Determining the level of creatinine in urine is carried out using several methods and is essential in the diagnosis of many pathological diseases and conditions. What is creatinine and why do we need it?
This element is formed as a result of the interaction of creatine with creatine phosphate in the blood. It is the end product of decomposition after complex biochemical reactions associated with the production of energy necessary for human life. If the filtering ability of the kidneys is impaired, this component can accumulate in the body and cause intoxication. Its decrease, or even more so its increase in urine, may indicate pathologies of various organs or be a consequence of the influence of physiological factors.
What is creatinine?
Creatinine is the main supplier of energy for muscles. The substance is synthesized mainly in muscle tissue. When they contract, creatine phosphate breaks down, creatinine is formed, and powerful energy is released.
The substance is synthesized constantly, entering the blood, and does not pose a danger if it is promptly excreted in the urine. With pathologies of the genitourinary system, the level of creatinine goes beyond the normal range. Therefore, this indicator is used as a marker that helps assess the condition of the excretory system.
Uric acid
Uric acid is the end product of purine metabolism occurring in the human kidneys (adenine, guanine). Uric acid is found in the liver, brain, blood, urine and sweat of a person in the form of urate (sodium salt) in high concentrations, therefore, even if it is slightly exceeded, crystallization of salts occurs.
Uric acid is poorly soluble in water and crystals of its salts - urates, deposited in the joints and urinary tract, cause the development of gout and the formation of urate stones in the kidneys.
Level of uric acid in the blood
| Age | kmol/l | mg/dl |
| in men under 60 years of age | 0,26−0,45 | 4,4−7,6 |
| in women under 60 years of age | 0,14−0,39 | 2,3−6,6 |
| in men over 60 years of age | 0,25−0,47 | 4,2−8,0 |
| in women over 60 years of age | 0,21−0,43 | 3,5−4,2 |
The bulk of uric acid is produced by the liver (up to 0.5 - 1.0 g per day). Most of the uric acid (up to 80%) is formed as a result of the metabolism of endogenous nucleic acids, only about 20% is associated with purines coming from food. The kidneys excrete about 0.5 g of uric acid per day, 0.2 g is removed through the gastrointestinal tract.
- Increased clearance and excretion of uric acid (uricosuria) is observed with:
- increased diuresis (drinking large amounts of water, mannitol, saline)
- increase in extracellular fluid volume
- decreased proximal reabsorption
- administration of large doses of salicylates, which block the reabsorption of uric acid
- A decrease in uric acid excretion is observed with:
- increased sodium reabsorption in the proximal tubules, for example in heart failure
- administration of small doses of salicylates
The circadian rhythm of uric acid excretion resembles the rhythm of sodium excretion - at night, excretion is 2 times less than in the morning (from 7 to 10 a.m.).
- Disorders of uric acid metabolism can be caused by:
- its excessive formation
- decrease in urate-binding globulin in the blood
- impaired excretion of uric acid through the kidneys (decreased filtration, increased reabsorption, decreased secretion)
An increase in the concentration of uric acid in the blood above normal is called hyperuricemia.
- Causes of hyperuricemia (increased uric acid)
- high purine content in food
- increased formation of uric acid
- pathology affecting kidney function
If the first reason, when hyperuricemia is caused due to the high content of purines in food, is quite easy to deal with - you just need to limit the consumption of red meat, liver and kidneys, fish, mushrooms, legumes, tea, cocoa, chocolate and beer (it is also worth noting that in general, in order to obtain the most accurate result of the study, 3 days before donating blood for analysis, it is necessary to follow a low-purine diet), then about the second, when the formation and removal of uric acid is impaired or there is a pathology that needs to be treated, it is necessary to talk in more detail.
Uric acid in the blood
Hyperuricemia against the background of pathology indicates either the presence of gout in the body or is determined by B12-deficiency anemia, leukemia, pneumonia, tuberculosis, hepatitis, diabetes mellitus.
Gout is usually divided into primary, when increased accumulation of uric acid has no connection with diseases, and secondary, in case of connection with kidney pathology, hematological diseases, cancerous tumors, and prolonged fasting.
Primary gout develops when uric acid is slowly excreted from the body (may be associated with renal failure) or when its synthesis in the kidneys is increased. In this case, urate salts formed as a result of crystallization of uric acid are deposited in the human kidneys and joints.
Gout
Gout. Development risk
| Uric acid in blood serum, mmol/l | Risk in men, % | Risk in women, % |
| below 0.41 | 2 | 3 |
| 0,42−0,47 | 17 | 17 |
| 0,48−0,53 | 25 | no data |
| above 0.54 | 90 | no data |
Gout
When gout occurs, the concentration of uric acid in the blood is usually 3-4 times higher than normal, but in particular cases it can fluctuate widely, a decrease down to normal can be recorded (at this point an acute attack of gout is possible), followed by an increase.
The diagnosis of gout is made when at least two of the symptoms presented below are present simultaneously.
