In women, one of the key indicators by which doctors assess their health is the concentration of neutrophils in the blood. Normally, this subtype of leukocytes supports the body’s protective functions, increasing its resistance to bacterial and fungal infections.
If there are significant differences between actual and reference values, general practitioners usually order additional examination of the patient to identify a reliable picture of her health status.
What are neutrophils?
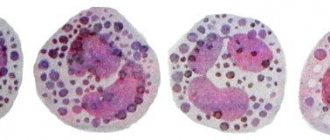
Neutrophils (the norm in women’s blood is generally accepted, regardless of the lifestyle of a particular person) are blood cells that play one of the main roles in forming the protection of the female body.
They come in two types:
- early;
- mature (another name for this type of cell is segmented neutrophils. They arise as a result of the generation of the type of leukocyte in question in the red bone marrow, its subsequent maturation to stab and entry into the circulatory system. After 3-5 hours, the stab neutrophil matures to segmented and spreads along the walls vessels in various organs).
Doctors prescribe tests to detect a specific level of neutrophils in a number of cases:
- Myocardial infarction;
- tuberculosis;
- blood loss on a large scale;
- chemical intoxication of the body;
- appendicitis;
- pneumonia;
- angina.
How are they designated in the analysis?
A clinical blood test allows the doctor to determine how many white blood cells are in the body. There are five types of white blood cells, and the test also shows how many of each type are present. The absolute number of neutrophils is called ANC. The indicator is not measured directly. It is obtained by multiplying the white blood cell count by the percentage of neutrophils in the various white blood cell counts.
The percentage of neutrophils consists of segmented (mature) cells and stripes (almost mature). The normal range for ANC is 1.5 to 8.0 (1500 to 8000/mm3). In practical clinical settings, safe ANC is 500–1500, low ANC is less than 500. When neutrophils are normal, this means that the patient's activities should not be limited.
On a note! Sometimes a deviation from the norm is a side effect after taking one or another strong medicine. Radiation therapy can also be a trigger.
The mechanism of action of neutrophils
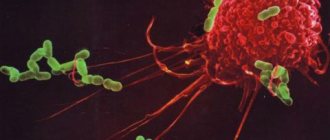
Neutrophils are macrophages in nature, which makes them capable of phagocytosis. They absorb foreign cells of extremely small size. After the destruction of pathogenic microflora, the type of leukocyte in question usually “dies,” resulting in the release of a large amount of biologically active substances into the blood.
“Beneficial” cells weaken the effects of fungi and bacteria, while simultaneously stimulating the protective functions of a woman’s immune system. The disintegrated neutrophils mix with cellular matter formed from inflamed tissues and are excreted from the body in the form of pus.
In 2004, scientists were able to identify another mechanism of action of neutrophils - NETosis. It consists of the disintegration of a neutrophil, which provokes the release of a DNA network that is destructive to pathogenic cells. Harmful bacteria become entangled in DNA traps and are absorbed by them, accelerating the body’s healing process.
Functions and types of cells
Neutrophils are a type of leukocyte - white blood cells that are vital to the immune system. These cells are heterogeneous; in total there are 4 types of neutrophils, which differ in their narrow purpose:
- myelocytes are preneutrophils, maximally immature cells without differentiation, which can eventually turn not only into a neutrophil, but into any blood element: from a platelet to an eosinophil;
- young neutrophils are an immature version of neutrophils, a conditional reserve of cells that begin to work in conditions of the body’s increased need for immune cells; in critical situations, a minimum number of such cells can be recorded in the bloodstream (no more than 1%);
- band neutrophils - make up no more than 5% of the total number of neutrophils, this is already a partially specialized cell of the immune system, it works in the bloodstream if the remaining neutrophils cannot cope with their functions;
- segmented neutrophils are the basis of neutrophil cells; up to 70% of the total number of structures constantly work in the bloodstream; they manifest themselves to the maximum during the infectious and inflammatory process in the body.
