You are here: Blood test -
Leukocytes in the blood -
Leukocytes in the blood during pregnancy
- Norm and reasons for deviation
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention and prognosis
Leukocytes in the blood during pregnancy is the number of white blood cells contained in the main biological fluid of a person. During this period, the concentration of these substances increases, which is normal. However, rates can rise and fall due to the influence of someone's disease.
Changes are often provoked by disorders such as purulent, infectious, viral, inflammatory and oncological processes. This can also be affected by irrational medication use and stressful situations.
Both high and low leukocytes in pregnant women make themselves known through the expression of characteristic signs. However, they can be mistaken for toxicosis or are often hidden behind the symptoms of the underlying disease.
A general clinical blood test will help determine the concentration of white blood cells, but this is not enough to determine the primary source. To establish the cause, a comprehensive examination of the body is necessary.
Low or high leukocytes during pregnancy can be corrected only by conservative therapeutic methods. It is worth noting that their use will be ineffective in the complete absence of treatment of the underlying disease.
Brief information about leukocytes and their position in blood tests
During analysis, blood is divided into liquid plasma and formed elements - the cellular part of the blood, including:
- Red cells are red blood cells (RBCs). They transport hemoglobin through the bloodstream, provide the body with oxygen, and regulate the acid-base composition of the blood (ABC).
- Blood platelets - platelets (PLT). Responsible for blood clotting.
- White (colorless) cells are leukocytes (WBC). They protect the body from viruses, bacteria, parasites, and allergens.
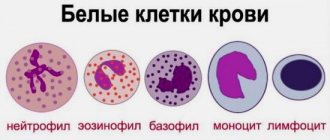
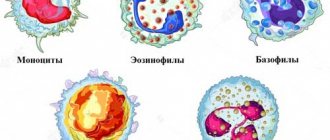
Leukocytes in the blood are represented by several types of cells, each of which performs its own function:
- lymphocytes (LYM) – provide the immune system’s response to invading bacteria and viruses;
- neutrophils (NEU) - divided into band and segmented, neutralize infections and viruses that have entered the body;
- monocytes (MON) – produce interferon, participate in tissue regeneration, inhibit the activity of cancer cells;
- eosinophils (EOS) - responsible for differentiation and destruction of parasites;
- basophils (BAS) - responsible for allergic reactions.
All groups of leukocytes interact with each other. From the meaning and ratio in the analysis it is represented by a leukogram, otherwise - by the leukocyte formula.
Signs and symptoms of increased
As a rule, leukocytosis does not manifest itself in any way, but if you pay close attention to your own well-being, the pregnant woman will notice some alarm bells indicating a high content of white blood cells.
- Fatigue, severe weakness and hypersweating may appear, and some may develop a fever.
- Sometimes, against the background of leukocytosis, bruises, bruises, and subcutaneous hemorrhages may appear, although the patient has not injured these areas of the body.
- At times, fainting, dizziness, and difficulty breathing are also troubling.
- Almost everyone has a lack of appetite, which can sometimes even manifest itself as an aversion to food.
- Sometimes patients experience a slight decrease in visual acuity, sleep disturbances, myalgia or arthralgia.
The most dangerous reactions for a patient in this position are considered to be hyperthermic reactions, which indicate the development of an infectious and inflammatory pathology in the mother’s body.
Normal indicators
In the laboratory, white blood cells are measured as the number of cells per ml of blood multiplied by a billion (10^9/L). In a leukogram, the ratio of formula varieties can be indicated both in quantitative equivalent and in percentage (%). For non-pregnant women, reference WBC values are 4-9 (*10^9/L).
Normal parameters of the leukocyte formula
| LYM | NEU (band/segmented) | MON | EOS | BAS |
| 19,4-37,4 % | 1,0-6,1 / 46,8-66,0 % | 3,0-11,0 % | 0,5-1,0 % | 0,1-1,0 % |
An elevated leukocyte level is called leukocytosis, and a low leukocyte count is called leukopenia.
Is it possible to recognize the disease on your own?
In pregnant women, the transformation of the body when leukocytosis appears does not always have sharp, distinct forms. Sometimes her general condition is characterized by specific points typical for a pregnant body:
- Manifestations of general weakness.
- Dizziness.
- Nausea, etc.
Therefore, many women treat such manifestations without much fear, considering them traditional for future mothers. It is extremely difficult to independently determine leukocytosis - only those pregnant women who are experienced in medicine can do this. Therefore, periodic examinations and examinations by a gynecologist should become a firm and unwavering rule for pregnant women.
