Calcium (Ca) is the most abundant mineral element in the human body: it not only ensures proper structural development, but also stimulates many metabolic functions.
Most of it (98-99%) accumulates in bone tissue (skeleton, teeth).
The remaining amount (1-2%) is distributed in liquid media, including plasma.
A constant level of calcium in the blood (homeostasis) is an important condition for maintaining the body in a healthy state.
The importance of calcium in our body
Calcium plays a significant biological role in the body, so it is important to know what the normal level of calcium is in the blood. Its main tasks are aimed at:
- iron metabolism;
- maintaining normal heart rate and the entire cardiovascular system;
- blood clotting, where good permeability in cell membranes is activated;
- regulation of enzymatic activity;
- normalization of the functioning of some of the endocrine glands;
- dental health;
- bone strength;
- rhythmic muscle contraction;
- normalization of the central nervous system;
- getting rid of insomnia.
The normal level of calcium in the blood helps a person feel active, cheerful and calm. After all, it takes part in many systems and organs.
What chemical processes in the body is this element involved in?
Calcium is a very common and vital element for humans. They pay special attention to its content in the child’s body, because the level of calcium in the blood of children determines their development. The bulk of calcium is found in bones, serving as a framework for our skeleton and strengthening it; it is also the basis for the growth and development of teeth, and is part of nails and hair. The high content of this microelement in the bones is due to the fact that they act as a reservoir for us.
Calcium is irreplaceable; it is found in almost every cell of the human body. It is found in especially large quantities in the cells of nerves, muscles and the heart. The trace element is necessary for the transmission of nerve impulses, and therefore it is found wherever neurons function. These organs include the brain, as well as nerve cells with endings (axons and dendrites). Muscles also use calcium to normalize their function.
Calcium is found in high concentrations in the blood, it is through it that it enters the muscles, bones, or, conversely, leaves the bones. Thus, it ensures the normal functioning of organs and the body as a whole. The normal level of calcium in the blood is 2.50 mmol/l for an adult.
What conditions indicate problems with calcium in the body?
With low and high levels of this element in the blood, a number of symptoms are observed, manifesting themselves in different ways.
With hypocalcemia (insufficient amount of calcium in a person), some pathological processes may occur, which are the body’s call for examination and treatment.
Mental symptoms are accompanied by:
- headaches, which are often migraine-like;
- dizziness.
From the skin and bones, hypocalcemia can manifest itself:
- with dry skin with subsequent appearance of cracks;
- for caries in teeth;
- with damage to the nail plate;
- with excessive hair loss;
- for osteoporosis (impaired bone density).
A disorder of the neuromuscular system is characterized by:
- severe weakness;
- tetanic convulsions after excessively enhanced reflexes.
A disorder of the cardiovascular system entails:
- prolonged blood clotting;
- increased heart rate;
- coronary heart disease.
Conditions with hypercalcemia are somewhat different from the previous ones, this allows the doctor to understand that the patient has calcium in the blood above normal.
Disorders of the central nervous system and muscles are characterized by:
- headache;
- loss of orientation in space;
- vomiting, nausea;
- general weakness of the body;
- sudden fatigue;
- increasing the intensity and number of reflex actions;
- in some cases, immobility.
A disorder of the cardiovascular system entails:
- calcium deposition on the walls of blood vessels;
- increased frequency and untimeliness of heart function;
- insufficiency of the functions of this organ.
Also very often there is a lack of urination and, as a result, kidney failure.
Symptoms of calcium deficiency and excess
The lack of calcium is most pronounced in women during lactation and menopause. Tooth enamel becomes dull and becomes sensitive to cold and hot foods. Pain in the bones and joint capsules is a frequent companion to calcium deficiency. The ends of the hair split, the hair follicles weaken and fall out.
Thrombophlebitis, thrombosis, varicose veins are common diseases of the veins and blood flow of the fair sex. A deficiency of the nutrient Ca aggravates these problems, so in advanced cases, stagnant effects develop in the blood vessels. The contractile function of the heart weakens, but the pulse rate remains at the patient’s usual level.
Hypercalcemia is fraught with cluster headaches, early puberty and increased sexual excitability, dry skin of the face and hands. Russian scientist N.G. A friend found that excess Ca affects life expectancy - calcium ions alkalize the blood of living beings, which is why the body's cells quickly age and die. Therefore, one of the most striking symptoms of hypercalcemia is slow cell regeneration and prolonged healing of wounds and cuts.
What hormones regulate calcium production?
The production of any microelements in the human body is regulated by special substances called hormones. The calcium content in the blood (the norm is within 2.50 mmol/l) is also under their control.
Calcitonin helps regulate calcium metabolism. It is produced by the thyroid gland and is one of the main informants that determine the presence of malignant neoplasms in the body.
Osteocalcin, it appears through the formation of bone tissue by special cellular structures.
Paratinin produces calcium interchange. It is secreted from the cells of the parathyroid gland.
Cortisol is the most active glucocorticoid hormone. It is produced by the adrenal cortex; it takes control of the production of other hormones and absolutely all processes in the body associated with synthesis.
Aldosterone. It carries out water-salt metabolism: it retains sodium salts and removes potassium salts from the body.
Somatotropic hormone is responsible for growth. Regulates mainly the growth of bone tissue, as well as organs and muscles.
The function of the adrenogenital hormone of the adrenal cortex is aimed at maintaining the condition of the genital organs and the development of distinctive characteristics.
Corticotropin is produced from the anterior pituitary gland. It activates the production of cortisol, regulates the appearance of hormones and normalizes metabolism.
Regulation of calcium metabolism
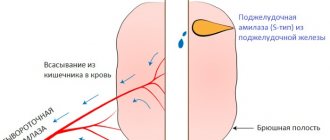
Calcium and phosphate (PO) metabolism are interrelated. Regulation of calcium and phosphate balance is determined by circulating levels of parathyroid hormone (PTH), vitamin D and, to a lesser extent, calcitonin. The concentrations of calcium and inorganic PO are related to their ability to participate in a chemical reaction to form CaPO. The calcium and PO concentration product (in mEq/L) is normally 60; when the product exceeds 70, precipitation of CaPO crystals in soft tissues is likely. Precipitation in vascular tissue contributes to the development of arteriosclerosis.
PTH is produced by the parathyroid glands. It has various functions, but probably the most important is the prevention of hypocalcemia. Parathyroid cells respond to a decrease in plasma calcium concentration, and in response to it, PTH is released into the circulation. PTH increases plasma calcium concentrations within minutes by increasing renal and intestinal calcium absorption and by mobilizing calcium and PO from bone (bone resorption). Renal calcium excretion is generally similar to sodium excretion and is regulated by essentially the same factors that control sodium transport in the proximal tubule. However, PTH increases calcium reabsorption in the distal nephron independently of sodium. PTH also reduces renal PO reabsorption and thus increases renal PO loss. Renal PO loss prevents increases in plasma Ca-binding product and PO as calcium levels rise in response to PTH.
PTH also increases plasma calcium levels by converting vitamin D to its most active form (1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol). This form of vitamin D increases the percentage of calcium absorbed in the intestines. Despite increased calcium absorption, increased PTH secretion usually leads to further bone resorption by suppressing osteoblastic function and stimulating osteoclast activity. PTH and vitamin D are important regulators of bone growth and remodeling.
Studies of parathyroid function include determination of circulating PTH levels by radioimmunoassay and measurement of total or nephrogenic urinary cAMP excretion. Urinary cAMP testing is rare, but accurate PTH testing is common. The best tests are for intact PTH molecules.
Calcitonin is secreted by parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland (Cells). Calcitonin reduces plasma calcium concentrations by increasing cellular calcium uptake, renal excretion, and bone formation. The effects of calcitonin on bone metabolism are much weaker than the effects of PTH or vitamin D.
It's no secret that vitamins, minerals and trace elements, including ionized calcium, play an important role in the functioning of the human body. There are two fractions of calcium in the blood: free and one that is combined with other substances, for example, plasma proteins and phosphates. Normally, the amount of free calcium should not exceed approximately 45% of the total level of this mineral. Almost all deviations from normal indicators can be considered pathologies.
Analysis to determine the amount of this element in the blood
Muscle cramps, nervousness, prolonged insomnia, as well as diseases such as cachexia, liver failure, spinal tuberculosis are direct indications for this calcium test. This effective test allows doctors to determine the amount of calcium and its content in the blood. Calcium in a blood test, the norm of which is always written as a result, is determined with accuracy only if the rules for preparing for the study are followed. It is carried out in the morning (do not eat food for 8-12 hours), physical activity is excluded for this period, alcohol is not consumed. If it is not possible to take the test in the morning, then blood is drawn after a 6-hour fast, and fats are excluded from the morning meal. The consumption of dairy products, cabbage and nuts is strictly prohibited, as they are the main source of calcium.
Indications for laboratory test
The proportional value of total and free calcium is normally constant, but various pathologies can lead to its imbalance. A test for total calcium content is not informative if it is necessary to check mineral metabolism.
An important diagnostic test is a test for ionized calcium in the blood. Normal levels of calcium in the blood depend on the person’s age (they were described above).
The main indications for testing for free calcium are as follows:
- The procedure is usually performed at the same time as a parathyroid hormone test, which can detect the presence of hyperthyroidism.
- Signs of hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia.
- During treatment in which blood replacement fluids are introduced into the body.
- In preparation for surgery, injuries and burns.
- For the diagnosis of oncology and osteoporosis.
By examining a sample of the patient’s venous blood, pathology is detected or the norm of ionized calcium is calculated. The analysis is performed in the morning on an empty stomach. For a reliable result, it is necessary to take preparatory measures before collecting the material: the day before the procedure, it is forbidden to drink alcohol, fatty and spicy foods, in the morning you are allowed to drink only clean water.
If signs of calcium deficiency appear, you must consult a specialist for examination, diagnosis and treatment.
Often, the symptoms of hypocalcemia are eliminated by consuming drugs rich in calcium and vitamin D. It is recommended to eat foods that contain the mineral in an easily digestible form. The most useful are cottage cheese and milk. If possible, you should try to sunbathe. With calcium deficiency, a decrease in immunity is observed, so it is necessary to use a multivitamin complex. It is also prescribed after operations, blood loss, after injuries, during hormonal changes, when the absorption of the element is impaired.
Only a specialist can prescribe the necessary treatment to remove excess calcium from the body. The patient independently has the opportunity to improve his health thanks to a balanced diet.
The mineral enters the body with food. Therefore, foods containing calcium should be avoided. These are dairy and fermented milk products, rice dishes, sesame seeds, nuts, chocolate, halva, and wheat flour bread.
It must be remembered that in case of abnormalities in calcium metabolism in the body, the final diagnosis, proper treatment and preventive measures can only be established and prescribed by a doctor.
- 1 Add the required studies to your order
- 2 Select the date of the test, medical center and time of visit
- 3 Fill out the registration form and pay for tests at a discount
- 4 Visit the health center at the selected time with referral forms
- Receive test results by email. mail or at the medical center
Paid separately
Taking biomaterial - from 10 rubles.
If you order several tests at once, you will pay once.
Annual subscription - 99 rub.
Gives you the opportunity to take tests at a discount of up to 50% an unlimited number of times during one year for a family (community) of 5 people. Not required when ordering via mobile app.
Selected
Ionized calcium, Ionized calcium, Ca2+, Ca++, B135, Bone diseases, Heart and blood vessels, Kidneys, Bones
Selected Select Price
in LAB4U: 450,225 rub. RU-MOW
210 rub. RU-SPE 165 rub. RU-ASTR 165 rub. RU-VLA 165 rub. RU-VOR 205 rub. RU-VOL 165 rub. RU-IVA 165 rub. RU-KOS 175 rub. RU-KAZ 165 rub. RU-KLU 185 rub. RU-KDA 165 rub. RU-KUR 180 rub. RU-NIZ 190 rub. RU-SAM 165 rub. RU-ORL 175 rub. RU-PRI 180 rub. RU-ROS 165 rub. RU-RYA 175 rub. RU-TVE 165 rub. RU-TUL 180 rub. RU-UFA 165 rub. RU-YAR
The amount of the discount depends on the date and time of your visit to the medical center. For example, in some medical centers in the morning the discount may be slightly less than at lunchtime. However, you can almost always find offers with a 50% discount, regardless of the date and time.