Thus, there are only two types of active, that is, capable of acting, neutrophils: segmented and band. They solve the main tasks that the body sets for neutrophils:
- lyse the cell membrane of the pathogen, killing viruses, bacteria, fungi, and other pathogenic microflora;
- enter into an antigen-antibody reaction with microbes, binding pathogenic flora, accelerating the relief of inflammation;
- absorb microbes and digest them (phagocytosis): one cell can destroy up to 30 “strangers”;
- inactivate viruses, reducing the rate of replication of pathogens, helping to stop inflammation of a viral nature.
Normal level of neutrophils in the blood of women. Table by age, during pregnancy
Neutrophils (the norm in a woman’s blood is determined by the characteristics of her current state) in their concentration can depend not only on the woman’s health, but also on acquired “temporary” characteristics of her body, for example, pregnancy.
In a healthy middle-aged person, in the absence of congenital pathologies that are in remission, the share of mature neutrophils in the blood should account for 47–73% of the total number of leukocytes, and 1–6% for young ones.
Neutrophils are normal in women’s blood, along with other blood parameters in the table.
Depending on the age of the woman, the reference values for the concentration of neutrophils in the blood are considered to be:
| Woman's age | Normal neutrophil count (from the total leukocyte formula) |
| From birth to 2 weeks | 32 – 57% |
| 2 weeks – 1 year | 16 – 50% |
| 12-24 months | 28 – 53% |
| 24 months - 5 years | 32 – 60% |
| From 5 to 7 years | 38 – 63% |
| From 7 to 9 years | 41 – 65% |
| From 9 to 11 years | 43 – 65% |
| From 11 to 15 years | 45 – 65% |
| 15 years and older | 47 – 77% |
When analyzing the test results of pregnant women, it is important to keep in mind the physiological tendency for the number of neutrophils in the blood to increase closer to the second trimester (from 10 to 18 weeks of pregnancy). At the end of this period, the values of the type of leukocytes in question level out and begin to fall back into generally accepted norms.
Norm
In the blood of an adult and a child over 13 years of age, all types of leukocytes should be 4-10 * 10 to the 9th degree / l of blood, of which neutrophils - 48-80%. Of these, the initial form of neutrophils is 1-3%, band neutrophils 1-6%, segmented - 45-72%.
In children under 12 years of age, the immune system is developing, so their leukogram is somewhat different. Babies are born with an “adult” norm of segmented neutrophils, which continues to increase in the first day of the child’s life, and then sharply decreases.
At 5-7 years, the number of segmented neutrophils increases again, and during this period, pediatricians and parents note that the child begins to suffer from colds less often.
Age norms of segmented neutrophils in the blood of children:
- first day – 50-70%;
- 1-5 days – 35-55%;
- 5-15 days – 25-45%;
- 15-30 days – 15-30%;
- 1-12 months – 20-35%;
- 1-6 years – 35-55%;
- 7-10 years – 40-60%;
- 11-15 years 40-75%.
Increased neutrophil levels
An increase in the level of neutrophils does not always require drug treatment, however, if there are visible deviations in test results, doctors strongly recommend undergoing an additional examination of the body’s condition in order to identify the causes of such changes.
Causes
The most common causes of increased neutrophil concentrations include:
- pregnancy (2nd trimester);
- inflammatory kidney diseases;
- pathologies of the venous system of the body;
- inflammation of the vermiform appendage of the cecum (appendix);
- diseases of the female reproductive system;
- pathologies of the skeletal system;
- damage to the mucous membranes of the female body;
- acute inflammatory processes of the respiratory organs;
- deviations from the normal state of the cardiovascular system;
- pathologies of the brain and spinal cord;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- gout;
- oncological diseases in advanced forms.
Despite the large number of diseases, the signs of which are a jump in the level of neutrophils in a woman’s body, the most common reasons for such changes are non-dangerous (provided measures are taken in time to eliminate them) circumstances.
