Iron deficiency in the blood is anemia, which can cause serious dysfunction of the body and the development of oxygen starvation of organs. Anemia is especially often diagnosed in women in the later months of pregnancy, when there is a real threat to the child. A lack of hemoglobin can cause delays in the development of vital organs and cause disability in the baby. Before giving birth, expectant mothers must undergo tests for timely diagnosis of anemia and its treatment, if necessary.
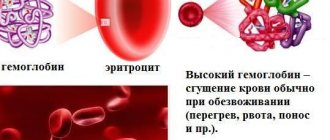
But an increased level is no less dangerous, when hemoglobin reaches 140-145 g/l. Against the background of high iron content, women develop headaches, heart pathologies, liver and kidney diseases, weakness and other problems.
Hemoglobin norms
For different ages and under certain circumstances, the norms of iron content in the weaker sex may fluctuate.
- In an adult woman leading a normal lifestyle, the level is in the range of 120-140 g/l
- In adolescence - from 14 to 18 years, the permissible range is somewhat wider - hemoglobin ranges from 113 to 145 g / l.
- In girls who smoke, hemoglobin is considered normal and does not exceed 145-150 g/l.
- For athletes, the permissible upper limit is 139-160 g/l.
- In pregnant women, the allowed level is within the range of 105-125 g/l.
- Elderly ladies over 65 years of age should consult a doctor if the hemoglobin level in the analysis goes beyond 120-160 g/l.
With a healthy lifestyle, hemoglobin in women of 143 g/l is not dangerous, since a deviation of 3-5 units to the upper or lower side is considered normal. For more pronounced changes in levels, it is worthwhile to undergo appropriate treatment.
Treatment methods for high hemoglobin
High hemoglobin in women poses a serious threat, especially during pregnancy. Therefore, when diagnosing a pathological condition, mandatory treatment is necessary. How to reduce hemoglobin?
Treatment and correction methods for elevated hemoglobin in women are aimed at thinning the blood and reducing the concentration of red blood cells. For this purpose, for example, the following drugs are prescribed:
- aspirin®;
- cardiomagnyl®;
- chimes®.
Important: independent selection of medications and dosages for treatment is prohibited. Such behavior can lead to a worsening of the condition and severity of the disease.
It is acceptable to prescribe hirudotherapy - treatment with leeches. When a leech bites, the enzyme hirudin contained in their saliva enters the human bloodstream. Hirudin has a bidirectional effect on the blood: on the one hand, it slows down the processes of blood clotting, and on the other, it reduces the risk of blood clots. It should be noted that for therapy it is necessary to use only medicinal leeches sold in pharmacies and diluted in laboratory conditions. For one session, 5 leeches are enough, each of which sucks no more than 15 ml of human blood when biting.
Menu for women with high hb
In combination with drug treatment and hirudotherapy, it is necessary to adhere to a certain menu:
- the amount of red meat in the diet should be reduced, and offal (liver, tongue, kidneys) should be completely excluded;
- the diet should be dominated by white meat and low-fat fish;
- the consumption of legumes (peas, beans, lentils) is allowed, since iron, which predominates in their composition, is poorly absorbed by the human body;
- vitamin complexes containing folic acid and B vitamins are excluded;
- It is forbidden to consume juices and rosehip decoctions;
- You need to drink clean water without gas often and in small portions: every half hour - 1 glass of water.
Reasons for increased hemoglobin
First of all, when hemoglobin is above 141 g/l in women, a blood test is taken for red blood cells and platelets. If their values exceed the norm, most likely, inflammatory processes or systemic blood diseases are occurring in the body, which is why the hemoglobin level increases.
If the quantitative indicators of blood elements are normal, other causes of high hemoglobin need to be considered. Its elevated level is characteristic of a wide range of pathologies and can be provoked by a number of external factors:
- prolonged stay at an altitude of more than 2 km from ground level,
- regular long-term exercise, especially in men and adolescents, which provokes increased oxygen consumption and a concomitant increase in hemoglobin levels,
- dehydration provokes thickening of the blood, which causes a sharp increase in the percentage of iron,
- gastrointestinal diseases accompanied by stool upset and vomiting,
- diseases of a chronic and systemic nature: diabetes, psychoemotional disorders, heart pathologies, respiratory dysfunction, Vaquez disease.
In addition, hemoglobin of 140 or more in women can be observed with long-term use of diuretics, and its excess can be caused by vitamins taken during pregnancy.
What are the differences between female and male hemoglobin?
A woman's hemoglobin level is slightly lower than a man's. Certain factors influence low testosterone levels, which affects monthly blood loss during menstruation.
During life, the level of hemoglobin is not constant; it either decreases or increases. Changes occur due to age, lifestyle and health status.
It is worth saying that at birth the child has a greatly increased level of hemoglobin, but in the first year of life it decreases without any treatment. Then it rises to normal until adulthood.
It is completely impossible to determine on your own the level of hemoglobin in the body, but specific signs can be used to determine its decrease or increase. The most reliable information can only be found after a blood test.
