toxic effects. According to the “reverse regulation” rule, in this case the TSH level in hyperthyroidism drops significantly.
The prognosis for diffuse toxic goiter is favorable in case of timely diagnosis and adequate treatment. Patients should avoid excessive exposure to sunlight, stress, fatigue, excessive physical activity, as well as taking iodine-containing medications and foods.
A similar decrease in the rate is characteristic of Plummer's disease - a benign tumor of the thyroid gland. Women are more susceptible to the disease; men get sick 4-6 times less often. The reason is a genetic mutation that leads to long-term, consistently high synthesis of T3 and T4. The prognosis for the outcome is often favorable, even spontaneous recovery is possible. However, there are isolated cases of pathology degenerating into malignant.
Critical exhaustion of the body (cachexia) also leads to inhibition of the secretion of thyrotropin. At the same time, the person suddenly loses weight. As a rule, cachexia is a secondary disease of the underlying pathology. In this case, treatment comes down to identifying and eliminating the root cause, and then symptomatic therapy to restore the human body.
A low TSH level with a normal free T4 value is observed in elderly patients and pregnant women, in patients with postpartum pituitary necrosis, thyrotoxic adenoma, pituitary injuries, latent thyrotoxicosis, as well as in self-medication of T4.
When is research required?
A sharp change in well-being is a reason to take hormone tests
For what problems is analysis prescribed:
- if a deviation in the concentration of thyroid hormones is detected;
- if you suspect a thyroid disease;
- when a married couple cannot conceive a child, the test is prescribed for both the man and the woman;
- there is a problem in the sexual sphere - impotence, frigidity;
- with long-term use of hormonal drugs of any spectrum of action;
- menstrual irregularities in women;
- baldness;
- identification of depression;
- in children with mental or physical developmental delays.
How to prepare for testing
First, you need to know the common mistakes of patients preparing for such a procedure. Many girls are worried - how important is it to get tested on a certain day of the menstrual cycle, and on which day? In this case, there is absolutely no need to try to check your indicators depending on a specific day of the monthly cycle, because all reference norms, without exception, for both males and females are the same. There are two exceptions:
- girls in a state of pregnancy, because their content is increased;
- in older people, on the contrary, thyroid hormones are reduced.
To properly test thyroid hormones, you need to carefully prepare so that the results are not distorted:
- No later than a month before the date of the proposed testing, the use of drugs for hormone replacement therapy (TSH, T4, T3) is canceled, but if, on the advice of the treating endocrinologist, it is not possible to cancel, then this item should be skipped.
- At least 3 days before the date of the thyroid hormone test, taking iodine-containing medications, minerals and special foods is also canceled.
- The day before the test, you cannot drink alcohol or smoke, and you cannot attend classes in the gym.
- Before the procedure itself, the patient should be at rest for at least half an hour and not worry about anything. To check correctly, you need to take the test on an empty stomach; you can only drink water in the morning. Studies using X-ray contrast agents should be carried out after the test.
- It is best to take it in the morning between 8 and 10 o'clock or before lunch.
- In order to get everything right, you can eat no earlier than 12 hours before the scheduled procedure.
- If the patient is taking aspirin, corticosteroids, combined oral contraceptives, or strong sedatives, this must be reported to the laboratory. It is advisable to stop taking this type of medication on the eve of testing, but if it is not possible to do so, be sure to inform your doctor.
Treatment
Treatment is aimed at normalizing the concentration of TSH in the blood, and this requires regular testing to monitor the indicators. Therapy is carried out until the test results show normality.
Note that in some cases, medications may not produce positive dynamics, therefore, the TSH level remains the same. In this case, the doctor is obliged to change the prescribed therapy.
It is better to carry out treatment at the initial stage when the first symptoms appear, this will avoid further surgical intervention.
Additional studies if test results deviate from the norm
For any deviations in the level of thyroid hormones from the norm, an additional examination is prescribed, which, depending on the indications, may include:
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland is the most informative method that allows you to determine the location, size, volume and weight of the gland, its structure, and the symmetry of the lobes; with its help, the blood supply is calculated, the structure and echogenicity of tissues are determined, and the presence of focal or diffuse formations (nodules, cysts or calcifications) is determined.
- An X-ray examination of the neck and chest organs will make it possible to confirm or exclude thyroid cancer and the presence of metastases to the lungs.
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the thyroid gland are methods that allow one to obtain a volumetric layer-by-layer image of the organ, as well as perform a targeted biopsy of the nodes.
- A puncture biopsy of the thyroid gland is the removal of a microscopic section of tissue for analysis followed by microscopic examination.
- Scintigraphy is a study using radioactive isotopes. The method makes it possible to determine the functional activity of tissues.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article: