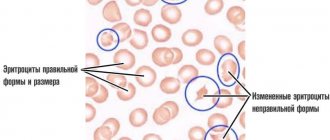
Clinical urine analysis is one of the traditional methods for diagnosing most diseases and displays the main parameters of metabolic processes in the human body. During the study, attention is paid to such characteristics as color, density, level of red blood cells, creatinine, urea, as well as the presence of protein and sediment in the form of salt crystals. Oxalates are always present in small amounts (no more than 5%) in the urine and are excreted in urine. However, exceeding the norm may indicate diseases of the urinary system, which require adequate therapy and the appointment of therapeutic nutrition.
Oxalate Prevention
The best way to cure a disease is to avoid it. Prevention measures must be followed. Go through diagnostics twice a year - take a urine test to assess the content of salts and other substances. This will allow timely identification of organ dysfunctions and avoid the development of pathologies of the excretory system and heart.
You need to drink 2 liters of water daily
If there is a hereditary predisposition to the formation of stones, including oxalates, clinical analysis is performed more often. It is recommended for such people:
- reduce the amount of foods containing vitamin C and any acidic foods;
- drink up to 2 liters of liquid per day, unless there are contraindications;
- those whose activities involve long, immobile postures are advised to take breaks from time to time and stretch their muscles and joints;
- do not put off going to the toilet if the urge arises. Otherwise, stagnation of urine, accumulation, and deposition of salts are provoked;
- when identifying salts of a specific type, exclude self-medication and follow the doctor’s recommendations;
- cleanse the kidneys with folk remedies (herbal decoctions, fruit drinks);
- sleep at least 8 hours;
- eliminate or minimize stress;
- lead an active life (walk, do gymnastics).
The listed measures will help reduce the risk of developing oxaluria and other problems.
Prevention
Limit the consumption of tomatoes, parsley, celery, sorrel, and sour fruits. Once a week he goes on a water diet - boil water for at least an hour over low heat or use distilled water. Leave for at least 24 hours. Slowly strain the top 2/3. If there are deviations in body weight, visit a massage therapist. If you are underweight, eat a large meal an hour before the session. Preferably meat without bread. If there is excess, drink 1 liter of liquid within 1.5 hours. Session is at least 30 minutes. Strong therapeutic massage. Treat soft tissues. For the first 7 days, do not resort to anti-cellulite massage.
Do not drink strong alcoholic drinks on an empty stomach. Avoid prolonged feelings of hunger. Don't overeat before bed, but don't overeat at night either.
There are oxalates in the urine, what does this mean, causes, treatment
What else can you find in urine?
- Ammonia smell
- Exogenous impurities
- Sediment (in the child’s urine)
- Ascorbic acid
- White clots
- Leukocytes
Oxalates in urine - what does it mean?
Each person's urine contains about 95 percent water, and the rest consists of various breakdown products that are excreted from the body, including oxalate salts. At the same time, these substances should not show themselves in any way in the analysis results, because the main amount of them leaves along with the urine. To accurately determine their content in a liquid, the tubes are first thoroughly washed and then sterilized. And tests must be stored at above-zero temperatures. If excess salts are found in the liquid, this may indicate any problems in the functioning of the kidneys. Oxalates can also be found in a child’s urine.
If oxalates occasionally appear in minimal quantities in tests, this does not at all indicate a disturbance in the functioning of the excretory system. If their number exceeds the permissible norm for a healthy person, then in this case the patient will require treatment, which should take place under the close supervision of a doctor. According to statistics, these substances are most often found in tests in people suffering from kidney problems. The reason for the change in their quantity can be determined by the doctor during special clinical studies of the fluid submitted for analysis.
Oxalate salts in urine: causes
2) The cause may also be the consumption of too much vitamin C in synthetic form, excessive amounts of parsley, figs, beets, plums and gooseberries in the diet. Or a lack of vitamin B6.
3) In urine analysis, oxalate salts can also appear as a result of constant stress. Indeed, in these cases, the kidneys do not have enough fluid to function normally.
4) And also for Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, pyelonephritis, diabetes, inflammation in the intestines or after surgical interventions in the intestines.
In order to notice such serious problems with your health in time, you should regularly take a urine test. Preferably at least 1-2 times a year. This will allow you to immediately notice possible deviations, begin treatment and avoid more serious and dangerous consequences.
Oxalate salts in urine: treatment
Only a specialist can tell you exactly what treatment the patient needs in this case. Most likely, it will include not only taking special medications, but also additional medical procedures. The main thing is to refuse self-medication and consult a doctor in time.
Most often, a special diet becomes the basis of therapy. The patient will have to exclude from his diet cocoa and chocolate, beets, any citrus fruits, sorrel, spinach, currants, ascorbic acid, meat, chicken and fish broths, lettuce and rose hips. This will be a temporary measure and, perhaps, later the doctor will allow you to again consume foods from this list in moderate quantities.
You will also need to reduce the amount of fruits, vegetables and any foods that contain a lot of oxalic acid consumed daily.
It is also important to eat in moderation, preferably in small portions every day at the same time. Bread (both white and black) should be peeled
Sunflower halva, buckwheat, oatmeal and wheat porridge, legumes, seaweed, any nuts, radishes and dried apricots are useful.
Having started treatment and changed your diet, after some time it will be necessary to take a general urine test again, oxalate salts will be examined as a result, and the doctor will be able to conclude whether the treatment and diet benefited the patient. If the amount of substances in the liquid has not changed, then the method of therapy can be changed. The main thing is to trust a specialist in this matter and not try to treat yourself at home.
As mentioned above, even a healthy person contains oxalate salts in the urine; the norm is 20-40 milligrams. But if it is exceeded, then there is no need to worry too much; by strictly following all the doctor’s recommendations, this can be easily corrected.
Oxalates in urine causes, diagnosis and treatment
- Oxalates in urine: causes, diagnosis and treatment
- How to dissolve a kidney stone in 2020
- How to lower uric acid in the blood
Reasons for the appearance of oxalates in urine
The causes of oxalaturia are varied. To get rid of this problem, it is necessary to find out its etiology. The formation of oxalates is associated with a diet based on the consumption of oxalic acid salts. It is logical that an increased intake of oxalates in food leads to their appearance in the kidneys and urine. People living in areas with low levels of magnesium in food and water are most susceptible to the formation of oxalate stones. The appearance of oxalates in the urine can be caused by congenital disorders of oxalic acid metabolism.
Oxalates in the urine are a consequence of urolithiasis or other kidney pathology. If clinical manifestations of the disease were not detected, then it was missed at an earlier age. Oxalates in the urine are often found in people who have had nephrolithiasis and pyelonephritis.
The settling of stones in the urine is associated with acute or chronic colitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, intestinal surgery, and diabetes mellitus. A lack of vitamin B6 or an excess of ascorbic acid can lead to the formation of oxalates. In quite rare cases, the cause of the pathology is poisoning with certain chemicals.
Diagnosis and treatment of oxalates in urine
Pathology is detected by characteristic clinical signs and urine test results. Patients often complain of increased fatigue, severe abdominal pain, and frequent urination in large quantities. If kidney function is impaired, it is necessary to undergo a full examination by a nephrologist. If the body is dehydrated, the drinking regime should be normalized after consultation with a specialist.
The main method of treating oxalates in the urine is a diet that excludes foods high in oxalic acid: sorrel, lettuce, spinach, beets, potatoes, tomatoes, cottage cheese, strong broths, milk, sweets, eggs, strong tea, chocolate, coffee. It is necessary to increase the amount of liquid consumed per day - water, fruit drinks, compotes.
Herbal medicine quite effectively dissolves stones and removes salts. Many herbs have a similar effect: dill, peppermint, knotweed, corn silk, horsetail, strawberry leaf. They are consumed in the form of decoctions or infusions.
Drug therapy consists of the use of magnesium oxide and vitamin B6. For preventive purposes, taking citric acid, sodium or potassium citrate is indicated. Surgical treatment is performed if conservative therapy is ineffective or if large stones are present.
Causes
First of all, it should be understood that the reasons can be completely different, ranging from those caused by health problems, as well as those caused by certain factors.
Natural reasons:
- A very small amount of magnesium enters the body with food;
- the body lacks vitamin B6;
- excess vitamin C in the body;
- the diet contains a lot of food that contains oxalic acid (celery, radishes, apples, chocolate, beets, parsley, spinach);
- poisoning of the body with antifreeze, as well as brake fluid;
- poor nutrition (the diet contains a lot of salty foods, meat, sugar);
- insufficient fluid intake per day.
Causes associated with metabolic disorders:
- diabetes;
- violation of acid-base balance, as well as urine pH;
- improper metabolism of oxalic acid.
Causes associated with kidney disease:
- pyelonephritis;
- urinary excretion disorder, which occurs when there is inconsistency in the urinary tract;
- kidney injuries;
- improper outflow of urine;
- hemorrhages into the kidney tissue.
Intestinal diseases:
- for diseases that are accompanied by an inflammatory process in the intestines;
- dysbiosis.
Hereditary diseases:
- impaired metabolism of oxalic acid, which is caused by genetic character;
- hereditary predisposition.
You can learn more about oxalates in urine by watching this video.
Oxalates in urine treatment
If you consult a nephrologist if necessary, you must strictly follow his medical recommendations. Treatment for oxalate in the urine directly depends on the person’s drinking regime. The adult daily intake with a high salt content should reach 2-2.5 liters of purified water. Among the medications, vitamin B6 and Magnesium are effective, which will help normalize the process of excretion of oxalic acid and get rid of the formation of stones inside the kidneys.
In this case, the level of hemoglobin in the blood should be monitored. To prevent crystallization of salts, potassium citrate (Potassium Citrate) and Asparkam are prescribed. Urolithiasis can be treated using traditional medicine. To remove excess salts, he recommends drinking diuretic decoctions - corn silk, knotweed, horsetail, peppermint, strawberry leaves, lingonberries. The daily dose of herbs brewed with boiling water is no more than 200-250 ml, which are infused for 20-25 minutes.
Treatment of oxaluria
Since with oxaluria there is an excess of oxalic acid and free calcium in the human blood, the main treatment for this disease is aimed at reducing the concentration of the above substances.
First of all, the patient is prescribed a diet that excludes plant and animal foods containing large amounts of oxalic acid and its salts. The consumption of dairy products and fruits rich in vitamin C is also limited, since when it is processed in the body, a small amount of oxalic acid is formed.
Prohibited herbal products:
- beet;
- tomatoes;
- spinach;
- sorrel;
- rhubarb;
- plums;
- cherry plum;
- red and black currants;
- strawberries and wild strawberries;
- raspberries;
- pomegranate;
- broccoli;
- eggplant;
- bell pepper;
- parsnip;
- beans and legumes;
- all citrus fruits;
- sauerkraut;
- potato;
- coffee;
- cocoa;
- chocolate;
- all nuts;
- ginger;
- hot and allspice;
- peanut;
- strong tea;
- soybeans
Prohibited animal products:
- liver;
- lungs;
- kidneys;
- stomach;
- brain;
- jellied meat and jelly;
- gelatin;
- milk;
- hard cheese;
- cottage cheese;
- canned fish and meat;
- strong meat broths;
- sausage and frankfurters.
If small oxalate crystals (up to 5 mm) are detected in the kidneys, patients are prescribed diuretics and plenty of fluids. In addition, patients are recommended to consume the following foods:
- watermelons;
- melons;
- sweet apples;
- peaches and nectarines;
- pears;
- quince;
- apricots;
- pumpkin;
- turnips, radishes and radishes;
- lean beef and sea fish;
- yogurt and curdled milk.
These products promote alkalinization of urine, which prevents the precipitation of calcium oxalate. For the same purpose, patients are prescribed magnesium carbonate and vitamin B6. To prevent the formation of urate stones, citric acid is prescribed.
During this procedure, stones are destroyed remotely using strong ultrasonic waves.
If for some reason lithotripsy is contraindicated for patients, they are prescribed a long, sometimes lifelong course of treatment with herbal teas that dissolve calcium oxalates. Medicinal teas based on knotweed are best at dissolving stones and salt conglomerates.
Standards for men, women and children
Whether the norm of oxalates is exceeded or not will be determined by a biochemical analysis of urine. It is almost impossible to identify this visually.
And if you neglect periodic examination, the crystalline structure of oxalates can lead to the formation of blood in the urine, and later, to urolithiasis.
To understand whether renal pathology is developing, you need to know the normal content of oxalate salts in the urine.
| Norm in µmol/day | Norm in mg/day | |
| Men | 228-680 | 20-60 |
| Women | 228-620 | 20-54 |
| Children under one year old | 91-228 | 8-20 |
| Children from one to 14 years old | 228- 570 | 20-50 |
A single excess of the norm does not indicate a disease. This may indicate improper preparation and collection of urine for laboratory research.
What analysis shows the oxalate content
Analysis for oxalate salts in urine is a laboratory test that determines the level of ethanedioic acid salts in single or daily urine. The test is performed together with an analysis for creatinine and carbamide (urea). Diagnostic results are used to assess the likelihood of stone formation in the urinary ducts, kidneys or bladder.
In urological practice, the following methods of collecting urine are used to identify oxalates in it:
- general urinalysis (UCA);
- daily diuresis.
Indications for laboratory testing:
- hematuria – bloody impurities in urine;
- polyuria – excessive urine production;
- proteinuria – the presence of protein components in the urine;
- cramping abdominal pain;
- renal colic;
- endocrine disorders;
- disruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dull pain in the lower back;
- increased blood pressure;
- severe swelling of the limbs.
An oxalate test is a highly specific test that is used when urolithiasis is suspected. Laboratory testing has no contraindications. But the results of the analysis largely depend on the correct collection and storage of the material.
Treatment and diet for oxalates in the urine
Treatment for oxaluria includes four stages:
- Drug treatment;
- Strict diet;
- Drinking regime;
- A complete change in previous habits.
At the first stage, therapy is carried out for the pathological processes that provoked oxaluria. To prevent complications, with increased concentrations of oxalate salts, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Containing magnesium oxide and vitamins “B6” - “Magurlit”, “Asparkam”, “Magnelis”, “Magnesium +”, “Magne-B6”.
- Prevention of the formation of stones is carried out by prescribing drugs - “Uronefron”, “Prolit”, “Pyridoxine”, “Xidifon”, “Citric acid”.
- If necessary, diuretics.
When kidney stones form, drug therapy is not always effective in either crushing or dissolving. Various surgical techniques are used to remove stones. Small lesions can be dealt with by adjusting the diet.
The diet minimizes the consumption of carbohydrates and salt. Products based on chemical additives containing large amounts of cholesterol and fat are excluded. The diet for oxalates in the urine recommends nutrition based on products and methods:
- Dairy diet, consumption of rye, gray and white bread.
- Lightly salted herring is allowed in small quantities.
- The first courses include vegetarian soups and borscht without frying.
- You can only eat the white in an egg.
- From meat and fish, only lean varieties.
- Second courses may consist of cereals and pasta.
- Fruits and vegetables, only raw or baked.
- Allowed are non-sour berries, fermented cabbage, juices, compotes and jelly.
Among the juices, pumpkin, cucumber and squash juices are useful. Their effect is due to good alkalization of urine, but they must be taken in combination with drugs (antihypoxants) that improve oxygen utilization (prescribed by a doctor).
Cucumber juice is very effective in removing oxalic acid salts in kidney pathologies. It is an excellent means of intensively removing urine from the body and has the property of restoring its structure. The potassium contained in cucumber promotes intensive leaching of urine from the body during polyuria.
To saturate the body with vitamins, it is recommended to use vitamin preparations – “Fitin” or “Riboflavin”, berries – sea buckthorn, raspberries, black currants and non-sour apples.
A balanced diet for oxalate in the urine is a mandatory step in treatment. Its principle is due to a decrease in the concentration of oxalic acid salts in the body, without interfering with the supply of necessary elements in sufficient quantities.
Symptoms
Over a long period of time, oxalates can accumulate in the body without showing any noticeable symptoms. Therefore, only by performing a urine test for oxalates can one detect excess salt levels and suspect the onset of the disease. When sharp, spiny crystals begin to pass through the ureter, injuring the mucous membrane and walls of the urinary tract, the following symptoms appear:
- pain in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- renal colic;
- frequent urination;
- blood and mucus in the urine;
- fatigue and weakness.
Single crystals form large stones in the kidneys; treatment is simply necessary. Otherwise, the pain becomes more and more severe, salt crystals clog the ducts, there is a danger of bacteria penetrating onto the wound surfaces of the mucosa, and an inflammatory process of internal organs may occur.
How to properly prepare and collect urine for analysis
Before taking a urine test for oxalates, preliminary preparation is needed. Failure to follow your doctor's recommendations may result in false positive or false negative results.
Preparation for daily diuresis and OAM:
- 2 days before urine collection, stop taking diuretics and vitamin C supplements;
- before collecting urine, limit physical activity and avoid stressful situations;
- foods high in ethanedioic acid are excluded from the diet;
- use a sterile plastic container with a tight lid as a container;
- Before the procedure for collecting biomaterial, the genitals are washed with neutral soap.
Rules for collecting urine for daily diuresis:
- morning urine is not collected immediately after waking up;
- subsequent portions are collected in a separate container, after which they are poured into a plastic container with a volume of 2.5-3 l;
- the last urine sample is taken the next morning immediately after waking up;
- measure the volume of liquid in a common container;
- pour 100 ml of biomaterial into a sterile container and send it to the laboratory for research.
During the day, the container with the biomaterial is stored in the refrigerator on the bottom shelf. After collecting the last portion, 100 ml of urine from a common container is delivered to the laboratory within 1 hour.
Prevention of oxalates in the urine of a child
To prevent the development of oxaluria in a baby, it is necessary to develop an adequate diet and drinking regime.
- Minimize the consumption of foods that contain large amounts of oxalic acid.
- If possible, avoid giving your child sweet soda and processed foods.
- Strictly monitor your intake of ascorbic acid.
- It is easy to explain to your child that you need to drink water not only in those moments when you are thirsty, but also use it regularly throughout the day.
- Provide your child with a balanced diet rich in vitamins.
- Spend as much time as possible in movement - on the playground, in the park, just walking in the fresh air.
- Monitor the duration and quality of your baby's sleep - at night he should sleep at least 8 hours.
Timely diagnosis of a disease or disorder in the functioning of the body is already halfway to its recovery.
Never ignore abnormal results in urine or blood tests, be it oxalates, white blood cells, red blood cells or other substances. Consulting a doctor if you have any doubts about your own health, and especially the health of your baby, will help put everything in its place. Always seek help from a doctor and follow all his recommendations. Be healthy!
The effect of oxalates on the body
Oxalate salts, if their concentration does not exceed the norm, have the following effects.
- Participation in the transport of calcium ions throughout the body.
- Strengthening the walls of blood vessels and tooth enamel.
- Increasing the contractile torque of skeletal muscles, stabilizing the rhythm of smooth muscle contraction.
- Together with vitamin D, strengthening bone structure.
- With vitamin B12, acceleration of the passage of nerve impulses in the brain and spinal cord.
- With phosphorus, normalization of phospholipid metabolism.
- With vitamins B2, B6, A – strengthening the membranes of cells of the internal secretion organs, especially hepatocytes.
Article on the topic:
What does the level of creatinine in the blood show in women? What should be the normal values?
Important! Oxalates do not have much effect on the regulation of acidity in the body. Deviation from the norm in the PH level is a consequence of an excess of the concentration of these compounds or their deficiency. The pH is affected by oxalic acid or its radicals.
Initial symptoms and further investigations
Since calcium oxalate crystals have sharp edges, when they pass through the urinary tract, a person may experience unpleasant sensations, most often a burning sensation and pain when urinating. In addition, when large crystals pass through the ureters, colic may occur - acute pain radiating to the perineum. Colic may be accompanied by minor bleeding, which is not life-threatening and stops quickly even in people with poor blood clotting. Patients may also feel heaviness in the back, which makes it difficult to stand or sit in one place for a long time.
When large conglomerates of salts form in the kidneys, they can compress and injure surrounding tissues with their sharp edges and lead to inflammation of the renal pelvis - pyelonephritis. With this disease, a person feels a loss of strength, begins to feel chills, and then the urine takes on a very dark shade or becomes cloudy. It is in this condition that most patients go to the clinic, where they are prescribed an extensive urine test, the results of which reveal black or red crystals of calcium oxalates.
After detecting oxalate salts based on the results of a urine test, you should firstly conduct an ultrasound examination of both kidneys and the bladder to determine the possible presence of pathologies, the stage of development of urolithiasis and the size of oxalate stones.
Secondly, it is necessary to take a blood test for the content of calcium ions. This is necessary to prescribe the correct treatment.
