Functions in the body
Hematocrit number is a specific laboratory sign that characterizes the ratio of blood cells to the total volume of biological fluid.
The source of a decrease or increase in the content of erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets are various factors of an age-related, physiological, pathological nature:
- dysfunction of internal organs;
- inflammatory processes;
- malignant or benign neoplasms;
- pregnancy;
- hormonal changes;
- various diseases of the endocrine system;
- injuries;
- bacterial and viral infections, much more.
Each indicator separately does not have significant diagnostic significance. To assess the entire clinical picture in its entirety, a hematocrit value has been developed.
This laboratory sign makes it possible to identify pathological abnormalities at the initial stage of their development and formation. It provides grounds for more detailed diagnostics.
This is the main function of hematocrit in the body. This number is a kind of marker of diseases and pathological disorders. Based on the percentage of the liquid fraction of blood and formed components, the level of plasma state and active agents is determined.
Measuring indicators
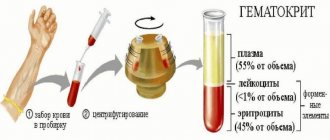
How to calculate hematocrit in blood? As an example, we will give a method for measuring this indicator with the naked eye. You need to collect the blood and let it stand for a while, waiting for the red blood cells to settle. Then look at what percentage of blood volume is erythrocytes and what percentage is plasma.
Calculation of hematocrit in a blood test
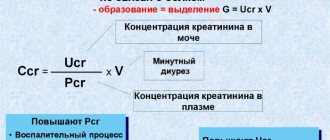
Note. Doctors have a special formula for calculating hematocrit levels. The content of red blood cells in the blood (in%) or its expression as a fraction (liter per liter), multiplied by 0.01 - the result obtained is the hematocrit.
How and under what conditions is it produced?
Red blood cells, called red blood cells, are special cells that deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues. This laboratory indicator determines their content relative to other formed elements.
Red blood cells consist of hemoglobin, a specific protein that captures oxygen atoms and transports them into cells, simultaneously removing carbon dioxide. The standard blood formula of a healthy person consists of 60% plasma (liquid) fraction and 40% formed elements.
Hematocrit (the norm in women varies by age under certain physiological conditions) characterizes their ratio with leukocytes and platelets, the total content of which does not exceed 1%. Indirectly, this laboratory parameter acts as an indicator of cell respiration.
The hematocrit value is used for:
- diagnosing anemia and assessing the effectiveness of its treatment;
- determining the level of tissue dehydration;
- making a decision on the advisability of hemosorption;
- obtaining data on the results of transfusion.
This specific laboratory sign is a component of a biochemical blood test and is not assessed separately. The hematocrit number is always directly related to the volume of red blood cells, provided that the latter are of standard size.
There is no relationship between the factors influencing the synthesis of intracellular hemoglobin and the level of their content in the blood plasma. The deviation of this laboratory indicator from the standard value does not necessarily indicate the presence of pathology, but serves as a basis for additional examination.
Diagnostics
If an elevated hematocrit is detected, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient, including:
- collecting anamnesis with clarification of hereditary predisposition to genetic pathologies. It is necessary to exclude the patient's state of chronic dehydration;
- A repeated extended clinical blood test is performed. Particular attention is paid to the level of red blood cells, eosinophils, neutrophils and platelets. Their combined increase indicates erythrocytosis;
- laboratory analysis of gases contained in the patient’s blood is necessary. It is known that the number of red blood cells circulating in the bloodstream is inversely proportional to SaO2;
- in people who abuse tobacco smoking, it is necessary to measure the carboxyhemoglobin content. Its excess of 5% leads to erythrocytosis. It should be noted that smoking also causes a significant increase in the number of neutrophils.
Differentiation of relative from absolute erythrocytosis is carried out using 51Cr. This is a highly sensitive technique using labeled antibodies. The intensity of radiation is directly proportional to the number of antigen-antibody complexes formed.
In order to exclude hypovolemia (decreased blood plasma volume), a technique is implemented using labeled albumin protein.
Advanced diagnostics involves the use of ultrasound and computed tomography methods of the abdominal organs.
Indicator table is normal
The hematocrit number correlates with age and gender. Permissible deviation from the norm is no more than 5%.
Reference values are summarized in the table:
| Age | Women, % | Men, % |
| Newborns | 42-52 | 42-52 |
| Infants 6 months old | 34-44 | 34-44 |
| From 6 months to a year | 32,5-41 | 27,5-41 |
| 1-3 years | 30-40 | 28-40 |
| 3-6 years | 31-40 | 31-39 |
| 6-12 | 32-41 | 32-41 |
| 12-16 | 33-43 | 34-47 |
| 16-19 | 32-43 | 35-48 |
| 19-30 | 33-44 | 38-49 |
| 30-40 | 33-44 | 38-49 |
| 40-50 | 33-45 | 38-49 |
| 50-65 | 34-46 | 37-48 |
Hematocrit (the norm for women by age is indicated in the table) decreases in the presence of iron deficiency anemia. This is due to a decrease in the size of red blood cells. A hematocrit number below 30% and above 55% is considered critically dangerous.
With such indicators, the rheological properties of blood, in particular coagulation, are disrupted. Leukocytes, which perform a barrier function, cease to cope with their task.
This leads to the body's vulnerability to bacterial and viral invasion. At different ages, hematocrit values change, which is associated with an increase in blood volume and, accordingly, the formed elements of its formula.
Normal during pregnancy
When carrying a child, the hematocrit norm in women changes, as the body undergoes restructuring. Physiological changes make it possible to maintain pregnancy and prevent the development of complications in the expectant mother. In order to notice a deviation of HCT from normal values in time, you need to regularly visit the doctor and take the suggested tests.
Early
The hematocrit value in the first trimester varies from 33 to 36%. 1.5-3 months after conception, plasma volume increases by 10-15%. A decrease in hematocrit is observed at the end of the first or middle of the second month of pregnancy.
NBT less than 33% is an alarming symptom that may indicate the presence of anemia.
In the 2nd trimester
In the second trimester, the norm of hematocrit in the blood of women continues to remain at the same level (the same as in the first trimester). At the same time, the BCC (circulating blood volume) increases slightly, which requires constant monitoring of the expectant mother’s body.
A decrease in HT to 31% poses a threat to the health of the mother and fetus. This indicates the development of iron deficiency anemia or another pathological condition. An increase in hematocrit should also be feared, since it may be a sign of dehydration (dehydration). Loss of fluid in a pregnant woman can occur due to eating disorders (vomiting, diarrhea), toxicosis, profuse sweating, etc.
Important information: Normal ESR levels in the blood of men by age (table)
In the 3rd trimester
In the last 3 months of pregnancy, BCC increases even more strongly (the most rapid increase is observed during 30-34 weeks of pregnancy). During this period, the hematocrit rate decreases until it reaches the minimum possible value: 32-34%. A further decrease in the indicator indicates the development of pathological conditions and requires treatment.
If your blood hematocrit rises above 36%, this may be a sign of dehydration.
Symptoms of increase and decrease
Signs of an imbalance in the proportions of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets are manifested in various conditions.
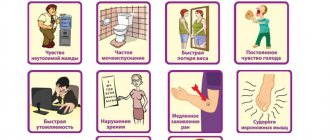
Common symptoms with low hematocrit:
- apathy;
- prostration;
- chronic fatigue;
- constant drowsiness;
- dyspnea.
The symptoms are caused by the pathology or physiological condition that caused the change in the hematocrit number.
When this specific laboratory indicator increases, pain occurs:
- in the joints;
- spinal column;
- ribs;
- chest;
- in the limbs.
A common sign of an increase in hematocrit value is causeless swelling of soft tissues. The pain syndrome in each case has different intensity and duration.
A violation of hematocrit may be accompanied by a rise or fall in body temperature, suppression of appetite, and a yellowish tint to the skin of the face. Often the mucous membrane dries out, and ulcerative destruction appears in the oral cavity.
In especially severe cases, tactile sensitivity decreases and visual function is partially inhibited. If such alarming symptoms occur, there is every reason to suspect the development of a dangerous pathological process.
Reasons for promotion and demotion
The etiology of hematocrit disorders is numerous and varied. A decrease or increase in this specific blood parameter is caused by both natural causes, which resolve themselves over time, and pathologies that require immediate medical intervention.
Type 1 etiological factors include:
- heavy blood loss due to trauma or surgery;
- a debilitating diet and an unbalanced vegetarian diet low in iron;
- sedentary life (physical inactivity);
- dehydration of the body;
- taking diuretic medications and a course of treatment with loading doses of corticosteroid drugs;
- oxygen starvation, which the body tries to compensate for by increased synthesis of hemoglobin.
The latter reason may be caused by the region of residence (mountainous areas located high above sea level) or abuse of nicotine, which constricts blood vessels.
Pathological factors for hematocrit disturbances and deviations from the norm given in the table in women by age include:
- leukemia and other blood diseases;
- erythremia - proliferation of red blood cells;
- secondary erythrocytosis;
- tumor neoplasms in the renal organ, causing increased synthesis of erythropoietin;
- hydronephrosis and polycystic pathologies;
- Congenital heart defect;
- hemoglobinopathy;
- dysfunction of the lungs and other respiratory organs;
- sickle anemia.
Hodgkin's lymphoma, a malignant destruction associated with the proliferation of lymphoid tissue cells, leads to a violation of the hematocrit number. Red blood cells destroy some pathogenic agents and inhibit intoxication of the body with synthetic or organic poisons.
Decreased hematocrit
Mechanisms contributing to a decrease in the hematocrit number may be as follows:
- decrease in the number of red blood cells;
- an increase in plasma volume due to increased fluid content in the body;
- an increase in the amount of proteins that bind fluid, preventing it from being excreted from the body.
Conditions in which one of the mechanisms leading to a decrease in hematocrit occurs are as follows:
- massive blood loss, in which the volume of blood volume is restored quickly in a hospital setting due to infusions, but it takes time for the body to produce its own red blood cells;
- overhydration – increased fluid content in the body due to edema, prolonged infusion therapy, or ingestion of excessive amounts of fluid;
- anemia and leukemia, in which hemoglobin synthesis may be impaired or the mechanism of red blood cell formation may be slowed down;
- poisoning with chemical and biological poisons (pesticides, snake venom, toxins of poisonous mushrooms);
- hematocrit decreases during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester, when plasma volume increases and the number of red blood cells remains at the same level; in this case, the doctor determines whether this condition is a normal variant or a pathology.
Indications for the study
A blood test to determine the hematocrit number is prescribed if the patient has a history of genetic mutations, hereditary diseases, or renal failure.
Common provocateurs of disturbances in the proportions of blood cells:
- oncology of any localization;
- abnormally low levels of protein compounds in plasma and serum;
- thalassemia - inhibition of the secretion of polypeptide chains that are part of the structure of hemoglobin;
- multiple myeloma;
- peritonitis;
- dynamic injuries of internal organs;
- fractures;
- hemoblastosis – a tumor of hematopoietic and lymphatic tissue;
- renal vessel stenosis;
- dysbacteriosis;
- cirrhosis;
- malaria;
A laboratory analysis to determine the Ht indicator is prescribed by a hematologist or family doctor for varicose veins of the esophagus, damage to the spinal cord of any origin, poisoning with hemolytic poisons and salts of heavy metals.
In 20-25% of cases, hematocrit disorder is provoked by anemic pathologies.
The risk group includes people with certain physiological conditions:
- consuming a large daily volume of liquid;
- 4th month and later pregnancy;
- active stage of the menstrual cycle;
- excessive absorption of table salt;
- postpartum period.
Women and children are more likely to experience a decrease in Ht, while men are more likely to experience an increase.
Etiology
As already mentioned, an increase in hematocrit is most often a consequence of the onset of development or progression of a disease.
The most common causes of this disease:
- Severe dehydration (dehydration) occurs against the background of the fact that a person in one situation or another ingests a small amount of liquid, which affects the functioning of internal organs and systems. This problem can be caused by excessive vomiting, persistent diarrhea and prolonged exposure to sunlight.
- Chronic hypoxia is a lack of oxygen in organs and tissues. Most often, such a pathology is detected in diabetes mellitus and in those individuals who have been smoking for many years.
- Erythremia.
- Neoplasms of the kidneys.
- Polycystic adrenal gland.
- Any type of anemia.
- Peritonitis.
- Internal hemorrhages.
- Poisoning with toxic substances or drugs, in particular hormonal and glucocorticoids.
- Chronic heart diseases.
- Emphysema.
- Congestive heart failure.
- Chronic bronchitis.
- COPD
- Hypoventilation syndrome.
- Pulmonary hypertension.
- Apnea.
- Oncological neoplasms.
- Ischemic kidney disease and other ailments of this organ.
- Extensive burns.
- Internal wounds.
The above factors influence the increase in hematocrit levels in both adults and children. However, it is worth noting that a slight increase of 10-12% in infants under one year of age is quite normal.
However, there are several possible negative reasons for the increase in this indicator:
- previous transfusion of biological material;
- transfer of placental blood to the baby after birth;
- chronic intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
In addition, physiological sources of this condition are:
- the period of bearing a child, especially during pregnancy in the 2nd and 3rd trimester;
- changes in air composition;
- long-term influence of stressful situations;
- specific working conditions - the main risk group consists of people forced to work at height.
Normal values for hematocrit
How to determine
Venous blood is taken for analysis. It is filled with special medical test tubes made of transparent graduated glass or plastic. The biological fluid is processed by centrifugation to separate the blood into fractions.
Hematocrit (the norm in women by age depends on the physiological state to a greater extent than in men) is calculated using a micro- or macroscopic method. The latter is considered more accurate.
The blood is mixed with an anticoagulant laboratory reagent, which prevents the clotting of biological fluid. The test tube containing the compositions is installed in a centrifuge apparatus. The blood processing process lasts about 1.5 hours.
During this time, the test tube is spun to the maximum speed for the technical characteristics of the laboratory centrifuge model. All components of the blood formula differ in specific gravity and density. Therefore, they are easily separated into layers.
After the centrifugation process is completed, the laboratory assistant determines the percentage of each fraction using a high-precision scale applied to the test tube. Since red blood cells are the heaviest formed elements in blood, they settle to the bottom of the flask.
Leukocytes and platelets are placed sequentially above them. The topmost layer is occupied by plasma purified from functional cells. For maximum analysis accuracy, the test tube is marked with 0.01 to 100.00%.
All biological material placed in a laboratory vessel is taken as 100%. Further definition is not difficult. The resulting indicator is considered the hematocrit number. If the test is taken after blood loss, including menstruation or surgery, it may be distorted.
Determination of hematocrit level
Hematocrit, in addition to blood indicator, is called a special glass device - a graduated capillary with 100 divisions. Blood is drawn in the morning on an empty stomach from the ulnar vein or from the pad of the phalanx of the finger. The hematocrit is filled with the collected blood and immediately centrifuged within one to one and a half hours. During this time, red blood cells settle to a certain level, which shows the hematocrit number of the patient being studied. Currently, specialized equipment is more often used, with the help of which the level of hematocrit, as well as other indicators, is determined automatically by a computer program. Indications for analysis:
- preventive medical examination;
- any disease (general or detailed blood test);
- diagnosis and screening for the effectiveness of treatment of blood diseases;
- tumor processes;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- pathologies of the digestive system;
- persistent swelling;
- renal pathologies;
- dehydration (dehydration);
- suspicion of overhydration;
- upcoming surgery;
- tendency to bleed, repeated bleeding;
- upcoming transfusion of blood, red blood cells, plasma;
- condition after transfusion of blood, red blood cells or plasma.
Preparing and conducting analysis
The established rules for preparing for donating blood for laboratory testing also apply to determining the hematocrit number:
- The biomaterial is collected in the morning on an empty stomach.
- The last meal should be at least 8 hours before the test.
- Blood sampling will be facilitated by drinking plenty of clean water without gas and sugar, which dilutes the biological fluid.
- The analysis is not carried out against the background of drug therapy with diuretic, anticoagulant and corticosteroid drugs.
- Before the procedure, it is better not to take any medications at all.
The concentration of blood cells is significantly affected by physical activity and psycho-emotional stress. Therefore, it is advisable to be in a state of rest and balance during the procedure.
The puncture site is pre-treated with an antiseptic composition. Blood is drawn into a regular 20 cc syringe or into a special vacuum container with a medical needle. From there it is poured into a graduated laboratory test tube.
The analysis result is distorted:
- helminthic infestations;
- colds;
- influenza strain;
- food poisoning;
- any intoxication of the body;
- avitaminosis;
- changes in hormonal levels.
If you have such conditions, it is advisable to refrain from taking tests.
Decoding the results
The analysis is interpreted by a doctor. However, the results of the study are not difficult to understand on your own. A balanced blood formula has a 6:4 ratio between plasma and the total content of formed elements.
Depending on the fluctuation in one direction or the other, the Ht indicator is considered increased or decreased. The average (reference) value is strictly correlated with age and gender. Additional physiological factors are usually at play.
Hematocrit (the norm for women by age should not go beyond 30-45%). For men, this figure varies in the range of 35-49%. A 5% deviation is acceptable. If it is greater, the hematocrit number is considered underestimated or overestimated.
This result may be caused by temporary natural causes and may not have diagnostic significance. But in any case, medical consultation and additional examination are strongly recommended.
Disturbances in the balance of blood cells are often associated with dangerous pathologies - oncological, endocrine, cardiovascular.
What does hematocrit show?
Hematocrit readings accurately reflect the volume of blood contained in red blood cells (erythrocytes). In addition, the indicator reflects the size of red blood cells. The standard unit of measurement is %.
Normal values for women from 18 to 45 years old range from 35 to 45%, for men of the same age - from 40 to 50%. With age, the value of this indicator begins to increase. Thus, for women over 60 years of age, the permissible norm ranges from 37 to 49, for men – from 40 to 55%.
A hematocrit value of 35% means that 100 ml of blood being tested contains 35 ml of red blood cells.
The study is prescribed by a general practitioner, pediatrician, surgeon, hematologist, gynecologist or endocrinologist. The analysis is carried out as part of a routine examination or if the development of diseases is suspected, as well as if it is necessary to prepare for surgery. Repeated measurements of the indicator are necessary to dynamically monitor the effectiveness of selected treatment methods. The indicator is also relevant when assessing the patient’s condition after prolonged dehydration.
How to get it back to normal
The success of therapy and restoration of the Ht indicator lies in eliminating the imbalance of the blood count. In frequent cases, special clinical measures are not required. It is enough to change your lifestyle, give up addictions to alcohol and nicotine, and adjust your diet.
They will help quickly bring the hematocrit value back to normal:
- regular walks in the fresh air;
- ventilation of the room and daily wet cleaning;
- drinking large amounts of water;
- refusal of uncontrolled use of medications - Analgin, Aspirin and others, which are in every home medicine cabinet;
- playing sports or morning exercises;
Alcohol and caffeine are diuretics that lead to an imbalance of red blood cells. It is necessary to stop using them. These drinks dehydrate the body and stimulate urinary function.
This category also includes carbonated water and sweet juices. Antioxidants protect the body from free radicals, helping to saturate cells with oxygen. For sports activities, morning jogging and leisurely cycling are recommended.
Medications
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause of the imbalance of blood cells. A universal technique has not been developed. The doctor prescribes treatment only after a complete examination and identification of the cause of the hematological disorder.
For peptic ulcer disease, which often leads to a violation of the Ht indicator, a gastroenterologist develops therapeutic tactics. Usually it includes a complex intake of drugs that suppress symptoms - anabolics, antiemetics, antispasmodics.
Additionally, analgesics are prescribed. To maintain the body's defenses, vitamin complexes and immunostimulants are prescribed.
Inflammation and dysfunction of the renal organ are treated:
- antibiotics;
- sulfa drugs;
- uroseptic agents;
- antibacterial drugs of the nitrofuran group.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are used. Therapy for anemic syndrome, which leads to a violation of the blood formula, is developed depending on the severity of the pathology. If the hematocrit is elevated, a course of medications is often prescribed to dilute the biological fluid.
In severe cases, a replacement solution is infused, which reduces the viscosity of the blood and improves its rheological properties.
Traditional medicines for hematocrit disorders:
- Interferon;
- Hydroxyurea;
- Anagrelide;
- Myelosan;
- radioactive phosphorus.
The doctor prescribes the duration of the course of treatment, dosage and combination of drugs individually based on the patient’s clinical picture and medical history.
Traditional methods
If a hematocrit disorder occurs, diet correction is necessary.
Traditional recipes include the use of iron-containing and protein-rich foods:
- chicken eggs;
- beef and pork;
- seaweed;
- legumes;
- sturgeon caviar.
It is advisable to include apples, dried apricots, and raisins in your diet. If the cause of an imbalance in the blood formula is iron deficiency anemia, you can make a special nutritious cocktail from carrots, beets and radishes.
They are passed through a coarse grater, squeezed out and the juice is poured into a saucepan. It is placed in the oven and simmered for 3 hours on the lowest flame. Take the resulting decoction 3 times a day after meals. The full course of traditional therapy is 3 months.
Other methods
If a decrease in hematocrit number is associated with loss of strength and chronic fatigue syndrome, you can take 1 tbsp before meals. garlic squeeze with honey, boiled over low heat for 5 minutes.
150 ml of aloe extract mixed with 200 g of natural honey and a glass of Cahors wine helps well in this condition. This remedy will increase the hemoglobin content in the blood. They drink it 1 tbsp. 3 times a day before meals.
To treat hematocrit disorders with home methods, use garlic tincture in 96% alcohol. The vegetable is crushed and filled with flammable liquid. The solution needs to be kept for 2-3 weeks in a hermetically sealed bottle. Take 20 drops three times a day per glass of fresh cow's milk.
Causes and symptoms of increased hematocrit levels in adults
The global reason for the increase in hematocrit is clear - it is an increase in the number of red blood cells (overproduction in the bone marrow) or an increase in their size, which creates additional volume.
Triggers for hematocrit growth in men and women can be physiological and pathological conditions.
Among the physiological reasons, the most significant are: 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy, changes in air composition, stress, work at height, muscle mass gain due to anabolic steroids.
The most common triggers of pathological changes are: dehydration as a result of intoxication, infection or as a result of insufficient fluid intake, long exposure to the sun, hypoxia due to endocrine, metabolic disorders or chronic cigarette abuse. In addition, the reasons for increased hematocrit in the blood in adults can be:
- erythremia;
- polycystic kidney or adrenal gland disease;
- tumors of any location;
- anemia of various origins;
- diabetes;
- thrombosis;
- leukemia;
- bleeding;
- peritonitis;
- drug poisoning;
- cardiopulmonary pathology in different variants;
- apnea;
- renal ischemia, chronic renal failure;
- burns with a large area of damage;
- internal organ injuries.
An increase in the indicator can be observed with blood transfusions.
An increase in blood hematocrit in most cases does not go unnoticed, and the clinical picture directly depends on the etiology of the underlying cause. Rarely are there no external signs of pathology, but symptoms of malaise and weakness still bother the person.
The main symptoms of high hematocrit are dizziness, shortness of breath, numbness of the extremities, constant nausea, chronic fatigue syndrome, disorientation in space and time. There are no gender or age differences; the only difference may be the severity of clinical symptoms.
Possible complications
Imbalance of the blood formula leads to acid-base imbalance in the body, dysfunction of internal organs, and creates favorable conditions for the invasion of pathogenic pathogens. This is fraught with numerous complications and the formation of severe pathologies.
With increased blood viscosity, it is difficult to remove waste and toxins from the body, and the protective abilities of the immune system are suppressed.
Life-threatening pathologies resulting from hematocrit disorders:
- myocardial infarction;
- ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- airway spasm;
- gangrene of the limbs requiring surgical amputation.
A change in the rheological properties of blood in a pregnant woman’s body leads to highly complicated labor and fetal hypoxia. A child may be born with severe disorders of the central nervous system, destruction of bones and muscle fibers.
In such a responsible physiological state, a woman needs to carefully ensure that the hematocrit is normal. By age, such a deviation is more typical for pregnant women after 35 years of age than for young girls. If the Ht value is very high, the risk of developing thrombosis and vein blockage increases sharply.
In pregnant women
During pregnancy, a lot of changes occur in a woman’s body; the body is completely rebuilt. All these modifications occur with only one purpose - to preserve the fetus. In this case, the blood also undergoes a number of transformations.
After 3-4 months of pregnancy, a woman experiences increased production of plasma in her blood. Despite the fact that the number of red blood cells also increases, as a percentage, along with plasma, there are significantly fewer of them. It is this process that leads to lower performance.
A blood test for hematocrit in pregnant women helps to identify the percentage balance of red blood cells and plasma. As a rule, a low hematocrit level is normal in such cases. The average hematocrit in pregnant women varies from 31% to 36%.
A reduced hematocrit level in pregnant women may also occur for some other reasons:
- for infections;
- in case of disruption of the immune system;
- failure of the liver and kidneys;
- gastritis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- anemia;
- deficiency of vitamins in the body.
However, in some cases, the hematocrit number may, on the contrary, be higher than normal. This negatively affects not only the functioning of the cardiovascular system, but also the entire body as a whole. Such deviations can cause disturbances in the physical and mental development of the fetus, and even lead to its death.