Synonyms: rheumatoid factor, RF, Rheumatoid factor, RF.
One of the main studies in rheumatology is the analysis of rheumatoid factor. RF are proteins (immunoglobulin antibodies) that are produced by the body’s immune system to destroy its own cells that it mistakenly perceives as foreign. In laboratory diagnostics, rheumatoid factor plays the role of an indicator of the inflammatory process and autoimmune disorders.
The RF test is a fairly informative test that allows one to determine the presence of autoimmune pathologies, in particular rheumatoid arthritis and Sjogren's syndrome, as well as a number of other diseases that have a non-immune etiology: chronic bacterial and viral infections, some cancers, pulmonary, urinary and hepatobiliary pathologies systems
Deciphering indicators
There are their norms, so a deviation upward or downward immediately indicates pathologies due to illness.
Suspicion of a disease based on rheumatic tests requires mandatory further examination. An indicator of how total protein can tell about the body.
Too high a level is caused by:
- Vomiting;
- Diarrhea;
- Taking hormonal or diuretic drugs.
If the situation is the opposite, the person:
- Doesn't finish eating;
- Is on a diet;
- Physically exhausted;
- Drinks too much water per day.
When the ratio of protein fractions - albumin to globulin - is disturbed compared to the norm, the problem lies in the kidneys and liver. High rates indicate dehydration and the use of diuretics or contraceptives.
Low albumin indicates:
- Pregnancy;
- Breastfeeding;
- Frequent diets;
- Nicotine addiction.
The level of rheumatoid factor indicates the presence of antibodies to various diseases in the human body, which immediately indicates a specific pathology or inflammatory process. Often in healthy people this indicator is zero, but nevertheless norms have been developed that are considered negative at different ages.
If you eat foods that are too fatty before the examination, your rheumatoid factor will show increased results.
The same thing is observed in older people. Poor results are a consequence of treatment with Methyldop or a high content of fats in the human blood.
A circulating immune complex test is prescribed for suspected immune disorders:
- Arthritis;
- Allergy;
- Fungal or viral etiology.
If the indicator is elevated, the reason may be:
- Addiction;
- Use of oral contraception;
- Anticonvulsants.
The opposite situation occurs when a person is undergoing chemotherapy or taking antidepressants.
Look at the explanation of the rheumatic test in the table and the norm of indicators.
Inflammation and autoimmune diseases can be seen through a C-reactive protein test. When its level goes off scale, the possibility of developing oncology or myocardial infarction cannot be ignored.
An increased result in adults, giving a rheumatic complex, indicates:
- Overweight;
- Smoking;
- Surgical interventions;
- Other wounds.
Reduced data is shown when:
- Taking steroids;
- Hemolysis;
- Fat in the blood.
Specific antibodies in human blood to streptococcus increase the antistreptolysin level.
If treatment is not started, autoimmune pathologies such as:
- Sore throats;
- Scarlet fever;
- Chronic tonsillitis.
But it happens that the reason for the increased result is:
- Purulent inflammation;
- High cholesterol;
- Diseased kidneys and liver;
- Great physical activity.
A decrease in results is provoked by taking hormonal drugs.
How to normalize?
Additional hardware tests will help establish an accurate diagnosis.
High levels of RF titers do not yet indicate rheumatoid arthritis, but are included in the list of diagnostic criteria and allow one to assess the degree of activity of the inflammatory process. To confirm the suspected cause, additional examinations are prescribed:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- rheumatic tests (SRP, ASLO);
- biochemistry on Anti CCP;
- total titer of immunoglobulins;
- x-ray of the affected area;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- CT, MRI and arthroscopy - according to indications.
A comprehensive examination allows you to confirm or exclude RA, assess the degree of activity and prescribe treatment. In case of doubtful or negative results, it is recommended to take the test three times. However, in cases of rheumatoid arthritis, in 20-25% of cases, a seronegative variant of the disease is possible, when RF is not detected in the plasma. To reduce the level of rheumatic factor, you need to undergo a course of treatment.
Volumes and boundaries
- The C-reactive protein level in the absence of disease is zero - a positive reaction, but a maximum of 5 mg/l is still considered a negative result.
- As for circulating immune complexes, the norm is 30-90 units per ml in any age range.
- Rheumatoid factor in children under 12 years of age is less than 12.5 IU/ml, and in people under 50 years of age it is about 14 IU/ml.
- In healthy patients, antistreptolysin shows from 0 to 200 units per ml, and in children under 14 years of age - up to 150 units.
- The albumin level in children under 14 years of age is minimal – 38 g/l, maximum – 54 g/l. Up to 60 years of age, this figure is from 35 to 50 g/l, and in older people – 34-48 g/l.
- Total protein in infants is 46-73 g/l, up to 4 years old - 61-75 g/l, up to 15 years old - 58-76 g/l, up to 60 years old - 65-85 g/l, in people over 60 years old – 63-84 g/l.
Rheumatic tests should only be commented on by a specialist who knows the general picture of the patient’s complaints and other tests, and understands what is included in this procedure. Knowing his health status is important because often really sick people get normal results, while healthy people get elevated results.
Which doctor should I contact?
In a state of ill health, manifested by expressive symptoms, it is necessary to consult a therapist. He, as a generalist, will be able to make certain assumptions and prescribe the necessary studies. If his assumptions are confirmed, he will give a referral to the appropriate specialist - a rheumatologist, an infectious disease specialist, an orthopedist, a vertebrologist.
Rheumatoid factor in a blood test is one of the undoubtedly important indicators, which is still not the main research method. Like every analysis, it has its own errors, so conclusions are drawn based on the complex result of diagnostic measures.
Indications
Rheumatic blood tests represent a complex of examinations that can be used to diagnose rheumatic and autoimmune system diseases.
From one blood sample, an analysis is made for ESR, protein and its fractions, antistreptolysin and other indicators. Thanks to rheumatic tests, it is possible to identify diseases that are associated with oncology from the very beginning.
Doctors often prescribe rheumatic tests to their patients to confirm or refute the diagnosis and to correctly adjust treatment in case of changes.
Analyzes of each indicator have their own limits, since at different ages they can differ significantly. Some indicators are generally absent in healthy people, but occur in minimal quantities, without indicating such a disease.
More often, rheumatic tests are prescribed to determine:
- Lupus erythematosus or discoid lupus;
- Rheumatism;
- Burns;
- Heart attack;
- Sepsis;
- Kidney and liver diseases;
- Pancreatitis;
- Malignant formations in the body.
Antinuclear antibodies (ANA)
Using the ANA test, you can determine the presence of antinuclear antibodies (antibodies to nuclear antigens) in the blood.
ANAs are a group of specific autoantibodies that are produced by our body's immune system in case of autoimmune disorders. Antibodies have a damaging effect on the body's cells. In this case, a person experiences various painful symptoms, such as pain in muscles and joints, general weakness, etc.
Detection of antibodies belonging to the ANA group (for example, antibodies to double-stranded DNA) in blood serum helps to identify an autoimmune disease, monitor the course of the disease and the effectiveness of its treatment.
Blood for antinuclear antibodies is taken from a vein in the elbow, on an empty stomach. Before the study, you do not have to adhere to any diet.
In some cases, in order to differentiate various autoimmune diseases, additional clarifying tests for autoantibodies from the group of antinuclear antibodies, the so-called ANA immunoblot, may be required.
Antinuclear antibodies (also called antinuclear factor) indicate the presence of some kind of autoimmune disorder, but do not precisely indicate the disease that caused it, since the ANA test is a screening test. The goal of any screening is to identify people at increased risk of a particular disease.
A healthy person with normal immunity should not have antinuclear antibodies in the blood or their level should not exceed the established reference values.
A normal ANA value implies an antibody titer not exceeding 1: 160. Below this value, the test is considered negative.
A positive test for antinuclear antibodies (1:320 or more) indicates an increase in antinuclear antibodies and the presence of a disease of an autoimmune nature in a person.
Currently, two methods are used to detect antinuclear antibodies: indirect immunofluorescence reaction using the so-called Hep2 cell line and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Both tests complement each other, and therefore they are recommended to be performed simultaneously.
If the test for antinuclear antibodies is positive, it is necessary to perform an immunoblot of antinuclear antibodies to clarify the type of autoimmune disease and make a diagnosis.
Preparation for delivery
These precautions increase the possibility of obtaining reliable results of the analysis of rheumatic tests:
- It is recommended to take tests first thing in the morning and on an empty stomach.
- You can only drink still water the day before, and you can eat it 8 hours before the test.
- It is better to donate blood before starting medication treatment, as they can significantly distort test results. Otherwise, it is better to postpone the examination.
- Subsequently, at least 2 weeks should pass between the end of taking the drugs and the delivery of rheumatic tests.
In cases where rheumatic tests are urgently needed, but the course of treatment cannot be interrupted, specialists should be warned about the patient’s medications. 24 hours before the test, it is important to exclude strong coffee and tea, alcoholic beverages, fatty foods and stress on the body physically and psychologically from the diet.
If these recommendations are completely ignored, the results will be erroneous.
How is a rheumatoid factor test done?
It is worth considering that this analysis is prescribed quite often, since it is easy to carry out and does not require significant costs. To carry it out, venous blood is taken, and serum is isolated from it by centrifugation, from which the study is performed.
The analysis is that if rheumatoid factor is elevated, it reacts with antibodies, which are contained in a certain concentration in the test solution. Express tests are also widely used, which make it possible to immediately obtain results.
Experts, as a rule, recommend using several methods to obtain the most accurate data.
It is best to take blood for analysis before lunch and on an empty stomach. At the same time, the day before the planned diagnostic study, you should avoid fatty foods, alcoholic beverages and cigarettes, not take medications, and also reduce physical activity.
Definition of diseases
The analysis is prescribed by doctors to determine inflammation in the body and its location.
In total, there are about a hundred rheumatic diseases that can be detected, but rheumatic tests are prescribed to determine the most common diseases.
Only a specialist can decipher the results obtained by comparing norms and deviations. Based on the full picture, he has the opportunity to prescribe treatment.
The main reasons why rheumatic tests are prescribed:
- Pain in the back and joints.
- Joint aches and swelling.
- Aching muscles and ligaments.
- Severe headaches.
- High body temperature lasting more than half a month.
- Gout, lupus and other diseases.
Methods for determining RF in blood
There are three ways to detect rheumatoid factor.
- Nephelometry. Classic laboratory test. It is based on an approximate calculation of the quantitative index of autoantibodies.
To perform the test, a small amount of blood is taken. Then an intense light flux is passed through the biomaterial (it is specially prepared in advance).
The presence and actual amount of rheumatoid factor are determined by the degree of turbidity and the quality of the “solution”. This is one of the simplest and therefore popular diagnostic methods.
- Qualitative methods are sometimes used for screening. For example, latex test. For this analysis, a special reagent based on class G immunoglobulins is used. Rheumatoid factor is “tailored” to attack this substance, so it quickly reacts to a foreign compound.
Kinds
To confirm autoimmune diseases, a rheumatic complex of several types of markers is used:
- Antistreptolysin-O (ASLO) – identification of the body’s protective cells to streptococcal antigens. This is a kind of test for rheumatism; ASLO in the blood helps to distinguish a similar disease from rheumatoid arthritis (the concentration of this marker in such pathologies is different).
- Rheumatoid factor (rheumofaktor). With rheumatoid disease, a protein appears in the blood, which the immune system accepts as a foreign body and begins to develop protection against it. The test for rheumatic factor consists of detecting such antibodies to self-antigens. The results allow the identification of connective tissue disease.
- C-reactive protein (CRP) is a type of rheumatic test that indicates an acute inflammatory process in soft tissues. The analysis helps to identify pathology and prescribe antibacterial therapy.
- Total protein. The marker makes it possible to determine the level of protein and its components - albumin and globulin.
- Circulating immune complexes (CICs). Identification of cells that are damaged by the body's protective compounds.
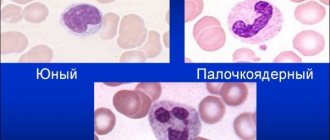
- General blood test (with leukocyte formula) - study of biological material for changes in the number of lymphocytes or neurophils. The test helps identify inflammation caused by infections.
Rheumatological analysis makes it possible to accurately determine the type and localization of negative changes in soft tissues. Studying rheumatic tests in a biochemical blood test allows you to prevent the further development of a dangerous disease and select effective treatment.
What does elevated rheumatoid factor indicate?
In cases where, based on laboratory tests, a positive rheumatoid factor was determined that exceeds the established norm, it is advisable to talk about the likelihood of having one of the ailments:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- Sjögren's syndrome;
- rubella;
- syphilis;
- salmonellosis;
- scleroderma;
- systemic and sensitizing vasculitis;
- tuberculosis;
- malignant neoplasms and leukemia;
- parasitic infections;
- flu;
- pulmonary silicosis;
- brucellosis;
- mixed cryoglobulinemia;
- connective tissue diseases of mixed etiology;
- juvenile arthritis;
- leprosy;
- chronic hepatitis;
- subacute bacterial endocarditis;
- polymyositis and others.
But, despite the fact that an increased rheumatic factor may indicate the development of any of the above diseases, most often it is reliable confirmation of a diagnosis such as rheumatoid arthritis. This disease is characterized by the destruction of connective tissue, resulting in damage to the joints.
Normal indicators
For this analysis, the norm is a conditional name. You need to understand that rheumatic tests represent a complex of studies that consist of determining various independent indicators that will not be related to each other in any way.
Each of the studied indicators has its own individual standards. They significantly depend on age, physiological state of the body, life history and illness.
Rheumatic tests are negative
Negative results are said when the indicators are within the normal range or below it. It all depends on the specific sample. Low levels indicate a functional state, for example, pregnancy, overwork, nervous tension.
Rheumatic tests are positive
Specific indicators depend on the type of study. For example, CRP levels increase with the development of an acute inflammatory process in the body. In this case, an increase in streptococci is indicated by antistreptolysin.
It should be taken into account that rheumatic tests may increase slightly after eating fatty, fried foods, or after intense exercise. Some indicators may remain elevated after an infectious disease in older people, which is associated with many changes occurring in the body.
Rheumatic tests in children
Children sometimes have to take rheumatic tests. More often, this need arises against the background of inflammatory and infectious diseases. If a streptococcal infection is suspected, antistreptolysin levels are needed.
Many scientific studies have confirmed that in school-age children the level of antistreptolysin depends on many factors, even on the region of residence.
It should be taken into account that even the presence of a high titer of antistreptolysin does not indicate the presence of a disease, since antibodies persist for quite a long time, and sometimes even a lifetime, after an illness.
A high titer may indicate that the child has stable immunity to streptococcal infection. After treatment, a high level of antibodies is observed for 5-6 weeks, then slowly returns to normal levels. Recovery can take from 1 month to several years or even longer.
The level of seromucoids indicates the development of infection, including chickenpox, rubella, and measles. This level is high in the first days of the disease. In newborns, unlike adults, CRP is not an indicator of infection. Protein levels may not increase even if sepsis develops. The reason is the functional immaturity of the immune system, kidneys, liver and other systems.
ACDC
A blood test for ACCP consists of determining the titer of antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide and is one of the accurate methods for confirming the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. With its help, the disease can be detected several years before symptoms appear.
Citrulline is an amino acid that is a product of the biochemical transformation of another amino acid - arginine. In a healthy person, citrulline does not take part in protein synthesis and is completely eliminated from the body.
But with rheumatoid arthritis, citrulline begins to integrate into the amino acid peptide chain of proteins in the synovial membrane and cartilage tissue of the joints. The “new” modified protein, which contains citrulline, is perceived by the immune system as “foreign” and the body begins to produce antibodies to citrulline-containing peptide (ACCP).
ACCP is a specific marker of rheumatoid arthritis, a kind of precursor of the disease at an early stage, with high specificity. Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide are detected long before the first clinical signs of rheumatoid arthritis and remain throughout the entire disease.
To detect ACCP, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is used. A blood test for ACCP is carried out according to the “in vitro” principle (translated from Latin - in a test tube), serum from venous blood is examined. The ACCP blood test can be ready within 24 hours (depending on the type of laboratory).
Detection of ACCP in rheumatoid arthritis may indicate a more aggressive, so-called erosive form of the disease, which is associated with more rapid resolution of joints and the development of characteristic joint deformities.
If the test result for ACCP is positive, then the prognosis for rheumatoid ACCP arthritis is considered less favorable.
The normal range for the ACCP test is approximately 0-5 U/mL. The so-called “ACCP norm” may vary depending on the laboratory. The “ACCP norm” values for women and men are the same.
The so-called “Increased ACCP,” for example, an ACCP of 7 units/ml or more, indicates a high likelihood of rheumatoid arthritis. An analysis result assessed as “ACCP negative” reduces the likelihood of rheumatoid arthritis, although it does not completely exclude it. A rheumatologist with experience in diagnosing and treating rheumatoid arthritis should always evaluate the ACCP values and interpret them; only a rheumatologist can take into account all the nuances.
To get tested for ACCP, you need to come for examination on an empty stomach.
If you want to know the cost of a blood test for ACCP, please call.
Contact center specialists will tell you the price of the ACDC and explain how to prepare for the study.
Indications for blood tests
The doctor may recommend undergoing a blood test for rheumatic tests if the patient has complaints about:
- pain in the joints, especially of a “volatile” nature, aches, stiffness, morning stiffness;
- swelling, redness of periarticular tissues;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- increased body temperature;
- new shortness of breath, palpitations, irregular contractions and poor tolerance to physical activity;
- severe weakness, sweating, heart pain after suffering from a sore throat, scarlet fever;
- persistent headaches (if vasculitis is suspected);
- skin rash.
After the tests, the doctor can, based on the detected abnormalities and clinical signs of the disease, make a diagnosis of an autoimmune disease. Its peculiarity is a violation of the immune system in the body. Own tissues change their properties after exposure to viruses, microbes, intoxication, and cells of the immune system (leukocytes) perceive them as foreign.
As a result, immune complexes consisting of antigen and antibody are formed. They circulate in the blood and accumulate on the surface of the joint, in the skin, kidneys, lungs, and vascular walls, causing an inflammatory process. Its indicators are detected during rheumatic tests .
Often, with an already known diagnosis (lupus, scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, endocarditis, myocarditis, vasculitis), it is necessary to determine the degree of inflammation. This is necessary for choosing drug therapy and dosages of hormones and cytostatics.
We recommend reading about tests for vasculitis. From the article you will learn about visual diagnosis of vasculitis and what blood tests need to be taken to identify the disease. And here is more information about atherosclerosis and its examination.