Homocysteine is an amino acid synthesized in the body from methionine, which we get from food. Homocysteine levels gradually increase with age, with slightly higher levels in men than in women. In this article, you will learn how homocysteine levels can affect your health, why homocysteine can be toxic and promote inflammation. You will also find out what ways you can normalize your homocysteine levels.
The article is based on the findings of 107 scientific studies
The article quotes the authors:
- International Biotechnology Center, Moscow State University. M.V. Lomonosov, Russia
- Department of Laboratory Medicine, Harbin Medical University, China
- Department of Internal Medicine, University of Brescia, Italy
- Department of Clinical Medicine, Trinity College, Ireland
- Department of Psychiatry, University of Kuopio, Finland
- Department of Biochemistry, Manipal University, India
- and other authors.
Please note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, 3, etc.) are clickable links to peer-reviewed scientific studies. You can follow these links and read the original source of information for the article.
What is homocysteine
Homocysteine is a sulfur-containing amino acid that is synthesized from methionine through a multistep metabolism process. Homocysteine can be converted back to methionine with the help of B vitamins . Homocysteine also acts as an allosteric antagonist at dopamine D2 receptors. It has even been suggested that homocysteine may have played an important role in the emergence of life on earth.
Homocysteine levels are generally higher in men than in women and rise steadily with age. Average homocysteine levels in adults range from 10-12 µmol/L, and values of 20 µmol/L and higher are observed in older people or those with vitamin B12 deficiency.
Homocysteine values above 15 µmol/L indicate hyperhomocysteinemia, which is a significant risk for the development of thrombosis , neuropsychiatric diseases , bone fractures , and is also considered a marker for an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and kidney disease. Approximately 70% of homocysteine in the kidneys is converted to methionine, so kidney disease and a decrease in their effective functioning contribute to an increase in homocysteine levels and an increase in the risk of developing cardiovascular pathologies. Homocysteine affects the tissue of blood vessels so that they become loose, local inflammation occurs due to the action of immune cells, and cholesterol and calcium are deposited on this surface, which contributes to the formation of plaques.
HOMOCYSTEINE – PROMOTES THE DEVELOPMENT OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
An increase in homocysteine levels by 5 µmol/l leads to an increase in the risk of vascular damage by atherosclerotic plaques in women by 80%, in men – by 60%.
Homocysteine is able to stimulate inflammation in blood vessels through an increase in the production of C-reactive protein, which is mediated through the NMDAr-ROS-ERK1/2/p38-NF-kB signaling pathway. []
Additional examinations
There are not many auxiliary activities:
- Ultrasound of the digestive tract.
- General blood test and biochemistry.
- Consultation with a hematologist and other specialized specialists. With an oral interview and anamnesis.
- Chest X-ray.
- Bone marrow puncture.
- MRI, CT with contrast enhancement. Gadolinium and iodine, respectively.
Also, if necessary, other methods are available.
Homocysteine in the blood is an essential amino acid, a building material for the body and its cellular structures. All deviations need to be checked more carefully. To promptly detect pathological processes. Treatment is prescribed according to need.
Source
Synonyms:
Homocysteine
Homocysteine is the most important sulfur-containing amino acid that is part of the body's cells. This component is involved in general metabolism, ensures normal blood flow and the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
A blood test for homocysteine allows you to identify the risk of developing pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, and assess the degree of absorption of vitamins and microelements. This study is also used in the diagnosis of homocysteinuria.
Elevated homocysteine – toxic and inflammatory
Attachment of homocysteine to proteins
In people with high levels of homocysteine, this amino acid can attach to proteins, leading to the appearance of modified proteins - homocysteine thiolactone (thiolactone) and N-homocysteinylated protein .
Homocysteine thiolactone can attack various types of proteins, including blood albumin, hemoglobin, immunoglobulins (antibodies), LDL, HDL, transferrin, antitrypsin, fibrinogen. []
Homocysteine thiolactone can inhibit Na+/K+- ATPase (an enzyme responsible for the conduction of nerve signals) in the hippocampus, cerebral cortex and other brain cells (experiments in rats), which can interfere with the normal functioning of neurons and impair brain health. []
These modified proteins can activate genes that are involved in the development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease . []
ATTACHMENT OF HOMOCYSTEINE TO PROTEINS
The immune system may also not recognize these modified proteins and begin to attack them, resulting in autoimmune diseases and inflammation. In addition, the introduction of homocysteine into blood vessels can lead to damage to the vessel walls. []
Homocysteine increases oxidative stress
The chemical groups in homocysteine can affect the overall electrical potential of proteins and cells, which increases oxidative stress in those cells. This can lead to an increase in cellular toxicity and loss of proteins of their normal functionality (protein misfolding), which is associated with the development of neurodegenerative diseases (Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and other prion diseases , Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, amyloidosis , as well as a large number of other diseases, including type 2 diabetes and cataracts ). []
DISEASES WITH IMPROPERLY DISTRIBUTED PROTEINS (PROTEIN MISFOLDING)
If protein misfolding disease occurs, proteins can become sticky and aggregate through multiple steps, eventually becoming fibers, and these nonfunctional protein aggregates can be toxic. Abnormal protein diseases affect multiple organs and can be identified histologically by the presence of specific protein deposits.
Increasing values
- Diabetes;
- Hypothyroidism (underfunction of the thyroid gland);
- Psoriasis (non-infectious dermatosis);
- Kidney dysfunction;
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, due to which vitamins are poorly absorbed and their deficiency occurs;
- Gene mutation, as a result of which the body produces defective enzymes;
- Homocystinuria.
These pathologies require timely and effective treatment - only in this case can homocysteine levels return to normal levels.
On a note:
if homocysteinuria is suspected, an additional examination is performed - a biopsy of liver tissue and skin to determine the enzyme cystathionine beta synthase. Its absence in tissue cells confirms the preliminary diagnosis. Genetic tests may also be prescribed to clarify the diagnosis of homocysteinuria.
Homocysteine production and breakdown
Methionine is a methyl donor in the body, while homocysteine is a methyl acceptor. When methionine donates a methyl group (demethylation), it becomes homocysteine. [] When homocysteine takes on a methyl group, it becomes methionine. Homocysteine can also be irreversibly converted to glutathione and cysteine.
Foods high in methionine include egg whites, seafood, sesame seeds, Brazil nuts, chicken, tuna, wheat germ, meat. []
FOOD RICH IN METHIONINE
Homocysteine can be converted into less toxic and more beneficial amino acids through 2 biochemical pathways:
- Remethylation Vitamin B12 is an important co-factor in this process, as is the MTHFR enzyme. [, ]
- Transsulfuration . Vitamin B6 is an important cofactor in this process. [, ]
Blood test for homocysteine
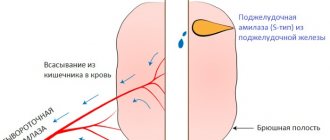
Approximately 80-90% of homocysteine in the blood is bound to protein. About 70% of homocysteine is converted to methionine in the kidneys. Less than 1% of homocysteine is present in free form in the blood. []
Measuring total homocysteine in blood is technologically challenging because blood cells release homocysteine even after the blood has been drawn and is in a tube. [, ] For this reason, it is very important for the laboratory to extract the blood cells from the collected sample by centrifugation no later than 30 minutes after drawing the blood. After this, the blood cells are stabilized for 4 days at room temperature.
Because of the variability of laboratory methods for tracking homocysteine levels over time, it is important to use the same laboratory to ensure consistency of tests.
Eating more protein can significantly increase homocysteine levels. Thus, when taking a homocysteine test, it is important not to eat for 8-14 hours before the test (you can drink water). []
When is the test ordered?
It must also be said that the amino acid performs some functions outside the body. A homocysteine test can provide a lot of information.
