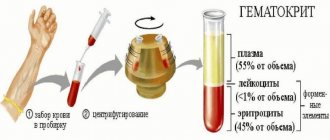
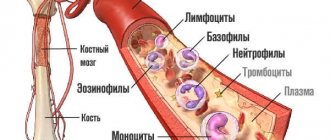
Analysis for rheumatic tests, what is it?
The study is a complex of biochemical studies that is aimed at identifying diseases of the body’s connective tissue and pathologies of the autoimmune system.
The study of biomaterial makes it possible to recognize the presence of an inflammatory reaction, its localization, as well as the type of irritant.
Next, let’s take a closer look at what kind of analysis this is, who this procedure is indicated for, what exactly is included in it, a table of indicator norms, what their decoding is and other nuances related to the topic of the question.
Rheumatoid diseases
Rheumatoid pathologies include over 120 types of diseases, characterized by systemic damage, in some cases local. Main symptoms of diseases:
- damage to joints and muscles;
- damage to tendons and ligaments;
- damage to bone tissue.
Pathologies developing as a result of rheumatic lesions, having an inflammatory and autoimmune nature:
- rheumatism;
- systemic vasculitis;
- diffuse connective tissue diseases: Sharp's syndrome, lupus erythematosus;
- joint pathologies: gout, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis.
That is why, if you suspect the development of any of the diseases, you need to take a blood test for rheumatic tests.
Causes of rheumatic diseases
There is no clear answer to the question posed.
Medicine has a number of assumptions about why rheumatic lesions develop, but most doctors agree that the main reason is heredity.
Predisposition, coupled with provoking factors, leads to a malfunction of the immune system, as a result of which the gene that provokes rheumatic diseases is activated. Provoking factors include:
- infectious diseases;
- poisoning of the body with toxins;
- stress;
- hormonal imbalance;
- exposure to UV rays on the dermis.
The risk zone for rheumatic pathologies includes people over 50 years of age, and males are more susceptible to this, and in rare cases, young people and women of childbearing age.
Indications for blood testing for rheumatic tests
Rheumatoid tests can be prescribed by your attending physician to verify autoimmune diseases:
- arthritis;
- polymyositis;
- compaction of connective tissue;
- multiple sclerosis;
- autoimmune prostatitis.
Often blood for rheumatoid tests is necessary to understand the changes occurring in the connective tissue and what condition it is in: gout, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus. Indications for taking rheumatoid tests:
- pain syndrome, swelling in the joints;
- obvious changes in body asymmetry;
- difficulty in mobility of ligaments and joints;
- pain in the lumbar region, body aches;
- frequent migraines that cannot subside even under the influence of analgesics;
- elevated body temperature for a long period of unknown etiology.
A blood test for rheumatic tests in the presence of the described symptoms makes it possible to determine the activity of development of the pathology and predict the course of the disease in the future.
When is the test ordered?
The study can be prescribed for adolescents and adults, including the elderly. Children require analysis less often.
Indications for analysis of rheumatic tests are:
- regular joint pain for no reason;
- reaction of joints to weather changes;
- swelling and redness, burning sensation in the joints;
- swelling of the joints;
- crunching in joints and bones when moving;
- red and bluish nodules on the skin, particularly in the area of the finger joints;
- numbness and decreased joint mobility, especially after sleep;
- pain in the lumbar region, more often when bending over;
- constant increase in body temperature and enlarged lymph nodes for no reason;
- frequent headaches and migraines;
- skin rash of unknown origin, “butterfly” rash on the face;
- heartache;
- frequent sore throats, cystitis and other inflammatory diseases;
- presence of rheumatic and other autoimmune diseases in the family.
Patients with already diagnosed gout, autoimmune disorders, and inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system are also regularly tested for rheumatic tests. This is necessary to determine the degree and severity of the disease and assess the effectiveness of treatment.
What tests are included in rheumatic tests and what do they indicate?
A blood test for rheumatic tests is characterized by a set of studies that identifies the number of main factors that provoke cancer and other diseases.
