Normal blood and urine sugar levels in pregnant women in the 1st, 2nd, 3rd trimester
Due to the general restructuring occurring in the body of a pregnant woman, glucose levels in the blood and urine change. Also, the norm values will vary depending on the growth rate of the fetus.
- 1st trimester. At this stage, the embryo requires energy to form organs. And in a woman’s body the hormonal levels change (including an increase in insulin production). As a result, sugar levels are slightly lower than the norm for a healthy person. In the blood, digital values are in the range of 3.2-5.1 mmol/l. There should be no sugar in the urine.
- 2nd trimester. This period is characterized by stabilization of hormonal levels and small size of the fetus. Blood and urine sugar levels should correspond to the general norm. The range of blood glucose concentration is 3.3-5.5 mmol/l. There is no sugar in urine.
- 3rd trimester. Hormonal changes occur again as the body prepares for the birth of a child. The fetus already has the appropriate size, takes nutrients from the mother’s blood and puts pressure on the kidneys. As a result of increased load and compression of the kidneys, glucose may be observed in the urine. Its permissible range is 1.7-2.7 mmol/l.
Due to an increase in the total weight of the mother and the grown fetus, the pregnant woman’s thyroid gland may not cope with the load and produce insulin below the required norm (this provokes an increase in blood glucose).
The mother also exchanges nutrients with the fetus, as a result of which the glucose concentration may decrease. Taking into account changes in the body, the range of blood sugar concentration is 3.8-6.1 mmol/l. At 28-32 weeks, the gynecologist often prescribes a stress test to exclude the onset of gestational diabetes.
4. Birth of a child. After the baby is born, the last hormonal change occurs. The body prepares for breastfeeding, as well as for the formation and normalization of the menstrual cycle. As a result, the amount of sugar in the blood and urine is equal to the values of the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. Gradually the indicators return to normal.
Deviation of indicators from the norm (in any direction) is dangerous for the health of the mother and the development of the fetus. Regular testing allows you to identify abnormalities at an early stage and begin gentle therapy (prescribed by a gynecologist who manages the pregnancy).
Possible consequences
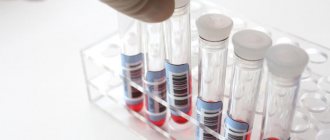
Measuring blood sugar levels with a glucometer
High blood sugar during pregnancy is a risk of developing gestational diabetes. If a woman does not receive timely treatment, the consequences of hyperglycemia negatively affect the health of the child. In the first half of the perinatal period, the formation of the baby’s nervous system and brain occurs.
A high level of glycemia can provoke psychopathological disorders and mental deviations in the child. Constant intrauterine poisoning of the unborn baby with toxic breakdown products of glucose creates the danger of hypoxia (oxygen starvation), cerebral ischemia (insufficient blood supply), and fetal obesity.
If sugar is constantly elevated, uncompensated hyperglycemia can cause the following complications:
- fetal death, miscarriage, premature or complicated delivery;
- fetoplacental insufficiency;
- polyhydramnios (increased volume of amniotic fluid);
- preeclampsia (severe toxicosis in the later stages);
- retinopathy (damage to the vascular system of the visual organs);
- nephropathy (disruption of the blood vessels of the renal apparatus).
Important! Timely diagnosis of hyperglycemia will allow a set of therapeutic measures to be carried out and the development of GDM to be avoided.
A consistently low sugar level means “starvation” of the fetus. As a result, the child may be born prematurely, that is, be born premature, have low birth weight, or have congenital pathologies of the endocrine system.
Reasons for the increase in indicators
Glucose levels in pregnant women are monitored during pregnancy for timely detection of abnormalities in the thyroid gland and the onset of gestational diabetes. This disease goes away on its own after childbirth, but in rare cases it can develop into type 2 diabetes.
Factors influencing the increase in blood sugar:
- the presence of excess weight or rapid weight gain during pregnancy;
- presence of predisposition to the development of diabetes;
- there were cases of increased glucose before the child was conceived;
- age over 35 years;
- the presence of an increased amount of water;
- if during previous pregnancies children were born with increased body weight or miscarriages occurred;
- the presence of stressful situations during pregnancy;
- improper diet with easily digestible foods and a large amount of sweet foods;
- infectious diseases during pregnancy;
- dysfunction of the ovaries and thyroid gland;
- diseases of the kidneys, liver and pancreas;
- the presence of pathologies causing disruption of the metabolic process in the body.
If a woman has at least one of the listed reasons, then the gynecologist must be warned about this in advance. Then blood and urine tests for sugar will be given more attention and will be carried out more often.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) manifests itself in mild symptoms, making it quite difficult to detect in a timely manner. According to statistics, at least 10% of pregnant women experience it. Usually it makes itself felt by the end of the second or beginning of the third trimester. In 90% of cases, this disease goes away on its own after childbirth, even if no treatment was prescribed. Women whose gestational diabetes resolves after childbirth are at risk of developing type 2 diabetes later. A blood sugar test is the best way to detect this disease. This test can be carried out either in a special laboratory or at home, the main thing is to know your blood sugar levels.
Gestational diabetes is dangerous because it harms the health of the woman and the unborn child.
A number of consequences that gestational diabetes leads to:
- fetal loss;
- overweight in a pregnant woman;
- problems with the cardiovascular system;
- hypoxia and asphyxia during childbirth;
- hyperbilirubinemia;
- diabetic fetopathy in an infant;
- disorders in the child’s bone tissue;
- disorders in the central nervous system of the fetus.
Why do glucose levels drop during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, glucose levels may also decrease. This condition is no less dangerous for the mother and fetus. The main threat is the lack of energy to properly maintain the functioning of the mother’s body and the development of the child.
Reasons for low glucose in pregnant women:
- lack of protein and glucose in the daily diet of a pregnant woman;
- early or severe toxicosis;
- increased physical activity;
- fasting or eating small portions with long breaks;
- sweet carbonated drinks. They provoke a rapid but short-term increase in glucose. As a result, not all of the insulin is used to metabolize sugar. Its increased amount leads to a decrease in glucose levels;
Glucose levels in pregnant women increase with the consumption of fast carbohydrates, such as sweet sodas.
- dysfunction of the liver and pancreas;
- the presence of a tumor of any etiology.
The presence of these reasons should also be reported to the gynecologist. Their timely elimination will avoid a drop in glucose in the blood of a pregnant woman.
Low sugar level
Low blood sugar is very rare; high blood sugar is much more common. Reasons for decreased glucose levels:
- laboratory error;
- excessively low body weight of a woman;
- malnutrition, starvation, exhausting diet;
- severe toxicosis during pregnancy;
- insulin overdose (if the pregnant woman has already been diagnosed with diabetes and is on insulin therapy).
By the way, we recommend reading the article Everything you need to know about glycated hemoglobin.
It is easy to correct this condition, establish a balanced, nutritious diet, and you may need intravenous administration of glucose.
What are the dangers of high and low glucose levels during pregnancy?
Glucose levels in pregnant women may vary during pregnancy, but should not go beyond the range. When sugar levels decrease/increase in the mother and fetus, the following consequences may develop.