In what cases is such a study prescribed:
- Tendency to thrombosis. In this process, the substance in question plays an important role. Blood clots can break off and block the pulmonary artery or can cause vascular occlusion in the lower extremities.
In the first case, death cannot be avoided. And fast.
In the second situation, gangrene occurs, tissue death at the local level.
The analysis allows you to quickly and accurately diagnose the problem. Long before the development of direct thrombosis itself.
- Homocystinuria. Hematological disorder. Typically congenital. In this condition, a triad of symptoms is observed: arthralgia due to damage to the joints, musculoskeletal system, dysfunction of the central nervous system and cardiovascular disorders.
This problem is quite rare and is genetically determined. But it carries enormous danger.
Attention:
If treatment is not started, the patient is almost guaranteed to die within a few years.
- Impaired cognitive functions in elderly patients. Homocysteine testing is required for classic dementia, senile and other forms of dementia. The disorders are accompanied by a sharp jump in amino acid levels. He is consistently high.
Restoring a normal state allows you to reduce the intensity of the symptoms of the pathological process. Although the underlying disease needs to be treated.
- Lack of vitamins B. 9, 12. Provoke megaloblastic anemia. Recovery is carried out by correcting the main diagnosis. Without this, it will not be possible to change the concentration of homocysteine. The issue of therapy falls on the shoulders of the hematologist.
- A blood test for homocysteine is required for diabetes mellitus to monitor the condition of the body. This diagnosis is generally associated with unstable levels of the amino acid in question.
As a rule, the parallel course of diabetes and a disorder in which homocysteine increases increases the risk of complications. Like gangrene, diabetic foot, retinal angiopathy with the growth of defective vessels in the fundus.
- Alzheimer's disease. A type of dementia occurs mainly in women. Although there are exceptions. An urgent analysis of homocysteine concentration is required, as this can indirectly diagnose Alzheimer's disease. Distinguish it from other forms of dementia. As part of regular screening, it is possible to detect the dynamics of the pathological process.
- Pregnancy. During gestation, the amino acid level is unstable. It rises and falls. High concentrations of homocysteine in women are associated with fetal malformations. Including Down syndrome and other rare anomalies.
It is necessary to carry out such screening regularly. At least 1-2 times per trimester. To detect deviation in time. Of course, high rates do not guarantee problems in the fetus, but it’s not worth the risk.
A blood test for homocysteine is a kind of universal marker of abnormalities in a patient: in this way, congenital diseases, disorders of the central nervous system, and heart are detected.
Normal Homocysteine Levels
Analyzes and various studies over the past 20 years have shown that the average normal level of homocysteine is in the range of 9-10 µmol/l . []
Based on the same studies, it is believed that homocysteine levels > 9 µmol/L indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular disease , and values above 15 µmol/L indicate very serious risks for the heart. [, ]
It is worth noting that there are reference values in each laboratory, where homocysteine levels may be higher than normal healthy levels. If the test result falls within the reference range, but more than 9-10 µmol/l, it does not indicate a healthy state of the body.
Norm
The level of homocysteine differs depending on gender and age; as the latter increases, the concentration of the amino acid also increases. In men, the level of the substance in the blood will always be higher, and in pregnant women a slight decrease is allowed depending on the trimester. Indication standards:
| Normal, up to µmol/l | Male | Female |
| Children | 5 | 5 |
| Teenagers (puberty) | 7 | 6 |
| Adults | 6,2-15 | 5-12 |
Diseases associated with high homocysteine levels
Homocysteine increases oxidative stress, promotes inflammation, and is toxic to brain neurons. In addition, homocysteine promotes the deposition of abnormal proteins. Therefore, elevated homocysteine levels are associated with many diseases.