For example:
- eating large amounts of heavy food on a regular basis;
- prolonged depression or severe stress suffered on the eve of the test;
- recovery period after surgery;
- strength training and a large amount of physical activity;
- a tendency to exhibit allergic reactions (or a reaction that occurs at the time of taking a blood test).
Degrees of neutrophilia
Neutrophilia is the process of changing the concentration of neutrophils in a woman’s blood by more than 6.5 * 109 per 1 liter of blood.
It comes in three types:
- moderate (the number of neutrophil cells in 1 liter of blood reaches 10 billion);
- pronounced (the number of neutrophil cells in 1 liter of blood reaches 10 - 20 billion);
- severe (the number of neutrophil cells in 1 liter of blood reaches 20 - 60 billion).
Based on the degree of neutrophilia, doctors determine the severity of the progressive disease, as well as the current stage of its development. With extensive damage to the body, the number of neutrophils is as high as possible, and neutrophilia is advanced.
When the pathology in question is identified, drug treatment is prescribed only after the doctor is convinced that there are no secondary circumstances, the presence of which allows us to consider this process a variant of the norm.
Neutrophilia as a normal variant
In women carrying a child, neutrophilia may be a variant of the norm (if the number of leukocytes of the type in question is up to 10 billion in 1 liter of blood).
In addition to pregnancy, high neutrophil levels can be affected by:
- eating heavy food before taking the test (for example, if a woman donates blood in the morning, and in the evening her dinner consisted of a fatty steak and a high-calorie side dish);
- excessive emotional stress (not necessarily at the time of the test. The indicators can be affected by stress suffered by a person the day before, for example, 3-4 weeks before the test);
- excessive physical activity the day before (before donating blood to determine the level of neutrophils, it is recommended to minimize physical activity and not go to the gym both on the day of the test and the day before it).
In these circumstances, adjustment of neutrophil levels with drug therapy is not necessary.
The child has low neutrophils
Often, the doctor can make an accurate diagnosis only after seeing the test results. For example, a general detailed blood test tells the doctor much more about the state of the body than any symptoms or descriptions of the patient.
Why are neutrophils needed in a child’s blood?
Neutrophils are a type of leukocytes that protect the body from various types of infections, bacteria and fungi. They are the first to stand in the way of pathogenic microbes, fight back and signal that something is wrong in the body. Also, the function of neutrophils is to absorb old dead cells and bodies, i.e.
they help wounds and scratches heal faster, which is important for children’s health
The following types of neutrophils are distinguished:
- segmented or mature;
- band or immature.
The norm of neutrophils in children depends on age. The number of segmented neutrophils varies from 15 to 70% (in newborns below 30%), band neutrophils - from 2-5% (in newly born - 3-12%).
An increase or decrease in cells indicates an inflammatory process occurring in the body or a developing malignant tumor, or poor functioning of the immune system. The more of these cells a blood test shows, the stronger the inflammation; the fewer of them, the more weakened the body is.
What to do if a child has increased or decreased neutrophils?
If the increase in white cells is insignificant, then perhaps this is the fault of heavy physical or mental stress, stress, and emotional changes. This phenomenon may also be associated with recent vaccinations and the use of immunostimulants or anti-inflammatory drugs. That is, a periodic increase in neutrophils and their subsequent return to normal is considered a common occurrence, which indicates adequate functioning of the immune system.
But if segmented neutrophils are very elevated in a child, then it is necessary to immediately conduct additional diagnostics to detect the disease and begin treatment.
Diseases that increase the level of this type of leukocytes:
- angina;
- bronchitis;
- appendicitis or inflammation of other internal organs;
- oncological diseases;
- diabetes;
- gangrene and other infectious processes;
- anemia;
- kidney and liver diseases;
- radiation sickness, etc.