Period of execution
1 day (except the day of taking biomaterial)
Completion period: 1 day (except for the day of taking biomaterial)
Material for analysis
Blood serum
Research method
Ion selective
Description
Calcium ions play an important role in the regulation of many cellular functions. A change in the concentration of calcium ions in the cell is a signal for the activation or inhibition of enzymes, which in turn regulate metabolism, cell growth, adhesion, contractile and secretory activity. In the diagnosis of diseases associated with calcium metabolism, it is the ionized one that plays an important role, since, compared to the general one, it better reflects the metabolism of calcium in the body. All physiological effects of calcium are carried out by its ionized form: blood clotting, muscle contractions, nerve impulse transmission and many others.
With hypoalbuminemia, as a result of a decrease in calcium-binding proteins, the concentration of total calcium may decrease, but the ionized form does not depend on the binding proteins, so the expected effects of hypocalcemia may be absent. Determinations of ionized calcium are used in the diagnosis of “physiological activity” or the level of free calcium in patients with acid-base disorders, protein disorders (nephrotic syndrome, chronic renal failure, multiple myeloma, malabsorption, etc.). Determining the concentration of ionized calcium is important in cases where the clinical condition of the patient and the level of total calcium concentration indicate a possible disorder of calcium metabolism. Calcium ion levels should be determined at a pH of 7.4.
Indications for use
- Diagnosis of diseases of the parathyroid glands.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment for diseases of the parathyroid glands.
- Diagnosis of bone diseases.
- Diagnosis of chronic kidney diseases.
- Diagnosis of tetany (transient muscle contractions or spasms).
Preparing for analysis
- It is recommended to donate blood for testing on an empty stomach; you can only drink water.
- At least 8 hours must pass since the last meal.
- Blood sampling should be done before starting medications (if possible) or no earlier than 1-2 weeks after stopping them. If it is impossible to discontinue medications, the referral for the study must indicate which medications the patient is receiving and in what doses.
- The day before taking blood, limit fatty and fried foods, do not drink alcohol, and avoid heavy physical activity.
- It is not recommended to donate blood for testing immediately after radiography, fluorography, ultrasound examination, rectal examination or physiotherapeutic procedures.
Factors influencing the results of the analysis
- Increase the test result: androgens, Ca salts, calusterone, danazol, dihydrotachysterol, constant use of diuretics, ergocalciferol, isotretinoin, lithium, progesterone, parathyroid hormone, tamoxifen, testolactone, vitamin D, vitamin A.
- Reduce the test result: albuterol, alprostadil, aminoglycosides, asparaginase, calcitonin, carbamazepine, carbenoxolone, carboplatin, corticosteroids, ergocalciferol, estrogens, fluorides, gastrin, glucagon, glucose, indapamide, insulin, isoniazid, magnesium salts, methicillin, phenytoin, plicamycin, those tracycline , fluorides, oxalates, sulfates.
Calcium levels in the blood of adults and children
In an adult, this element occupies only 1% of the total amount of calcium in all organs, tissues and systems. Therefore, the level of calcium in the blood (its norm) is in a small range, only 2.15 - 2.50 mmol/l. Deviations from these values already seriously affect our body.
Indicators from adult studies differ from those from child analyses. The test for calcium levels in the blood is no exception. The norm for newborn babies is 1.75 mmol/l, for children of the first month 2.2-2.5 mmol/l. In adolescents under 14 years of age, the content of this element is 2.3-2.87 mmol/l.
Correct diagnosis
To determine the level of ionized or free calcium in the blood, it is necessary to conduct a biochemical study. This analysis is done for both adults and children.
Several conditions are considered indications for its use:
- Symptoms of not enough or, conversely, too much calcium.
