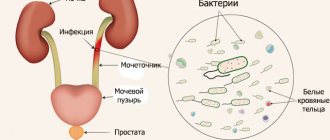
If there is an inflammatory or infectious process in the urinary system, specialists often prescribe an Addis-Kakovsky test. This technique, developed by Russian and American scientists, allows you to evaluate the composition and properties of urine collected within 24 hours. By examining daily diuresis using centrifugal force, an increase in the level of leukocytes, red blood cells and casts can be detected. For laboratory diagnostic results to be reliable, the patient must know all the nuances of collecting and storing the material.
Urine collection
The classic version of urine testing using the Kakovsky-Addis method requires strict adherence to the rules for collecting urine and storing it for a long time. In this case, urine is collected during the day: in the morning the patient empties the bladder, and then within 24 hours collects the urine in a vessel with 4 - 5 drops of formaldehyde or 2 - 3 thymol crystals; the urine should be stored in the refrigerator.
However, in practice, they often use another, simpler method of collecting urine - urine is collected within 10 - 12 hours. With this method, the accuracy of the result suffers. With this variant of urine collection for the Kakovsky-Addis method, before going to bed, the patient empties the bladder and notes this time. In the morning, 10 to 12 hours after evening urination, the patient urinates in a prepared container, and all urine is sent to the laboratory for testing. The referral form must indicate how long the urine was collected. If it is impossible to retain urine for 10-12 hours, the patient collects it in several doses, observing the conditions for its storage. In women, urine is collected with a catheter.
Preparation
A few days before collecting urine for examination using the Addis-Kakovsky method, you should limit the consumption of foods containing large amounts of protein.
In addition, the analysis itself requires preliminary preparation. You will have to limit your fluid intake. Every time you go to the toilet, you must thoroughly wash your genitals. It is best to refrain from excreting urine at night, collecting it all at once in the morning. But this depends on the individual capabilities of the body, and one should not focus on this fact.
In children, the time interval for fluid collection is reduced to ten hours, because they cannot hold urine in the bladder at night.
Another important feature is that urine collection is best done in a hospital rather than at home. In this case, the process will be monitored by medical professionals. The total amount of the selected liquid is recorded and thoroughly mixed. After this, twenty to thirty milliliters of urine is collected and sent for research.
Progress of the study:
The delivered urine is thoroughly mixed, its quantity is measured and an amount corresponding to 12 minutes or 1/5 of an hour is selected for research. This quantity is determined by the formula:
Q = V/(t*5),
where: Q is the amount of urine (in ml) excreted in 12 minutes, V is the total volume of urine collected (in ml), t is the time (in hours) for which urine is collected, 5 is the number for calculating the volume of urine excreted in 12 minutes.
The calculated amount of urine is placed in a graduated centrifuge tube and centrifuged for 3 minutes at 3500 rpm, or 5 minutes at 2000 rpm.
The top layer is sucked off, leaving 0.5 ml of urine along with the sediment. If the sediment exceeds 0.5 ml, then leave 1 ml of urine. The sediment and supernatant are thoroughly mixed and the Goryaev chamber (or other counting chamber) is filled. In this chamber, the number of leukocytes, erythrocytes and casts is counted separately (epithelial cells of the urinary tract are not counted).
Note. To count cylinders, it is necessary to view at least 4 Goryaev (or Bürker) chambers or 1 Fuchs-Rosenthal chamber. The number of cylinders counted in 4 Goryaev or Burker chambers should then be divided by 4, and only then the resulting number can be inserted into the formula to determine the number of cylinders in 1 μl of urine sediment.
Calculate the number of formed elements in 1 μl of urine sediment (x). When counting in the chamber of Goryaev and Burker, x = H/0.9, where H is the number of cells counted in the chamber, and 0.9 is the volume of the chamber. When calculating in a Fuchs-Rosenthal chamber, x = H/3.2, since the volume of the chamber is 3.2 mm3.
Then, based on the fact that 0.5 ml, or 500 mm3, was taken for the study, the resulting amounts of formed elements in 1 mm3 are multiplied by 500 (and with a sediment of 1 ml - by 1000), and the number of formed elements isolated from urine in 12 minutes. In terms of 1 hour, this amount is multiplied by 5, and when calculated per day - by another 24. Since 500, 5 and 24 are constant numbers, the corresponding number of red blood cells, leukocytes and cylinders (x) is multiplied by 60,000, if 0.5 ml of urine was left in the test tube, or at 120,000, if the sediment was abundant and 1 ml was left.
Reasons for deviations from the norm
An increase in leukocytes will indicate that pyelonephritis is developing in the kidneys, and the ureteral canals are infected. In the chronic stage of the disease, the level of this element will reach 200 million.
With a predominance of erythrocytes, we can confidently say that glomerulonephritis is progressing in the paired organ. This disease can disrupt the vascular system and capillaries. Because of this, blood will begin to flow into the bladder in large quantities. The urine will turn burgundy-brown in color.
In addition, the high content of red blood cells in the biological fluid suggests that there is hidden bleeding in the body.
If both indicators are at the same level, but their value is high, calculous pyelonephritis, new malignant formations, tuberculosis of the genitourinary system, and other pathological abnormalities in the kidneys and ureteric canals can be diagnosed.
A large number of casts in daily urine confirms the progression of inflammatory diseases in the kidney tissues. In hypertensive patients, the results of analysis using this method will be normal if sclerosis of the paired organ does not occur. And when such a process is already in the active stage, the leukocytes will be normal, and the red blood cells will exceed normal levels.
Disadvantage of the Kakovsky-Addis method
- not every patient can hold urine for 12 hours, especially with nocturia;
- not every patient can completely empty the bladder on their own (adenoma, prostate cancer);
- obtaining urine by catheterization is possible only in a medical institution;
- the Kakovsky-Addis method is difficult to apply in pediatric practice;
- an increase in indicators in this study can be observed not only with kidney pathology, but also with chronic purulent processes, exposure to poisons (sublimate, carbon monoxide poisoning), heparin therapy;
- the main disadvantage of the method is its lower information content: when collecting urine over 12 or 24 hours in parts, the need for long-term storage of urine leads to partial lysis of formed elements (especially leukocytes) due to alkaline fermentation, which leads to false results;
- the Kakovsky-Addis method is not an express method;
- the method is unsuitable for unilateral kidney damage (gives a summary result).
Clinical significance of methods for the quantitative determination of formed elements in urine.
Flaws
These include the following:
- The analysis will require a certain amount of time to complete.
- During the preservation of daily material in urine, minor destruction of elements occurs.
- The readings may be influenced by medications taken and inflammatory processes occurring in the body.
- When analyzing the indicators, it is not possible to accurately assure which kidney or ureter is damaged.
Another disadvantage is that this type of analysis is difficult to conduct for young children.
Negative points prove that the method is not perfect enough, and it can be used as an additional examination. By the way, for pyelonephritis, this method is considered informative; an accurate diagnosis is not made using it.
Literature:
- Kraevsky V. A. Atlas of urine sediment microscopy. Moscow, “Medicine”, 1976
- Handbook of Clinical Laboratory Research Methods, ed. E. A. Kost. Moscow “Medicine” 1975
- Kozlovskaya L.V., Nikolaev A.Yu. Textbook on clinical laboratory research methods - Moscow, Medicine, 1985.
- Guide to practical classes in clinical laboratory diagnostics, edited by Bazarnova M. A., Morozova V. T. - Kyiv, “Vishcha School”, 1988.
- Handbook “Laboratory research methods in the clinic”, ed. prof. V.V. Menshikova. Moscow, “Medicine”, 1987
Features of the Addis-Kakovsky test
The study owes its name to the famous scientist, Dr. Kakovsky A.F., who calculated the number of red blood cells in urine collected over 8 hours. Subsequently, the study was improved, and urine began to be collected per day, while reducing fluid intake.
It is believed that under such conditions the analysis result will be the most accurate, and this is the only way to identify disorders in the functioning of the kidneys. The time at which urine collection begins is important.
Purpose of the analysis
Most often, this study is prescribed to hypertensive patients to identify renal pathologies. Often, the Addis-Kakovsky test is performed in cases of obvious disease of the urinary system with normal urine analysis performed by another method.
The purpose of the analysis is to:
- determination of the quantitative content of leukocytes and erythrocytes in daily diuresis;
- ratio of formed elements (allows you to diagnose inflammatory processes and their severity);
- the number of cylinders in urine (necessary for identifying bacterial infections);
- determination of protein and other organic compounds that may indicate concomitant diseases.
In some cases, doctors use this research method to track the dynamics of the disease and its treatment.
Disadvantages of the analysis
This test has enough disadvantages, so it is used only to confirm or clarify the diagnosis. The result of the analysis cannot be the only indicator for determining pathology.