Reference values for pregnant women
In early pregnancy, leukocyte counts should not seriously deviate from the general norm. Acceptable values are 6.8-7.4 (*10^9/l). The general leukogram also changes slightly:
| LYM | NEU | MON | EOS | BAS |
| 27-29% | 68% | 3-6% | 1,5-1,6% | 0 |
From the second half of the perinatal period, the norm of leukocytes in the blood of pregnant women increases. The body mobilizes, protecting the woman and the fetus from negative influences.
The production of leukocyte cells increases in response to any threat - viruses, bacteria, excessive exercise, stress. In the second trimester, up to 11-12 (*10^9/l) inclusive is considered normal, in the third trimester – up to 14-15 (*10^9/l).
Reference leukogram values
| Term | LYM | NEU | MON | EOS | BAS |
| 2nd trimester | 25-27% | 67% | 4-6% | 2% | 0 |
| 3rd trimester | 25-27% | 64% | 4-5% | 1,2% | 0 |
A consistent slight increase in leukocytes corresponds to an increase in the perinatal period. The body is preparing for serious stress - childbirth, so the production of protective cells is activated. In the absence of pathologies and complications, immediately before birth, a reading of 20(*10^9/l) is considered normal.
Important! An increase in the concentration of leukocytes may be associated with overeating on the eve of blood donation, eating immediately before the procedure, and other non-pathological reasons.
Urine analysis during pregnancy: rules for taking the test
A urine test is required during pregnancy and must be taken before each visit to the gynecologist, i.e. in the first trimester, a woman takes the test once every 3-4 weeks, in the second - once every 2 weeks, then until the end of pregnancy the woman takes it once a week.
Urine analysis for a pregnant woman
In order for a urine test to give reliable results, it must be collected correctly:
- Before taking the test, you need to perform hygiene of the external genitalia
- The entrance to the vagina must be covered with a cotton swab or tampon so that the discharge does not spoil the analysis
- the sampling is done in a sterile container, which can be purchased at a pharmacy
- the first urine is passed, the middle portion is collected
- no later than 1.5 hours after urine collection, it must be delivered to the laboratory
If the urine test is bad, the doctor will ask you to retake it in case it was collected incorrectly and this affected the results.
How to properly prepare for the UAC?
In order for the test results to be objective, on the eve of blood sampling, a woman should:
- eliminate fatty foods from the menu, limit the consumption of protein foods;
- observe a fasting regime of 8-10 hours;
- get a full night's sleep;
- reduce physical activity.
Nervous tension and psycho-emotional overload can lead to a temporary increase in white blood cells. Before the blood donation procedure, a woman is advised to avoid anxiety.
How to treat
To treat leukocytosis, you need to contact a gynecologist who is managing your pregnancy. He will conduct an examination, prescribe tests, and only then will he be able to select the most effective therapy. In complex clinical situations, when an increase in leukocyte cells is present directly in the bloodstream, the patient may be referred for consultation to a hematologist.
The main goal of therapy is to eliminate the root cause of leukocytosis; only after this can successful normalization of leukocyte concentration be possible.
Medication
Drug therapy is usually complex, but all prescribed drugs must be safe for the fetus and mother.
Given the variety of etiological factors, it is not always possible to select an absolutely safe therapy. But if we take into account the likely threat posed by leukocytosis, the consequences of the pathology can be much more dangerous than treatment with medications. Sometimes situations arise when the doctor insists on an urgent termination of pregnancy in order to save the life of the mother herself.
Antibiotics are usually prescribed to eliminate leukocytosis. If the pathology is caused by taking certain medications, then you must immediately stop taking them and replace them with other medications. The treatment program may also include antacid drugs, corticosteroids, cardioprotectors and hepatoprotectors, medications to maintain renal and gastrointestinal activity. In severe cases, blood purification from excess leukocytes through leukopheresis is prescribed.
Diet
You need to carefully monitor your well-being
If leukocytosis in a pregnant woman is physiological in nature, then patients are advised to reconsider their daily routine, eliminate any stress and psychological overload, and emotional experiences. It is also important to review your diet. Experts have identified a list of specific products that provoke a short-term increase in leukocyte levels. Therefore, pregnant women need to limit the consumption of such products to reasonable limits, especially in cases where the content of white cells in the blood is already increased.
And to normalize the leukocyte level, pregnant patients are recommended to eat offal and fish, seafood and lean meat, fermented milk products and cereals (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal), freshly squeezed grape, carrot or pomegranate juice, and fruits.