If a child has low segmented neutrophils, then you should pay attention to his immunity. Most likely, the body is weakened by some current or untreated disease
Low levels occur with measles, chickenpox, hepatitis, and some types of fungus.
But there are cases where a reduced amount of these substances in the blood is genetic.
An increase in band neutrophils in children is a call for immediate action. Their level usually drops with a decrease in segmented cells. Most often, this indicates the presence of a malignant tumor. If a child has increased band neutrophils, this may also indicate intoxication, overexertion, inflammation; if they are decreased, this may indicate anaphylactic shock, blood diseases, and thyrotoxicosis.
Preparing for analysis
It is necessary to properly prepare for the study. To do this, you need to limit yourself in food the night before and in the morning on the day of the test. It is also prohibited to drink sweet, carbonated drinks. Physical activity is not recommended. It is better to rest, get some sleep, and relax before donating blood.
Thus, an increase and decrease in neutrophils in children is considered a pathology. A pediatrician can determine what kind of disease it is caused by.
View the discussion thread.
Indicators below normal values
Neutrophils (the norm in women’s blood should be assessed taking into account the results of previous studies), when they are insufficient in the female body, weaken the immune system without preventing the proliferation of bacteria and fungi.
Causes
The concentration of neutrophils, significantly lower than normal, indicates the presence of neutropenia in the female body.
Most often it occurs due to:
- excessive amounts of pathogenic microorganisms;
- depletion of the circulatory system;
- inability to produce the required number of neutrophils due to external circumstances;
- serious blood diseases;
- bacterial lesions of the female body;
- viral diseases (identified by an increase in the number of lymphocytes and monocytes along with a decrease in the concentration of neutrophils);
- individual reactions of the body to drug therapy (for example, taking immunomodulators, interferon);
- radioactive exposure;
- carrying out chemotherapy or radiation treatment for cancer patients;
- leukemia;
- low level of hemoglobin in the blood;
- vitamin deficiency (lack of folic acid and B vitamins can especially affect the level of neutrophils).
Degrees of neutropenia
Neutropenia, depending on the reasons that provoked its occurrence, can be of three types:
- soft (the number of neutrophil cells in 1 liter of blood ranges from 1 to 1.5 billion)
- moderate (the number of neutrophil cells in 1 liter of blood ranges from 0.5 to 1 billion);
- severe (the number of neutrophil cells in 1 liter of blood does not reach 0.5 billion or the type of leukocyte in question is completely absent).
When diagnosing neutropenia, doctors usually monitor the trend of changes in the woman’s blood test results, since a single decrease in neutrophils cannot be regarded as a pathological condition requiring medical intervention.
Particular situations of neutropenia
In three cases, neutropenia can be considered normal and not provoke the need for additional examination of the woman’s health status.
For example:
- physiological feature of the body , or benign neutropenia (diagnosed in the absence of deviations of other indicators from the norm);
- cyclic neutropenia (implies a cyclic variation (a cycle can range from 2 weeks to 3 months) in the level of the type of leukocyte in question - from minimal values to normal without drug intervention in the process);
- Kostman's neutropenia (a genetic disease that causes a complete absence of neutrophils in the body. If a person with this feature managed to survive the first year after birth, over the following years his body adapts to the circumstances, producing monocytes and eosinophils in sufficient quantities to compensate for the lack of neutrophils).
Reasons for the downgrade
There are also many factors that shift the leukocyte formula to the left.
- HIV. Huge problem. The pathological process provokes depression of the entire immune system. In this case, even against the background of a real threat, damage to the body, there will be no growth indicators at all. On the contrary, they will be lowered. Maintenance therapy is required.
- Aplastic anemia. Accompanied by a violation of the synthesis of all possible formed blood cells. Leukocytes of different types are no exception here. Without specific treatment, potentially fatal complications are likely. Action needs to be taken faster.
- Severe infectious processes. In this case, the need for shaped cells for active combat is growing. The body may not have time to produce new ones, hence the temporary decline.