The method is labor-intensive and has many disadvantages:
- data on the number of red blood cells may be distorted due to long-term storage of urine (24 hours) or non-compliance with the storage temperature;
- for examination of infants, collecting urine during the day poses a certain problem (now children are prescribed urine collection for 10-12 hours);
- the amount of formed elements in the urine changes during intoxication with various chemical compounds or poisons (the test result does not always indicate kidney disease);
- collecting material takes a lot of time, the sample cannot be used as a rapid analysis, if the indicators are needed urgently, other research methods are used;
- in some diseases there are difficulties with collecting urine, the catheter can only be used in a hospital setting; in addition, not all patients can restrain urination at night;
- With the help of this study, it is impossible to identify which side of the kidney is affected; if only one kidney is diseased, the result is uninformative, the indicators will be summary.
For these reasons, the Addis-Kakovsky test is prescribed quite rarely. To obtain an accurate result, it is necessary to create conditions under which the specific gravity of urine and its acid level will meet certain standards (1023 and 5.5, respectively).
Sequence of taking the Addis-Kakovsky test
The total number of hours required to collect material depends on when the process begins. If urine is collected in the morning, then the first portion is not included in the analysis. Collecting urine begins with the second urination and ends with the first of the next day. Be sure to record the time of your first and last urination.
If urine collection began in the evening, then it is also completed with the morning portion of urine, which is taken from the first urination immediately after waking up. The urine that is excreted by the body during the day is collected in special sterile containers and submitted to the laboratory.
In order for the analysis result to be as accurate as possible, certain rules must be followed when collecting urine.
- before each trip to the toilet, you must wash yourself with warm water and soap, this will prevent bacteria from the external genitalia from entering the urine;
- the time of the first urine collection should be recorded;
- all urine is collected in one container, to which a few drops of formalin are added;
- The collected material should be stored in a cool, dark place (a household refrigerator will do);
- The collected urine must be delivered to the clinic within 1-2 hours, otherwise the result will be useless.
Modern doctors use urine collected for 10-12 hours for this test, and other tests are often prescribed for infants, for example, using the Amburger method.
Indications
Hemorrhoids kill the patient in 79% of cases
In medical practice, the Addis-Kakovsky test is used to detect hematuria and leukocyturia and determine the degree of these conditions. Hematuria is the appearance of a large number of red blood cells in the urine, leukocyturia is an increase in the number of white blood cells. Based on the degree of predominance of one of these conditions, a conclusion is made about the presence of pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis. Chronic pyelonephritis is usually accompanied by a significant increase in the number of leukocytes (up to 3-4 million or more) and their predominance over red blood cells. If, with an established diagnosis of pyelonephritis, hematuria is determined, then it is probably secondary in nature and caused by urolithiasis. With glomerulonephritis, the results of the Addis-Kakovsky test show that erythrocytes predominate over leukocytes.
Another common indication for the Addis-Kakovsky test is diseases that secondarily lead to impaired renal function. The study is prescribed for progressive and long-term arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, amyloidosis and other systemic pathologies. Thus, hypertension with renal arteriolosclerosis is characterized by an increase in the concentration of red blood cells in the urine. Thus, the analysis is used for the diagnosis and monitoring of pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, urolithiasis, chronic renal failure, as well as for assessing renal function in systemic diseases.
Compared to other quantitative studies, such as general analysis and Nechiporenko analysis, the Addis-Kakovsky test takes into account daily fluctuations in urine composition. This gives a more accurate and complete picture of the functioning of the urinary system. The disadvantages of the method include the laboriousness of the procedure for collecting material and the high probability of errors when performing the test (especially if the bladder is not completely emptied), the possibility of partial destruction of the formed elements as a result of long-term storage of urine, and the unsuitability of the test results for unilateral kidney pathology.
Features of the study
Why does the analysis have this name? The first such method of urine examination was proposed by the Soviet scientist, clinician A.F. Kakovsky. He suggested examining the number of blood cells in the urine by collecting it over 8 hours. And his colleague from America improved this method, clarifying that it would be more accurate to collect urine during the day, while significantly reducing the amount of liquid consumed. According to the American scientist, only under such conditions it is necessary to determine the number of blood cells in the urine, and only in this way will the analysis show the true condition of the kidneys and the presence of the alleged disease in it. Nowadays, Aesculapians use both options. However, everything depends on the start time of urine collection.