Folk remedies
There are many folk recipes that help normalize the content of white blood cells. One such remedy is an oat milk drink. To prepare a medicinal drink, you need to clean and thoroughly rinse the oat grains. Then fill the pan halfway with oats and add milk to the brim. Place the pan on low heat and cook for about 20-30 minutes. Take this remedy instead of water for several days.
Lime-chamomile decoction is also effective in reducing leukocyte levels. To prepare it, you need to grind chamomile and linden until smooth, take two large spoons of the herb and pour a glass of boiling water. Place the mixture on the fire and cook after boiling for 10 minutes. Then filter and drink 2-3 cups per day, like tea. Any, even the safest folk remedy can become a threat during pregnancy, so you must first discuss the likelihood of using this remedy with your doctor.
Physiological causes of an increase in leukocyte cells in the blood
Leukocytosis during pregnancy is provoked by two factors: physiological and pathological. The first factor includes reasons not related to disruption of internal organs and serious diseases.
For physiological reasons there are:
- Myogenic leukocytosis. Sports (physical) loads that are not appropriate for a woman’s position increase the amount of all blood elements.
- Emotionogenic leukocytosis. Psycho-emotional instability caused by changes in hormonal status. Pregnant women are susceptible to stress for any reason.
- Adhydremic leukocytosis. Prolonged stay in a stuffy, warm room, in the heat, or in a bath (sauna) causes hyperhidrosis (increased sweating). Trying to protect itself from overheating and dehydration (dehydration), the body begins to produce more leukocyte cells.
- Dietary leukocytosis. Predominance of meat products in the diet.
Other physiological causes may include smoking and medications, but it is assumed that this is not relevant for pregnant women.
Treatment of leukocytes during pregnancy
Most of the diseases listed above are dangerous for both the mother and the fetus, so it is very important to detect the problem in time and begin treatment as early as possible.
Treatment of pregnant women is somewhat more difficult due to their situation, because not every drug can be taken during pregnancy due to their negative effect on the development of the fetus.
Treatment of leukocytes during pregnancy
But not getting treatment at all is also not an option, because... Most diseases can provoke miscarriage, premature birth, defects in fetal development, and the presence of chronic diseases. Therefore, the expectant mother should undergo treatment under the strict supervision of a doctor.
Timely and qualified treatment, as well as constant monitoring by a doctor, will allow the pregnant woman to enjoy the happiest time of her life.
Pathological factors
A pathologically elevated level of leukocytes is a consequence of inflammatory processes or dysfunction of the bone marrow in the production of white blood cells. Inflammation can affect any organs and systems:
- local damage to tissues and cells;
- systemic disease;
- ARVI and colds;
- infections;
- exacerbation of existing chronic pathology.
When assessing indicators, the doctor focuses on the symptoms presented by the patient. Violation of the production of formed elements in the blood may be associated with the development of oncohematological diseases (cancerous lesions of the circulatory and lymphatic systems) and other malignant neoplasms.
Absolute leukocytosis is an increase in the levels of all types of leukocyte cells, characteristic of acute inflammation, septic and purulent processes. In accordance with complaints of malaise in a pregnant woman, one can assume:
- inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes (salpingoophoritis);
- diseases of the bronchopulmonary system – pneumonia, bronchitis;
- ENT diseases - laryngitis, sore throat, pharyngitis, rhinitis, etc.;
- intestinal infections and parasitic infestations;
- infection with herpes virus, influenza, chickenpox, Koch's bacillus (tuberculosis);
- sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis);
- inflammation of the renal apparatus (glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis);
- inflammation of the walls of the bladder and urethra (cystitis, urethritis).
The number of leukocytes increases sharply in acute conditions - appendicitis, peritonitis, sepsis, abscess (suppuration) of soft tissues.
Types of pathological leukocytosis
When assessing a leukogram, the doctor determines which types of white cells are high and which are low. Based on the general leukocyte picture, he makes a diagnosis or refers the woman for further examination.
Types of leukocytosis:
- Neutrophilia. Band neutrophils are immature white blood elements. Their increase, in most cases, means psychophysical overload. A consistently high level indicates the development of cancer. In clinical medicine, a bias towards band neutrophils is called a “shift of the leukocyte formula to the left.” Segmented neutrophils are mature leukocytes of “pre-retirement age”; their increase is interpreted as a shift of the leukogram to the right and means cellular aging of the body, depletion of bone marrow resources. General neutrophilia is characteristic of acute infectious processes caused by staphylococcus and streptococcus bacteria, and purulent inflammations of different locations.
