What does a CEC blood test show? Let's figure it out.
Circulating immune complexes in blood plasma indicate the presence of various inflammatory processes in the human body. Thanks to this analysis, it is possible to find out whether the patient has autoimmune pathologies and observe their activity. This diagnosis is prescribed by a doctor in a situation where it is impossible to diagnose the patient for a number of reasons, but he has reason to suspect the presence of fungal and viral autoimmune diseases. A blood test for CEC is done among both adults and children. Such a study can be done as a separate procedure, or simultaneously with other blood tests.
What are circulating immune complexes?
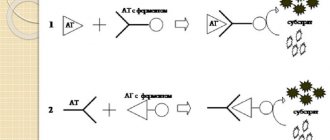
Circulating immune complexes are high molecular weight elements (complex proteins) of immune origin. Immune complexes (IC) are formed due to the interaction of antibodies of significant energy when complement elements combine with antigen molecules that are easily dissolved.
An increase in CEC indicators is observed when a person is diagnosed with inflammation, infection, allergies and malignant tumors. A study to determine the degree of CEC concentration is indicated for persons with signs of autoimmune pathologies. In such situations, the CEC indicator is increased.
Complexes are formed and circulate in the bloodstream due to the influence of a pathogenic agent (antigen) that has entered the body through any route. The formation of complexes, collectively represented by three components, is a natural protective mechanism that can quickly overcome agents of endogenous and exogenous nature.
What is the CEC?
It is known that the fight against foreign microorganisms and any infection takes place on several fronts. There are two types of immunological reactions: cellular and humoral immunity. Thus, the physical absorption of a harmful microbe by leukocytes is an example of cellular immunological reactions, and the release of a large amount of antibodies into the blood is an example of humoral immunity.
Humoral immune reactions include the formation of circulating immune complexes, CECs. Antibodies have a specific configuration and approach the “harmful” antigen like a key to a lock, arranging their active centers in the corresponding centers of the foreign structure, and thereby depriving the antigens of their dangerous effect.
Such antibody-bound antigen is simply passive ballast that must be disposed of. The main condition for good utilization is that antigens must be highly soluble. An antigen molecule blocked by antibodies no longer poses any specific danger, like garbage packed in a sealed container.
However, this immunological debris cannot always be removed from the body in a timely manner, and hence the term circulating immune complex. In addition, they can not only circulate in the peripheral blood for some time, but also be deposited in various organs and tissues. In addition to external antigens - bacterial, fungal, toxic, allergic antigens, there may also be so-called autoantigens. They are formed in the human body itself, sometimes due to metabolic characteristics, and sometimes due to any diseases.
Normally, all circulating immune complexes are quickly removed from the peripheral blood with the help of ordinary phagocytes, which include segmented neutrophils, or white blood cells. But it is impossible to remove circulating immune complexes just like that, “without permission.” To do this, a rather complex system of enzymatic cellular reactions must work, and the complement system must also be activated.
Behavior and tasks of the Central Election Commission under normal conditions
Normally, ICs are occupied by phagocytes (cells of the defense system that absorb harmful agents) and are destroyed by them. A similar metabolic process takes place in the bloodstream and in liver tissue, after which the associated elements of the complex are removed from the body.
But to eliminate CEC, a complex structure of enzymatic cellular reflexes must function when the complement system is activated. Without this, the removal of the Central Election Commission is impossible.
It is known that in medicine there are two types of immunological reflexes:
- cellular immunity;
- humoral immunity.
Sorption of a foreign agent by leukocytes occurs at the level of cellular immunity, and the release of a huge number of antigens into the plasma is a mechanism of humoral immunity. It is precisely the latter type of protective reflexes that includes the formation of the CEC.
The antibodies produced by the system have a specific structure and perfectly combine with the antigen, adapting their own energy centers to the energy centers of foreign organisms, thereby stopping their harmful effects.