Atherosclerosis
High levels of homocysteine (hyperhomocysteinemia) have been recognized since the early 90s as a risk factor for diseases caused by damage to blood vessels. []
High levels of homocysteine have been associated with an increased risk of plaque formation in the arteries and the development of coronary heart disease . [, , , ] Even moderately elevated homocysteine levels increase the risk of cardiac, cerebrovascular and peripheral arterial ischemia. []
STAGES OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS DEVELOPMENT
In fasting tests, the level of homocysteine in the blood of patients with coronary heart disease was significantly higher than that of healthy people. []
People with homozygous mutations in the MTHFR gene can develop very high levels of homocysteine. People with these mutations have a very high risk of early development of cardiovascular disease. []
One study found that homocysteine levels were a better predictor of cardiovascular disease than conventional risk factors such as smoking, cholesterol levels or blood pressure. []
Stroke
During a stroke, additional neuronal damage can occur when excitatory amino acids such as glutamate and aspartate (related compounds) activate the NMDA receptor, causing neurons to become overexcited. Thus, high homocysteine levels may increase neuronal damage in stroke . []
Insulin resistance
Elevated homocysteine levels are a marker of insulin resistance due to the effects of insulin on homocysteine metabolism and renal clearance. []
Diabetic retinopathy
The higher the blood homocysteine values in diabetic patients, the worse the condition of retinal degeneration due to high blood sugar levels. []
Free radical damage
High levels of homocysteine can cause an increase in the rate of methionine synthesis and thus a decrease in cysteine levels. This can lead to an overall lack of cysteine, which is essential for the production of glutathione (the most powerful antioxidant). [] This process can lead to increased free radical damage, perhaps the underlying cause of the atherosclerosis seen in hyperhomocysteinemia.
Brain damage
Homocysteine is neurotoxic because neurons grown in a solution with homocysteine die. []
Homocysteine acts as an agonist for glutamate receptors, including NMDA receptors, so it can kill neuronal cells by activating the MAPK and P38 MAPK pathways. Homocysteine also kills other cells in the brain, such as glial cells (a type of immune system cell in the brain). []
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN INCREASED HOMOCYSTEINE AND PARKINSON'S DISEASE (www.omicsonline.org)
In the brain, homocysteine causes mitochondrial damage and suppresses energy production (ATP), as well as promoting the release of cytochrome C and reactive oxygen species. []
Homocysteine can cause damage to the blood-brain barrier in the brain through:
- increase in MMP-9 []
- acting as an excitatory neurotransmitter at NMDA receptors, which may increase oxidative stress in the brain [, ]
Elevated homocysteine and depression
One study of 924 men found that those with homocysteine levels in the top third of reference values were twice as likely to be diagnosed with depression as men with homocysteine levels in the bottom third. []
Another study found that people with high homocysteine levels (>12 µmol/L) tend to have lower levels of important substances that are necessary for the production of neurotransmitters associated with improved mood. [] Indeed, a recent study found that high homocysteine levels are associated with low serotonin levels .
Some scientists believe that postpartum depression is caused by temporarily high levels of homocysteine . []
Supplementing with vitamins B2, B6, B12, and folic acid has been shown to effectively lower homocysteine levels and help reduce depressive symptoms [].
Elevated homocysteine and Alzheimer's disease
High homocysteine levels have been linked to cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. [, ].