| Complications from high glucose levels | Complications from low glucose levels |
| Miscarriage early in pregnancy or early birth. This condition occurs due to the rapid aging of the placenta (the nutrition of which is deteriorating due to the poor condition of the blood vessels). When the placenta ages, the fetus does not receive the necessary substances and dies in the womb | Children do not receive enough glucose and are born with low birth weight, often premature |
| The child may develop hypo- or hyperglycemia (as the functioning of the fetus's pancreas will be impaired) | Underdevelopment of internal organs, possible presence of congenital pathologies |
| The presence of congenital diabetes, as a result, is poor vascular condition and impaired kidney function. Diabetes can also develop in a child at a later age. | Miscarriage due to lack of energy for gestation and development of the fetus |
| The baby is born with a large weight, which aggravates the birth and often ends with ruptures of the birth canal in the mother and birth injuries in the child | Impaired functioning of the pancreas, resulting in the development of diabetes |
| Children are often born with impaired breathing due to underdeveloped lung tissue | During pregnancy, the mother will experience constant weakness and loss of strength. |
| The development of late toxicosis, which has a detrimental effect on the development of the child (possible development of hypoxia). The woman experiences increased blood pressure, swelling and decreased vision. Heart function also worsens and frequent infectious diseases occur. | Due to lack of energy, labor may end up with sluggish labor. |
| Development of polyhydramnios. This condition can lead to fetal suffocation due to the umbilical cord entangling the neck, as well as malpresentation during childbirth. | |
| Delayed physical development |
To prevent the development of complications in the fetus and mother, it is necessary to promptly diagnose the development of pathology and follow the specialist’s instructions during therapy.
Let's sum it up
Don't neglect getting your blood sugar tested. A lot depends on your glucose level. If the level is elevated, the likelihood of developing obesity in the fetus increases. If the level is low, then the baby in the womb experiences a lack of nutritional energy, for this reason it is difficult for him to develop, which can lead to death. If your blood sugar deviates from the norm, do not panic prematurely; a repeat test will be ordered to clarify the result. It is necessary to inform the doctor leading the pregnancy about any symptoms that appear, this can prevent the development of any disease. Eat healthy and varied, and what foods will be good for you - check with your doctor.
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common endocrinological pathologies. In our country, the number of patients suffering from this disease is approaching the epidemic threshold. Therefore, determination of blood sugar is included in the population health screening program.
Preparation, how to take a sugar test
Tests to determine the amount of sugar in urine and blood will give an accurate result after preparation and if the sampling is carried out correctly.
Blood analysis
Before taking a blood test, a pregnant woman should eat regular food (if she refuses sweet foods and drinks, the result will not be accurate). It is advisable to stop taking vitamins and other medications for 3 days.
A woman should not eat food 10 hours before blood sampling. In the morning you are allowed to drink clean water without gases. It is forbidden to brush your teeth or do exercises.
It is important to remain calm during the procedure.
Methods for determining blood glucose concentration:
- Standard analysis. Blood is taken from a finger in the morning.
- Carrying out a tolerance test. Prescribed at 28-32 weeks of pregnancy, even if an increase in sugar has not previously been noted.
In this case, blood is taken from a vein 3 times. The initial portion is taken on an empty stomach. Next, the woman should drink water with 50 g of glucose. After 30 minutes, the second portion of blood is taken. After 1 hour, take 3 servings.
3. Using test strips at home. Standard training required. Glucose concentrations can be measured throughout the day and the data recorded. They must be transferred to a specialist who monitors the pregnancy.
If an increased/lowered indicator is detected, the tests are repeated. If the results are confirmed, further examination and treatment are prescribed by an endocrinologist.
Analysis of urine
To properly collect a urine test, it is recommended to follow a normal diet, but exclude foods that can color the urine (tea, beets, coffee). Medicines are also stopped for 3 days. Before collecting urine, it is necessary to sterilize the container for collecting the analysis. It is also necessary to carry out a thorough washing procedure.
Methods for determining the concentration of glucose in urine:
- Standard analysis . It is necessary to collect the morning urine sample (150 ml is enough) in a sterile vessel and immediately take it to the laboratory. After 4 hours the material will be unsuitable for research.
- Daily analysis collection. Urine is collected in a single container within 24 hours. In this case, the collected material is stored in the refrigerator. It is important to sterilize the container for collecting material each time it is emptied, as well as to carry out the washing procedure. The collected material must be delivered to the clinic within 4 hours.
- Using test strips at home. A similar preparation schedule must be followed. You can measure the concentration of glucose in your urine several times during the day. The results obtained must be provided to the gynecologist.
If there is glucose in the urine, a blood test is necessary. If a change in sugar concentration is confirmed, further examination by a specialist is necessary.