- Signs of gout (at least 2 at a time)
- the level of uric acid in the blood in men is above 0.48 mmol/l, and in women 0.38 mmol/l
- detection of sodium urate salts in the synovial fluid of joints or tissues
- the presence of tophi (gouty nodules, usually located around the joints)
- at least one attack of acute arthritis, which ended suddenly after 1-2 days
- swelling of the affected joint
Gout
Secondary gout develops with B12-deficiency anemia, leukemia, polycythemia pneumonia, scarlet fever, tuberculosis, hepatitis, diabetes mellitus, acidosis, eczema and psoriasis. Also, the so-called “alcoholic’s gout” develops against the background of severe alcohol intoxication.
Uric acid in the blood can be elevated for a number of reasons: primary and secondary.
- Primary causes of increased uric acid in the blood
- a defect in the enzyme hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase, which catalyzes the conversion of hypoxanthine and guanine to IMP and GMP. As a result of the defect, hypoxanthine and guanine are not reused in the synthesis of mononucleotides, but are completely converted into uric acid. Clinically, the defect can manifest itself in different ways - from asymptomatic hyperuricemia, through “familial” forms of gout to very severe Lesch-Nychen syndrome. This syndrome is gender-linked and is detected only in boys whose heterozygous mothers are carriers of the disease. Signs of gout appear between six months and 16 years of age. In addition, the disease is characterized by choreoathetosis, spastic paralysis, impaired thinking, aggressiveness and a tendency to self-mutilation. The mechanism of neurological disorders may be associated with a decrease in dopamine synthesis in the extra-pyramidal system. Laboratory: high levels of uric acid in the blood and urine, the ratio of the concentration of uric acid to creatinine is 2-3 times higher than normal (normal 0.21 - 0.59), reduced enzyme activity in lysates of washed red blood cells
- increased activity of the enzyme phosphoribosyl-phosphate synthetase, which stimulates the destruction of purine metabolic products to uric acid
- decreased sensitivity of tissues to increased concentrations of uric acid (loss of feedback)
- deficiency of a protein in the blood plasma that binds and transports uric acid
- congenital functional characteristics of the kidneys
- Secondary causes of increased uric acid in the blood
- consumption of foods containing a large amount of purines: offal (liver, kidneys, tongue), veal, meat extracts, smoked meats, caviar, coffee and strong tea
- starvation (tissue destruction)
- hematological diseases (decomposition of nuclear cells, lysis of red blood cells that contain large amounts of uric acid)
- leukocytosis, erythrocytosis
- renal failure
- epilepsy, increased muscle strain
- glycogenosis type I
- hyperlactatemia, ketonemia (competition for the mechanism of uric acid secretion in the kidneys)
- dehydration
- diabetes
- hypertonic disease
- malignant neoplasms
- psoriasis
Hippuric acid is excreted in the urine of a healthy person in the amount of 0.1-2.0 g per day. Such large fluctuations depend on the composition of the food. On a vegetarian diet, when eating large amounts of fruits containing aromatic compounds, the amount of hippuric acid in the urine is higher. Taking benzoic acid, salicylic acid and its derivatives is also accompanied by increased excretion of hippuric acid. This synthesis is protective because it eliminates benzoic acid, which is toxic to the body.
Normal creatinine levels
Creatinine in urine, the norm of which must correspond to the values established by WHO, extremely rarely goes beyond acceptable limits.
The substance content is affected by:
- patient's lifestyle;
- age;
- level of physical activity;
- eating habits;
- weight;
- floor.
It should also be taken into account that for people who have only one kidney, the norm will be 180-190 µmol/l.
In elderly patients, people debilitated by a long-term illness or poor nutrition, the indicators may decrease significantly.
Women, pregnant
When carrying out the analysis, it should be taken into account that the level of creatinine in women may be reduced in early pregnancy, especially if the expectant mother suffers from severe toxicosis. And after the onset of menopause, the content of the substance may be slightly increased.
Creatinine in urine. Norm
Creatinine standards for women:
| Age | In urine, ml/min | In blood, µmol/l |
| from 18 to 60 years old | 81-116 | 53-97 |
| over 60 years old | 58-110 | 53-106 |
Men
Creatinine in the urine (the norm in men is slightly higher than in women) in representatives of the stronger sex after 60 years of age is also present in increased quantities, since their filtration capacity of the kidneys decreases. In addition, the muscle activity of men is higher than that of women, and protein foods predominate in their diet, which explains the increase in indicators.
Creatinine standards for men:
| Age | In urine, ml/min | In blood, µmol/l |
| from 18 to 60 years old | 107 to 139 | 60 – 115 |
| over 60 years old | 71 – 115 |
Children
In children, the norm of the indicator also depends on age. In girls, the level of the substance may be lower than in boys.
Creatinine standards for children:
| In urine, ml/min/1.7 m2 | From birth to one year | 65–100 |
| From 1 year |
| |
| In blood, µmol/l | In newborns | 27-88 |
| From birth to one year | 18-35 | |
| Up to 10 years | 27-62 | |
| During adolescence | 44-88 |
Albumin to creatinine ratio in urine
Albumin is a protein that is excreted in urine. Characterized by small molecular size compared to other proteins. This means that if there are problems with the kidneys in the human body, then albumin will be the first indicator of disease. The concentration of this protein fluctuates greatly due to several factors that have nothing to do with overall health, such as time of day and intense exercise.