An Italian study found that older adults with elevated blood levels of homocysteine showed a higher risk of developing dementia . They also performed poorly on tests of mental functioning. []
Another study found that older adults with homocysteine levels greater than 14 µmol/L were almost 2 times more likely to develop Alzheimer's disease . []
For example, scientists found that incubating neuronal cells with homocysteine for 5 days increased the production of reactive oxygen species by 4.4 times. This caused dramatic toxicity to neurons. []
Elevated homocysteine and Parkinson's disease
High homocysteine levels can cause Parkinson's disease. This conclusion was made in a study where homocysteine was injected into the brains of rats, which led to the development of Parkinson's disease. []
It is worth considering that high doses of Levodopa (L-DOPA, L-Dopa), which increases dopamine levels, and the main method of treating Parkinson's disease, promote an increase in homocysteine. []
SOME EFFECTS AND CONSEQUENCES OF INCREASED HOMOCYSTEINE LEVELS (www.fxmedicine.com.au)
Homocysteine for autoimmune diseases
Elevated homocysteine levels in Hashimoto's thyroiditis (autoimmune thyroiditis)
In patients with autoimmune thyroiditis, serum homocysteine is elevated. [] When receiving Levothyroxine (synthetic T4), serum homocysteine levels decrease. []
Pernicious anemia often occurs in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis, suggesting that vitamin B12 deficiency may lead to elevated homocysteine and increased susceptibility to thyroid disease. []
Improving thyroid function can help lower homocysteine , especially when getting adequate levels of folic acid . []
Elevated homocysteine in rheumatoid arthritis
Homocysteine levels are elevated in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. This increase is associated with low levels of folate, vitamin B12, complement components C3 and C4, and high markers of inflammation , including cystatin C and C-reactive protein.[]
Elevated homocysteine levels in psoriasis
People with psoriasis, a common autoimmune skin disease, tend to have high blood levels of homocysteine and low levels of folic acid . []
One study found that “homocysteine levels may be considered an independent risk factor for patients with psoriasis.” [] It is likely that elevated homocysteine increases the risk of heart attack in patients with psoriasis, although there may be other risk factors. []
Studies have shown that folate are lower in patients with psoriasis than in healthy people (, , , ) and blood homocysteine levels are inversely associated with folate levels in people with psoriasis. (, ) An increase in homocysteine levels may be caused by a decrease in folate levels.
One proposed mechanism for decreased folate levels in psoriasis may be related to inflammatory changes in the intestinal mucosa, which causes decreased absorption of dietary folate. () Another rational explanation may be due to the rapid turnover of skin cells in psoriasis with increased consumption of folic acid, which reduces its level in the blood. ()
Obesity
A connection has been established between psoriasis and obesity. (, ) A number of studies have demonstrated that homocysteine levels are significantly increased in obese patients compared to normal weight people. (, ) Thus, obesity can also be recognized as one of the factors between elevated homocysteine levels and psoriasis.
Elevated homocysteine and systemic lupus erythematosus
Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have elevated plasma homocysteine levels compared to healthy individuals. [] Moreover, this level of homocysteine is directly related to the severity of the disease. []
Elevated homocysteine and type 1 diabetes
Homocysteine is elevated in people with type 1 diabetes with complications such as eye and kidney damage, but in the absence of complications, homocysteine is not elevated. []
Homocysteine and multiple sclerosis
Some studies indicate elevated homocysteine levels in multiple sclerosis, but another study found no such association. [] Higher homocysteine values are observed more in male patients. []
VARIOUS FACTORS – HYPERTENSION, OBESITY, DIABETES, NUTRITION AND LIFESTYLE LEAD TO DISORDERS HOMOCYSTEINE LEVELS (www.sciencedirect.com)
Homocysteine and cancer
Rapidly growing cancer cells require large amounts of methionine to produce cellular proteins because methionine is used as the first amino acid in every protein synthesis.
Normal cells can obtain methionine by remethylating homocysteine, but cancer cells cannot do this, so when diagnosed with cancer high levels of homocysteine are usually . [ ] Moreover, it is suggested that high homocysteine may be associated with the rate of tumor proliferation and with the increase in the number of cancer cells. This may indicate homocysteine as a marker of tumor progression and treatment effectiveness.
Elevated homocysteine and osteoporosis
High homocysteine levels are a risk factor for osteoporosis. []
Homocysteine is capable of [R]:
- Increase the activity of osteoclasts (cells that destroy bones)
- Reduce the activity of osteoblasts (cells that build new bone tissue)
- Increase MMP (an enzyme that degrades bone matrix)
- Damage hydroxyproline (an important amino acid for bone), mitochondria and collagen
- Reduce blood flow to the bone.
