Reasons for the increase
Proteins (albumin and globulins) enter the urine due to the filtration function of the kidneys.
When this biological barrier is violated, proteinuria becomes pronounced and can be a diagnostic indicator for the underlying disease. In medical practice, physiological and pathological causes of increased protein in urine should be distinguished.
There are 9 main physiological reasons:
- Alimentary - detected after eating foods high in protein, salt and sugar.
- Working – associated with heavy physical work.
- Emotional stress.
- Postural - associated with a long stay of the body in an upright position.
- Transient - associated with dehydration, hypothermia, or prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays.
- Palpation - due to prolonged palpation (palpation) of the kidneys.
- Pregnancy - The pregnant uterus puts increased pressure on the kidneys.
- Age - after 75 years, the kidneys cease to fully perform their filtration function.
- Obesity – Obesity also reduces kidney function.
Pathological causes are divided into renal and extrarenal.
Attention! There are many reasons for increased protein in the urine in women. If you notice rapid fatigue, loss of appetite or nausea, you should immediately make an appointment with a therapist or gynecologist.
There are 7 renal causes:
- Glomerulonephritis is an inflammation of the glomerular system of the kidneys.
- Stagnant kidney - develops due to impaired blood supply, as a result of which the vessels become full of blood, which leads to degenerative processes in the organ.
- Nephrosclerosis is the replacement of functional kidney cells with connective tissue ones, which leads to their dysfunction.
- Hypertension - persistent high blood pressure leads to a decrease in the filtration capacity of the kidneys.
- Renal amyloidosis is the accumulation of amyloid (fibrillar proteins and polysaccharides) in the kidney tissue.
- Renal vein thrombosis is a lack of blood flow from the kidneys due to the formation of a blood clot.
- Pyelonephritis is damage to the kidney tubules due to inflammation.
There are 16 extrarenal causes:
- Lymphoma is a malignant tumor of lymphoid tissue.
- Multiple myeloma is an oncology of the bone marrow, as a result of which the synthesis of a special protein with a low molecular weight increases in the blood, which easily penetrates the biological barrier of the kidneys.
- Monocytic leukemia is a malignant tumor formation that consists of leukocytes. There is an increased level of a peptide (lysozyme) in urine.
- Myopathy is a dystrophic muscle disease, when diagnosed by the presence of myoglobin in the urine.
- Rhabdomyolysis is the decomposition of muscle cells (myocytes) and their excretion in the urine from the body.
- Heart failure - the contractile function of the heart is inhibited.
- Tuberculosis is an infectious disease, one of the manifestations of which is an increased concentration of peptides in the urine.
- Cystitis is a disease of the bladder of inflammatory etiology.
- Urethritis is an inflammatory disease of the urethral walls.
- Urolithiasis - the integrity of the walls of the pelvis or ureter is compromised, which is accompanied by the appearance in the urine of blood cells (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets) and plasma, which contain protein.
- Diabetes mellitus - when glucose levels increase, kidney tissue is damaged and pressure in the glomeruli increases, which causes a disruption in filtration function.
- Chemotherapy - has a detrimental effect on the barrier function of the kidneys.
- Medicinal - is a consequence of long-term use of antibacterial drugs.
- Transfusion of donor blood to a recipient of the wrong type and Rh factor.
- Injuries, burns - protein enters the urine in excess due to its breakdown in the tissues.
- Intoxication with harmful substances (mercury or lead salts).
If leukocytes and protein are found in urine, what should you do?
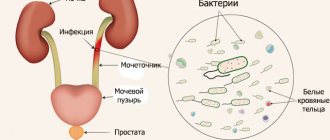
The detection of protein and leukocytes in urine analysis indicates inflammatory processes occurring in the urinary system. White blood cells, performing a protective function, do not allow pathogenic microflora to multiply. As a result of the fight against infection, they die and leave the individual’s body along with urine. The presence of these cells in the biomaterial in excess of permissible values is called leukocyturia. Its main causes are diseases:
- urinary system;
- genitals;
- venereal.
In addition, a long course of antibacterial treatment and poorly performed hygienic manipulations before donating biofluids provoke the appearance of leukocytes in urine. It should be noted that in children the norm is higher than in adults. This phenomenon is due to the fact that the kidneys are still forming and are not able to fully perform some functions.
Symptoms
A patient comes to the doctor with complaints of frequent dizziness up to loss of consciousness, fatigue, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, swelling of the face, lower and upper limbs and torso, increased blood pressure and heart rate, chills, high temperature.
The patient may also observe foam in the urine and a change in the color of the urine, which during diagnosis may contain not only proteins, but also red blood cells. In addition to the main symptoms, a pregnant woman experiences pain in the lumbar region and toxicosis; in complex cases, eclampsia occurs. The condition is characterized by convulsive symptoms, blood pressure 200/110 mmHg. or more, severe edema, impaired urination and loss of consciousness. The severity of the condition is dangerous due to the development of disorders of the central nervous, cardiovascular and visual systems, up to a coma.
