The onset of pregnancy, the period of intrauterine development of a child, is associated with significant changes in the functioning of the female body. It begins to function in a new way - a physiological restructuring of the internal organs occurs, the load on them increases, hormonal levels and blood composition change.
To understand what is happening with the pregnant patient and the developing fetus, doctors give directions for diagnostic, screening procedures and clinical tests - CBC, analysis for hCG and fibrinogen, determine the blood type and Rh factor, and conduct other studies. No less important is a biochemical blood test; deciphering its values in pregnant women is one of the accurate and informative ways to obtain data on their health status.
Biochemical blood test during pregnancy
A biochemical blood test during pregnancy is a mandatory laboratory procedure that must be performed regularly while carrying a baby.
The data from such a test are intended to monitor the condition of the body, but they will also be able to identify the course of any disease or the formation of complications even in the early stages of their progression, that is, long before the first signs appear. A hematologist interprets the results. Since the normal values of one or another indicator of the main biological fluid of the human body differ from similar values in healthy people, the clinician uses a special form, which he checks with during decoding.
Normal indicators of biochemical blood tests in women during pregnancy can deviate both upward and downward. In almost all situations, this indicates the progression of some disease that can pose a danger not only to the expectant mother, but also to the unborn baby.
In rare cases, the norm may be violated due to:
- irrational use of medications;
- poor nutrition;
- severe physical fatigue.
Blood biochemistry in a pregnant woman involves the study of venous biological material. This process has its own sequence of actions. It should be noted that in order to obtain the most reliable results, it is necessary to prepare for the analysis.
LHC for representatives of the weaker half of humanity has the following indications for implementation:
- control over the woman’s condition during clinical observation;
- assessment of the course of pregnancy;
- identifying complications and determining the effectiveness of their treatment;
- monitoring the course of concomitant diseases.
The entire blood sampling process takes no more than 5 minutes, and deciphering the results takes from 1 to 2 days.
Tests in the maternity hospital
If you have contractions and you arrive at the maternity hospital, no one will leave you alone either. First of all, you will be examined for cervical dilatation (how many centimeters is the opening). This will show how soon you will see your baby and how long you will have to endure the contractions. Depending on your indications, you may need to take the OAC again. If during contractions fluid is released from your vagina, it will also be taken for analysis, establishing almost on the spot what kind of fluid it is (to exclude the possibility of leakage of amniotic fluid).
After this, you, together with a friendly team of doctors, will wait for the start of labor; you don’t need any more tests, all that’s left is to give birth.
Normal values for pregnant women
The norms for biochemical blood tests in pregnant women will differ depending on the period of intrauterine development of the fetus. The age category does not play a decisive role.
As mentioned above, there is an official BAC form that is used in every medical institution.
The table below most accurately reflects the acceptable indicators:
Normal during pregnancy
It follows that a biochemical blood test in pregnant women includes the following substances:
- proteins and enzymes;
- lipids and pigments;
- carbohydrates and vitamins;
- indicators of nitrogen metabolism;
- wide range of microelements.
Causes and danger of hCG deviation
If the results of a laboratory blood test for the level of human chorionic gonadotropin are within acceptable limits, then the pregnancy is developing well and the unborn baby is not in danger.
In some cases, the analysis shows a deviation up or down.
A low concentration of hCG in the blood may indicate a pathological course of pregnancy, including:
| Cause | Features of development |
| Threat of spontaneous miscarriage | At risk are women in early pregnancy and hCG levels reduced by 50% or more. In most cases, hospitalization is necessary. |
| Ectopic embryo attachment | In this case, the woman herself is at risk. Pathology is fraught with rupture of the fallopian tube. |
| Frozen (non-developing) fetus | Often occurs with serious congenital abnormalities that are incompatible with the further development and life of the embryo. |
| Incorrect gestational age | If the monthly cycle is not regular, then it is not always possible to establish the exact date without additional examination (ultrasound, repeat analysis). |
| Placental insufficiency (chronic) | May threaten fetal developmental delays. |
| Congenital pathology | Edwards syndrome. |
| True post-term pregnancy | Associated with various maternal diseases (history of endocrine and gynecological pathologies). A pregnant woman should be under constant medical supervision. |
Read: How to thin thick blood: medications and recipes
Useful video about hCG blood test:
An increased level of the hormone-protein also signals possible problems, which include:
- Carrying two or more fetuses (the most pleasant cause of elevated hCG). The values increase in proportion to the number of embryos.