CHART OF THE INFLUENCE OF HOMOCYSTEINE ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF OSTEOPOROSIS (www.sciencedirect.com) PLEASE NOTE THAT VITAMIN D IS CAPABLE OF INHIBERING BONE RESORPTION (IT IS IMPORTANT THAT THE LEVEL OF THIS VITAMIN IS ADEQUATE)
Elevated homocysteine during pregnancy
One study found that women who had a miscarriage in the second or third trimester were diagnosed with elevated homocysteine levels during the first trimester. [R] Additionally, homocysteine levels were significantly elevated in women who showed increased blood pressure during pregnancy. [R]
Miscarriage (or spontaneous abortion, miscarriage) is associated with the MTHFR C677T mutation and high homocysteine levels among East Asian women. [, ]
Women with preeclampsia have high levels of homocysteine, and low serum levels of folic acid and vitamin B12 [].
Elevated homocysteine in periodontitis
Chronic periodontitis (inflammation of the teeth and gums) is associated with an increase in homocysteine levels. These high homocysteine levels return to normal levels after periodontitis is treated. [, ]
Elevated homocysteine in migraine
While science still doesn't fully understand the causes of migraines, some clinicians say homocysteine may contribute to migraines by inflaming blood vessels and increasing blood clotting (thrombosis). Homocysteine concentrations in brain fluid (CSF) are known to increase in migraine patients. []
Supplementing with B vitamins reduces the severity and frequency of migraine attacks. [].
Effects of Low Homocysteine
Although much less common and usually less problematic than high values, low homocysteine levels can also cause problems. For example, adequate levels of homocysteine are necessary for the production of factors important for detoxification (eg, glutathione production) such as cysteine, taurine, sulfate. Thus, low homocysteine levels can limit detoxification pathways in the body, which will contribute to an increase in oxidative stress. []
Factors that increase homocysteine levels
In addition to inflammatory diseases , which are associated with high homocysteine levels, there are other factors that contribute to elevated homocysteine levels. Typically, factors that increase the need for methylation increase homocysteine levels.
Diet rich in methionine
A diet high in methionine, such as a protein diet, can increase homocysteine levels in the blood. []
Guanidine acetate increases homocysteine
Guanidine acetate is a precursor to creatine. Methylation of guanidine acetate leads to the formation of creatine. Supplementing rats with guanidine acetate increases homocysteine levels by 50%, while creatine supplementation can reduce homocysteine levels by 25%. []
Kidney disease
The kidneys are responsible for removing homocysteine from the blood. [, ] The kidneys also help convert homocysteine into harmless substances. [] Therefore, any decrease in kidney function leads to the accumulation of homocysteine .
This explains why patients with severe kidney disease have very high homocysteine levels . They also show increased risks of developing cardiovascular disease up to 30 times higher than in healthy people. [, ] Moreover, even people with mild kidney problems have elevated homocysteine levels. [, , ]
FACTORS AFFECTING THE DEGRADATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONING. Associated diseases: diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, anemia and hyperphosphatemia. (www.semanticscholar.org)
High levels of homocysteine, despite the consumption of substances that help reduce it (for example, B6 and B12, folic acid), indicate kidney problems. [, , ] This fact highlights that improving kidney function may be an important step in reducing homocysteine levels.
