Anemia is a fairly common reason for the deviation of mental abilities and complex development among children, which confirmed by research. This is why pediatricians recommend regularly donating blood for analysis - to monitor the concentration of hemoglobin and prevent anemia.
At the same time, there are much more risk factors for anemia in children than in adults, since their body is actively growing and consumes more vitamins, minerals and iron, and almost all intercellular metabolic processes also proceed many times faster.
What foods should be given to a child to increase hemoglobin levels to an acceptable level? And most importantly, what level is considered such?
Why is low hemoglobin dangerous?
Low hemoglobin leads to anemia (often referred to as anemia).
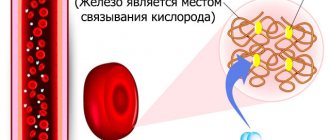
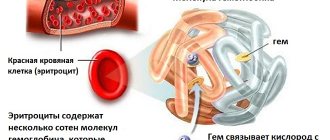
With a deficiency of hemoglobin, almost all tissues and organs receive much less oxygen , which affects their slow growth/development. This also applies to the brain, nervous system, cardiovascular system, skeleton, and so on.
Low hemoglobin is especially dangerous in newborns, in whose bodies there is active oxidation of red blood cells and the production of new ones (by the way, it is because of this that the blood type may change in the first months of life - this is a normal phenomenon).
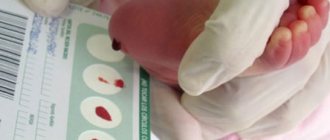
Therefore, the hemoglobin concentration is measured in the maternity hospital, literally in the first or second days of the child’s life (when the child is already breathing on his own and is not connected to the mother’s body by the placenta).
How to increase a child’s hemoglobin using folk remedies and medicines?
In severe forms of anemia, medications are prescribed (in the form of drops, syrups, tablets) that stimulate erythropoiesis (the formation of new red blood cells). In this case, medications are taken for a long time - from one month to several years. An active doctor of the highest category, Evgeniy Komarovsky, in his videos recommends refraining from excessively prescribing medications to children. Many of them can temporarily increase hemoglobin, but then it can drop sharply in the blood.
In very severe conditions, methods of red bone marrow cell transplantation or partial removal of the hypertrophied spleen are indicated. Typically, with these procedures, the hemoglobin will rise and remain stable.
Normal blood content
The normal level of hemoglobin in the blood of children is as follows:
- from 1 to 6 years – from 100 to 140 grams per liter;
- from 6 to 12 years – from 120 to 150 grams per liter;
- in newborns - from 90 to 110 grams per liter (and increases slightly with each month until the lower limit reaches 100 grams per liter or more).
In newborns, in the first days of life, hemoglobin changes in waves - this is a normal phenomenon. But if hemoglobin drops below 90 grams per liter, immediate medical intervention is required.
Traditional medicine tips
These alternative tips can be used in children after 2 years of age if they do not have allergies.
Most popular recipes:
- Take 1 glass of buckwheat and walnuts, grind everything in a blender (or meat grinder) and add 1 glass of May honey, mix. You need to keep the mixture in the refrigerator and give the child 1 tsp. 2 times a day.
- Take equal parts of dried apricots, prunes, walnuts (peeled), raisins and 1 lemon (with peel), chop thoroughly, mix with a glass of honey, keep in the refrigerator. The child should take 1 tsp. twice a day.
- 1 tbsp. pour 200 ml of boiling water into a thermos, let it brew for 3 hours, strain. Add 1 tsp. honey, a slice of lemon and let the child drink the infusion 2 times (morning and evening).
- Mix 100 ml apple, 50 ml carrot and 50 ml beet juice. Give the child 1 tbsp. sour cream, and then 1 glass of juice mixture 1 r. per day (you can divide the volume into 2 doses).
Signs of a low level
The only correct option to determine that a child has low hemoglobin is to take a blood test (you can do it from a finger or from a vein; it is recommended to take several samples with a break of a couple of days). But it is not always possible to seek qualified medical help.
You can recognize low hemoglobin by the following symptoms:
- pale skin color;
- decreased activity and chronic fatigue;
- sharp deterioration of appetite;
- deterioration of memory and concentration;
- rapid change in taste preferences;
- allergies (may indicate problems in the endocrine system);
- rapid heartbeat (sometimes accompanied by increased blood pressure);
- not the best condition of skin, hair, nails.
Also, children with anemia often experience shortness of breath for no apparent reason (including without physical exertion).
Symptoms
A child with anemia becomes lethargic, pale, and has poor appetite.
The manifestation of anemia in a child may include the following nonspecific signs:
- decreased appetite;
- increased fatigue;
- lethargy, decreased activity;
- increased fragility of nails and hair;
- thinning, dull hair;
- drowsiness;
- dizziness;
- painful cracks in the corners of the lips.
Upon examination, pale skin (with a jaundiced tint in some cases) and mucous membranes, dry and flaky skin, dark circles around the eyes, and rapid heartbeat are revealed.
Against the background of anemia, there is a decrease in immunity, the child often gets sick. Moreover, the disease can be severe, with complications. If left untreated, the child will lag behind in both physical and mental development.
Nutrition rules for children
First of all, it is necessary to point out that hemoglobin deficiency is often associated not with a lack of certain micronutrients, but with chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, hormonal, and cardiovascular systems.
Therefore, you should definitely consult your children’s doctor (pediatrician) about this. He will also direct you to all the necessary studies and tests that will help establish the exact cause of anemia.
Up to 1 year
To increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood of children under one year old, breast milk is the optimal diet. And it is more important during this period to follow a healthy diet for the young mother , including iron-containing foods in the diet, as well as those rich in B-group vitamins. These include:
- beef;
- lean pork;
- liver (beef or pork);
- apples;
- grenades;
- carrot;
- nuts;
- seafood;
- legumes;
- cereal porridge
And the most important thing is to eat a varied diet. That is, regularly prepare different dishes to normalize the biochemical composition of blood and breast milk.
If the child is bottle-fed (formula), then preference should be given to those that contain iron and B-group vitamins . You should consult your pediatrician about this. Formulas are always selected individually, depending on how well the child’s body assimilates them.
If the child is more than 9 months old, then complementary feeding is allowed. In this case, be sure to add ground grain porridge, meat puree, vegetable oil, natural compotes or juices to the diet (must be diluted with water).
From 1 to 3 years
During this period, preference should be given to vegetables, fruits, herbs, and meat purees. If you have low hemoglobin, you should not overuse dairy products, especially cottage cheese, yogurt, dairy desserts, kefir - they contain calcium, which makes it difficult to absorb iron.
Also, the diet must include applesauce (or dried apples), carrot juice or puree (with sugar), buckwheat porridge, and legumes (not earlier than 18 months). You should also give up wheat bread in favor of bran bread - this is a good prevention of constipation (and at the same time, bran has a high iron content, almost 20 mg per 100 grams).
And, if possible, the child should be breastfed up to 2–3 years of age . Mother's milk is a concentrated mixture of vitamins, easily digestible proteins, iron, which best helps increase hemoglobin, as well as comprehensively strengthen the immune system.
From 3 to 6 years
In addition to recommendations for children under 3 years of age (with the exception of breast milk), it is recommended to gradually add to the diet:
- chocolate (and other cocoa-based products, with the exception of white chocolate, as it has a high milk content);
- liver (can be in the form of puree or pate with vegetables, it is recommended to cook at home);
- berries;
- fruit juices;
- prunes, raisins, dried apricots;
- eggs (chicken eggs are also suitable, but quail eggs are much healthier and easier for the stomach to digest);
- pumpkin, potatoes (boiled or baked, without frying).
You can also give small amounts of table flaxseed oil - it is rich in omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids, which accelerate intercellular metabolic processes, including those involving iron molecules.
Not recommended foods at this age include fatty cheeses, sour cream, fermented baked milk, as well as various types of desserts.
From 6 to 12 years
At this age, you can quickly increase hemoglobin using the following foods and drinks:
- greens (including parsley, turmeric, basil);
- pomegranate juice (not recommended in concentrated form, must be diluted);
- fresh and baked apples;
- nuts;
- wheat or rice bran;
- seafood (preference should be given to fatty fish, as well as red and black caviar).
Also, many pediatricians recommend making tea at this age based on rose hips - this helps not only raise hemoglobin, but also strengthen the immune system.
But non-recommended foods at this age include soda in any form, dairy yoghurts, fried potatoes, and fast food - it’s best to avoid all of this .
You should also definitely avoid black tea, coffee and any other drinks that contain caffeine - they all significantly slow down the absorption of iron and increase the concentration of tannins in the blood (which interfere with biochemical reactions with amino acids).
Summary for parents
Often parents are faced with the problem of low hemoglobin or anemia in their child already in infancy. Before taking measures to increase hemoglobin, you should consult with your pediatrician and clarify the type and degree of anemia.
You should not ignore this problem and hope that it will “perhaps outgrow it.” A low hemoglobin level will negatively affect the child’s development – physical and mental.
The occurrence of iron deficiency anemia can be prevented by a balanced diet for the child.
If anemia develops, the child’s diet should be reviewed to ensure the consumption of healthy foods. If the baby still receives breast milk, then a correction of the diet is necessary for the mother.
When a pediatrician prescribes iron-containing drugs, parents must strictly follow the recommendations received regarding the dose and duration of treatment. You should not self-medicate!
Other Important Recommendations
Almost all metabolic processes in the body are accelerated when the level of vitamin D in the blood increases (as it helps accelerate the absorption of calcium and its concentration gradually decreases).
Therefore, doctors recommend walking outdoors as often and as much as possible , as well as sunbathing (with caution for children under 3 years old, since their skin is practically not protected from ultraviolet radiation and it is extremely easy to get burned).
You can also increase hemoglobin through active games and physical activity - all this also speeds up the absorption of proteins and amino acids, which precisely enter into a biochemical reaction with iron molecules.
It is also important to adhere to activity and rest regimes - blood is mainly produced at night during sleep. Therefore, the child needs to follow a routine and go to bed at the same time every day.
You can also increase hemoglobin using hematogen - this is a kind of dessert obtained from the formed elements of the blood of cattle. Sold in the form of candies or chocolates in pharmacies, it can be given to children aged 2 years and older (this information should be specified in the instructions).
There are also special variations of hematogen with a high content of iron and B vitamins - this can be used in the active treatment of anemia.
Prevention
Prevention of anemia in children includes:
- Antenatal prophylaxis: it is advisable for expectant mothers in the 2nd half of pregnancy to take ferromedicines or multivitamins enriched with iron orally for preventive purposes.
- Postnatal prevention:
- breastfeed your baby for as long as possible;
- introduce complementary foods in a timely and correct manner;
- provide the nursing mother with a balanced diet;
- Children receiving artificial feeding should be given (only as prescribed by a pediatrician) adapted formulas enriched with iron from the age of 2 months;
- from the 2nd half of the year, breastfed babies and bottle-fed children who do not receive iron-fortified formulas should take a prophylactic dose of iron supplements for up to 1.5 years.
- For children at risk, which includes babies from multiple pregnancies, premature babies, children with intense weight gain, preventive intake of iron supplements begins at 3 months.
RISK FACTORS
Iron deficiency and decreased hemoglobin in a child can be diagnosed as a result of a lack of iron in food, its poor absorption or increased loss. Such phenomena can occur at any age.
The following factors can cause a lack of iron and a decrease in hemoglobin in the baby’s body:
- the mother has anemia or chronic diseases of the endocrine glands, kidneys or liver during pregnancy;
- prematurity;
- high birth weight;
- multiple pregnancy in the mother;
- lack of vitamin C;
- rickets;
- dysbacteriosis;
- early transition to artificial formula feeding;
- late introduction of complementary foods;
- frequent colds and intestinal infections;
- high rate of growth and development.
- In an older child, hemoglobin can be reduced by:
- heavy bleeding, in girls - menstrual bleeding;
- vegetarian food;
- intense sports activities;
- chronic diseases of the digestive system;
- helminthiases;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- rapid growth.
- Naturally, in such cases the question arises of how to increase hemoglobin in a child. The doctor may prescribe ferrodrugs and give recommendations on dietary adjustments.