- Malignant tumors have appeared in the body or cancer is developing.
- There are diseases of the digestive system.
- Preparations for surgery are underway.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the heart and circulatory system.
- Cramps.
- Reduced sensitivity in tissues.
- Malfunctions of the kidneys, bladder and other organs of the urinary system.
- Decreased protein levels in the blood.
It is necessary to prepare for donating blood for analysis.
How to do it:
- On the eve of blood sampling, avoid intense exercise.
- Eliminate alcoholic drinks and fatty foods from your diet about a day before.
- You can eat your last meal 12 hours before the test.
- Do not smoke two hours before your laboratory visit.
- Before the analysis, you cannot undergo physical procedures.
- It is better to stop taking medications for a week or two, since many of them can increase or decrease the amount of calcium in the blood. If this cannot be done, you must inform the laboratory assistant. In addition, on the referral form you need to write what medications are taken and in what doses. This information will help you get the most accurate result.
Depending on what the blood test shows, the doctor will prescribe additional examination or treatment.
The difference between total calcium and ionized calcium
Total calcium is localized mainly in bone tissue. It actively interacts with blood serum ions. The main task of total calcium is to eliminate its fluctuations in the serum.
Ionized calcium is not bound to proteins in any way, which is why it is also called free calcium. Although it is present in the human body in smaller quantities, it performs very important functions. Metabolism, secretory function, cell growth, muscle contraction and much more are regulated by ionized calcium in the blood. The norm of this element is as important as the general one.
The total calcium content in bones is approximately 99%. Ionized calcium is contained in the blood (the norm of which is 1%) only in blood serum.
Increased and decreased amount of ionized calcium causes and methods of treatment
When conducting a biochemical blood test, the amount of ionized calcium is also checked, which shows the level of a microelement not bound to proteins. According to these indicators, hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia can be detected. These conditions are pathological and dangerous to human health, because calcium is involved in many vital processes occurring in the body.
Ionized calcium is a very important trace element in regulating metabolic processes. It makes up only 1% of the total mineral. Up to 99% of calcium is found in teeth, bones, hair, etc.
This microelement is responsible for the following functions:
- growth and development of bone tissue;
- blood clotting;
- conductivity of nerve fibers;
- regulation of enzymatic activity;
- hormone production;
- contraction of muscle fibers and cardiac muscle.
Calcium ions help strengthen the walls of blood vessels, increasing the body's resistance to infections and allergic irritants.
For these reasons, biochemical analysis for ionized calcium is one of the most common in medical institutions. Assessing its level allows you to clarify important information on the mineral metabolism of both an adult and a child.
An analysis of the level of ionized calcium is carried out in the following cases:
- signs of deficiency or increased amount of calcium in the body;
- preoperative preparation;
- malignant tumors;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the urinary system;
- convulsive manifestations;
- pain in muscles and bones;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- decrease in protein levels in the blood.
If the patient is undergoing therapy with intravenous administration of blood products and glucose-saline solutions, then the level of the mineral is monitored daily.
To obtain a reliable result, you must comply with the following basic requirements:
- avoid heavy physical activity before taking the test;
- do not drink alcohol or fatty foods during the day;
- do not smoke for an hour;
- do not eat for 12 hours (the test is taken on an empty stomach);
- do not submit biomaterial after instrumental examination methods and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Various medications can affect ionized calcium levels. Therefore, 1-2 weeks before the scheduled examination, it is recommended to stop taking medications. It is advisable to consult with your doctor about discontinuing medications. If temporary cancellation is not possible, then when submitting the biomaterial, the patient must indicate the medicine and in what doses it is taken.
It is recommended to maintain the amount of ionized calcium at these levels. Not only the lack of this element, but also its excess content is dangerous for human health.
If its level is elevated, a repeat test is performed, since the results may be the result of an incorrect blood test. The ionized calcium content can be affected by prolonged contact of the biomaterial with air. If a repeat analysis shows the same thing, then additional diagnostic procedures are performed.