- Eosinophilia. The concentration of eosinophils increases during parasitic infestations and allergic reactions. In case of leukocytosis with a predominance of eosinophils, it is necessary to check for worms and protozoal infections. The cause of allergies may be the development of bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis.
- Monocytosis. If a blood test reveals many monocytes, the development of complex infectious diseases should be suspected: tuberculosis, infectious mononucleosis, brucellosis, typhus or typhoid fever. Monocytosis is characteristic of syphilis, oncohematological diseases, autoimmune pathologies (lupus erythematosus, type 1 diabetes mellitus).
- Lymphocytosis. High levels of lymphocytes are observed in bacterial and viral infections, burns and injuries, cyanocobalamin deficiency (vitamin B12 deficiency).
- Basophilia. Characteristic of parasitic diseases and allergic reactions. If worms are not detected and there is no allergy, chronically elevated basophils indicate the development of cancer processes (usually in the lymphatic system).
Leukocytosis is not a disease, but a clinical diagnostic indicator of a violation of biochemical processes. To reduce leukocytes, it is necessary to know exactly the reason for their active production. It is not leukocytosis that needs to be treated, but the disease that provoked the blood disorder.
Leukocytes - what are they?
Leukocytes are white blood cells of different sizes and shapes that protect the body from aggressive attacks. The content of leukocyte cells is constantly changing, which is influenced by various factors such as stress, errors in diet, pathological conditions, etc.
- Based on the content of leukocytes, you can understand the state of the body’s immune defense. After all, it is leukocytes that protect against infectious, viral and other attacks on the body; they help the body to function normally.
- If there is frequent stress in the patient’s life, he eats poorly, does hard physical work or plays sports professionally, or often experiences some kind of conflict situations, then the leukocyte count increases sharply.
- If such situations occur almost constantly, then the increase in such blood cells can become pathological and leukocytosis occurs.
- Infectious lesions of bacterial or viral origin, purulent or inflammatory processes, internal bleeding and other pathological conditions are always accompanied by an increase in leukocyte concentration in the bloodstream.
Therefore, it is important to monitor such indicators, especially in pregnant women, because it is extremely important for mothers to maintain normal health during pregnancy. To establish the exact causes of such changes, diagnostic laboratory tests are prescribed, based on the results of which the doctor selects the necessary treatment tactics.
Finding the problem
If the number of white cells in the blood is abnormal, OKA must be repeated. Perhaps the woman did not follow the preparation rules and was very nervous before the blood draw. Consistently high rates require unscheduled screening of the pregnant woman, including:
Reduced protein in the blood during pregnancy
- blood biochemistry and coagulogram;
- flora smear;
- general urine analysis;
- blood tests for alphafetoprotein (AFP protein), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), free estriol (EC);
- fetal ultrasound.
If there is insufficient information, additional diagnostic measures are prescribed:
- urine tests (according to Nechiporenko, daily diuresis, etc.);
- coprogram;
- ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and kidneys;
- blood tests for tumor markers, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA);
- Dopplerography (assessment of the condition of blood vessels).
If pathology is detected, a course of conservative therapy is carried out. If the disease threatens premature birth or spontaneous termination of pregnancy (miscarriage), the woman is hospitalized in the antenatal department. It is possible to lower the leukocyte level only by eliminating the cause of the disorder.
Elevated leukocytes in a smear during pregnancy: causes
A smear is taken for analysis at least twice during the entire pregnancy. Among other substances, the laboratory assistant determines the number of leukocytes under a microscope. If the number of leukocytes is higher than the established norm, this indicates the presence of inflammation or some kind of infection.
The more leukocytes found in the smear, the more serious the disease, and the more dangerous it is for the pregnant woman and the fetus. An increased number of leukocytes acts as a beacon - it indicates the presence of the disease, but to determine the focus, the woman will need to undergo additional examinations and tests, for example, PCR, bacteriological culture, etc.
Flora smear during pregnancy. Norm of leukocytes in a smear
We should draw your attention to the fact that it is not necessary for a woman to become ill with a discovered disease during pregnancy; it quite often happens that the disease has been in the body for a long time, but it was in a latent form, and during the period of bearing a child, when the load on the body increased, it became more active and determined by elevated white blood cells found in the smear.