Medicines
Elevated homocysteine also occurs in people who take certain medications, including methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis, or metformin for diabetes, or cholestyramine for high blood triglycerides, or niacin for lowering cholesterol, as well as a number of antiepileptic drugs. []
Stress
Stress increases homocysteine levels in rats. [] In women, psychological stress temporarily increases homocysteine levels , which return to normal levels after stress. []
Quercetin (ambiguous)
In an experiment on liver cancer cells, the use of quercetin contributed to a significant increase in the concentration of homocysteine . [] This increase in extracellular homocysteine may be due to increased methylation. Thus, it is worth being more careful when using quercetin supplements. []
On the other hand, studies have shown that quercetin is effective in reducing serum homocysteine levels in methionine-fed rats, and one possible mechanism for this reduction is due to homocysteine transsulfuration. (135, 136) In another study, quercetin administration was able to reduce or have a protective effect against homocysteine-related oxidative damage. (137)
Other factors that increase homocysteine
- Smoking (through a decrease in vitamins B6 and B12)
- Alcohol (decreases vitamin B6 and folic acid)
- Caffeine (4 cups of coffee – 19-28% increase)
- Physical inactivity
- Low folic acid levels ()
Ways to reduce homocysteine
Elevated levels of homocysteine require close attention and steps to reduce it through diet, lifestyle, taking various medications, and restoring kidney function. [R] Here are the key factors that affect homocysteine levels.
B vitamins and folic acid
The best way to prevent elevated homocysteine levels is to provide your body with adequate amounts of folic acid, vitamin B12 and vitamin B6.
This can be done through food, as a diet containing fruits, vegetables, dark leafy greens, eggs and red meat should provide enough B vitamins needed to maintain homocysteine at healthy levels. However, in people with elevated homocysteine levels, taking supplements with folic acid, vitamins B6 and B12 can normalize homocysteine levels. []
POSSIBLE WAYS TO REDUCE HOMOCYSTEINE LEVELS (www.sciencedirect.com)
Folic acid is broken down by the enzyme MTFHR into 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, which supplies the methyl group necessary for the metabolism of homocysteine to methionine. [] 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF) is the active form of folic acid. Research has shown that supplementation with 5-MTHF provides protection against the dangers of high homocysteine levels .
For example, one study found that taking 5-MTHF at a dose of 113 mcg/day reduced homocysteine levels by an average of 14.6%. []
When reducing homocysteine levels, it is important to take 5-MTHF, which is almost 7 times more powerful than regular folic acid in increasing the level of this acid in the blood. []
In scientific studies, 5-MTHF at doses of 1,000 - 5,000 mcg/day helped achieve the desired reduction in plasma homocysteine concentrations.
Choline and betaine
Methyl group deficiency increases homocysteine levels, so getting additional methyl donor substances such as choline and betaine can reduce homocysteine levels. In rats, high homocysteine levels could be reduced by supplementation with choline and betaine. [, R]
Estrogen
High levels of estrogen are associated with lower average homocysteine levels. [] Indeed, during pregnancy, premenopause and postmenopause , women on estrogen replacement therapy have lower levels of homocysteine in their blood. []
This relationship between estrogen and homocysteine may explain why men show higher homocysteine levels than women. []
This also explains why estrogen therapy reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease. []
Exercise stress
In an experiment on rats with cancer, strength training improved homocysteine metabolism and helped the liver better regulate increased oxidative stress. Exercise prevented the rise in homocysteine that would have been caused by the tumor and also promoted an increase in glutathione. []
Substances that mitigate the harmful effects of homocysteine
- Melatonin []
- Vitamin E []
- Alpha lipoic acid []
- Astragalus []
- Curcumin []
- Statins
- Aspirin
The information on this site has not been evaluated by any medical organization. We do not seek to diagnose or treat any disease. The information on the site is provided for educational purposes only. You should consult your physician before acting on information from this site, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medications, or have any medical condition.
Rate this article
Average 4.5 Total votes (46)
Reasons for the downgrade
A decrease in homocysteine levels is less common compared to an increase. The reasons for such indicators may be dysfunction of enzymes involved in amino acid synthesis (cystathione synthase, methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, methionine synthase, methionine synthase reductase), multiple sclerosis. In case of multiple sclerosis, a hemostasiogram and coagulogram are indicated.
In other cases, doctors do not attach importance to reducing the level of the component. If a person is healthy, homocysteine concentration can be brought back to normal by adding foods rich in methionine (meat, fatty foods, eggs, milk, cheese, kefir, yogurt). Low concentrations of the substance occur in early pregnancy, and this has a positive effect on fetal development.