Measuring blood glucose concentration at home
To determine the concentration of glycemia in the blood, it is not necessary to go to the laboratory.
Today there are devices for self-measurement of sugar levels - glucometers. You can purchase the device at a medical equipment store. To check your glucose levels, you should additionally buy test strips. Before measuring glycemic concentration, you need to read the operating instructions for the device.
Algorithm for using a glucometer:
- wash your hands with toilet soap;
- warm your fingers to room temperature (to do this you need to massage your hands);
- treat the area of the finger where the puncture will be made with alcohol;
- turn on the device;
- enter code;
- insert the test strip into the special socket of the glucometer;
- Use a scarifier to pierce your finger in the side;
- drop a few drops of serum onto the area where the test strip is applied;
- Apply cotton wool soaked in alcohol to the puncture site;
- evaluate the result on the monitor after 10-30 seconds.
Sometimes your home blood glucose meter can be wrong.
The most common reasons for obtaining an unreliable result:
- using test strips intended for another device model;
- using expired test strips;
- non-compliance with the temperature regime when collecting a portion of plasma;
- excessive or insufficient amount of blood for testing;
- contamination of test strips and hands;
- penetration of the disinfectant solution into the plasma;
- the device was not;
- non-compliance with the storage conditions of the test strips (low or high temperature, not tightly closed bottle).
To check the accuracy of the result, it is recommended to retake the test at the laboratory.
How long to wait for answers, interpretation of results
The glucose level is used to determine the increase/decrease in its concentration in tests. Deviation of numerical indicators indicates the presence of pathology. The result of the test strips is assessed by its color. The color meaning is described in the instructions. If there are deviations in pregnant women, the necessary therapy is determined by an endocrinologist.
When tested in a laboratory, results can be obtained within 8 hours. In case of urgent request, they are issued 2-3 hours after delivery. Using test strips, the result is determined 5 minutes after the procedure.
Contraindications for the test
- all acute infectious diseases;
- myocardial infarction, stroke;
- disturbance of electrolyte metabolism;
- exacerbation of chronic pathologies;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- diseases of the endocrine system: pheochromocytoma, acromegaly, Cushing's syndrome and disease, thyrotoxicosis (the body has increased levels of hormones that increase the amount of sugar in the blood);
- intestinal diseases with severe malabsorption;
- condition after gastrectomy;
- taking medications that change the glucose level in a blood test.
Normalization of glucose levels at elevated levels
If the glucose concentration in the tests increases, a complex of therapy is prescribed by the endocrinologist. Taking into account the woman’s position, gentle therapy is selected. It consists of taking medications, using folk remedies and following a diet.
Drugs for pregnant women
During pregnancy, insulin is used to reduce sugar levels. It is harmless to mother and child and allows you to quickly normalize glucose concentration.
The drug is administered intramuscularly using a pen syringe. The dosage is selected taking into account the amount of glucose in the analysis. To do this, you need to purchase a glucometer. The measurement is taken after waking up, before eating and 2 hours after eating. And also before bed.
The use of glucose-lowering tablets is prohibited. They disrupt the formation and development of the fetus. The rules for using the glucometer and calculating the dosage are explained by the treating specialist.
Folk remedies
You can normalize the concentration of sugar by using folk decoctions and infusions.
Recommended recipes:
- infusion of white mulberry bark and leaves. You need to place the prepared mixture (40 g) in 400 ml of boiling water. After 2 hours you can use it. The infusion is divided into 3-4 doses and drunk during the day;
- A decoction of unpeeled oats. Boil 20 g of oats in 300 ml of water for 15 minutes. The decoction should be drunk throughout the day. Consume before meals;
- Decoction of blueberry leaves. Place 20 g of crushed leaves in 200 ml of boiling water and cook for 4 minutes. The product is divided into 2 doses. Consume before meals;
- Infusion of bay leaf. Place 10 laurel leaves in 200 ml of boiling water and leave for 24 hours in a thermos. Consume before meals. The serving is divided into 4 doses;
- Tea made from dry or fresh currant leaves. Steam like regular tea. Drink no more than 300 ml of this tea during the day.
When selecting products, it is necessary to take into account the likelihood of allergic reactions. And also some decoctions may have a diuretic effect, which is not desirable for a pregnant woman. It is recommended to discuss the choice of funds with a specialist.
Diet
The glucose level in pregnant women depends on the diet. Diet is a necessary condition for maintaining sugar in the required concentration. Meals should be in small portions and at regular intervals.
A woman should eat in portions, but not overeat. Lack or excess of food provokes changes in sugar in the body. A light dinner before bed is required. It is recommended to create a menu together with an endocrinologist for a week.
A pregnant woman's diet should consist of the following products:
- meat (beef, poultry);
- fish and other seafood;
- non-sweet dairy products;
- nuts, but in limited quantities;
- vegetables and fruits in any form.
Quickly digestible carbohydrates and sweet foods are excluded from the menu. The drinking regime is also limited to 2 liters per day. Fatty, salty and spicy foods are excluded, as they increase thirst.
Deviations from the norm and risk group
First of all, it should be noted that there is no need to panic due to deviations, especially minor ones. They can be caused by metabolic characteristics or even such little things as a mild cold, poor sleep, walking, and the like. In each specific case, only a doctor can tell whether there is a problem.
Risk group
Expectant mothers who are at risk for diabetes should approach this issue with particular caution. Signs include the following factors: . hereditary tendency to diabetes; obesity, excess weight before pregnancy; infectious or viral diseases during pregnancy; age over 30-35 years, especially if this is the first conception; hormonal treatment for infertility; stillbirths and previous miscarriages; the birth of children who are too large, children with developmental defects; polyhydramnios.
- hereditary tendency to diabetes;
- obesity, excess weight before pregnancy;
- infectious or viral diseases during pregnancy;
- age over 30-35 years, especially if this is the first conception;
- hormonal treatment for infertility;
- stillbirths and previous miscarriages;
- the birth of children who are too large, children with developmental defects;
- polyhydramnios.
If you are at risk, it is advisable, among other things, to check your glucose level monthly. You can purchase a glucometer to do this yourself at home and be able to detect changes in time.
You should also visit your doctor unscheduled if you notice the following signs:
- increased AT;
- bad breath;
- sour metallic taste;
- changes in appetite, including constant feeling of hunger;
- weight gain;
- increased thirst;
- increased frequency of urination;
- dry mouth;
- general weakness.
If the indicators are not normal
If the result is positive, you need to undergo a repeat test, and if it also indicates elevated sugar levels, a glucose tolerance test is prescribed earlier than usual. In addition, until the middle of the term, it is indicated for those who are at risk.
If the GTT result shows a glucose level from 7.8 to 11.1 mmol/l, then sensitivity to it is increased. A level that exceeds 11.1 mmol/l is the basis for a preliminary diagnosis of diabetes.
Gestational diabetes in expectant mothers is relatively common, and this phenomenon is temporary; it goes away after childbirth. However, there is a risk that it will develop into true diabetes.
A decrease in sugar levels is much less common, and is mainly caused by too long breaks between meals, very small portions of low-calorie foods. To avoid sudden changes, you need to limit the amount of simple carbohydrates you consume (baked goods made from white flour, sweets, soda) and eat such foods with something unsweetened. With a strong decrease in the amount of glucose in the blood, very toxic ketone bodies are formed, therefore, in no case should you neglect proper nutrition; if you cannot eat on time, you should at least have a snack with candy to maintain your sugar level.
A pregnant woman is responsible not only for herself, but also for her baby, therefore it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the body so as not to inherit diabetes mellitus to the child. The main thing that is required from a woman is to take responsibility for her health, listen to doctors and undergo prescribed examinations on time and correctly.
How to increase your glucose levels when your levels are low
A reduced glucose level is also restored through the use of medications, folk remedies and following the prescribed diet.
Drugs for pregnant women
To raise glucose levels, oral glucose intake is necessary. Other medications are prohibited. If there is a strong decrease, it is recommended to administer the solution intravenously. It is recommended to use a glucometer to control your sugar. You can check with your endocrinologist about the rules for its use.
Folk remedies
If the glucose level in pregnant women decreases, it can be restored using folk recipes.
Recommended and proven recipes:
- a decoction of rose hips, oregano and lavender. To prepare, take 200 ml of boiling water, 50 g of rose hips and 15 g of oregano and lavender. Consume after 2 hours. The drink can be divided into 2 doses or consumed at once;
- freshly squeezed potato juice 100 ml. consume immediately. Recommended for use in the evening;
- a mixture of honey and onion juice in a ratio of 3:1. Take 10 ml before meals;
- eating viburnum with honey (mix in equal proportions). Take 10 g before meals.
The use of folk remedies is discussed with the treating specialist.
Diet
To increase glucose, it is recommended to take food at certain times, in small portions. A woman must eat. Long breaks between meals are prohibited. If the indicator sharply decreases, it is recommended to consume a piece of chocolate, candy or refined sugar.
The basics of the diet should be:
- porridges made from coarse cereals;
- vegetables and fruits in any form;
- lean meat and fish;
- eggs and low-fat milk products.
Sweets and quickly digestible carbohydrates are excluded . Their use is allowed when you need to quickly increase your glucose concentration. Regular use will only lower the rate.
How the research is carried out
The first blood sample is taken on an empty stomach in the morning. Next, immediately drink a solution consisting of 75 g of glucose powder and 300 ml of water within a few minutes. You need to prepare it at home in advance and bring it with you. Glucose tablets can be purchased at the pharmacy. It is very important to make the right concentration, otherwise the rate of glucose absorption will change, which will affect the results. Also, you cannot use sugar instead of glucose for the solution. Smoking is prohibited during the test. After 2 hours, the analysis is repeated.
Prognosis for pregnant woman and child
Pregnant women are under constant supervision by a gynecologist and undergo regular tests. Therefore, deviations are detected in a timely manner. If you follow the recommendations of a specialist, pathologies do not have time to harm the child and mother. After childbirth, sugar levels in urine and blood return to normal.
If a pregnant woman is not registered with a specialist, then deviations from the norm may be detected late. As a result, a miscarriage or impaired fetal development may occur. Without therapy, the disease will become chronic, since the glucose level does not normalize on its own.
Author: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Frequently asked questions to the doctor
Insulin injections are not always necessary
Sugar has increased
Hello, my name is Elizaveta. Recently, fasting blood sugar was found to be 5 7 during pregnancy. The doctor said it was gestational diabetes and mentioned that I would probably need to take insulin for the rest of my life. I'm scared, I want to do without injections!
Hello, Elizaveta. No need to panic. You will need insulin if you cannot bring your glucose levels to normal on your own. It is necessary to follow a strict diet, move actively, and listen to the doctor. Then you may not need insulin injections.
Did the syrup have an effect?
Stress can affect test results
Hello, my name is Maria. Yesterday I donated blood for sugar, the result was 5.0 mmol/l. They sent me to a local therapist, and I found myself at risk for HD. Where does blood sugar come from if everything was normal before? I eat healthy and don’t overuse unhealthy foods. Could taking children's Nurofen at night or stress the day before affect the test result?
Hello Maria. Your result is acceptable for pregnancy, do not worry too much. It’s better to re-donate blood after being prepared: don’t be nervous, don’t eat in the morning. It is likely that the factors listed above increased the result.
Symptoms of problems
Deviation from normal values is accompanied by the manifestation of symptoms characteristic of normal diabetes. Attention should be paid to symptoms such as:
- significant increase in appetite;
- constant thirst;
- frequent urge to empty the bladder;
- general weakness, fatigue, drowsiness;
- instability of blood pressure.
It is not possible to confirm the presence of diabetes solely based on these signs, since they are natural for the state of pregnancy.
A diagnosis can only be made after a test that detects the amount of glucose in the blood.