An increase in the number of leukocytes above normal may indicate the following diseases:
- candidiasis
- vaginosis
- colpitis
- sexually transmitted diseases (more than 20 infections)
- and other diseases
Treatment of the cause of an increased level of leukocytes in a smear is prescribed by the doctor individually for each pregnant woman, depending on the duration of pregnancy, the stage of the disease and the sensitivity of the pathogen to certain drugs.
If the source of the disease is not found or local treatment does not give positive results, perhaps the expectant mother will be prescribed a course of antibiotics, the use of which should not be neglected, because infected genital tracts are very dangerous for the baby and can cause premature birth. In addition, during childbirth the child will need to go through them, so it is imperative to treat the cause of the increased number of white blood cells as soon as possible.
Elimination of physiological leukocytosis
If elevated leukocytes in the blood during pregnancy are a consequence of physiological reasons, the woman should correct:
- Diet. Partially replace meat dishes with vegetables, fruits, dairy products, and mushrooms.
- Work and rest schedule. Spend more time outdoors, be sure to get enough sleep.
- Temperature conditions. Do not overheat or overcool the body.
- Physical activity. Do not overexert yourself during sports activities and physical education for pregnant women. If possible, swim regularly in a pool (sea, lake, etc.).
- Psycho-emotional state. In consultation with your gynecologist, regularly drink herbal soothing infusions. If necessary, you can contact a psychotherapist.
To increase immune strength, the doctor will prescribe a course of vitamin therapy.
Compliance with the daily routine of a pregnant woman helps to normalize blood counts
Prevention
A healthy lifestyle during pregnancy is a necessity
The main prevention is for a pregnant woman to follow a healthy lifestyle and nutritious diet. It is also necessary to monitor the condition of the body and promptly identify violations by conducting regular tests on a schedule, without skipping them.
A disturbance in the composition of the blood during pregnancy is a serious signal that cannot be ignored.
In most cases, timely detection of deviations from the norm allows treatment to be carried out as safely as possible for the fetus. The YouTube ID of q2HWM2—FO8 is invalid.
Results
A slight increase in white blood cells during the perinatal period is not abnormal. The body tries to protect the woman and child from possible infections, stress, allergies, and therefore produces more white blood cells. If there are significant changes in the leukogram, it is necessary to find out why the violations occurred.
Pathological causes of leukocytosis are inflammatory, infectious, and oncological diseases that require treatment by a specialist. If physiological factors influence the increase in the concentration of leukocytes, it is necessary to change eating habits, review the work and rest schedule, and reduce physical activity.
The number of leukocytes in a smear during pregnancy: normal
A smear is taken for analysis from a pregnant woman at least 2 times:
- upon registration
- at 30 weeks
If any of the indicators were not normal, smears are taken several more times.
Leukocytes in a smear during pregnancy under a microscope
In a pregnant woman, the normal number of leukocytes in a smear is 10-20 units. If it is elevated, the woman will be prescribed additional tests to determine the cause of their increase and the source of the disease.
Treatment of pyelonephritis in pregnant women
Based on the results of the examinations, drug treatment is prescribed, taking into account all contraindications for the pregnant woman and the fetus: the gynecologist or nephrologist chooses the safest, least toxic drugs, taking into account their effect on the fetus.
Therefore, under no circumstances should you self-medicate, even if you carefully read the instructions. Only a doctor can select the right drug during pregnancy, taking into account the objective condition of the pregnant woman and the fetus, indications and all contraindications.
In pregnant women, the use of antibiotics is contraindicated throughout their entire pregnancy. Fluoroquinolones may be used. Also assigned:
- in the first trimester of pregnancy - semi-synthetic penicillins;
- in the second - third - you can add macrolides (erythromycin is not recommended, since it increases stone formation), cephalosporins.
Pyelonephritis as a cause of leukocyturia
For pregnant women, the development of pyelonephritis, an inflammatory kidney disease of an infectious nature, is especially dangerous. With pyelonephritis, the pathological process involves the glomeruli, renal pelvis, parenchyma, and tubular apparatus. Among pregnant women, 2-8% of women suffer from pyelonephritis. This is one of the main reasons for high blood pressure in women.
During pregnancy, there are many risk factors for the development of the disease:
- changes in a woman’s hormonal levels;
- pressure from the pregnant uterus on the bladder, which leads to the development of reflux of urine from the bladder to the kidneys;
- impaired innervation of the bladder with existing concomitant diseases (diabetes mellitus, damage to the nervous system)
In the presence of diabetes mellitus, the course of pyelonephritis can be complicated by urosepsis, the development of calciuria and result in death.