When the pathogenic mechanism is activated, CICs begin to be dynamically created, which favors an increase in their level and the deposition of ICs in the cellular tissue of internal organs.
Subsequently, excessive accumulation of immunological complexes and their activation together with lysosomal enzymes lead to damage to many tissues in the body. The highest degree of CEC concentration can be detected in individuals with cancer.
Norm and reasons for deviation
Each of the indicators studied within the framework of enzyme immunoassays and radioimmunoassays has normal values. Deviation indicates certain disorders in the body and requires a more thorough examination. An immunogram involves studying a whole range of indicators simultaneously. Deviation of each of them means pathological disorders in the body. The indicator norms have the following meanings:
An increase in IgA occurs in chronic liver diseases, autoimmune diseases, myeloma, glomerulonephritis, and alcohol intoxication. A decrease in the concentration of immunoglobulin A is facilitated by physiological changes in a child under 6 months, cirrhosis of the liver, radiation sickness, therapy with immunosuppressants, and poisoning of the body with chemicals. The level of IgE increases during infection with parasites, allergic diseases, urticaria, and bronchial asthma. A decrease occurs with ataxia and telangiectasia (persistent dilatation of small vessels).
An increase in IgG content is observed in autoimmune diseases, myeloma, HIV infection, mononucleosis of infectious etiology, and infectious pathologies. A decrease in immunoglobulin G occurs as a result of physiological changes in a child under 6 months of age, radiation sickness, chemical poisoning, and immunosuppressant therapy.
IgM increases in acute infections, liver pathologies, autoimmune diseases, and vasculitis. The decrease in content occurs for the same reasons as IgG, as well as after splenectomy (removal of the spleen).
Antinuclear antibodies increase in autoimmune pathologies, nephritis, chronic hepatitis, vasculitis. The ASLO indicator increases in acute forms of glomerulonephritis, rheumatism, erysipelas, scarlet fever and streptococcal infection. Antisperm antibodies are elevated at risk of infertility. The MAR test indicator is increased in case of probable infertility of a man. The levels of AT-TG and AT-TPO increase in autoimmune thyroiditis, Graves' disease, Down and Turner syndrome.
Analysis for CIC (circulating immune complexes) is prescribed for: examination for the presence of autoimmune pathologies and complement deficiency, immunopathogenetic kidney damage, arthritis of various etiologies, persistent infection. Circulating immune complexes are increased in acute infection of the body, persistent infection, autoimmune pathologies, allergic alveolitis, acute glomerulonephritis, local anaphylaxis, serum sickness, endocarditis, malignant tumors, Crohn's disease . Also, circulating immune complexes are examined as part of a general immunological examination.
What is the complement system?
In order for the two parts of the immune complex to work harmoniously and without interruption, their continuous regulatory function, the so-called complement system, is necessary. This definition is usually used to refer to various forms of proteins that regularly reside in the plasma and trigger a number of immune reflexes.
Let's look at an example:
One of the most well-known mechanisms of a protective reaction is the process of blood clotting. The chain of immune reactions is activated even with minor vascular defects.
They involve many compounds (in particular prothrombin and clotting factor). As a result, fibrin is produced. It favors the clogging of blood vessels in the affected areas. As a result, bleeding stops.
The functioning of the complement system occurs in an identical way, only the result is the correct immunological response. The components of the system are more than 20 types of proteins, which are produced, as a rule, by hepatocytes (liver cells). With organ dysfunction, natural protection is weakened, since proteins are a fraction of gamma (globulins) and make up 1/20.
In a strong and healthy body, they remain in a passive state, and begin their direct activity only when the plasma is enriched with pathogenic antibodies or antigens. This is how the elements of the system are activated.
Many components of the system have the ability to associate into large molecules, which subsequently destroy pathological cellular formations. By activating the system, membrane attack complexes (rather large associations) are formed that destroy target cells or mark them in a certain way.
“Marked” pathogenic organisms become visible to attacking leukocytes.
Circulating immune complexes are high-molecular elements that are produced in increased volume only under certain conditions:
- a large number of antigens are produced, exceeding the amount during the normal course of the infectious disease;
- self-education of the CEC in the absence of symptoms of the disease;
- weakening of the sensitivity of the immune reflex from the damaging effects of autoantigens;
- the processes of elimination of the CEC are disrupted (noted, as a rule, in pathological processes of an autoimmune nature).
CECs are usually highly soluble, which makes it easy for phagocytes to exclude them from the bloodstream. However, under negative factors they become relatively or absolutely insoluble. This stimulates the process of their deposition in the tissues of various organs.
In particular they suffer:
- small vessels;
- kidneys;
- lymph nodes;
- spleen.
The deposition of IR results in the fact that the complement system tries to bind them and bring them out by drawing attention to them by macrophages. This provokes the development of inflammation and damage to cellular tissues. As a result, CECs aimed at eliminating antigens lose their beneficial power and become the main root of diseases, as they are considered opportunistic.
The immune system reacts...
The immune system is able to distinguish between its own material and genetically foreign substances. These abilities, formed at the dawn of evolutionary development, formed the basis of protective mechanisms that make it possible to recognize and then destroy what is not suitable for the body in its properties. If our immune system were not constantly on alert, it is difficult to imagine what would happen. And so it is always at work, because the body, not being isolated from its environment, constantly encounters antigens: some of them it already “knows”, “saw”, while others turn out to be something new, unknown to it. The reactions of the immune system can be different:
- In the first case, if the antigens are “familiar” but not alien to the body, we simply do not notice what is happening inside us;
- On the contrary, in response to the appearance of an “enemy” the immune system “declares war” and then the development of a violent immune reaction cannot be avoided;
- However, it also happens that the proteins of one’s own body fall into the category of “enemies”; they are called autoantigens. Antibodies with which the immune system responds to its own antigens are called autoantibodies (autologous or autoaggressive, since they are directed at their own antigens) - this is the reason for the development of autoimmune processes;
- Cases cannot be excluded when an antigen seems to be foreign to the body, but for some reason the immune system does not notice it; such tolerance of a foreign substance is called immunological tolerance (this phenomenon, in general, has little relation to the topic of CEC, the example is given simply for clarification some concepts).
The interaction of antigens and antibodies also involves other proteins that never leave the blood to help carry out an immune response if necessary. This is a system of proteolytic enzymes, the complement system - it is very important for the body, its components also fight against foreign agents, providing protection at the level of humoral immunity.
Normal CEC indicators for adults, children
It should be noted right away that each research or diagnostic center has its own methodology for interpreting the results. They are due to several factors.
This:
- principle of conduct;
- reagents;
- analyzers.
CEC norm indicators:
| Abbreviation | Index |
| U/l (number of CECs per 1 liter of blood) | Less than 75 |
| Conventional units (cu) | In the range of 0.055-0.11 |
| Relative units (RU) | Range 0-120 |
When interpreting the analysis, doctors are guided by the specified CEC values, regardless of the age category of those diagnosed.
Patient preparation rules
To obtain objective results, it is necessary to act correctly before drawing blood. To do this, just follow these simple rules:
- It is better to undergo the examination in the morning, on an empty stomach. If this is not possible, it is permissible to donate blood at any other time after a 4-hour period of fasting;
- It is not recommended to drink alcohol, caffeine-containing drinks, or energy drinks for 3 hours before the test. Water and weak tea can be drunk without restrictions;
- Several hours before the procedure, you should not smoke or be in the presence of a person who smokes;
- Immediately before donating blood, significant physical activity (running, lifting weights, playing sports), contrasting water treatments, hypothermia/overheating of the body should be excluded;
- To obtain the most information, it is best to carry out an immunogram for a child and an adult during a period of complete health. During illness, the body will react to damage to its own tissues or to infection, so it is quite difficult to draw a conclusion about the blood picture.
UK”{amp}gt;Standard conditions: Fasting period 8 hours (unless otherwise determined by the doctor). You can drink water. Biomaterial is accepted in accordance with
schedule for taking biomaterial in the ML department of DILA.EN-US”{amp}gt;
Reasons for the increase
Circulating immune complexes is a value indicating the presence of CEC in the blood, but not in the tissues. That is, a high indicator already indicates that ICs are produced in excessive quantities and settle on tissues, thereby provoking the mechanism of inflammation. This condition can be diagnosed with a variety of pathological changes.
Diseases that provoke an increase in the concentration of CEC can be divided into three groups:
- allergic manifestations;
- autoimmune diseases;
- infectious lesions.
Pathological processes in which a high level of complement can be detected:
Circulating immune complexes are increased during allergic reactions
| Allergic manifestations | The entry of pathogenic agents into the body stimulates increased production of CEC. Phagocytes are not always able to cope with the process of their elimination. A similar mechanism can occur with the following problems:
|
| Autoimmune pathologies | As a rule, rheumatic diseases cause accumulation of IR in tissues and subsequent inflammation. This happens with the following diseases:
|
| Infectious lesions | The cause of infection is often fungi, bacteria, microbes, and viruses. The penetration of these agents into the blood stimulates the increased production of complexes; however, they do not always have time to undergo the elimination process and, as a result, settle in the cellular tissue. This group of pathologies also includes:
|
An increased value of this indicator can also be diagnosed in people who have previously undergone internal organ transplantation. In such a situation, doctors interpret the result as unfavorable. That is, the degree of organ survival is low.
When deciphering the analysis, it is necessary to focus on the patient’s clinical signs, since increased production of CEC can be detected even in completely healthy people. According to medical statistics, this is about 10% of patients. The information content of the result is significantly influenced by the presence of cryoglobulins and anti-C1q antibodies in the plasma.
How to take the test correctly and why is it prescribed?
To determine circulating immune complexes, regular venous blood is donated on an empty stomach. The only condition: it is advisable not to smoke in the morning of this day before taking the test, and not to overexert yourself physically, and to be in a calm state. Stress and hard work the day before can distort the result. The research method is a modern enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
In addition to this method, there may be other, older methods for determining the CEC, but different methods do not always give the same result. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method is based on the ability of these complexes to bind to a specific complement fraction. It allows us to isolate precisely those types of complexes that may be potentially pathogenic. This method is more sensitive than previous generation methods of analysis, such as gel precipitation.
But still, taken separately, this CEC blood test is both not sensitive enough and not specific enough when it comes to diagnosing autoimmune diseases. In this case, the doctor should prescribe, in addition to the study of circulating immune complexes, an assessment of the complement system, and, above all, its components such as C3 and C4. It is necessary to assess how the circulating immune complexes deposited in the tissues affected the function of certain organs, and this is most often done jointly by an immunologist and a rheumatologist.
It must be remembered that this analysis, namely determining the amount of CEC in the blood, will only show the activity of one or another process, but will not say anything about where and in what quantity the complexes are deposited in the tissues. It shows only that part of them that is soluble and found in the blood. Accordingly, a diagnosis cannot be made accurately based on such analysis alone.
Reasons for the decline
Circulating immune complexes are reduced when the first results of the study are received - this is not a sign of illness, but a completely normal state of the body. The value can also be zero, which is normal. And if the person who underwent the analysis was previously diagnosed with an increased degree of CEC concentration, then its decrease indicates a favorable outcome of the therapy.
If a reduced CEC result is detected during the second and third immunogram, and at the same time the person is diagnosed with all the signs of the disease, this may indicate various disease processes and defective tissue destruction.
Weak CEC production means that the natural defense system is weakened, and the body itself is unable to fight off the negative effects of endogenous and exogenous factors. This also leads to the fact that immune complexes are deposited in cellular tissue and grow.
Another feature of CECs is their ability to connect with red blood cells (erythrocytes). In excessive or insufficient volume, such chains do not have a significant destructive impact, therefore, when conducting analysis, all attention is paid to the presence of the CEC elements themselves.
Reduction of elements
If the number of CECs decreases, this entails various abnormalities and tissue destruction. Insufficient production of elements causes diseases of the immune system, since the body is no longer able to protect itself independently from pathological factors. If the content of complexes is insufficient, this leads to their accumulation on individual organs. The basic functions of substances are lost, they grow on the tissues of the body and destroy it.
This occurs due to cellular breakdown and a decrease in the density of the vascular walls. As a result, the degree of CEC in tissues increases, and phagocytes are no longer capable of breaking them down.
CECs can be present not only independently in blood plasma, but also bind to erythrocytes. These links, in deficiency or excess, do not have a destructive effect and do not significantly harm the body, therefore, during the analysis, attention is paid only to the presence of elements directly in the composition of human blood.
You can check the level of components using a reaction to substances such as C1g and C3d. With a significant decrease in indicators, we can talk about damage to the gene responsible for the transformation of protein elements in the body. A reduced degree indicates the presence of vasculitis, an autoimmune lesion or an allergic disease. This indicator often indicates the presence of endocarditis, infectious arthritis, HIV or hepatitis.
Indications for the study of immune complexes
Testing a blood sample for CEC has the following goals:
- establishing the level of CEC in the blood, as the body’s ability to overcome the disease and how sufficient its immune response is;
- monitoring of ongoing therapy;
- assessment of the severity of the pathological process.
Analysis is prescribed if there are signs of such disease processes:
- allergic manifestations;
- complications of surgical treatment;
- cancer;
- immunodeficiencies of various forms;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- long-term and recurrent infections.
High complement levels are not considered a specific sign of any disease, and its result cannot be used as a basis for diagnosis. This requires the results of additional samples.
They give a clearer picture of the disease. When a high level of CEC is initially detected, repeated blood sampling is required. This makes it possible to evaluate the constancy of IR concentration and its change with various clinical signs.
Indications for analysis
Examination with a detailed study of the CEC is used in immunology to identify and monitor dysfunctions. Their etiopathogenesis is based on the functional features of stage III sensitization. The analysis is prescribed for diagnosis:
- allergic and autoimmune diseases;
- chronic persistent infections;
- damage to the renal glomeruli;
- articular syndrome;
- injuries of cartilage tissue and central vascular walls;
- kidney and/or liver dysfunction.
Less commonly, the analysis is prescribed as part of a comprehensive immunological study during pregnancy, preparation for surgery, or when malignant neoplasms are detected. In such cases, it is carried out due to the reliability of the diagnostic tool, because the result will determine the pathogenetic mechanism of dysfunction and demonstrate the intensity of the course.
For your information! The analysis also has limitations associated with its low specificity: there is a discrepancy between the CEC level and the norm in numerous pathologies. To make an accurate diagnosis, the results of various studies are needed.
What tests are prescribed?
An immunogram is the main research method in which a number of other important tests can be performed to assess the state of the immune system. Thanks to the method, the effectiveness of phagocyte metabolism (phagocytosis) is revealed, how effectively the elimination process occurs.
The normal rate of phagocytosis ranges from 65 to 95%. The lower its metabolic degree, the greater the volume of CEC is based in tissues. A detailed study makes it possible to differentiate the state of natural defense in more depth.
Four important immunogram indicators are highly informative:
- lymphocytes - a low concentration of a substance indicates the predominance of a viral infection in the body;
- an increased number of lgE indicates manifestations of allergies or helminthic infestation;
- high levels of leukocyte formula - acute inflammation within the body;
- low degree of phagocytosis – development of inflammation or purulent damage to the tissues of internal organs.
The results of the immunogram are interpreted by specialists such as a therapist, rheumatologist, allergist, immunologist and others. The results obtained characterize the course of the disease and its severity. Based on them and the results of instrumental examination, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
Indications for the study
A person’s immune status is studied using various methods and tests. There are two main types of studies: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and radioimmunoassay (RIA). Certain test systems are used to study the immune status. In radioimmunoassay, the results are measured using radioactivity counters. There are a large number of different test systems for performing ELISA. The main types of enzyme immunoassays are: inhibitory, “sandwich”, immunometric, solid-phase indirect ELISA, immunoblot method.
There are a number of pathological disorders in which immunological blood testing is mandatory . The primary analysis for organ transplantation is an immunogram, especially if the patient is a child. The value of the indicators is important when selecting treatment for oncological diseases. Compliance with the norm is determined after therapy with immunosuppressants, since the drugs reduce the body’s protective function. An immunogram is prescribed for such pathological disorders as:
- hereditary disorders in the functioning of the immune system;
- heavy blood loss;
- viral and parasitic infections of various etiologies (syphilis, giardiasis, hepatitis, herpes and others);
- oncological diseases;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- physiological disorders of the immune system (during pregnancy, old age and childhood);
- autoimmune diseases;
- HIV infection;
- pneumonia with frequent relapses;
- long-term fungal infections;
- chronic inflammatory processes;
- purulent skin lesions;
- severe emotional shocks, prolonged depression;
- long stay in places with polluted ecology.
The study of immune status is especially important when examining patients with HIV infection. The test results allow us to assess the degree of damage to the body's defense system. The study of the immunogram facilitates the selection of drugs for treatment and the choice of direction of therapy. A decrease in protective function can lead to the development of serious diseases. If you feel unwell for a long time, it is recommended to take a blood test for immunity and check your health status.
Preparation
The preparatory stage for the analysis is very important, since failure to follow the rules may affect the result.
The preparation rules are as follows:
- blood is donated from a vein at the diagnostic center in the morning before 10 o’clock (the exact time is determined by the laboratory’s work schedule);
- Before submitting the biomaterial, you should not eat (it is advisable that the interval between the last meal and the analysis be 8 hours);
- on the day before the analysis, drinking alcoholic beverages and performing heavy physical activity is prohibited;
- if possible, it is recommended to avoid taking medications for several days (this issue is discussed with your doctor);
- a week before the test, you should try to avoid stressful situations.
When and why is research performed?
The test is usually used to diagnose the general condition of the patient. This is necessary before undergoing a major operation, during pregnancy, or in the presence of cancer. Through such diagnostics, it is possible to detect the presence of an immune pathology or a severe allergic reaction in the body.
Chronic infections that are present in the human body may not manifest themselves externally and may not be accompanied by pronounced symptoms, but they can be easily detected during analysis of circulating immune complexes. Such diagnostics make it possible to monitor the development of glomerulonephritis and adjust its treatment. In case of damage to the immune system, a blood test is the best way to monitor the trend of development or cessation of the disease.
Quite often, only such a blood test will allow the doctor to get a complete picture of the course of all allergic and viral processes in the body. The analysis is carried out more than once. If the diagnosis is part of a study of the state of the immune system, then the analysis will have to be repeated several times. During the treatment period, the patient does not need to follow a diet or resort to additional measures to prepare for the analysis. The process of donating blood can be quite painful, but these sensations disappear immediately after the procedure.
The doctor may prescribe such a diagnosis in several cases. Often the cause is an autoimmune pathology in the patient. If a person suspects arthritis, lupus, polymyositis, vasculitis or scleroderma, then this is a reason to conduct a diagnosis. She will be able to confirm or refute the diagnosis. Often, such a blood test is prescribed to patients with articular syndromes, damage to cartilage tissue and blood vessels, and kidney or liver dysfunction. This analysis is an integral part of the diagnosis when examining the immune system.
Collection of biomaterials
For research, blood is taken from a vein. The biomaterial is collected by laboratory assistants under sterile conditions and placed in a special sealed tube, which is then sent to a centrifuge, where the formed components are separated and only the liquid substance (plasma) remains.
Clotting factors are extracted from plasma, and the resulting serum is the biomaterial for conducting an immunogram. The diagnostic principle is based on the ability of immune complexes to bind to the complement system element C1q.
General concepts about analysis
CECs are components that begin to be produced by the human body and are formed in the blood as a response to the ingress of foreign bodies. Such complexes usually include antigens, antibodies and other elements. If a person does not have an appropriate reaction and the production of the CEC is disrupted, then this indicates that the patient’s body has experienced a malfunction of the immune system. The main task of such components is to recognize and remove harmful bodies and allergens from the body as quickly as possible. After the CECs have completed their function, they are usually destroyed by phagocytes.
Treatment of abnormalities
Circulating immune complexes are not a disease, but a natural reaction of the body to the pathogenic influence of antigens and other microorganisms. The study of CEC is of high importance in many branches of medicine. It allows you to assess the clinical situation, identify hidden inflammatory diseases and indicate the effectiveness of the therapy. The results of the analysis are interpreted by the attending physician.
Taking into account the etiological factor of the increase in the concentration of the indicator, the patient is referred for consultation and subsequent treatment to specialized specialists. An adequate model of therapy is developed by the doctor based not only on the immunogram, but also on a number of other additional research principles (instrumental and laboratory).
An analysis to determine the level of circulating immune complexes is not the main diagnostic method and cannot serve as a basis for developing a drug treatment model.
This is a method that allows you to assess the state of the body’s natural defenses, the degree of its damage from various pathogenic influences and the effectiveness of the therapy. An increase in the concentration of CEC always means the presence of some pathogenic process, however, an assessment of the patient’s condition and the results of additional diagnostic methods can indicate which one.
Immunogram indicators
A blood test for immune status involves examining a set of indicators. Decoding the results makes it possible to fully assess the correct functioning of the immune system. Thanks to the complex of studied indicators, radioimmunoassays and enzyme immunoassays make it possible to check the functioning of not just one specific organ or system, but immediately the whole organism. The study can be carried out at any age.
As part of the immunogram, the following indicators are studied:
- IgA (immunoglobulin A) – antibodies responsible for protecting mucous membranes;
- IgE (immunoglobulin E) – is involved in allergic reactions and protection against parasitic infections;
- IgG (immunoglobulin G) – antibodies of the secondary immune reaction. Protect the child at the embryonic level, penetrating the placenta;
- IgM (immunoglobulin M) are antibodies that are the first to react with infections. Allows the identification of infections transmitted through sexual contact in the early stages of development in adult patients. The value of immunoglobulin is important in the diagnosis of autoimmune diseases;
- alloimmune antibodies - produced against the Rh factor or other red blood cell antigens;
- antinuclear antibodies – a complex of antibodies produced as a result of a violation of self-tolerance in autoimmune pathologies;
- ASLO (antistreptolysin-O) is an indicator of infection of the body with streptococcus;
- antisperm antibodies are specific proteins to sperm membrane antigens. Investigated as part of a test to determine the causes of infertility;
- MAR test – determines the quantitative indicator of antisperm antibodies;
- AT-TG (antithyroglobulin antibodies) is a protein produced in the cells of the thyroid gland;
- AT-TPO (antibodies to thyroid peroxidase) - the indicator is studied as part of a test for diagnosing autoimmune pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- HLA typing class 2 – complex of histocompatibility antigens (compatibility of organs and tissues);
- CICs (circulating immune complexes) are formed when soluble antigens and antibodies come into contact in the blood. When functioning properly, circulating immune complexes are cleared from the body by the monocyte-macrophage system.
Each of the indicators determined as part of an immunological study is important in diagnosing pathologies. Based on the results of the analysis, the doctor receives a complete picture of the state of the immune system. The results of the study are interpreted in conjunction with existing complaints, other examinations and diagnoses in the medical history of the patient, as well as his close relatives.