In addition, doctors recommend donating blood in the morning on an empty stomach, in a calm state. After all, any physical and emotional fluctuations directly affect the amount of protein in the blood. A few days before blood sampling, you do not need to engage in sports activities, eat fatty and spicy foods, visit the sauna and bathhouse, smoke or drink drinks containing caffeine.
Sometimes women have hemoglobin levels ranging from 146-153 g/l for various reasons, which are presented below.
Concomitant symptoms with hyperhemoglobinemia and iron deficiency
Often, with a slightly elevated iron level, a woman feels normal, but in general, if hemoglobin is 144 in women, whether she will feel bad or good depends on the characteristics of the condition and health of the body. Doctors consider the problem of high levels of red blood cells only when their value exceeds the norm by 20-30 g/l. It’s another matter when tests show a decrease in hemoglobin. Moreover, even minor deviations from the norm indicate a health hazard.
Symptoms of high hemoglobin levels:
- yellowing of the sclera, skin, palate,
- liver enlargement,
- constant itching of the skin,
- arrhythmia,
- weight loss,
- weakness.
But all these manifestations are associated with the influence of external factors. When the body is affected by pathological processes and diseases, the symptoms are supplemented by:
- localized redness of the skin,
- constant thirst,
- blood pressure jumps,
- sleep disorders and psycho-emotional instability,
- prolonged menstruation with pain.
With low hemoglobin levels, a woman experiences:
- frequent headaches and general malaise,
- depressive state
- weakness,
- dizziness,
- frequent ARVI.
In most cases, the signs of high and low iron levels are similar, so it is impossible to make a correct diagnosis only from the patient’s words. This is why doctors recommend regularly taking hemoglobin tests even if there are no pronounced symptoms.
Low hemoglobin in women
A condition in which hemoglobin falls below normal is called iron deficiency anemia (or anemia). An experienced doctor is able to detect pathology even before undergoing laboratory tests, barely looking at the patient who contacts him. A pale face, dry skin, pockets in the corners of the mouth, dull hair and sluggish movements are the main symptoms of low hemoglobin. And if, in addition to this, a woman complains of increased fatigue, “spots” in the eyes and frequent dizziness, then the diagnosis is not at all in doubt.
In pregnant women, anemia is often accompanied by eating and smell disorders. The desire to eat chalk, coal, sand, smell whitewash or gasoline is by no means a “cute whim” of the expectant mother, but a reason to see a doctor.
The danger of anemia lies in the insufficient supply of oxygen to the tissues. At the initial stages of the disease, the body tries to cope with the lack of a vital element, depriving it of the least significant organs from its point of view (hair, nails, teeth). However, over time, oxygen deficiency increases and everyone has to “starve”, including the brain and heart. In order to prevent serious complications, it is important to identify and eliminate the cause of the disease at an early stage of its development.
Causes of low hemoglobin in women
Anemia can be caused by:
- Poor nutrition. In order for hemoglobin to be synthesized in the required quantity, a sufficient amount of iron must be supplied to the woman’s body with food. Its main source is animal products: meat, liver, kidneys. Plants also contain iron, but in a form that is much less easily absorbed. This is why vegetarianism and low-meat diets are becoming one of the most common causes of anemia. A decrease in hemoglobin can also be caused by excessive consumption of foods that inhibit iron absorption: coffee, tea, chocolate, cereals.
- Lack of folic acid, vit. C or Vit. B12 in the body. All these elements play an important role in the formation of hemoglobin. Vitamin deficiency B12 is most often caused by helminthic infestation, and a lack of vit. C and folic acid - an unbalanced nutritional diet.
- Blood loss. They can be both obvious (with systematic donation, heavy long menstruation, uterine bleeding) and hidden (blood loss associated with hemorrhoids, ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract, polyps in the large intestine, etc.).
- Hypothyroidism. The thyroid hormone, thyroxine, regulates the absorption of iron in the intestines. Its deficiency also entails a lack of hemoglobin.
- Diseases of the digestive system. Gastritis, ulcerative lesions of the stomach or intestines lead to thinning of the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, as a result of which iron practically ceases to be absorbed.
- Premature death of red blood cells. This condition can be caused by long-term infectious diseases (hepatitis, tuberculosis, etc.) or immune disorders (for example, lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis).
- Sedentary lifestyle. Physical activity is one of the factors influencing the synthesis of red blood cells. If the blood is not rapidly dispersed throughout the body, the brain receives signals that there are “enough” red blood cells and their additional synthesis is not required.
- Stress. They can cause a decrease in appetite and, as a result, insufficient intake of iron from food.
On topic: 5 superfoods to quickly increase hemoglobin!
Complications with high iron levels
Like any disease, hyperhemoglobinemia can lead to the development of complications:
- angina pectoris
- disorders of the blood supply to the brain,
- stroke, which develops as a result of increased blood viscosity and density.
While hemoglobin 140 may cause concern in an adult woman, this figure is considered normal in a child. In newborn babies, the maximum level can reach 225 g/l, which is considered acceptable by doctors and does not require treatment. Therefore, you should not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication. The doctor examines each individual clinical case, draws conclusions and makes a diagnosis, on the basis of which the optimal course of therapy is selected, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Symptoms
Elevated hemoglobin in women has a nonspecific and mild clinical picture, so often characteristic signs go unnoticed or are masked as manifestations of the underlying disease.
Clinicians identify the main symptoms that occur regardless of the etiological factor. The following signs indicate an increase in hemoglobin concentration in the blood:
- local redness of the skin, which alternates with areas of pallor;
- general malaise and weakness;
- constant drowsiness;
- body aches;
- dizziness;
- muscle, joint and headaches;
- dry mucous membranes and skin;
- emotional instability;
- increase in blood tone indicators;
- thirst and shortness of breath;
- increased irritability;
- decreased ability to work;
- partial or complete lack of appetite;
- excessively painful and prolonged menstruation;
- the appearance of bruises and hemorrhages even with minor trauma to the skin;
- bloating of veins;
- violation of the act of defecation and urination;
- coldness of the fingertips of the upper and lower extremities;
- nausea without vomiting;
- absent-mindedness and memory impairment;
- decreased hearing and visual acuity;
- pain and bloating in the abdomen.
The severity of clinical manifestations depends on how high the hemoglobin level is in women. If symptoms occur, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
Diagnostics
Often, increased hemoglobin is a sign of a developing pathology that needs to be detected and treated. By taking a blood test, you can only determine iron deviations from the norm, but this will not help to find out the reason for the change in its level. Therefore, if the indicators are too high, women are prescribed additional comprehensive diagnostics to help clarify the root cause of the high level of red cells in the blood.
If the analysis shows that hemoglobin is at the level of 136-144, then the patient is unlikely to be prescribed additional diagnostics, since these values fall within the definition of normal and are not dangerous to health. However, it is possible that the doctor will insist on repeating the study after 2-3 months to make sure that the woman does not have a tendency to increase indicators.
Summary of this article
To summarize, it is necessary to emphasize:
- hemoglobin 153 in women is a normal value, however, a slight deviation is not a sign of the disease;
- consistently high indicators of the criterion under consideration are a sufficient reason to prescribe a comprehensive laboratory and instrumental examination of the patient in order to identify the causes;
- One of the reasons for high hemoglobin levels in women may be pregnancy, in which case there is no need to take measures to reduce it;
- the obtained analysis data is influenced by proper preparation for the delivery of biomaterial, as well as taking medications;
- The treatment regimen for hyperhemoglobinemia is prescribed by the attending physician. As a rule, it consists of taking blood thinners and diet;
- complications of increased hemoglobin concentration manifest themselves in the form of blood clots, so it is necessary to strictly adhere to the treatment regimen and follow all doctor’s recommendations.
Certified specialist, in 2014 she graduated with honors from the Orenburg State University with a degree in microbiologist. Graduate of the graduate school of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education Orenburg State Agrarian University.
In 2020 At the Institute of Cellular and Intracellular Symbiosis of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, she completed advanced training in the additional professional program “Bacteriology”.
Laureate of the All-Russian competition for the best scientific work in the “Biological Sciences” category 2020.
source
Ways to lower hemoglobin levels
First of all, when hemoglobin exceeds 142 g/l, a woman should reconsider her diet. You should think about proper nutrition, even if the level has not yet exceeded the norm, but is already at the borderline level of 137-138 g/l.
Products useful for hyperhemoglobinemia include:
- low-fat cottage cheese, milk, cheeses,
- green vegetables and fruits,
- rice and other cereals, except buckwheat.
Bad foods that can increase hemoglobin levels include:
- pomegranate,
- apples,
- any meat products, poultry and offal,
- alcohol,
- some dietary iron supplements,
- multivitamins,
- buckwheat,
- sweet and fatty foods.
The diet helps normalize hemoglobin and adjust its level to normal. This is the most reliable way to reduce its content, because there are no special medications to reduce iron.
If a woman’s hemoglobin level of 145 or higher is due to a disease, then for therapy the doctor may prescribe medications that thin the blood to avoid thrombosis. However, without consulting a doctor, taking any medications is strictly contraindicated, since there is a risk of aggravating the pathological process with medications if it is caused by blood diseases, for which taking such medications is extremely dangerous.
Diseases and medications as the cause of pathology
When blood does not completely flow through the vessels to the brain, this leads to oxygen starvation. In case of poisoning, prolonged vomiting or diarrhea, dehydration occurs, which directly affects the increase in hemoglobin. Due to the use of diuretics, in particular for weight loss. Often those medications that are taken independently, without the correct prescription from a specialist, have an effect.
What is dangerous, possible consequences
With increased hemoglobin, the blood becomes thick and viscous. At the same time, the internal organs, oddly enough, do not receive enough oxygen and other nutrients.
Therefore, with prolonged erythrocytosis, the following may develop:
- disruption of the kidneys and genitourinary system, up to painful colic;
- infertility;
- recurrent miscarriages;
- decreased visual acuity;
- heart attack;
- heart attack;
- thrombosis.
In this regard, it becomes clear that high hemoglobin can be no less dangerous than low hemoglobin levels and requires medical help.