It is important to know the ratio of indicators as a percentage, because the slightest change can indicate different forms of the pathological condition. Using indicators, you can find out the severity and stage of the disease.
The analysis allows you to determine the cause and decide on a treatment regimen. Thanks to rheumatic tests, doctors monitor the therapeutic process and can adjust it if necessary. The basis of a blood test for rheumatic tests includes:
- Rheumatoid factor (RF) is an indicator of an acute pathological process. In healthy people this factor is absent, i.e. equal to zero. Also, a figure not exceeding 14 IU/ml is considered to be an indicator of the RF norm in analysis in adults. In this case, the results are negative; if the value is above the norm, the results are positive. Inflated indicators are a sign of an inflammatory process of any etiology or location. This mainly occurs with: rheumatoid arthritis;
- hepatitis of any form;
- infectious mononucleosis;
- autoimmune pathologies.
The presence of RF in the blood may be due to physiological reasons. For example, an increase occurs when a person’s diet in anticipation of the test included fatty foods, or the body was subjected to physical activity.
In old age, this protein is always present in the blood plasma due to age-related changes. A decrease may occur as a result of taking certain groups of medications, causing the analysis to be false negative.
- ASLO (antistreptolysin O) is an indicator of the increased presence of streptococcal infection. Often, an increase in streptococci is caused by a primary lesion: the urogenital canal;
- respiratory tract;
- intestinal tract;
- kidney
When the infection and its activity remain in the body for a long time, autoimmune diseases begin. However, in a healthy person, antistreptolysin is present in the blood, the levels of which are equal to the norm.
The figure may increase for several reasons - excessive cholesterol, stress, physical labor (stress). A false negative indicator can be recorded when taking hormonal and antibacterial agents.
- C-reactive protein is an indicator of acute inflammation in the body. It is used both for diagnosis and for monitoring the results of therapy. An increase in this indicator in the blood indicates the development of an inflammatory process. It could also be a sign of a tumor, a sign of a heart attack. A decrease in plasma protein during treatment indicates the failure of therapy. A low C-reactive protein level is not taken into account because it is not particularly significant.
Protein performs necessary functions for the human body - it increases the number of antibodies to resist infection, stimulates and activates the immune system.
On the other hand, strong stimulation of the body's protective function can provoke autoimmune diseases, due to which internal organs are attacked by their own antibodies.
The protein reaction rate is high, already 5 hours after infection enters the body. The protein level is proportional to the rate of development of the pathological condition. This means that the more the disease progresses, the higher the C-reactive protein becomes. For this reason, tracking this indicator over time is important.
It should be taken into account that protein reacts to an aggravated disease; when it enters the chronic stage, the indicator returns to normal. Renewal of the amount of protein in the blood plasma also occurs during exacerbation of the chronic form.
Additional laboratory testing includes:
- CIC analysis (Circulating Immune Complexes) – antibodies and enzymes produced by the immune system. An increased indicator in the analysis indicates the accumulation of the components of the complex in the tissues of the body.
- Albumin is a substance present in all organisms and is part of the blood (protein compound). Its level characterizes the functioning of the liver and kidneys. An increase in levels occurs with dehydration and when taking diuretics.
- Seromucoids are a set of serum glycoproteins based on a carbohydrate component, due to which certain functions are carried out. This indicator increases sharply in the presence of an inflammatory reaction in the body and is a primary method of early diagnosis even before symptoms appear. This allows you to prevent the further development of pathologies such as: diabetes mellitus;
- myocardial infarction;
- pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis;
- tuberculosis of the lungs and other organs.
In some cases, an analysis for CCP, cyclic citrullinated peptide, which is a more specific indicator than RF, may be necessary. A hemotest to identify markers is prescribed if the patient has radiological evidence of rheumatoid arthritis.
Protein level
Analysis for rheumatic tests - what is it? Many people ask this question after a doctor prescribes this test. The main thing you need to understand is that the study is carried out to diagnose inflammatory diseases and detect protein, this is called rheumatic testing. The transcript of the analysis also shows the number of protein fractions.
When various infectious diseases occur, antibodies are formed to them, as a result of which the protein in the blood plasma increases. Consequently, detection of an increase in the number of globulins may indicate the occurrence of inflammatory diseases in the body. It can also occur due to an autoimmune lesion.
If the ratio of certain proteins in the blood changes, this allows the specialist to have complete information. Rheumatic tests can indicate a decrease in protein in a pregnant woman, breastfeeding, and in people who smoke. An increase in protein occurs due to dehydration and a decrease in the amount of fluid in the body.
Rheumatic tests indicating a decrease in protein serve as a reason for a specialist to suspect liver disease, intestinal disease, infection, heart failure, malignant tumors, and even drug overdose. Reduced protein is a consequence of fasting and taking medications (estrogens, contraceptives, hormones).
Table of acceptable values of rheumatic samples
In medical practice, there are generally accepted indicators of rheumatic tests that indicate the presence or absence of a pathological condition in the human body. The normal level table is as follows:
| Index | Age category | Normal level |
| ASLO | Adults | 0-203 |
| Children, teenagers | up to 150 | |
| RF | Adults | up to 15 |
| Children's age up to 12 years | up to 13 | |
| C-reactive protein | Any age | 0-5 |
| Albumen | Over 60 years | 35-50 |
| Adults | 60 | |
| Children under 14 years old | 37-54 | |
| CEC | Any age | 30-90 |
| Total protein | Elderly people over 60 years old | 63-84 |
| Teenagers and adults from 15-60 years old | 65-85 | |
| Newborns up to 1 year | 46-74 | |
| Children from 1 to 4 years old | 60-76 | |
| Children from 5 to 15 years old | 58-77 | |
| Seromucoids | In any age category | 0,22-0,28 |
| Uric acid | Men | 200-480 |
| Women | 140-380 | |
| Month old babies | 80-311 | |
| Children from 2 months to one year | 90-372 | |
| From 1 year to 14 years | 120-362 |
IMPORTANT! Standard indicators may vary slightly depending on technical equipment, initial biomaterials, and laboratory research methods.
Interpretation of indicators, their norm and deviations
The diagnosis of an autoimmune disease can be excluded if:
- ASL-O up to 7 years is less than 100, up to 14 – less than 250, and then at any age in an adult it does not exceed 200 units per 1 ml;
- C-reactive protein is not detected or is not more than 5 mg/l;
- rheumatoid factor up to 30 IU/ml;
- leukocytes contain from 4.5 to 11 thousand per 0.001 ml;
- ESR for women is up to 12, and for men no higher than 10;
- antinuclear antibodies are absent.
Sometimes the laboratory may measure in other units. In this case, the form always indicates the range of normal values. If an increase in indicators is detected, this may indicate the following diseases:
- rheumatism,
- scleroderma,
- Waldenström's macroglobulinemia,
- Sjögren's syndrome,
- rheumatoid arthritis,
- lupus erythematosus.
An increase in ASL-O most often occurs in the following diseases:
- rheumatism;
- erysipelas, pyoderma;
- tonsillitis, tonsillitis, scarlet fever;
- osteomyelitis;
- glomerulonephritis.
It should be taken into account that pathologies of internal organs, infectious processes, as well as some physiological conditions can lead to changes in results. For example, a moderate increase in rheumatoid factor occurs with tuberculosis, syphilis, hepatitis, mononucleosis, malaria, and viral infections, including in newborns.
An increase in C-reactive protein levels is caused by:
- surgeries, especially organ transplants;
- inflammatory processes in the stomach, intestines, pancreas, gall bladder;
- malignant neoplasms;
- amyloidosis;
- tuberculosis;
- meningitis;
- the use of female sex hormones for contraception or replacement therapy during menopause.
During myocardial infarction, this protein appears a day after the onset of the attack, and disappears on the 15th - 20th day. It is important that during angina pectoris it remains within normal limits.
Scheme of binding of CRP to bacterial cell wall components
Antinuclear antibodies can be present in the blood with active hepatitis, infective endocarditis, tuberculosis and HIV, type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis. ESR in women increases during menstruation, pregnancy, and after childbirth. An increase in this indicator occurs with any inflammation, infection, poisoning, injury, or fractures. Kidney diseases and tumors are also accompanied by high values.
Rules for preparing for the delivery of biomaterial
The test for rheumatic tests must be taken early in the morning on an empty stomach. You must first adhere to the following rules, otherwise the result of the study will be distorted:
- the interval between donating blood for testing and the last meal should be 8 hours or more;
- You must stop taking any medications 14 days before the test. If the patient cannot interrupt the course of treatment, and rheumatic tests are urgently needed, then it is imperative to give the laboratory assistant a list of the names of the drugs being taken;
- one day before donating blood for examination, exclude mental and physical stress;
- It is also recommended to remove fatty, fried foods, caffeine-containing drinks, and alcohol from the diet 24 hours before the test.
How to get tested for rheumatic tests
Blood for analysis of 3 main markers (RF, ASLO, C-reactive protein) is taken from the patient from a vein only once and examined in vitro in vitro.
If rheumatism is suspected (poor ASLO indicator), the biomaterial will need to be taken again in a week to monitor the dynamics of the pathology.
If necessary, the doctor prescribes a rheumatic test, including additional indicators - CEC, albumin, total protein.
To do this, material is taken from a vein several times. The duration of the study depends on the laboratory. Usually the result form is ready after a day.
Rheumatology screening
In order to make a diagnosis of a rheumatic or autoimmune disease, it is necessary to evaluate all blood tests for acute phase and specific indicators simultaneously. To do this, they were combined into a complex called rheumatological screening (selection). It is prescribed to patients at risk. This includes people with atypical and erased signs:
- chronic fatigue;
- prolonged slight increase in body temperature;
- constant headache;
- decreased performance;
- unexplained weight loss.
Laboratory diagnostics help to exclude or confirm changes in the body's immune response. If abnormalities in rheumatic tests are detected, the patient is referred to more accurate instrumental examination methods. During the treatment process, rheumatic complex tests are periodically monitored to assess the severity of the disease, the results of medication use, and determine the dosage and duration of medication use.
We recommend reading the article about protein in the blood. From it you will learn about the definition of terms when an analysis for protein C and protein S is needed, as well as about C-reactive protein.
And here is more information about the ASL-O analysis.
Rheumatic tests help identify inflammation and its severity in autoimmune pathologies and rheumatism. The set of tests includes general (extended leukocyte formula, ESR), rheumatoid factor, antinuclear antibodies and antistreptolysin O. Their results are evaluated together with clinical manifestations, concomitant diseases, used for screening and in the process of monitoring treatment.
Although the laboratory gives the values of the indicators, only a doctor can make a diagnosis based on their increase. None of the tests included in rheumatic tests are 100% specific.
Decoding the analysis results
Each of the indicators performs its own specific functions, so only a comprehensive examination reveals the development of pathology with high accuracy.
Doctors mainly rely on 3 main indicators, the values of which indicate the presence or absence of any disease. What kind of diseases these may be, we will consider in the table below.
| Index | Above normal |
| RF | Indicates viral diseases, rheumatological arthritis, identifies seronegative and seropositive types of arthritis. |
| ASLO | Acute rheumatic fever, streptococcal infection, rheumatism. |
| C-reactive protein (CRP) | Acute inflammation caused by rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism, or myocardial damage. S-RB exceeding the norm by 20 times - exacerbation of acute rheumatic disease; an off-scale indicator (up to 120 mg/l) - acute bacterial infection. |
Objectives of the assigned study
Based on the level of rheumatic test indicators, one can conclude that there is inflammation in the body, damage to body tissues by its own antibodies. Used in the diagnosis of diseases such as:
- rheumatism and rheumatoid arthritis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- autoimmune kidney damage (glomerulonephritis);
- malignant neoplasms.
Rheumatic tests reflect the body's response to treatment, the degree of disease progression and the extent of organ damage over time.