Thirdly, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination of the gallbladder, since oxalate crystals often form in parallel in this organ, leading to the development of cholelithiasis.
If a person, before detecting oxalates, did not follow a diet rich in foods containing oxalic acid and its derivatives, did not lose weight sharply, did not have congenital pathologies of internal organs or chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, then he should undergo an enzyme-linked immunosorbent blood test to detect antibodies to chronic hepatitis B, C and D. These hepatitis slowly destroy the liver and lead to metabolic disorders, which most often causes oxaluria.
Oxalates in a child
Expert opinion
Kovaleva Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor-Laboratory Assistant. 14 years of experience in clinical diagnostic services.
Ask a question to an expert
If a child complains of pain or discomfort in the abdomen, is bothered by a frequent urge to urinate, and the child’s urine is dark in color, then this is a serious reason to immediately contact a local pediatrician at the clinic.
An increase in oxalate salts in the urine of children over 5 years of age is quite common due to the general restructuring of the body at this age and has the same signs and symptoms as in adults. In this case, it is necessary to identify the cause of the increase in these salts and carry out (if necessary) special treatment, which can only be prescribed by a pediatrician.
Reasons for the appearance of oxalates in urine
If a urine test shows the presence of oxalate salts, this is a clear cause for concern. However, you should not immediately raise all the doctors to their feet, go to famous clinics and take other serious measures - oxalate salts in the urine can appear due to various reasons, including the use of certain foods, low intake of fluids and improper daily routine. Therefore, first we will understand what oxalates are, what they are, the reasons for their appearance and possible diseases. And then we’ll look at what treatment is prescribed for standard pathologies and what we should be wary of as the disease develops.
Oxalates – what is it?
Oxalates are salts of organic oxalic acid, present in the body in excess and excreted along with urine. Salts contain a huge amount of chemicals, so not every analysis is a verdict. Nephrologists emphasize that a patient who has an increased content of compounds may suffer from frequent urination and an increase in urine volume - reasons that are quite common, especially in men. But if there are no clinical indications, and there are calcium oxalate crystals in the urine, stone formation is possible.
Important! Exceeding the permissible norm of salts in urine per day is up to 40 mg in an adult healthy person, 1-1.3 mg in a baby, is a deviation. And this is a signal of poor kidney function, detected through tests.
Most often, this is the collection of daily urine, laboratory tests, on the basis of which the nephrologist will draw the necessary conclusions.
Ocasalate tests: what exactly do they say?
Decoding the tests is up to the doctor, but if a person is attentive to his health, he will be interested in looking at the results. What the analysis can show:
- Oxalates and urates. The compound is a sodium salt of uric acid, which indicates an increase in acidity due to excess protein foods or dehydration. In addition, an increase in the standard also means the presence of chronic diseases: pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, renal failure.
- Oxalates and protein. Pathology is detected during hypothermia, overwork, high temperature, scarlet fever. In pregnant women, the compound signals the onset of nephropathy.
- Oxalates and phosphates. If there is a similar compound in urine, you will have to reduce the consumption of fish, buckwheat, oatmeal, and fermented milk products. The result is also possible with leukemia; in children this is an indicator of rickets (lack of vitamin B).
- Oxalates and leukocytes. An increase in the standard is a signal of the development of pyelonephritis, cystitis or utretritis, as well as possible inflammation of the vaginal mucosa.
Thus, oxalates can appear in urine sediment both in the presence of existing chronic disorders and in the event of a threat of the onset of inflammatory processes.
What are oxalates?
Oxalates are salts of oxalic acid, which include ammonium and calcium. These compounds are widely distributed in nature and mostly enter the human body from there. There are many of them in sorrel, sorrel, grapes, tomatoes, apples, and spinach. The roots and leaves of buckwheat, rhubarb, beets, beans, black pepper, cocoa, and chocolate are also rich in oxalic acid salts.
In addition, a separate part of oxalates is formed in the body as a result of incomplete oxidation of carbohydrates during various metabolic disorders. Small oxalates are most often smooth and light brown in color, while large ones acquire a dark brown color and roughness.
Reference! A large amount of oxalates is contained in tea leaves, but due to the insignificant dose of their consumption, the compounds are not capable of having a serious effect on the body.
Oxalates are toxic in large quantities. They have the ability to form insoluble deposits in the body by combining with cations such as calcium (Ca), iron (Fe) and magnesium (Mg). As a result of such reactions, crystals of these salts accumulate, which, due to their shape, injure or irritate the inner surface of the urinary and gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
Since the action of oxalates in the body is aimed at binding vital elements, prolonged consumption of food containing a lot of these substances can lead to health problems. For a person who does not have diseases, food with a moderate content of oxalic acid salts does not pose any particular danger. Whereas people with a history of gout, rheumatoid arthritis and various kidney diseases should avoid foods with large amounts of these compounds.
Calcium oxalate crystals in the urine, or so-called kidney stones, often cause blockage in the urinary tract. According to many scientists, about 80% of kidney stones form oxalate salts. And, accordingly, a significant intake of Ca along with products containing this compound causes the deposition of calcium oxalate in the gastrointestinal tract, reducing the level of the latter by 97%.
Vegetarianism or veganism often causes the accumulation of oxalates in body tissues. The condition in which calcium salts are detected in a urine test is called hyperoxaluria, and it can be primary (congenital) or secondary (developed as a result of diseases) in nature.
Primary hyperoxaluria is a rather rare congenital anomaly associated with metabolic processes, in which excessive formation and excretion of oxalic acid salts occurs. It should be noted that the concentration of the latter in the urine increases long before the increase in the blood plasma. Therefore, the determination of Ca oxalates in urine is considered one of the main stages in identifying primary hyperoxaluria not only in adults, but also in children.
Increased excretion of oxalic acid salts in urine can be caused by taking certain medications or substances: calcium, gelatin, ascorbic acid, ethylene glycol, methoxyfluorane anesthesia. A decrease in level is often observed during therapy with Pyridoxine and Nifedipine.
General characteristics of oxalates
Decoding oxalates in urine analysis
Let's see what the decoding of oxalates in a urine test can show and what gives urologists and nephrologists grounds to draw conclusions regarding certain metabolic disorders and the presence or absence of pathologies of the kidneys and urinary system.
So, normally, urine should be transparent, but when it is processed in a centrifuge, a sediment is obtained, which is studied under a microscope.
Urates and oxalates in urine
In addition to oxalates, urate, the sodium salt of uric acid, may be present in the urine. Most often this occurs against the background of increased acidity of urine with increased consumption of protein foods and foods containing large amounts of purines (young meat, liver and other offal, brewer's yeast, porcini mushrooms, cocoa and chocolate). Urates and oxalates in the urine can appear when the body is dehydrated (after severe vomiting or diarrhea), as well as in a number of diseases, including chronic kidney failure, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, gout, tumor formations, leukemia.
Protein and oxalates in urine
If the analysis reveals protein and oxalates in the urine, then proteinuria (protein in the urine) may be the result of excessive physical activity or significant hypothermia that preceded the analysis, as well as elevated temperature or the patient having scarlet fever, infectious hepatitis, or osteomyelitis. Protein and oxalates in the urine of pregnant women are possible due to nephropathy.
Oxalates and phosphates in urine
Lime phosphate, calcium or magnesium phosphate, that is, phosphates, appear in the urine with a reduced level of acidity, which is facilitated by a diet rich in phosphorus: sea fish and seafood, milk and fermented milk products, buckwheat and oatmeal. In addition, such an analysis result is possible in hyperparathyroidism, diabetes, some mental illnesses, and also in leukemia. And in children under 5 years of age, oxalates and phosphates in the urine indicate not only problems with the excretion of oxalic acid salts, but also vitamin D deficiency (rickets).
Oxalates and leukocytes in urine
If, when examined under a microscope, one to five leukocytes fall into the field of view, then this is considered a completely normal indicator. But if oxalates and leukocytes in the urine are elevated, then this indicates either chronic pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys) or inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract such as cystitis or urethritis. By the way, with these same diseases, as well as with inflammatory processes in the urethra or vagina, oxalates and mucus secreted by their mucous membranes can be found in the urine.
Diagnostics
Calcium oxalate crystals in the urine are detected during general and biochemical analysis of urine. With the help of such diagnostics, the level of leukocytes and red blood cells is determined, as well as the causative agent of infection, if any.
The presence of oxalaturia will be indicated by a result of “++” or more. Additionally, a blood test is prescribed. Based on its results, the presence of an inflammatory process is determined.
An increased content of oxalates in the urine against the background of a high level of leukocytes in the blood will indicate inflammation, and then it is important to conduct an ultrasound examination of the kidneys, because such indicators may indicate their pathology, in particular nephritis.
To determine the level of oxalic acid salts or sediment, you need to take a Nechiporenko test. Before collecting urine, external hygiene of the genital organs is carried out, then a portion of morning urine is immediately collected (exclusively the first). The first 10-20 mm of urine must be passed, the rest is placed in a special container and sent to the laboratory on the day of collection.
Treatment
The rate of excretion of oxalate salts is up to 40 mg per day in adults, 1-1.3 mg in children.
Oxalaturia should be treated with a special diet and drug therapy, as well as using folk remedies. To reduce the level of calcium oxalate in urine, it is recommended:
Stick to a diet.
Urologists always prescribe a diet when they detect elevated levels of any salts in the urine. But if the oxalate content exceeds, it is necessary to limit the intake of oxalic acid from food.
How to get rid of oxalates. It is recommended to exclude from the diet:
You need to eat foods high in vitamins B1, B6, and magnesium. Consume limited amounts of low-fat meat or fish (100 g at a time). You should not eat a lot of foods that contain a lot of oxalic acid (gooseberries, plums, figs, parsley, sorrel). There are specially designed diets that help dissolve oxalate stones in the kidneys or prevent their formation, which must be strictly followed.
Establish proper drinking regime.
To flush out salt crystals from the kidneys and dilute the urine and to avoid the formation of stones, it is necessary to establish a drinking regime. Drink at least 1.5-2 liters of liquid (weak tea, still water, juices, fruit drinks)
To reduce the concentration of salts in urine that accumulate at night, it is important to drink a glass of still water or weak tea or other recommended liquid before going to bed.
Use folk remedies to alkalize urine.
It is necessary to strictly observe the dosage and duration of administration, using juices and herbal decoctions to alkalize urine, since exceeding them can provoke the formation of phosphate stones.
Traditional medicine will help dissolve oxalate stones in the kidneys and remove small stones. Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs and berries wash salts out of the kidneys and help remove crystals and small stones with urine from the body.
To prepare decoctions of infusions, use:
- linden flowers;
- Birch buds;
- dog-rose fruit;
- nettle leaves;
- lingonberry berries.
Juices (rowanberry, carrot) help dissolve stones. Before using traditional recipes, be sure to consult your doctor.
Some juices and decoctions can provoke increased movement of stones, blockage of the passages of the urinary system, which will cause severe pain and even a threat to life. They should be consumed in moderation, following the doses prescribed by the doctor.
Drug therapy is used with the intake of antioxidants, membrane stabilizers and antibacterial drugs.
Therapeutic drugs used for oxaluria contain large doses of potassium and magnesium (asparkam, magnesium B6), vitamins E and B, antioxidants (potassium citrate), retinol, and diuretics. Only a doctor can advise how to get rid of oxalate kidney stones and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Treatment of oxalate complications
General recommendations from specialists allow you to get rid of oxalate salts in the urine and prevent their subsequent accumulation. Treatment involves an integrated approach and includes drug therapy, diet and drinking regimen, and in case of extreme neglect of the condition, surgical intervention. The scheme is selected in accordance with the diagnostic results.
Diet and drinking regime
Oxalate kidney stones are difficult to dissolve, so litholytic therapy is carried out for a long time. A balanced diet plays an important role in the process of healing the excretory system. The basis is a properly composed menu. The diet itself should be chosen in such a way as to include all types of foods in the diet, with the exception of certain categories.
The following types of food should be limited:
- foods rich in oxalic acid to prevent an increase in oxalates;
- food rich in protein, as it promotes the release of salts;
- baked goods – bread, sweets, cakes;
- alcohol, chocolate, nuts, cocoa, herbs, some varieties of fruits and vegetables.
The diet should include the following products:
- containing calcium - kefir, fermented baked milk, yogurt, cottage cheese;
- porridges from grains rich in fiber;
- vegetable products consisting of coarse fiber.
Patients are advised to drink plenty of fluids (2.5-3 liters per day). The use of alkaline mineral waters is indicated - “Essentuki 17”, “Slavyanskaya”, “Dilizhan”, “TIB-2”. Drinking plenty of fluids increases daily diuresis, normalizes urine pH and its electrolyte balance, as well as the acid-base state of the blood, which will restore normal excretion of oxalates from the body.
Medicines
Medicines are prescribed to prevent the formation of new salt crystals or to relieve repeated attacks of colic. Their use is also justified in cases where, due to a violation of the outflow of urine, inflammation develops in the renal tissues and the mucous epithelium of the excretory tract is damaged.
Among the groups that may be useful in the treatment of oxalaturia are the following.
- Herbal medicines with antispasmodic, dissolving and diuretic properties - “Blemaren”, “Urolesan”, “Cyston”, “Rovatinex”.
- Diuretics of plant origin - “Canephron”, “Uriflorin”, “Fitolysin”.
- Litholytic preparations with a combined composition - “Blemaren”, “Uralit”, “Cimalon”.
- Vitamin complexes and magnesium and potassium preparations - Asparkam tablets.
When oxalate stones form, doctors strongly discourage self-medication. Taking medications on the advice of friends or pharmacists can aggravate the situation and cause stones to move. The consequence of this is the formation of a persistent pain syndrome, the development of attacks of renal colic, possible damage (ruptures) to the mucous membrane of the ureter with subsequent inflammation and blockage of the excretory duct, which can lead to the cessation of the outflow of urine.
Surgical intervention
If oxalate conglomerates have reached large sizes and conservative methods are ineffective, the doctor may decide on surgical intervention. To remove stones, the following procedures may be indicated:
- crushing kidney stones with ultrasound;
- laser destruction;
- surgical, including endoscopic, stone removal.
It should be remembered that for oxalate deposits in the kidneys, surgery is often the only and truly effective method of treatment.
Therapeutic diet for oxaluria in children
To balance the balance of beneficial microelements in a child’s body, doctors recommend enriching his daily diet with foods with sufficient amounts of B vitamins, magnesium and natural antioxidants.
These include:
- potatoes, cabbage, cucumbers, pumpkin, legumes;
- bananas, pears, grapes, apricots, prunes, dried apricots;
- meat products;
- dairy products, including hard cheese;
- cereals;
- vegetable oil.
The child must receive proper nutrition
If you have oxaluria, you should exclude sorrel, beets, oranges, lemons, chocolate, plums, and strawberries from baby food. It is recommended to limit the consumption of sour apples, tomatoes, currants, radishes, chicken, onions, carrots and cranberries.
If the baby is breastfed, these dietary recommendations should be followed by the mother. The duration of the diet for an excess of oxalic acid salts is three weeks.
Causes and symptoms of oxalates in urine
The primary disease occurs due to hereditary oxalosis (hyperoxaluria). Secondary oxaluria is a condition of the body caused by reasons that arose during life, such as:
- insufficient activity of small intestinal enzymes;
- diabetes;
- hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis, blockage of the urinary tract;
- unbalanced diet;
- nervous shock, stress, shock;
- excess bile production;
- ethylene glycol poisoning;
- intestinal neoplasms, operations on it, peptic ulcer;
- insufficient intake of magnesium and B vitamins;
- indiscriminate use of medications.
One of the main reasons for the occurrence of excess oxalates in the urine is dehydration, which can occur for various reasons. The insidiousness of oxaluria lies in the fact that it begins asymptomatically. With an increase in the amount of oxalates, the following appear:
- pain when changing position;
- disorders of the central nervous system in the form of headaches, neuroses;
- nagging pain in the lower back, abdominal cavity;
- weakness, general malaise;
- bright color of urine;
- often increased, less often limited urination;
- attacks of renal colic.
Causes of dehydration in men
The peculiarity of dehydration in men is that they experience a large amount of physical activity and sweating increases. Another reason for the development of oxaluria is inflammatory processes caused by infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
Causes of dehydration in women
Female dehydration is often associated with vegetarian diets and fasting.
In pregnant women, the reason for this is toxicosis, the fight against swelling. They also often take excessive amounts of vitamin C and consume more fruits and vegetables containing oxalic acid. As the size of the uterus increases, pressure on the bladder increases, which leads to congestion. Toxicosis in late pregnancy indicates the accumulation of calcium oxalates.
Causes of dehydration in children
The presence of vegetative-vascular dystonia, allergies, and low blood pressure in a child are symptoms of exceeding the norm of oxalates.
The causes of the disease in newborns are often congenital abnormalities of the intestines and the metabolism of oxalic acid salts. In the future, this can lead to severe kidney damage.
What diseases are salts found in and how is it diagnosed?
Unfortunately, it is not only dietary habits that can cause an increase in salt in the urine. Sometimes increased oxalates indicate the development of a serious disease in the body:
- Kidney diseases;
- Diabetes;
- Crohn's disease;
- Oxalosis. This disease is inherited;
- Ethylene glycol poisoning.
Before we begin to identify the development of a possible disease, a more thorough urine test is performed. So, first, the person will need to take a repeat urine test. When confirming the presence of excess oxalates in it, two types of oxalate recognition methods are used for more accurate diagnosis:
- Daily urine collection;
- Examination of fresh urine.
It should be noted that excess oxalate levels can also occur in children. But in most cases, their excess in children’s urine can rarely be detected. Up to 5 years, symptoms of the present concentration in the urine practically do not appear. If there is even the slightest suspicion that this element is exceeded, a daily collection of children’s urine should be collected for analysis.
It is worth knowing that an increase in the concentration of oxalates also occurs in places where there is a hot climate. Prolonged stay there and increased consumption of drinking water containing various calcareous compounds can provoke the development of urolithiasis.
In addition to taking a urine test, the patient may also be prescribed an ultrasound of the kidneys. This procedure allows you to accurately determine whether oxalate stones are present in the kidneys. If the excess of oxalates was carried out at the beginning of their increase, then appropriate treatment can completely eliminate the likelihood of stone formation.
Reasons for the appearance of oxalates in urine in children
Today, metabolic disorders in children are diagnosed everywhere and the appearance of oxalic acid salts in urine is not uncommon. Manifestations of this pathology are observed even in the urine of newborns, caused by genetic disorders in the metabolism of aldehyde acids and amino acids due to oxalosis (primary hyperoxaluria).
In addition, the presence of oxalates in a child’s urine means the presence of intestinal pathologies:
- malabsorption in the small intestine (malabsorption);
- impaired absorption of bile cholic acids from the gastrointestinal tract;
- the presence of a congenital short intestine, or its partial atresia (fusion).
This is facilitated by the child’s fairly extensive diet, including foods saturated with oxalic acid salts - first courses in steep broths and jellied meats in gelatin, cottage cheese casseroles, green and sour apples, chocolates and cocoa, salads from beets and radishes, parsley and spinach. , jelly and currant juices.
If oxalates are regularly observed in a child’s urine, this is a sure sign of kidney dysfunction. In this case, urine may be released in smaller quantities and will be of a rich color. With oxalate nephropathy, children are normally developed, but such children are characterized by:
- headaches and allergic reactions;
- large weight gain with fat deposits;
- neurocircular dysfunctions (VSD);
- manifestations of arterial hypotension.
As a rule, during puberty all these signs become aggravated, the disease rapidly progresses, which can lead to the development of pyelonephritis and urolithiasis.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of oxalates in the urine may not appear for a long time and may not bother the person. In this case, pathology can only be detected using laboratory urine analysis. Externally, oxalate stones look like thorns, so when they pass through the ureter, they injure the mucous membrane. As a result, the first sign of pathology is blood in the urine. The patient has the following symptoms:
- pain in the abdomen and lumbar region;
- renal colic;
- general weakness;
- frequent trips to the toilet;
- mucus in urine.
Blood in the urine can cause oxalate stones.
With a large amount of salt of this type, single crystals appear, which over time form a large calculus. It clogs the ducts and prevents urine from leaving the body. This leads to severe pain and the penetration of bacteria, as a result of which inflammation of the internal organs is diagnosed.
Why are high rates dangerous?
Oxalates are dense, spiky stones that injure the organs of the urinary system. Potential complications of hyperoxaluria include:
- kidney stone disease;
- urinary tract obstruction;
- inflammation of the bladder;
- renal failure;
- hematuria (blood in the urine);
- dilation of the renal pelvis.
Kidney failure is one of the most dangerous complications, which leads to intoxication and death of a person.