Nowadays, you can easily calculate the ratio of albumin and creatinine in urine, and for this you do not need to collect all the urine in a day, as was customary before, but a very small amount will do.
There is a certain albumin indicator that can be used to determine the stage of kidney damage in men and women:
- normally - less than twenty milligrams per liter;
- mild kidney damage - from twenty to two hundred milligrams per liter;
- severe - from two hundred or more.
The normal level of creatinine in urine was mentioned above. Using these two values, a urine test for albumin and creatinine is calculated. For a healthy man these will be the values (mg/g):
- standard – less than seventeen;
- the initial stage of kidney dysfunction - from seventeen to two hundred and forty-nine;
- severe stage - over two hundred and fifty.
For woman:
- the norm is twenty-five or less;
- the first stage of kidney damage - from twenty-five to three hundred and fifty-four;
- second stage – more than three hundred and fifty-five.
Why does the concentration decrease?
A slight decrease in the level of a substance does not always indicate the occurrence of a pathological process in the body.
The reasons may be related to some physiological characteristics of the body:
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- weight loss due to poor nutrition or excessive exercise;
- exhaustion associated with vegetarianism, strict diets;
- glucocorticoid therapy.
Kidney diseases
The most common pathological cause of the disorder is diseases of the urinary organs. As a result of autoimmune or infectious processes occurring in the kidney tissues, the nephrons, which act as a filter that purifies the blood, suffer.
In this case, there is a drop in the level of creatinine in the urine . This can occur with pyelonephritis, damage to the glomeruli of the kidneys. Also, the cause of the disorder may be renal amyloidosis or oncological processes. Such pathologies lead to narrowing of the arteries of the organ, the occurrence of ischemia of its tissues, which is reflected by the reduced level of the substance in the analysis.
Pathologies of muscle structures
Deviations in analyzes are also observed during inflammatory processes in the muscles. For example, the concentration of creatinine decreases with muscular dystrophy and myositis. The disorder also occurs when muscle mass decreases as a result of malnutrition and protein deficiency in the diet.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is an endocrinological pathology characterized by an increase in the level of thyroid hormones. One or both lobes of the thyroid gland are involved in the pathological process. At the same time, biochemical parameters change, the level of creatinine drops. However, deviations in the analyzes are not detected in all cases.
Tumor processes
The formation and growth of some tumor-like formations, both benign and malignant, is accompanied by loss of muscle mass and disruption of the functioning of many systems and organs. At the same time, test results change and creatinine levels drop.
general information
There are no specific complaints indicating that its level is increased or decreased, because it is a kind of marker of some diseases, which we will talk about below.
Athletes often use creatine to increase the duration and intensity of physical activity, but this method is fraught with problems for people who have some problems with the musculoskeletal system, nervous and/or urinary systems.
Since this carboxylic acid, after breakdown, forms creatinine, which is excreted by the kidneys. We must not forget that the “throughput capacity” of the kidneys is not limitless, especially if it concerns the culprits of this article, since their structure has a macromolecular structure, which does not allow the renal tubules to freely pass these products through themselves.
When a large amount of creatinine accumulates in the body, the latter begins to act as a poison, since its structure is acidic.
Why does concentration increase?
The doctor, depending on the severity of the disorder, draws conclusions about how serious the patient’s health problems are. Inflated indicators are not considered a pathology if this is caused by the use of various dietary supplements that increase endurance and help people who are professionally involved in sports build muscle mass.
Other cases require careful diagnosis to exclude serious pathologies.
Diseases of the urinary system
The substance can accumulate in the body if metabolic processes are disrupted. Creatinine can be synthesized by muscles in large quantities and accumulate if the filtration process is defective. If abnormalities are detected in the tests, it is necessary to conduct additional studies to exclude renal failure.
Other renal pathologies in which an increase in the level of the substance is observed:
- amyloid dystrophy;
- diabetic nephropathy;
- tubular necrosis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- pyelonephritis;
- tumors, kidney stones.
Diabetes
Pathological processes associated with metabolic disorders require constant monitoring to ensure normal conditions for kidney function. One of these diseases is diabetes mellitus. People with this diagnosis usually have elevated creatinine levels.
Hormone imbalance
Deviations from norms in analyzes are also detected in pathologies caused by hormonal imbalance. For example, in patients with acromegaly and gigantism, in which there is excess production of growth hormones, creatinine levels are higher than normal.
Other reasons
Increased levels of the substance can also be observed in other diseases and conditions:
- destruction of muscle tissue. In conditions accompanied by the destruction of muscle tissue, significant amounts of the substance enter the bloodstream. This occurs with prolonged compression syndrome, internal bleeding. Also, the causes of the disorder can be traumatic brain injuries, deep burns;
- high protein diet. Deviations in analyzes are often found in people whose diet is dominated by meat;
- infectious and inflammatory processes (leptospirosis, sepsis, gangrene, sexually transmitted infections);
- pathological processes in other organs (heart failure, cirrhosis and malignant liver tumors, intestinal obstruction).
Deviations in tests are also detected when taking drugs with nephrotoxic effects:
- antibacterial agents;
- barbiturates;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- salicylates;
- hormonal medications;
- antihypertensive drugs;
- immunosuppressants;
- immunoglobulins.
What do these indicators mean?
Creatinine is a product of metabolic biochemical reactions of protein breakdown. Its formation occurs continuously and is associated with metabolic and energy processes in striated and smooth muscle cells.
Muscle contraction requires a large amount of energy, and the number of muscles in an adult exceeds 650. This is why muscle contractility requires a powerful source of power to supply the muscles in case of an emergency.
The main source of energy substrate is the content of creatine phosphate, which, under the action of the body's enzymatic systems, is converted into another compound. The result is that the energy obtained during the biochemical reaction is used for life, and the residues are excreted in the urine.
Urea is a biologically active result of the breakdown of nitrogen-containing proteins. With prolonged transformation of proteins, ammonia is neutralized - a dangerous toxic substance that depresses the central nervous system and causes damage to neurons and other cells of the body. In case of renal dysfunction and renal failure, its amount may increase.
A blood test for urea and creatinine must be performed on every patient admitted to the hospital, regardless of his disease. Such an examination allows us to identify hidden pathologies.
When is the test ordered?
A specialist, examining the patient and collecting anamnesis, will recommend testing the level of the substance if there are such symptoms indicating kidney damage:
- pulling, cutting, sharp pain in the lumbar region;
- feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied;
- frequent (including false) urge to urinate;
- inclusions of pus, blood, mucus in the urine;
- discomfort during urination, burning and pain;
- swelling in the face, arms and legs;
- fatigue, decreased activity, muscle weakness.
The doctor may also suspect the presence of other pathologies, which will manifest itself:
- muscle pain, increased weakness, decreased activity, hematomas with muscle damage;
- a feeling of weakness, apathy, disturbances of the digestive processes - with liver diseases;
- problems with stool, feeling of nausea, vomiting, increased gas formation, pain - if the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted;
- vomiting with blood, red urine, black stool, which indicates internal bleeding;
- weight fluctuations, excessive urine output, tachycardia - with endocrine pathologies;
- edema, arrhythmia, pressure surges - with heart disease.
With an isolated increase in the level of the substance, no negative manifestations are observed.
Urea (urea nitrogen) blood
Urea is the end product of protein metabolism in the body.
It is excreted from the body by the kidneys using glomerular filtration. The vast majority of dietary nitrogen atoms are ultimately excreted from the body in the form of urea, which accounts for about half of the nitrogen in the blood and 80-90% of the nitrogen in the urine. Urea is synthesized in the liver in the ornithine cycle. Urea freely penetrates into all cells, including red blood cells, where its concentration is about 80% of the concentration in plasma.
Urea is excreted from the body mainly through the kidneys by filtration in the glomeruli. About half of the filtered urea is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule. In the descending limb of the loop of Henle, part of the urea along the concentration gradient can again enter the lumen of the tubule. The collecting ducts of the renal medulla, under the influence of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), significantly increase the permeability of their wall to urea, which is absorbed along with water.
Urea can also be excreted from the body extrarenally. Less than 10% of the total urea concentration in plasma is excreted through sweat and feces. However, in case of renal failure, the excretion of urea through the gastrointestinal tract is not very effective, since urea in the intestine is destroyed by urease and the resulting ammonia is reabsorbed and passes through the portal system into the blood.
Healthy kidneys can excrete several times more urea than is synthesized in the body, but the level in the blood only rarely and slightly falls below normal values. If there is too much filtration, reabsorption in the kidney tubules increases. Perhaps this is necessary in order to maintain the amount of guanidine groups in the body at a certain level.
Due to reabsorption in the tubules, the clearance of urea is variable, but is always equal to or less than that of creatinine. The urea content can increase even with minor damage to kidney function, impaired blood flow in them, and with an increase in its production much earlier and easier than the content of other nitrogenous wastes, such as creatinine.
Urea itself has very little toxicity. It is often used as a drug - an osmotic diuretic that causes dehydration in the treatment of pulmonary and cerebral edema.
Its severity is determined not by the accumulation of urea itself, but by other substances, in particular potassium and toxic derivatives of guanidine - guanidine succinic acid, methyl guanidine, guanidyl acetic acid, which appear in the body due to disruption of the normal pathway of urea formation from arginine. At the same time, it should be borne in mind that urea, passing relatively easily through the cell membrane and being an osmotically active substance, carries water associated with it into the cells of parenchymal organs. This leads to an increase in cell volume and disruption of the functional state of vital organs and tissues.
There are several causes of elevated urea levels in the blood (a condition called azotemia):
- Reasons for increased urea levels in the blood:
- adrenal
- renal
- renal
- Reasons for decreased urea levels in the blood:
- congenital deficiency of urea synthesis
- severe liver failure
- Adrenal causes of increased urea levels in the blood:
- rich protein diet
- high protein catabolism during fevers, heavy muscular work
- diet low in chloride ions (compensatory adaptive reaction aimed at maintaining colloid osmotic blood pressure)
- heart failure
- blood loss
- reduction in filtration pressure
- acute dehydration
- leukemia
- severe infectious diseases
- burns
- shock
- Renal causes of increased urea levels in the blood:
- diseases and pathologies of the kidneys, accompanied by a decrease in glomerular filtration and loss of nephrons
- Subrenal causes of increased urea levels in the blood:
- urinary tract obstruction
- prostate adenoma
- tumors of the urinary system
The level of urea in the blood may increase due to the consumption of large amounts of food rich in proteins, but such an increase will be one-time in nature, and with a decrease in the amount of protein consumed in food, the level of urea will return to normal (adrenal azotemia).
In the case of repeated determination of an elevated level of urea in the blood (more than 50 mg/dl), renal azotemia is diagnosed - it is caused by chronic pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, hydronephrosis, and kidney tuberculosis. When urea levels in the blood are high (more than 130 mmol/l), acute renal failure is diagnosed.
Subrenal azotemia is associated with problems with urine excretion - prostate adenoma, stones of the genitourinary system.
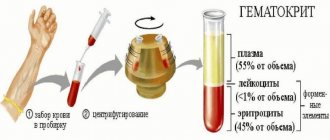
Diagnostics
To determine the level of the substance, blood and daily urine are examined. Based on the test results, it is recommended to be examined by specialized specialists (endocrinologist, nephrologist, gastroenterologist, cardiologist).
Analysis of urine
To carry out the analysis, the patient collects urine, which is excreted during the day. It is recommended to drink a lot of water. In the morning, the patient urinates in the toilet, and the rest of the urine should be collected in a special sterile container (4-5 l).
Blood analysis
In parallel with the urine test, a blood test is performed. Biomaterial from a vein is taken on an empty stomach in the morning. You can eat food no later than 8 hours before the test.
The indicators obtained from the study of biological fluids are used to determine the value of glomerular filtration and evaluate kidney function (the study is called the Rehberg test).
Rehberg's test
The Rehberg test is the most accurate analysis that allows you to understand whether kidney function is impaired. During the study, the average plasma filtration rate is determined. If an increase in the level of a substance in the blood is detected, and a decrease is observed in the urine, this may be a sign of kidney dysfunction.
The study is carried out by:
- patients who must constantly monitor their kidney function;
- to monitor the condition of a person with endocrine diseases;
- pregnant women to assess kidney function.
When performing an analysis in a hospital, the patient is asked to drink about 600 ml of water, then urinate. In this case, the time is recorded, and a portion of urine is poured out. After 30 min. They do a blood test to determine the level of the substance. And after 1 hour, the patient is again asked to urinate and collect the entire portion of urine.
Creatinine in blood and urine
Creatinine is a product of the breakdown of creatine phosphate in muscles, and, as a rule, is formed at an almost constant rate; Its serum level normally depends on muscle mass. Creatinine is freely filtered by the kidneys and is practically not reabsorbed in the tubules
Thus, creatinine is characterized by five properties:
- This is an endogenous product, i.e. a product that is formed in the body itself, it does not need to be introduced into the blood;
- Constant rate of formation for each individual (muscle mass of a person changes slowly);
- As a small molecule, creatinine is freely filtered by healthy glomeruli;
- Like waste, creatinine is not reabsorbed in the glomeruli; as much creatinine enters the urine as was filtered in the glomeruli;
- It is practically not secreted in the tubules, which means that blood creatinine enters the urine only through the glomeruli.
The last property of creatinine needs clarification. In acute renal failure, when glomerular function is sharply impaired in a matter of hours, the level of creatinine in the blood plasma rapidly increases and part of the creatinine is secreted by the tubules. As a consequence, in acute renal failure, urine creatinine does not fully reflect glomerular function.
Economic component: determination of creatinine is available in a laboratory of any category. The listed properties of creatinine underlie the use of this metabolite to assess the filtration function of the kidneys.
Normally, per minute the kidneys clear 110-150 ml of blood from creatine in men and 100-130 ml in women. The volume of plasma that is completely cleared of creatinine in a minute is called creatinine clearance. Serum creatinine clearance thus reflects the glomerular filtration rate.
The indicator of creatinine clearance and glomerular filtration rate is used for diagnosis:
- renal failure,
- monitoring the development of renal failure,
- assessing the effectiveness of therapy.
The diagnosis of kidney failure is usually suspected when the serum creatinine level is higher than the upper limit (boundary) of its normal range. Serum creatinine levels can change due to muscle activity, nutrition, and health status. Serum creatinine is elevated in non-renal diseases such as muscular dystrophy, anemia, leukemia and hyperthyroidism.
Preparation for analysis. Urine collection
To get a reliable result, you need to properly prepare for the study:
- Refrain from eating 8 hours before the test, and 24 hours from drinking alcoholic beverages. The day before the procedure, avoid eating fatty foods;
- 1 hour before the test, do not smoke, stop drinking juices, tea, and coffee. Still water is allowed;
- eliminate excessive physical activity and emotional distress;
- limit taking medications after consulting a doctor.
Before the analysis, physiotherapeutic procedures, instrumental examinations, X-ray and ultrasound examinations, massage and other medical procedures are not carried out, as this may affect the result. To monitor the indicator over time, the analysis is repeated in the same laboratory.
Urine that is collected for analysis must be stored in a special container in the refrigerator. When the last portion is added, the volume of liquid is measured, mixed and poured into a container that will be delivered to the laboratory. Before collecting biomaterial, hygiene procedures are mandatory.
The result of the analysis is affected by the intake of alcohol and drinks containing caffeine. It is important to consider that you should not drink at night. The last time you are allowed to consume liquid, as well as food, is 8 hours before the test.
What does deviation from the norm mean?
The analysis results often reveal deviations from acceptable indicators - excess or underestimation. The substance depends directly on diet and stress, pathologies and acute conditions of the body. Let's look at what each research result means.
High level
An elevated creatinine level indicates a failure of filtration by the renal system. But decoding can only be done by a doctor who evaluates not only the indicators of the substance, but also other symptoms not related to the kidneys. Often high creatinine occurs when there is only one kidney due to surgery or a developmental abnormality.
More on the topic: What appears in the urine during proteinuria?
Exceeding the norm may mean one of the following factors:
- Consumption of high-protein foods, active training for muscle growth, pregnancy, breastfeeding or dehydration;
- Fractures, injuries, internal bleeding, burns;
- A course of treatment with certain drugs - Captopril, Cimetidine, Cyclosporine. There are also creatine supplements that affect test results;
- Metabolic diseases - gout or diabetes;
- Diseases of the endocrine system, gigantism, hyperthyroidism, hypercortisolism or acromegaly;
- Cancer or kidney failure, urolithiasis and other pathologies of the urinary system.
Low level
Low concentrations are detected very rarely, and the phenomenon is not associated with kidney problems. creatinine is underestimated in the following cases:
- vegetarianism with a lack of protein or insufficient consumption, fasting and exhaustion of the body;
- muscular dystrophy, loss of muscle mass;
- chronic liver diseases;
- taking corticosteroids;
- toxicosis during early pregnancy;
- increased thyroid function;
- for anemia and leukemia.
Clearance below acceptable standards occurs with heart or kidney failure, problems with blood flow in the kidneys, or rhabdomyolysis. An important indicator during the examination is urea, the end product of protein metabolism. When urea (carbamide) decreases, the most common cause is a malfunction of the renal glomeruli.
What distorts the results of the analysis?
Creatinine in urine, the norm of which depends on many factors, may be present in insufficient quantities if:
- improper collection of biological fluids. This leads to the destruction of red blood cells, releasing their contents, which distorts the result;
- pregnancy. A woman carrying a baby has an increased blood volume. At the same time, the filtration process is activated and creatinine is actively removed.
A false positive result can be obtained when:
- diabetes mellitus;
- excess muscle mass, taking steroids;
- extensive tissue damage;
- taking medications with ascorbic acid, barbiturates or aminoglycosides;
- dehydration;
- during a period of active growth;
- under high physical activity;
- in patients on a low-carbohydrate diet.
Before carrying out the analysis, it is necessary to exclude, if possible, factors that may affect the result. If this is not possible, you must notify the doctor of the existence of circumstances that may lead to the receipt of inaccurate data. When making a diagnosis, such information must be taken into account.
Creatinine in the first morning urine sample
Is something bothering you? Do you want to know more detailed information about creatinine in the first morning urine sample or other tests? Or do you need a doctor's examination? You can make an appointment with a doctor - the Eurolab clinic is always at your service! The best doctors will examine you, advise you, provide the necessary assistance and make a diagnosis. You can also call a doctor at home. The Eurolab clinic is open for you around the clock.
How to contact the clinic: Phone number of our clinic in Kyiv: (+38 (multi-channel). The clinic secretary will select a convenient day and time for you to visit the doctor. Our coordinates and directions are listed here. Look in more detail about all the clinic’s services on its personal page.
| (+38 |
If you have previously performed any studies, be sure to take their results for consultation with a doctor. If the studies have not been performed, we will do everything necessary in our clinic or with our colleagues in other clinics.
It is necessary to take a very careful approach to your overall health. There are many diseases that at first do not manifest themselves in our body, but in the end it turns out that, unfortunately, it is too late to treat them. To do this, you simply need to be examined by a doctor several times a year in order not only to prevent a terrible disease, but also to maintain a healthy spirit in the body and the body as a whole.
If you want to see a doctor, use the online consultation section, perhaps you will find answers to your questions there and read tips on caring for yourself. If you are interested in reviews about clinics and doctors, try to find the information you need on the forum. Also register on the Eurolab medical portal to be constantly aware of the latest news and information updates on the site about creatinine in the first morning urine sample and other tests on the site, which will be automatically sent to you by email.
Other services of clinics starting with the letter “K”:
| Computed tomography of the pelvis |
| Cadmium in urine |
| Potassium, Sodium, Chlorides |
| Calcium in urine |
| Ketamine |
| Creatinine in the first morning urine sample |
| Computed tomography of the brain |
| Creatine kinase (CK) |
| Potassium, sodium, chlorides in urine |
| Silicon in the blood |
| Creatinine in daily urine |
| Creatinine |
| Cortisol |
| Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) |
| Candidiasis, qualitative definition |
| Colpocytology (“hormonal mirror”) 1 study |
| Creatinine in urine over 72 hours |
| Total acid phosphatase |
| Computed tomography of the neck |
| Cardiotocography |
Why is creatinine dangerous and how to normalize it?