With an increased amount of calcium in the blood, hypercalcemia is diagnosed. This condition is dangerous because an excessive amount of this microelement settles on the walls of blood vessels, liver and kidneys. As a result, heart failure, pathological condition of the liver and biliary tract, and urolithiasis may develop.
An increase in the level of ionized calcium in the blood can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- chronic nausea and vomiting;
- decreased ability to work;
- feeling of thirst;
- convulsive syndrome;
- heart rhythm disturbance, shortness of breath;
- weakness.
To normalize the amount of microelement in the blood, it is necessary to establish the causes of hypercalcemia. If it is caused by improper nutrition, then the diet is adjusted. In the case of any pathologies, it is necessary to urgently begin treatment of the underlying disease.
A reduced level can be identified by the following clinical manifestations:
- slow blood clotting;
- destruction of nails and teeth;
- increased heart rate;
- hair fragility;
- nervous excitability;
- dry skin;
- headaches and muscle pain;
- dizziness;
- fractures even with minor injuries or stress.
Calcium deficiency is detrimental to a child during his development. This trace element is very important for the formation of the spine and bones. If there is a deficiency, children may have bent limbs and poor posture.
To successfully treat a deficiency of this microelement, the root cause must also be identified. As a rule, patients are prescribed a special diet or vitamin supplements.
There are several main reasons why the level of ionized calcium may be elevated:
- oncological diseases;
- increased vitamin D content;
- chronic enteritis - inflammation in the small intestine (typical for children);
- increased levels of growth hormone;
- endocrine diseases;
- metabolic disorders;
- abuse of foods containing calcium.
Calcium deficiency can indicate certain pathologies in the body:
- kidney diseases;
- lack of magnesium or vitamin D;
- pancreatic diseases;
- infectious diseases;
- consequences of the operation;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- endocrine diseases.
Often, low levels of ionized calcium are diagnosed after 50 years in women during menopause. This is due to hormonal changes. Patients who abuse diets for weight loss often suffer from its deficiency. During pregnancy, a deficiency of this microelement is also often observed. Calcium can be washed out of the body when taking diuretics or consuming salty foods.
If you receive a blood test result with a low or high level of ionized calcium, your diet is adjusted. Products containing this microelement are added to or excluded from the diet, respectively.
Calcium rich foods
Even with adequate consumption of foods rich in this mineral, its absorption is dependent on vitamin D and magnesium. Therefore, it is necessary to simultaneously eat foods containing them.
Magnesium Rich Foods
There are 4 ways to eliminate hypercalcemia:
- decreased microelement absorption by the intestines;
- increased excretion of calcium in urine;
- removal of excess by dialysis;
- reduced bone destruction.
The medications and treatment regimen are selected strictly individually by the doctor.
All information on the site is provided for informational purposes. Before using any recommendations, be sure to consult your doctor.
Full or partial copying of information from the site without providing an active link to it is prohibited.
To reduce the concentration of ionized calcium, therapy with diuretics is prescribed. The dosage of medications and the regimen are determined only by the doctor. Diuretic drugs have an aggressive effect. This means that along with excess Ca, nutrients and vitamins will be washed out of the body.
In addition, diuretics increase the load on the renal apparatus. Treatment should be carried out under strict monitoring of blood counts and kidney condition. Microelement deficiency is compensated by proper nutrition and taking pharmaceutical mineral complexes or calcium single preparations.
An example of a drug to compensate for calcium deficiency
The main list of products containing a macronutrient includes cottage cheese, cheeses, feta cheese, natural yogurt, whey, almonds, poppy seeds, sesame seeds, chia, canned fish in oil (salmon and sardines), white beans, spinach, rhubarb. To maintain a stable calcium balance, it is recommended to adhere to the daily intake standards for this macronutrient.
- growth and development of bone tissue,
- blood clotting,
- conductivity of nerve fibers,
- regulation of enzymatic activity,
- hormone production,
- contraction of muscle fibers and cardiac muscle.
- signs of deficiency or increased amount of calcium in the body,
- preoperative preparation,
- malignant tumors,
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract,
- diseases of the urinary system,
- convulsive manifestations,
- pain in muscles and bones,
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system,
- decrease in protein levels in the blood.