Purpose of the study
This study is used to generally determine the number of red blood cells and white blood cells in daily urine, as well as the predominance of some elements over others, which may be indicative when making a diagnosis. Plus, the analysis allows you to monitor the dynamics of pathology development. A urine test according to Addis-Kakovsky is indicative for renal dysfunction accompanied by hypertension. It is often resorted to when renal pathology is evident, however, other urine tests do not show any deviations from the norm.
In addition to red blood cells and white blood cells, sometimes doctors are interested in the cylinder ratio in this study. This allows you to see the presence or absence of infection in the genitourinary canals. In addition, this study helps to determine protein in the urine, as well as other indicators that, in addition to the main ailment, allow one to notice or exclude other ailments of the genitourinary system.
Algorithm for collecting urine analysis according to Addis-Kakovsky
The total time for collecting the analysis depends on the time of day when the process began. If urine is collected in the evening, then 10-12 hours are enough to completely collect the analysis. If the collection starts in the morning, then the total sampling time is 24 hours, that is, the last portion of urine should be collected the next morning. In both cases, you should record the exact time of the beginning of the urine analysis, that is, the first urination, as well as the time of the last trip to the toilet for analysis.
All urine, without exception, excreted during the time specified for analysis must be collected. Urine should be collected in one dry, sterile container. Before each urination, you should thoroughly toilet your genitals. The collected bladder contents must be stored in a cool place. After collecting the last dose, the entire volume of urine must be sent to the laboratory as quickly as possible, since after two hours the result will be invalid.
Decoding
The Addis-Kakovsky analysis indicates the amount of formed elements released per day.
The following figures are the norm for indicators:
- leukocytes – up to 2 million per day;
- red blood cells – up to 1 million;
- cylinders - up to 20 thousand over the same period of time.
The norm for children is practically no different:
- leukocytes – up to 2.5 million per day;
- red blood cells – up to 1 million per day.
Deviations from the norm indicate various diseases. Thus, an excess of leukocytes indicates an inflammatory process. An excess of leukocytes over red blood cells indicates pyelonephritis, as well as infectious diseases of the urinary tract. The excess of red blood cells over white blood cells indicates glomerulonephritis.
Indications for analysis
Urine examination using this method is used to identify kidney pathologies. It is effective in diseases of the organ due to hypertension, when other laboratory tests are uninformative. Other indications for the Addis-Kakovsky urine test:
- kidney cystosis;
- glomerulonephritis. A pathological condition in which the renal glomeruli are affected;
- pyelonephritis. Inflammatory process affecting the renal tubules;
- urolithiasis disease;
- chronic renal failure. Here the test is needed to monitor the effectiveness of the chosen therapeutic strategy and evaluate the effectiveness of the measures taken.
Urine examination according to the method is used to identify kidney pathologies
How to collect urine for analysis?
In order to eliminate external factors as much as possible and obtain the most reliable analysis results, you should adhere to some rules for collecting biomaterial:
- A few days before the analysis, it is worth limiting your diet, namely, not eating food that contains aggressive pigments that can change the color of the biomaterial;
- Before the analysis, be sure to carry out hygiene procedures for the genital organs of men and women.
- A sample of the biomaterial is taken in the morning, and the first portion is poured into the toilet, and the second is collected in a specially prepared sterile container;
- Fresh samples are required for analysis, so make sure to bring the sample to the laboratory no later than two hours from the moment the material is collected.
Preparing for the test
The procedure itself for preparing to take a sample and submit the material is not difficult. This is a routine urine test. It is necessary to adjust the diet - enrich the diet with protein products for 1-2 days in order to determine the number of cylinders.
Such cells are highly sensitive to acidic urine; if it is neutral or alkaline, they disappear, which makes the diagnosis insufficiently informative. To get results, urine is acidified by eating protein-rich foods.
For some kidney diseases, including urolithiasis, this is not required. The attending physician, when referring for an Addis-Kakovsky test, knows in advance what the acidity of the urine is. The question of preparation for collecting samples should be clarified with him.
Positive test values
The following values indicate the normal state of the body and its functions:
The norm is considered to be up to 1,000,000 red blood cells, no more than 2,000,000 leukocytes and no more than 20,000 cylinders. In some cases, the values may be increased, but will not in any way affect the health and the body as a whole.
If you receive elevated values, you will need to undergo an examination and identify the reason why this happened. Inflated values may be a manifestation of diseases in the renal area, in particular failure.