If there is a single and slight increase in the level of the substance, there is no need to worry, since creatinine is sensitive to food, physical activity and other factors. If the indicators go off scale, the accumulation of the substance provokes intoxication of the body.
The seriousness of the situation depends on what particular pathology caused the deviations. The problem cannot be ignored; it is necessary to take care of your health as quickly as possible. After the underlying pathology is eliminated, the level of the substance returns to normal.
Regardless of what caused the problem, it is necessary to restore health using complex methods using medications intended to treat the underlying disease, nutrition correction, traditional methods, and lifestyle changes.
To eliminate the manifestations of intoxication, it is recommended to take sorbents, and detoxification agents are administered intravenously. For patients with diabetes, the insulin dose is adjusted.
Those diagnosed with kidney pathologies are recommended to take diuretics and nephroprotectors, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. If protein metabolism is disrupted, medications are used to normalize the metabolism of nitrogenous substances.
If the cause of the disorder is poor nutrition, the condition can be normalized by adjusting the diet and thereby reducing the load on the excretory system:
- refuse or reduce to a minimum the consumption of foods that increase the amount of creatinine (pork, lamb, seafood, cottage cheese);
- reduce the amount of salt and sugar in the diet, avoid products with food additives;
- give up seeds and nuts;
- exclude peas and beans. Avoid spinach, zucchini, eggplant, and potatoes;
- do not consume chocolate, alcoholic beverages, or drinks containing caffeine;
- do not forget about compliance with the drinking regime;
- eat food at regular intervals.
However, you should not completely give up protein.
Easily digestible sources of amino acids are:
- chicken meat, rabbit meat, turkey;
- low-fat fish;
- dairy products;
- plant products (lentils, tofu).
The diet needs to be replenished with cereals, vegetables (beets, carrots, tomatoes, cucumbers are useful), fruits (apples, pears), and berries. The consumption of whole grain bread and durum pasta is allowed. Eggs can also be consumed, but not more than 3 pieces. in 7 days.
Creatinine in urine, the norm of which was indicated in the tables, can increase with physical and emotional fatigue, so proper rest is necessary to normalize the condition. People who work out in the gym should avoid strength training and intense cardio training.
To maintain physical fitness, yoga, Pilates, and swimming are suitable. To stabilize the nervous system, you can take baths with various additives (sea salt, pine needles, essential oils).
Traditional methods can also be used as part of complex therapy, but they must be treated with caution. With the help of herbs, you can improve the condition of the kidneys and remove excess substances, but chronic pathologies require the use of more serious methods.
To normalize indicators, you can drink teas from plants such as:
- calendula;
- chamomile;
- nettle;
- dandelion (root);
- sage.
To prepare the drink, 1-2 tsp. herbs need to be poured 1 tbsp. boiling water, leave for 30 minutes, strain. The infusion is consumed instead of tea 1-2 times a day. The course of therapy lasts 2-3 weeks. If the indicator does not return to normal, you need to visit a specialist.
Cinnamon also helps normalize kidney function. This restorative and tonic spice can stimulate filtration. The main thing is not to exceed the dosage. You can consume no more than 1 tsp per day. spices.
Creatinine is an important indicator that allows you to evaluate kidney function. An increased level of a substance in the urine may be a sign of pathological processes in the genitourinary system.
However, additional research is needed to make an accurate diagnosis, since the amount of creatinine can change under the influence of many factors. After eliminating them, the test results will return to normal. If a disease is discovered that affects the amount of the substance, serious therapy will be needed under the supervision of a specialist.
Causes of the disease
If we ignore such points as pregnancy, burns and fractures, we can grasp the connection of all diseases with two fundamental reasons: heredity and lifestyle.
It is impossible to influence heredity without the gross intervention of specialized medical institutions, but improving yourself by changing your lifestyle for the better will never be superfluous.
How to prevent the development of hereditary diseases
First of all, you need to lead an active lifestyle. “Movement is life” is not just a catchphrase; any doctor will confirm that it is so.
If we consider the body as an independent system, divided into many subsystems, then we can see that the movement of blood or lymph through the body is good, but stagnation means an increase in viscosity, the formation of blood clots, thromboembolism, which, to put it mildly, will not lead to anything good.
From urology: urine movement is good. Stagnation of urine - stone formation, development of infection, decreased reproductive function in men, an increase in the size of the kidneys and their cavity structures, which will ultimately end in disability at best.
We must not forget about human muscle activity. Muscle tissue not only performs the function of a frame, moving the body in space, but also helps, for example, the movement of venous blood through the calf muscle.
Nutrition
When changing your lifestyle in general, you should not forget about changing your diet and approach to food in general. First of all, we must not forget that food, first of all, is a source of energy, and not a means of obtaining pleasure.