Preparatory activities for analysis. Urine collection rules
For the results to be reliable, the following conditions must be met:
- on the eve of the test, get a good night's sleep;
- eliminate any overloads;
- warn the doctor about taking medications;
- do not change the diet and drinking regime before and during the collection of biomaterial;
- exclude any alcohol-containing drinks.
To conduct a daily protein test, urine must be collected correctly. To do this correctly, you will need:
- prepare a sterile container;
- the first portion of urine is not collected, starting from the second and continuing throughout the day, it is added to the prepared container and the time of each urination is recorded;
- store the collected biomaterial in the refrigerator;
- after collecting urine, you need to record its volume;
- mix and pour about 200 ml into a separate sterile container;
- take to the laboratory a container with biomaterial, a urination schedule, a recorded daily volume of urine, information about your height and weight.
Before collecting each portion of urine, hygiene procedures are carried out.
Treatment
Treatment of proteinuria depends on the presence of the underlying disease. Having eliminated the cause, the protein in the urine returns to normal. However, when correcting protein in urine, regardless of etiology, a specific list of medications with a pronounced nephroprotective effect is prescribed:
- ACE inhibitor (angiotensin-converting enzyme);
- angiotensin II receptor blockers;
- statins;
- calcium channel blockers.
If the underlying disease is caused by infectious agents, the doctor will additionally prescribe antibiotics that are sensitive to this infection.
Nutritional factors play a major role in increasing protein in the urine, so diet is important in treatment.
The doctor excludes meat and fish from the patient’s diet, minimizes the consumption of salt and salt-containing products (no more than 2 grams per day), and limits the amount of liquid consumed: water, soups, juices and other liquid products.
The consumption of rice, low-fat fermented milk products, steamed vegetables, beets, pumpkin, dried fruits, rosehip tea and blackcurrant juice is allowed.
When the protein in the urine is normalized and the underlying disease is cured, the doctor gradually introduces excluded foods back into the diet.
Factors influencing the results of the study
There are some factors that greatly change the results of a 24-hour urine test. The reasons for the appearance of a falsely high indicator may be as follows:
- urine contamination with feces;
- taking sodium bicarbonate, penicillins, sulfonamides, cephalosporins;
- use of radiocontrast agents containing iodine.
False underestimation of indicators provokes increased diuresis, forced by taking diuretics, consuming large amounts of liquid, and diuretic products.
To avoid receiving false data, you should properly prepare for the analysis and then correctly collect urine.
Complications
If proteinuria is not detected in a timely manner, serious complications may develop: acute or chronic renal failure;
acute or chronic heart failure; disruption of tissue regeneration, which reduces the complete recovery of the body. In pregnant women, undiagnosed proteinuria leads to the addition of other kidney dysfunctions (concentration abilities and leaching of salts in the urine). In patients, blood pressure increases and can reach 200/110 mmHg. Eclampsia occurs, characterized by a sharp increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure. The occurrence of convulsive symptoms and coma leads to the death of the expectant mother or her fetus.
Diagnostics
If a repeated check reveals an increase in protein in a woman over 0.033 g/l, then the proteinuria is not temporary. To establish the exact cause of the pathological condition, additional testing is necessary. :
- Collection of daily urine (according to Zimnitsky, according to Nechiporenko).
- Ultrasound or CT to visualize the condition of the kidneys and urinary tract. This is necessary to identify stones, tumors, abnormalities, etc.
- General blood analysis.
- Kidney biopsy. It is carried out when identifying problems with this particular organ.
Prevention
A regular medical examination with a general urine test helps the patient to detect the disease in a timely manner.
Timely detection of proteinuria allows doctors to begin early diagnosis of the cause of the appearance of protein in the urine and subsequent treatment. To prevent an increase in protein in urine, the following recommendations should be followed:
- drinking alcohol in reasonable doses;
- sufficient drinking of filtered, boiled water (at least 1.5 liters per day);
- adequate consumption of protein foods;
- avoid emotional stress, heavy physical activity and hypothermia;
- do not neglect and promptly treat diseases of the urinary and reproductive systems, endocrine disorders, cardiovascular diseases and other causative factors.
Therapeutic techniques
Exceeding the daily amount of protein excreted is dangerous to human health. Therefore, this condition requires mandatory treatment. The treatment tactics used will depend on the characteristics of the identified disease. The following methods can be used:
- Use of medications. If infection is present, antibiotics are prescribed. To eliminate surges in blood pressure, the use of antihypertensive medications is indicated. If neoplasms are detected, antitumor agents must be used.
- Proper nutrition. A rational menu helps prevent protein loss. You need to eat vegetables, greens, berries and fruits every day. Try not to eat large amounts of protein foods. Minimize the amount of salt in your dishes.
- Lifestyle adjustments. A complete cessation of bad habits is required. Try to protect yourself from stress, psychological and mental stress. Control your level of physical activity.
With pronounced proteinuria, therapy in a hospital setting is required. The doctor must constantly monitor the patient’s condition and, if necessary, adjust the treatment program. A slight deviation of protein from standard values can be corrected at home.
A person can encounter the problem of proteinuria at any age. Therefore, it is important to know how to recognize such a deviation and how to take a daily test correctly. This will help identify the disease at an early stage and begin therapy.