- avoid heavy physical activity before taking the test,
- do not drink alcohol or fatty foods during the day,
- no smoking for an hour,
- do not eat for 12 hours (the test is taken on an empty stomach),
- do not submit biomaterial after instrumental examination methods and physiotherapeutic procedures.
To achieve a long-term and sustainable effect, drug therapy must necessarily eliminate the vicious mechanism mentioned above. As a result of the action of a particular drug, it is necessary to either reduce bone resorption, or reduce the reabsorption of calcium in the kidneys, or reduce its absorption in the intestines. Thus, it is necessary to know the cause in order to eliminate high calcium levels in the blood.
Of course, treatment of hypercalcemia does not always necessarily involve the use of drugs. In some cases, for example, with tumor lesions of the bones, an increase in calcium in the blood can be prevented through surgery or radiation therapy.
But still, in most cases, various medications are used. Let's look at the most popular of them and explain the mechanism of their action:
- normal physiological isotonic sodium chloride solution. It dilutes calcium in the blood serum, reduces its concentration by increasing volume and stimulates urine excretion;
- a diuretic such as Furosemide reduces electrolyte reabsorption in the nephron loop and also increases the amount of urine;
- glucocorticoid hormones also prevent an increase in calcium in the blood. Their action is associated with antagonism towards vitamin D, and at the same time they also reduce calcium reabsorption;
- bisphosphonates (Aredia, Aclasta) act on osteoclasts, which are called “bone crusher” cells, they destroy bone tissue and promote the transition of the substance into a dissolved state. They react with the bone tissue matrix and make it more resistant to the action of osteoclasts, as a result of which resorption also decreases.
Hypocalcemia, causes
If the calcium level in the blood (the norm of which is noted above) is significantly lower than required, you need to find out the reasons for this condition. Among them the following are often found.
- Insufficient vitamin D content in the body.
- Minimal intake of calcium from food.
- Pathological processes in which malabsorption occurs. These include bowel resection, pancreatic insufficiency and frequent diarrhea.
- Rickets.
- Oncological diseases.
- Chronic sepsis.
- Low mobility (hypodynamia).
- Allergic reactions.
- Liver dysfunction caused by damage to toxins (poisoning after drinking alcohol or exposure to heavy metal products).
- Taking medications (interleukins or corticosteroids).
- Increased estrogen levels.
If such conditions occur in a person’s life, then a test can be done to determine the total calcium in the blood. The norm will indicate that the organs and systems are not affected by the pathological process.
Treatment
Calcium deficiency is treated by changing diet, artificially introducing nutrients, and taking medications. Hospitalization in a hospital is not provided. Medicines containing Ca are prescribed together with phosphorus-containing supplements. In this case, Ca+ blockers are excluded or their analogue without a restraining effect is selected. Calcium antagonists:
- Verapamil.
- Lacidipine.
- Manidipin.
- Diltiazem.
- Magnesium.
- Iron.
- Zinc.
For exogenous causes of calcification deficiency, a gastrointestinal examination is prescribed, special attention is paid to the microflora of the small intestine and the number of spiral-shaped bacteria Helicobacter pylori, which is considered an identifier of gastritis.
Excess of positively charged Calcium is treated with blood oxidation and glandular plasmapheresis, in which bound Ca falls on Fe molecules and does not pass through the superfine filter. Dairy products, sorrel, spinach, and celery are excluded from the diet. Prescribe plenty of drinking of weak green tea and coffee beans; red meat and lightly salted sea fish.
How can you increase the content of this microelement in the body?
In order for there to be a normal level of calcium in a person’s blood, it is necessary to carry out certain actions. Firstly, you need to contact a specialist, since you yourself will not be able to determine the reasons for such a deviation. Secondly, if there are no serious reasons for low calcium (complex diseases or cancer), its level can be corrected with nutrition.
The main products containing calcium are hard cheese, cottage cheese, sesame and its oil, eggs, milk, dairy products, herbs, and nuts. The average person should consume between 800 and 1,200 mg of calcium per day.