Urinalysis according to Addis Kakovsky. Element content norm
Urine analysis according to Kakovsky-Addis is one of the methods of urine analysis, based on counting the precipitated structural elements and reflecting their concentration as a percentage of the total volume of urine excreted per day.
Initially, this method using special counting chambers was published at the beginning of the twentieth century by the Kyiv scientist, associate professor of medical sciences A.F. Kakovsky. Later, after a decade and a half, significant additions to this method were made by the American scientist, professor of medicine Thomas Addis.
A referral for a urine test according to Kakovsky-Addis is often given to a patient if a general urine test shows deviations from the norm, in order to understand the patient’s health condition in more detail, accordingly establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe timely treatment.
What are the disadvantages of the Kakovsky-Addis urine test?
- This method is extremely inconvenient for patients with urinary incontinence;
- Patients with severe diseases of the genitourinary system are unable to physically correctly collect biomaterial;
- Urine collection using a catheter is carried out exclusively in laboratory conditions;
- This method is not used in pediatrics;
- Indicators above normal when analyzed according to Kakovsky-Addis may indicate the presence of kidney disease or other pathologies (intoxication, inflammation of the genitourinary system);
- The method is not too informative. Due to the long shelf life of the biomaterial, some elements are lost, which leads to incorrect analysis results.
- This method is not useful for diagnosing unilateral kidney disease, as it determines the total concentration of elements.
What is the essence of the method?
It is possible to calculate how many leukocytes and red blood cells a urine sample contains using a regular one-time collection. The excretory system is characterized by specific work, which affects the composition of urine at different times of the day. Urine indicators change under the influence of poor or abundant drinking conditions and the food consumed.
This means that a one-time collection may provide inaccurate information, while the collected urine will show daily fluctuations in substances in the biological fluid.
The technique was first proposed by Addis-Kakovsky. The clinician believed that an adequate red blood cell count could be obtained by examining the volume of body fluid collected over an 8-hour period. Over time, the technique was changed; urine is collected per day, and 1/50 of the volume is taken for evaluation.
Laboratory assistants examine the biomaterial, identifying the following elements:
- red blood cells. These are red cells. The sample may contain two types of red cells - unchanged and modified. The former contain hemoglobin, and the latter are leached, without hemoglobin. In a healthy person, red blood cells should not be detected; if they are detected, a doctor’s consultation is necessary;
- leukocytes. These are white bodies that can be detected in the urine of healthy people;
- cylinders. These are cells whose name is due to their shape. They are granular, proteinaceous, and hyaline. Hyaline appears due to severe physical overload. Other types of cylinders indicate that the kidneys are not working well and there are pathologies. The type and number of cylinders help the physician determine the type of infection affecting the kidneys.
It is important to identify the listed elements not only quantitatively, but to determine their relationship to each other. In addition to counting substances, the Addis-Kakovsky analysis serves to monitor the effectiveness of therapy; medications will certainly affect the composition of urine.
The analysis is done for adults and children. The scheme is the same, but in children it is difficult to collect the daily volume of urine; for them, the Amburge test is provided, which will be discussed in the article. The Addis-Kakovsky analysis itself is common; there are two methods for conducting it:
- Addis method. Reduces to the accumulation of biological fluid in 24 hours. The patient urinates into a sterile container and pours the biological material into a bulk container. The container is stored in a cool, dark place; a preservative is added to ensure the consistency of the shaped components.
- Kakovsky's method. More common than the first option, it involves a simplified method of collecting material. Urine is collected over a period of 10-12 hours, the first time the bladder is emptied before bed, the second - after 11-12 hours.
To obtain time-lapse results, the volume of urine is mixed and a tube containing a small amount of sample is placed in a centrifuge for 5 minutes, run at 200 rpm.
Analysis is done for adults and children
Then excess urine is collected, leaving 0.5 ml of sediment, which is examined for the presence of these components.
Analysis results
The research itself is carried out as follows:
- The collected urine is thoroughly mixed, and an amount equal to a fiftieth of the total volume is taken for testing. The same unit corresponds to the amount of fluid released by the body in 12 minutes. There is a certain formula according to which the calculation is made.
- The selected material is poured into a test tube and placed in a centrifuge; two modes are selected for processing - 3500 rpm (for 3 minutes) and 2000 rpm (for 5 minutes).
- As a result, a precipitate is obtained and sent to a counting chamber for counting cylinders, leukocytes and erythrocytes.
The analysis does not take much time, it all depends on the workload of the laboratory. If necessary, the doctor can get the result within a few hours, or as usual – the next day. If the patient is hospitalized and a sample is prescribed to track dynamics, the result is issued immediately after the material is received and studied. Sometimes this is necessary to change treatment tactics.
Normal indicators
The standards for research using the Addis-Kakovsky method for adults and children are almost no different:
| Red blood cells | Leukocytes | Cylinders | |
| Adults | up to 1000000 | up to 2000000 | up to 20000 |
| Children | up to 1000000 | up to 2500000 | up to 20000 |
Violations of the recommendations for preparing for urine collection and the procedure itself can lead to distorted results and the uselessness of the sample.
Deviations from the norm and their causes
Deviations from normal values (in this study, this is an excess of established standards) are an indicator of a developing disease. Depending on the test result, the doctor can confirm the following pathologies:
- Increased number of leukocytes. Indicates an inflammatory process in the urinary system. This may be pyelonephritis or a bacterial infection of the ureters. Inflammation of the kidneys in chronic form is characterized by the number of leukocytes in the range of 200 million. In this case, leukocytes predominate over red blood cells.
- An increased content of erythrocytes and a predominance of their number over leukocytes indicates the progression of glomerulonephritis. This disease destroys the walls of blood vessels, their permeability increases, and blood enters the urine. This is also confirmed by the color of the urine - it turns brown. In addition, this result may indicate internal bleeding caused by urolithiasis or the presence of a neoplasm.
- If the indicators exceed the norm, but are approximately the same in relation to each other, tuberculous damage to the genitourinary system, oncology or calculous pyelonephritis can be suspected. Sometimes this study helps diagnose cancer at an early stage or at least suspect a malignant process and conduct a comprehensive examination.
- An increased number of urinary cylinders is typical for hypertensive patients or people suffering from renal sclerosis. In this case, leukocytes may show normal levels, and erythrocytes will predominate.
The advantage of urine testing using the Addis-Kakovsky method is the determination of daily fluctuations in excreted elements, which reliably characterizes the functioning of the kidneys and the entire urinary system of the body.
Recommendations for patients
The Addis-Kakovsky test differs from a general urine test in the method of collecting and storing biomaterial. Daily diuresis is examined, starting at 8 pm or in the morning, after missing the first urination. You need to urinate in a sterile dry container for 24 hours, then take it to the laboratory, collecting everything in a three-liter bottle.
Proper preparation
A few days before the test, to increase the acidity of the urine, increase your protein intake (meat, dairy products, eggs). This will allow you to count the number of cylinders that quickly dissolve in an alkaline medium. To maintain the reliability of the results, during urine collection, avoid alcohol, carbonated drinks, and stop taking medications.
Collecting urine according to Addis-Kakovsky is necessary, adhering to the following recommendations:
- reduce fluid intake;
- try not to urinate at night, but collect everything in the morning;
- Before urinating, wash yourself thoroughly without using hygiene products;
If children are being examined, it is recommended to limit urine collection to 10-12 hours. To do this, the analysis begins with the second urination in the morning and ends with the last one before bedtime. For everything to go right, it is better to be in a hospital under the supervision of medical workers.
Urine collection, storage and delivery
Urine collection lasts 24 hours, and after extreme urination, it is necessary to deliver the contents to the laboratory within 1-2 hours. Otherwise, the composition of urine will change, and the results will be unreliable. Therefore, it is recommended to start the analysis at 20:00 and finish at 8:00-10:00. Be sure to indicate on the form the period for which the analysis was carried out. It is also recommended to calculate and record the amount of water you drink per day.
The resulting urine is kept in the refrigerator for 24 hours with the addition of 5 drops of formaldehyde or several thymol crystals. During examination, it is mixed again and about 0.6 ml of liquid is separated. In addition to the composition of urine, its density, the presence of visible sediment, color and transparency are assessed.
If the patient is paralyzed or experiences urinary disturbances (frequent urination, leakage), he is examined in a hospital setting. A catheter is used to collect urine. In this case, the analysis begins in the morning, after draining the first portion of urine.
The Invitro laboratory is considered one of the best centers conducting this analysis in Ukraine, Russia and the Republic of Belarus. Specialists quickly assess the composition and properties of urine, after which they notify the patient by telephone or using an application installed on a smartphone.