- Early manifestation of toxicosis or gestosis (late toxicosis).
- Down syndrome.
- Post-term pregnancy.
- Increased blood glucose (sugar) levels, diabetes.
- Inappropriate gestational age.
In men and non-pregnant women, an increased level of hCG may indicate diseases of the reproductive system, hydatidiform mole, chorionic carcinoma, and oncology of the gastrointestinal tract. After a medical or spontaneous abortion, hormone levels will remain elevated for some time.
Preparing for the LHC
When deciphering the results of a biochemical blood study, a hematologist may receive distorted data. This is explained by the fact that the patient was incorrectly prepared for such a diagnostic test or completely ignored the following measures:
- Refusal to eat food 12 hours before taking biological fluid (only purified water without gas is allowed to drink).
- The day before the test, you should avoid drinking strong green or black tea.
- Maintain a gentle diet for 3 days before visiting a medical facility. You need to minimize your consumption or completely avoid fatty, fried and spicy foods.
- The day before blood biochemistry, it is necessary to reduce physical activity.
- Refusal to take medications several weeks before the expected date of the clinic visit. If for any reason this cannot be done, then you need to inform the hematologist about this.
- On the day of the diagnostic test, the influence of stressful situations, emotional arousal and nervous tension should be excluded.
About 10 minutes before visiting the doctor, the woman needs to sit down and calm down. This is necessary to normalize breathing and heart rate.
If these rules are not followed, the study will need to be repeated, which is undesirable for pregnant women. However, if such a need arises, then the test must be taken in the same laboratory as the first time. This is due to the fact that biochemistry indicators differ slightly depending on the equipment of the medical institution.
How to prepare for the analysis?
A clinical analysis of blood biochemistry will be accurate if the patient takes into account the rules of preparation for it. The sample is taken from a vein and placed in a test tube; 10 ml of material is enough for study. The patient should not eat food before the procedure; the break should be at least 8 hours. “Morning” blood gives a reliable result, so it is recommended to donate it no later than ten o’clock in the morning. Before carrying out the manipulation, you are allowed to drink some clean water.
It is worth remembering that taking medications, fatty, salty, spicy or sweet foods can influence the result and distort it. An unstable emotional state, increased physical activity, smoking and alcoholic beverages that are clearly prohibited for pregnant women significantly distort the diagnostic result. Before the analysis, you need to rest well and get enough sleep.
When is it appointed?
The analysis is not considered integral, but is prescribed if the expectant mother has chronic diseases:
Depending on the signs and severity of the pathology, the range of parameters studied can increase.
In addition, biochemical study makes it possible to establish the degree of glucose.
The analysis may be needed for women who are obese or overweight, that is, those who are at risk of developing gestational diabetes.
How does hCG change during pregnancy?
Active secretion of the hormone-protein begins from the moment the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus and reaches its upper limit towards the end of the first trimester.
If the analysis is performed early (no more than 2 weeks from conception), the result may not exceed 25 mU/ml and the doctor will prescribe a repeat test a few days later to confirm pregnancy. If the fetus develops correctly, then the next result will show 156–4870 mU/ml, which corresponds to a short period of 2–3 weeks after fertilization.
Throughout pregnancy, a gynecologist monitors the development of the fetus based on the level of hCG concentration in the blood.
Depending on the period, this indicator changes values:
- For 3–4 weeks, the hormone norm should be in the range from 1100 to 31500 mU/ml.
- During the period from 6 to 7 weeks of pregnancy, the lower limit of hCG is 27,300 mU/ml, and the upper limit is 233,000 mU/ml. The maximum value of 20900–291000 mU/ml corresponds to a period of 7–11 weeks.
- In the second trimester, the amount of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood of a pregnant woman decreases. In the period from 10 to 13 weeks, it is necessary to undergo the first biochemical screening: a blood test for hCG and PAPP-A (protein). The hormone level during this period is at the level of 20,000–60,000 mU/ml. Deviations from the norm indicate possible congenital pathologies and require additional diagnostics.
- At weeks 22-24, hCG levels range from 10,000–35,000 mU/ml.
- At the beginning of the last trimester of pregnancy, the amount of “pregnancy hormone” in the blood continues to fall.
- Before birth, the concentration increases again and at 38-40 weeks reaches the highest values at 78,100 mU/ml.
It is difficult to independently understand the result of a blood test for the hormone-protein hCG. Each laboratory has its own limit values, which depend on the research method. The values depend on many factors and are individual for each woman expecting the birth of a child.
Preparation rules
Preparation for taking samples.
- On an empty stomach, the contents of sugar, creatinine, bilirubin, and lipid profile are studied.
- There is a 10-hour period between eating food and taking samples. Tea, sweet coffee, fresh juice are strictly prohibited. It is possible to drink water.
- Characteristics change throughout the day, for this reason it is recommended to take tests in the morning.
- The day before the collection, it is preferable to avoid physical stress.
- Stop drinking alcohol and change your diet and daily routine.
- If possible, avoid taking medications.
It is important not to become emotionally overexcited before the study.
What does this analysis show?
Doctors warn that compared to rapid tests, the study of blood serum is a much more informative study. The concentration of hCG in the blood exceeds the concentration of the hormone in the blood by almost 2 times, due to which the determination of pregnancy will be accurate. Depending on the concentration of hCG in the blood of a pregnant woman, the doctor will also be able to guess the period when conception occurred.
You will have to donate blood for hCG not only in the first weeks of pregnancy, but throughout the entire period of waiting for the baby, since this analysis helps to identify pathologies and abnormalities in the development of the fetus. The first screening is usually carried out from 11 to 14 weeks of pregnancy. Also at this stage, the plasma protein PAPP-A is examined and an ultrasound examination of the fetus is performed, which makes it possible to determine chromosomal abnormalities.
A secondary study is carried out during the period from 16 to 20 weeks of gestation. Based on the data obtained, it is possible to assess the likelihood of genetic abnormalities in the baby and prescribe further studies. If the concentration of chorionic hormone is deviated from the norm, this may indicate serious problems, including a frozen or ectopic pregnancy, an increased likelihood of miscarriage, or pathologies in the development of the fetus.
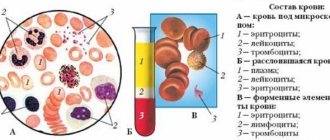
At an appointment with a specialist, women often want to find out whether a general blood test will determine pregnancy. It shows the following data:
- hemoglobin;
- blood cells (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets);
- hematocrit (volume of red blood cells in biological fluid);
- leukocyte formula (ratio of leukocytes by type);
- color index (number of red blood cells saturated with hemoglobin);
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate).
Increases and decreases in indicators are observed in various conditions and diseases. They may be influenced by physiological factors that resolve over time. One of them is pregnancy. Since it is not the only thing that affects these formations in the blood, the doctor cannot tell whether a woman is pregnant based only on the readings of a clinical blood test. Therefore, it is not true that a general blood test will show pregnancy before the delay.
Norms of indicators
Protein – characterizes protein metabolism, reflecting the number of proteins in plasma.
During pregnancy, the coefficient can decrease - 44-54 g/l to 52-72 g/l. Protein increases with increased blood density and lack of water due to its rapid loss. Lipids - cholesterol - the main indicator of lipid metabolism. A physical increase from 4.25-6.3 to 5.1-7.3 mmol/l is acceptable. It is explained by an increase in the formation of magmatic sterols secreted by the liver, which are necessary for the formation of blood vessels in the child and the placenta.
Research during registration
The very first test a woman encounters during pregnancy is a home pregnancy test from a pharmacy, which will show two characteristic lines after the first day of the delay. After such a primitive confirmation of conception, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a qualified gynecologist who will confirm the fact of pregnancy.
- If there are any doubts, the doctor will prescribe a blood test for the patient to determine the content of gonadotropic chorionic hormone, which can be performed as early as 8-14 days of expected conception. The levels of this hormonal substance at conception will exceed 25 mU/ml.
- Also, to determine pregnancy, you need to undergo ultrasound diagnostics, which can be performed as early as 3-6 days of delay. The fertilized egg with an embryo inside will be visible during ultrasound diagnostics at approximately 5-7 weeks; the heartbeat will also be heard at this period, but only during an intravaginal examination.
It is necessary to make a visit to the consultation for registration no later than 7-10 weeks. At the appointment, the doctor will create a card, indicating the necessary information about the pregnant woman, the beginning of sexual relations, the first and last menstruation, the duration of the cycle, etc. Two cards are created, individual and exchange, the first is kept by the doctor, and the second is given to the pregnant woman. The exchange card contains the results of all studies and tests that a woman undergoes during pregnancy. During the initial examination of a pregnant woman, the obstetrician-gynecologist takes smears and tells you which tests will need to be taken first during pregnancy, writing out the appropriate directions.
Decoding the results
Pregnant women should know the rules. If there are deviations, consult a doctor. Interpretation of a biochemical blood test in pregnant women:
Possible reasons for deviations
| Protein | 64 – 83 g/l | A decrease indicates insufficient dietary intake or excessive excretion, for example, in toxicosis with kidney damage. |
| Albumen | ||
| Globulin | 40-60 g/l | |
| Urea | 2.5 - 6.4 g/l | Urea in the blood is reduced during pregnancy and the value does not fit into the given standards, which means problems with the urinary system. |
| Cholesterol | An increase in cholesterol is typical during pregnancy. It is advisable to consult a doctor; in some cases, a detailed analysis is needed. | |
| Creatinine | 43 – 87 g/l | If creatinine is low during pregnancy, then there is impaired renal function. A significant increase can indicate a disruption in their work. Slight increase with excessive consumption of beef before donating blood. |
| ALT, AST | It must be remembered that differences from generally accepted standards do not guarantee a quick diagnosis, but only indicate problems in the body. It is important to evaluate each coefficient both individually and in conjunction with others. Below we analyze what is evidenced by the high or low content of the elements. Alkaline phosphataseAlkaline phosphatase during pregnancy indicates problems with the body. These could be gallstones, cancer and other liver pathologies. Proteins and amino acidsA low coefficient can indicate the presence of pathologies: substance disorders, chronic bleeding, anemia. However, low protein is normal in late pregnancy, during lactation and exercise. Nitrogen exchangeLow levels indicate liver problems, malnutrition, and poor metabolism. High – about gout, leukemia and skin problems. Carbohydrates and glucoseIndicates problems with the liver, thyroid gland and pancreas. PeptidesIndicate the presence of diabetes mellitus and tumors. The diagnosis is made only when combined with other indicators. Vitamins and microelementsThis test determines potassium and sodium levels. If it is small, toxicosis and low blood pressure appear. Headache, convulsions and even coma appear.
|
Changes in enzyme content
Specific proteins are enzymes involved in important metabolic processes in the human body. The level of fibrinogen, ALT, AST, pancreatic amylase and alkaline phosphatase makes it possible to diagnose dangerous changes in the maternal body.
If the ALT level in a blood test becomes more than 35 units, a woman most often experiences symptoms of toxicosis, which is normal for pregnancy. Another factor that increases the ALT value is the development of pathological processes in the liver.
Another protein is AST. The upper limit of its norm corresponds to 31 units. If the value is exceeded, the doctor may suspect dangerous processes that negatively affect the woman’s health indicators:
- pathological processes in the kidneys,
- disorders of the liver associated with the outflow of bile,
- previous myocardial infarction,
- blood clot formation,
- inflammatory processes in the pancreas,
- dropsy.
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase is responsible for saturating organs and tissues with essential phosphorus and transporting this element in the body. Its permissible level is limited to values from 40 to 150 units contained in a liter of blood. If the result of the analysis displays increased values of this element, the pregnant woman may experience processes associated with improper functioning of the liver, the production of bile is disrupted, and there are problems with its outflow from the gallbladder. Decreased alkaline phosphatase occurs due to a lack of magnesium or zinc associated with thyroid hormone deficiency.
Low enzyme levels can be caused by abnormal placental development, fractures, and bone injuries.
Pancreatic amylase should be contained in serum in an amount not exceeding 50 units per liter. If the level is higher, the patient may have pathological changes in the functioning of the thyroid gland.
How to take it
Having received a referral for a biochemical blood test, the expectant mother is usually not puzzled by the question of how to do this study correctly. This is a big mistake, because many factors can affect the results of biochemistry.
As a result, the doctor will receive an unreliable laboratory report. By mistake, a woman may be treated for a disease that she actually does not have. But it will be much worse if treatment does not begin for a disease that exists, but which is not reflected in the results of laboratory diagnostics.
The test must be preceded by some preparation. Before going to the treatment room or laboratory, it is advisable for a woman to limit the consumption of fatty foods, strong tea and coffee, spices , as well as give up an abundance of sweets and minimize salt intake.
The analysis is carried out exclusively on an empty stomach, since only in this way the picture of biochemical processes in the body will be the most truthful. However, you should not fast for a long time; prolonged absence of food also distorts the result. The optimal time period from the last meal to the test is 6-8 hours.
If you are taking any medications or dietary supplements, you should definitely inform your doctor about this, but if the situation allows, it is better to stop taking both medications and dietary supplements a couple of days before.
If a woman plays sports, and even during pregnancy does not limit herself in physical activity, she should temporarily reduce it, also a few days before donating blood. Loads activate and slow down certain processes in our body , which causes fluctuations in values in one direction or another, possibly distorting the real picture.
With severe stress against an unfavorable psychological background, a woman’s blood chemistry also changes due to certain hormones, such as cortisol. Therefore, you should maintain peace of mind , and if this is not possible, then postpone the analysis to a later time, when “passions have subsided.”
Blood is taken from the cubital vein. If it is impossible to make a puncture in this place, then doctors can take venous blood samples for examination from any other vein. This will not affect the results.
Video: what tests do pregnant women undergo?
In this video, the doctor talks in detail about what tests and examinations are recommended for pregnant women, how often and why you need to visit a doctor. Be sure to read this information, it will be useful to every young mother.
Don’t think that all doctors are paranoid, and that they “just want to rip off money by rushing them to offices and tests.” The doctor is no less interested in your health than you are, and sometimes even more interested in your baby’s health. Every test you are sent for is justified and necessary; it is the key to the safety of the baby and the health of the young mother. Don't neglect this moment, and everything will be fine.
What tests did you take during pregnancy? Have you been prescribed additional examinations? Did the doctor explain why this is necessary and important? Share your experience in the comments, this will guide those young mothers who are expecting a new addition to their family for the first time. Have an easy pregnancy and successful birth!
Possible mistakes
The accuracy of this analysis is high, which is why the examination technique has found such wide application in medicine, especially in gynecology and obstetrics. However, no one is immune from errors, so the likely erroneous results should be considered.
Elevated levels of gonadotropin can be found in women who took hormonal medications or were treated for infertility. The level of the hormone may also be elevated during tumor processes in the body. If the result is in doubt, it is advisable to donate blood again after 4-6 days. If the hormone level does not increase or increases very slightly, there is no pregnancy, you should look for the true cause of the change in hormonal levels.
Often, a woman can get a negative result at home using a strip test, but the hCG in the blood will be high, and this indicates that there is a pregnancy, it’s just that its term is still so short that the hormone is not detected in the urine.
A pregnant woman can also get a negative result from the laboratory. This becomes possible if she came for examination too early - implantation has not yet taken place, the hormone is not produced. Too early - the concept is quite specific - until 10-12 days after ovulation, or better yet until 14 days after it, there is nothing to do in the laboratory.
A result in which the hCG level is significantly lower than the level that should be at a given period can also be negative or weakly positive. In this case, doctors may suspect an ectopic pregnancy, a pregnancy that is not developing. A careful dynamic blood test is required (every 2 days), and a little later, ultrasound diagnostics are required to establish the site of attachment of the fertilized egg and its viability.
Indications for use
An hCG test is carried out at the beginning of the first trimester, from the very beginning of a missed period. If a woman has no suspicions of pregnancy, rapid tests show a negative result and no changes in her health are observed, you can postpone going to the clinic.
Interpretation of a blood test for hCG
In addition to mandatory studies, an hCG test may be prescribed in the following cases:
- suspicion of an ectopic pregnancy;
- suspicion of multiple pregnancy;
- the age of the expectant mother is over 35 years;
- the woman is at risk of having a child with Down syndrome;
- increased risk of miscarriage or missed pregnancy;
- the woman was exposed to radioactive radiation.
If these indications are not available, the hCG level can be determined at 10 weeks of pregnancy. If the pregnancy is progressing properly, a later analysis may be performed at 15–17 weeks. In this case, an examination is carried out to confirm the absence of pathologies in the fetus. This blood test is called a triple detailed test. With its help, you can find out not only the level of chorionic hormone, but also the content of gonadotropin, estriol and AFP.