Should be excluded:
- fatty. This does not mean that, after reading this article, you need to immediately throw out all foods that contain at least a small amount of fat from the refrigerator. The most important thing is not to overuse fats of animal origin (lard, butter, fatty layers on meat). It’s not for nothing that they say: “Everything is good in moderation.”
- fried. And, again, this does not mean that you need to throw away everything that even remotely resembles a frying pan as soon as possible. You just shouldn’t base your diet on multiple daily consumption of fried foods.
- limiting table salt. It is worth starting (or continuing) to reduce the amount of salt to a minimum.
Each disease has its own restrictions and its own diet; only a specialized specialist can tell you more. Also, do not forget about periodic checks of your health (medical examination), because a disease is much easier to prevent than to treat it.
Conclusion
Despite the low awareness of the population about such an indicator as creatine, the latter is an important component of the body, performing a couple of extremely important functions, such as participation in energy metabolism in the body, a marker for identifying diseases in the early stages of such.
How are tests performed?
Creatinine clearance is a measure of the level of protein product formed in muscles from the breakdown of creatine phosphate and pure creatine. The resulting protein is excreted by the kidneys, and if their functioning is disrupted, it accumulates in the body.
The study of serum creatinine clearance through urine allows early detection of a decrease in glomerular filtration in the kidneys. Thus, primary renal failure can be established. But there is a problem with the test's accuracy. It lies in the difficulty of collecting urine within 24 hours. Problems arise during its storage and due to the loss of part of the urine during bowel movements.
A blood test completes the information. When the kidneys lose their ability to filter, the amount of this indicator in the blood increases.
Reference values for creatinine clearance depend on age, gender and body weight.
| Age | Women | Age | Men |
| {amp}lt; 3 months | 0,3–0,9 | {amp}lt; 2 months | 0,3–0,7 |
| 3–5 months | 0,5–1,2 | 2–4 months | 0,5–1,2 |
| 5–8 months | 0,6–1,5 | 4–6 months | 0,6–1,4 |
| 8–10 months | 0,7–1,7 | 6–9 months | 0,7–1,7 |
| 10–15 months | 0,8–1,8 | 9–12 months | 0,8–1,9 |
| 15–21 months | 0,9 – 2,3 | 12–18 months | 0,9–2,3 |
| 21–30 months | 1,0–2,6 | 18–24 months | 1,0–2,5 |
| 30 months–3 years | 1,1–2,8 | 24 months – 3 years | 1,1–2,9 |
| 3–4 years | 1,2–2,9 | 3–4 years | 1,2–3,2 |
| 4 years – 5 years | 1, W–W, 6 | 4 years – 5 years | 1,4–3,6 |
| 5–6 years | 1,5–4,0 | 5–6 years | 1,5–4,0 |
| 6–7 years | 1,7–4,5 | 6–7 years | 1,7–4,5 |
| 7–8 years | 2,0–4,9 | 7–8 years | 2,0 – 5,0 |
| 8–9 years | 2,2 – 5,5 | 8 – 9 years | 2,2–5,5 |
| 9–10 years | 2,5–6,2 | 9–10 years | 2,4–6,1 |
| 10–11 years | 2,7 – 6,9 | 10–11 years | 2,7 – 6,8 |
| 11–12 years old | 3,1 –10,7 | 11–12 years | 3,0–10,4 |
| 12–13 years old | 3,5–12,0 | 12–13 years old | 3,5–11,9 |
| 13–14 years old | 3,9–13,3 | 13–14 years old | 3,7–12,8 |
| {amp}gt; 14 years | 5,3–15,9 | {amp}gt; 14 years | 7,1–17,7 |
| Age, gender | Normal creatinine |
| Baby 0-1 year | 3,0 – 11,0 |
| Preschooler 1-7 years old | 2,0 – 5,0 |
| Child 7-14 years old | 3,0 – 8,0 |
| Boy, girl 15-16 years old | 5,0 – 11,0 |
| Grown man | 8,4 – 13,6 |
| Adult woman | 6,6 – 11,7 |
To more accurately assess kidney function and the extent of kidney damage, other available means of assessing glomerular filtration, such as cystatin C analysis, are used.
The best diagnostic value is a comprehensive study of several indicators simultaneously - for example, urea and creatinine together.
This condition where urea levels are elevated but creatinine status is normal is called prenatal azotemia. This picture can be observed with burns, fasting, fever, hemorrhage in the upper gastrointestinal tract, etc.
An increase in creatinine is recorded with increased consumption of one's own protein (for example, endogenous protein of muscle tissue). And with an increased urea content, increased exogenous consumption is more often observed - from food.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and press Ctrl Enter.
Measurement of urea and creatinine levels in two biological media is currently used
A biochemical blood test is taken on an empty stomach, and the day before it is recommended to follow the patient’s usual diet. Indicators are determined in serum or blood plasma, which is taken from the elbow. If blood plasma is used for diagnostic testing, an antiplatelet drug is added to the test tube in advance.
To conduct a biochemical urine test, a special large container is required in the medical laboratory. The patient is asked to collect all urine excreted during the day into this container. To avoid the introduction of foreign impurities, the container should be kept in the refrigerator during the entire duration of the study.