- General weakness of all systems. Neutrophils are lower than normal if a person has suffered a serious illness in the recent past or does not receive enough nutrients.
- History of alcoholism. The same goes for those who drink heavily. The concentration of neutrophils is less than adequate values, since their synthesis is suppressed by ethanol breakdown products. The general exhaustion of the body of such people also affects.
- Hepatitis. Inflammatory process of the liver. It has an infectious, particularly viral origin.
- Sepsis. Generalized damage to the body.
- Radiation sickness.
- Intoxication. In case of poisoning with certain poisons. A group of drugs also has a similar effect. The possibility of such a side effect is reflected in the annotations for specific pharmaceutical products.
All causes and mechanisms of development of neutropenia (low concentration of neutrophils) are described in this article.
When and how is a neutrophil level test performed?
To conduct a study on the concentration of neutrophils in the blood, medical workers take capillary blood (from a finger). Such an analysis does not require any special preparation.
It will be sufficient to follow the basic recommendations related to donating blood for general examination:
- exclude heavy meals 4 hours before the intended procedure (breastfed children are allowed to feed);
- Before taking the test, wash your hands with soap and running water at room temperature;
- disperse the blood in the hands of the upper extremities at their low temperature (the normal rate of blood circulation contributes to the rapid collection of biomaterial without subsequent disruption of its consistency).
Biomaterial is taken in the traditional way:
- A woman's ring finger is treated with an alcohol wipe.
- A puncture or incision is made in the pad of the finger (depending on the medical equipment used).
- The required amount of blood is squeezed onto a sterile glass or into a disposable tube.
Decoding the results
The neutrophil norm determined for a particular woman can only be compared with the result of a blood test by a professional doctor. The ability to decipher a study is mandatory for making a diagnosis and prescribing medical treatment.
A standard blood test involves examining 5 types of leukocytes. If cells of an atypical structure are detected, the analyzer signals the need to double-check the result “manually” under a microscope. The list of results most often includes only the “leukocytes” criterion.
In case of diagnosed abnormalities, the study results form will also include a detailed leukocyte formula. The obtained indicator values should be compared not only with their reference analogues, but also with the generally accepted norm for women of a particular age and the characteristics of their current physical condition.
How to avoid false results?
To avoid a false test result on the concentration of neutrophils, you need to know what exactly has a direct effect on them.
Namely :
- drinking coffee, tea, alcoholic beverages before donating blood;
- taking antibacterial medications;
- eating fatty, smoked foods, semi-finished products and marinades (less than 24 hours before taking biomaterial);
- excitement or stress at the time of submitting the biomaterial (before the analysis, you should spend 10-15 minutes in silence, normalizing your breathing and heart rate);
- recent vaccination.
What to do in case of deviations?
The sequence of actions when identifying abnormalities in the neutrophil count is determined by a doctor who has an idea of the health status of a particular woman. It is highly not recommended to independently attempt to influence the concentration of active components.
Ways to increase neutrophil levels
To increase the level of neutrophils, in the vast majority of cases, doctors prescribe:
- adjust your diet, focusing on foods enriched with vitamin C, E, B, zinc, omega 3;
- taking narrow-acting medications, for example, Neuprogen;
- wash your hands regularly with antibacterial products;
- avoid contact with sick people;
- Clean your mouth daily to minimize the burden on your immune system.
Decreased neutrophil levels
The following may help reduce neutrophil levels:
- eliminating the root cause of the jump in the indicator (for example, eliminating pathogenic microflora using antibacterial drugs);
- refusal to consume animal products;
- normalization of the emotional state (to quickly resolve psychological problems, it is recommended to consult a psychologist).
The norm of neutrophils is determined by the woman’s health status, her age, as well as psychological stability. By making a harmonious lifestyle, a person in some cases manages to normalize the concentration level of the main blood components, thereby minimizing the risk of developing life-threatening diseases.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky