Diseases that mainly affect the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), for the most part, can lead to serious consequences if not properly treated. In order to detect an emerging disease in a timely manner, doctors conduct special studies, which often identify even an asymptomatic disease at an early stage of development, allowing timely and appropriate measures to be taken to eliminate the problem.
Among the most important diagnostic procedures is stool analysis for Helicobacter - it makes it possible to detect pathogenic organisms that parasitize the gastrointestinal tract and at the same time interfere with its normal functioning.
What is Helicobacter pylori?
Helicobacter is a pathogenic single-celled organism with a spiral-shaped body, which makes it possible to freely “screw in” into the thick mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. A living pathogen is equipped with several long flagella (from 4 to 6), with the help of which it moves along the walls of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
This parasite, unlike the vast majority of other bacteria, thrives in an acidic gastric environment. Harmful toxic substances released by Helicobacter pylori daily affect the mucous layer of the gastrointestinal tract, which can lead to inflammatory processes, perforation, erosion, as well as carcinogenesis (the formation of oncological foci).
Interestingly, when the Helicobacter parasite senses danger, it takes the form of a curled up ball covered with a dense protective shell. This form allows you to wait out unfavorable environmental factors, but at the same time destroys the parietal areas of the stomach with much greater intensity, creating a threat of the development of malignant tumors.
Symptoms indicating infection with Helicobacter pylori do not make themselves felt immediately, so often this or that disease caused by flagellated organisms is detected quite late, which affects both the increase in the number of complications and the duration of the course of treatment.
Helicobacter exhibits resistance to a number of antibiotics - this quality contributes to better survival of the organism in less comfortable living conditions
Determination of Helicobacter by cultural method
The bacterium itself is extremely rarely found in feces in its usual S-shape entirely. The large intestine and feces are not a favorable environment for the microorganism, therefore, when it enters them, it can take on a round coccal form, occasionally occurring in feces in this form.
The cultural method involves sowing part of the test material onto a nutrient medium in which the bacteria will feel good and begin to multiply.
Thus:
Colonies grow, which are analyzed, stained with special reagents and examined under a microscope. In this way, pathogenic microbes are literally grown for the purpose of further study.
In addition to detecting the bacterium itself, the method allows one to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to a particular antibiotic. If, when adding a drug, the growth of the colony continues - H. pylori is resistant to the antibacterial agent, and if the microorganisms die, it makes sense to prescribe this drug to the patient for the purpose of treatment and eradication, the bacteria are sensitive to it.
The cultural method is very reliable, but only if the S-form of the microbe is found in the biological material taken. The method has its drawbacks, and for this reason is not very widespread:
- The research period takes from 6 to 12 days
- Expensive media for sowing Helicobacter bacteria
- Specific conditions for media that ensure colony growth that are difficult to reproduce in the laboratory
- Rare occurrence of S-shaped bacteria in feces suitable for growth under nutrient conditions (coccal forms are not studied)
Indications for the study
A stool test for Helicobacter pylori is usually prescribed to people who have been bothered by symptoms indicating a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract for a long time. Signs of this kind include:
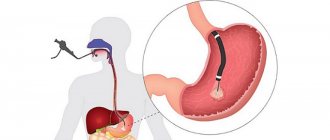
Endoscopic examination of the stomach
- a sharp decrease in body weight without any visible prerequisites;
- sour belching;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- diarrhea (regular loose stools);
- obstipation (constipation);
- stomach pain after every meal;
- causeless loss of appetite;
- attacks of heartburn;
- flatulence (excessive accumulation of gases in the gastrointestinal tract, causing bloating);
- constant rumbling in the stomach, not associated with hunger;
- nausea;
- intolerance to food of animal origin;
- unquenchable thirst;
- vomiting accompanied by blood discharge;
- increased salivation;
- bad breath;
- dysphagia (difficulty swallowing).
If there are serious disturbances in the functioning of the stomach and intestines, then the above symptoms can be combined with migraine, irritability, anemia, general weakness, hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating), pallor of the skin, insomnia (sleep disturbance), tachycardia and high fever (37– 38 °C).
Among other things, doctors strongly recommend taking a stool test for Helicobacter for those who have been diagnosed with the following pathologies:
- atrophic gastritis;
- duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum);
- dyspepsia (indigestion);
- lymphoma of the stomach;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- Ménétrier's disease (pathological thickening of the gastric mucosa with further damage to the endocrine glands, which leads to the formation of multiple cysts and adenomas);
- malignant tumors localized in the gastrointestinal tract;
- thrombocytopenia (sharp decrease in the number of blood platelets);
- duodenal or gastric ulcer;
- intestinal dysplasia.
Sometimes the patient needs to undergo testing for Helicobacter in order to exclude various types of abnormalities before prescribing medications that provoke insufficient production of hydrochloric acid by the stomach. Diagnosis is also carried out after the main course of antibiotic therapy - this makes it possible to clarify its effectiveness. In case of stagnation or worsening of the condition, specialists adjust treatment tactics.
If a close relative has a history of a malignant tumor of the upper gastrointestinal tract, a stool test for Helicobacter is performed to identify a genetic predisposition to the disease
Diagnostic methods
Determining the presence of a pathogenic microorganism in the stomach is possible using such effective diagnostic methods as:
- Stool examination using PCR (polymerase chain reaction). This is a simple and at the same time very sensitive way to diagnose infection in the body. It is based on the study of a DNA fragment of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which is a carrier of hereditary information. Detection of an infectious agent using molecular genetic diagnostics makes it possible to determine its presence even if the sample contains only a few molecules of bacterial DNA. The method is characterized by the absence of any inconvenience or pain. This bacteriological analysis determines the presence of parasites extremely accurately (up to 90-95%).
- ELISA – enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The Helicobacter pylori antigen begins to produce immunoglobulins (antibodies) in response to the appearance of an infectious agent. ELISA determines the presence of antibodies to parasitic infection in the blood. If they are detected, it means that the immune forces have recognized the infection and are trying to develop protective agents. The presence of immunoglobulins IgG, IgM, IgA in the test indicates the need to continue the examination to find out how large the deviation from the norm is and whether the presence of bacteria in the body is dangerous for the patient’s health.
For this purpose, the Western blotting method is used, which is recommended when detecting antibodies to a parasitic infection. Its value lies in the fact that it makes it possible to obtain differentiated information about antibodies and their quantity.
Blood from a vein is used as a biomaterial for hemotest.
Other parasite detection methods
Despite the fact that the results of stool PCR and ELISA are considered the most accurate laboratory data, in some cases additional diagnostic procedures are resorted to.
The following measures can be used as an auxiliary survey:
- Urease respiratory test. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection using it is based on the release of a special substance by the bacterium - urease, which protects it from the aggressive influence of hydrochloric acid. The presence of ammonia and carbon dioxide in the breath test, formed as a result of the action of urease on urea, makes it possible to conclude that a parasitic infection is present in the body. This test is recommended for children and pregnant women. It is convenient and safe.
- Urease rapid test. The study is similar to the previous test. But a scraping from the gastric mucosa is taken as sample material. It is tested in a medium containing urea.
- Biopsy and histology. The method is characterized by exceptional reliability of the analysis and does not allow false positive results. Material for examination is taken from areas of the gastric mucosa that are expected to be heavily populated by microorganisms.
To obtain the most accurate information about the presence/absence of Helicobacter pylori, two or three research methods are used.
Laboratory identification of the pathogen
At the moment, 3 methods have been developed for examining stool for Helicobacter pylori, which are used by specialists in laboratories:
- Cultural research. It involves introducing the resulting biomaterial into a nutrient medium that promotes the reproduction of colonial organisms. Identified representatives of Helicobacter pylori are studied using various types of chemical dyes and drugs. The latter make it possible to determine the degree of sensitivity of Helicobacter to different types of drugs.
- Immunological method. A solution containing special protein structures (antibodies) is added to a certain amount of feces, which actively react to the presence of dangerous Helicobacter antigens, letting diagnosticians know that the corresponding sample is infected with pathogenic bacteria.
- PCR (or polymerase chain reaction). This method involves the isolation of “enemy” DNA using special enzymes with further doubling of the deoxyribunucleic acid particle. Artificial DNA replication is carried out until a complete genetic code is obtained, which is then compared with the existing Helicobacter pylori sample.
The overwhelming majority of medical laboratories prefer the PCR method, the reason for this is a higher quality and more reliable diagnostic result in comparison with other types of testing for Helicobacter. Moreover, processing the data from such an analysis requires only a few hours, i.e., the final form with the indicators is given to the patient or attending physician the next day.
Tactics for determining Helicobacter bacteria using stool analysis
The doctor prescribes a specific test for helicobacteriosis. The specialist takes into account the individual clinical picture of the patient’s health status. You can get tested for Helictobacter pylori yourself if you suspect a functional deviation of the digestive tract.
Molecular diagnostics
Molecular analysis reveals the specific DNA of the bacterium. The code is duplicated on a special device. When the bacteria reaches the desired size, it is compared with ethanol. If parts of the DNA match the original, then the test result is positive (Helictobacter pylori infection has been detected). The technique is characterized by a high degree of information content.
Cultural analysis
Bacterial inoculation (or cultural analysis) belongs to the category of microbiological research methods. During the procedure, biological material is placed in an environment that is most favorable for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. After a week, the stool is examined using a microscope.
To identify Helicobacter pylori, the color of the bacteria and their ability to enter into certain reactions are taken into account.
Features of the technique:
- the procedure allows you to identify a pathological antigen;
- in the process of studying biological material, a sensitivity test to antibacterial drugs is carried out;
- The results of the study allow us to select the most effective treatment regimen.
Determination of Helicobacter pylori antigen in feces by immunological method
The main purpose of immunological tests when identifying Helicobacter pylori is to determine antigen + antibody complexes. Labeled antibodies are used for the study. When they react with feces, such substances undergo certain changes. Antibodies are able to detect the presence of not only pathogenic bacteria in the stool, but also their parts, as well as waste products.
Advantages and disadvantages of PCR diagnostics
PCR diagnostics has a number of advantages and disadvantages. Some types of pathogenic bacteria can only be detected using this technique (for example, cytotoxic types of microorganisms). Collecting material for analysis does not imply causing pain or discomfort to the patient. The procedure shows the most reliable results.
Advantages of the technique:
- the procedure allows you to identify various strains of pathogenic bacteria;
- the method has a high degree of sensitivity;
- the analysis is safe for the patient (no medical instruments are used to collect material);
- non-invasiveness and simplicity of the process of collecting biological material;
- high degree of specificity of the test;
- The method allows you to determine not only spiral-shaped, but also coccal types of bacteria.
The high degree of sensitivity of the test is its simultaneous advantage and disadvantage. The analysis accurately determines the presence of bacteria, but if the biological material or container is contaminated, the results of the procedure may be false positive.
To exclude false indicators, you should follow all the rules for collecting stool for testing.
Other disadvantages:
- relatively high price of the procedure;
- inability to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to antibacterial drugs;
- lower sensitivity compared to the procedure for examining a biopsy of the gastric mucosa.
In vitro stool test for Helicobacter pylori antigen
Procedures for studying feces are carried out outside the patient’s body (“in vitro” - “in glass”, “in vitro”). To detect a microbe, such methods are as accurate and effective as possible. However, the procedures have some disadvantages. Some processes occurring in the human body cannot be recreated artificially.
Tests can show the level of sensitivity of bacteria to certain antibiotics, but such tests do not provide 100% information.
Explanation of parameters
The norm is the complete absence of Helicobacter pathogens, which is usually expressed in several ways:
- the inscription “not detected” or “not detected”;
- stamped “negative” or “absent”;
- number "0";
- with a dash.
PCR has only two possible results - negative and positive; the presence of the latter mark indicates the detection of Helicobacter pylori. The situation is similar with other types of research. Sometimes the degree of Helicobacter infection is indicated by plus signs: the higher the level of pathogenic flagellated parasites, the more corresponding icons appear on the form (their number varies from 1 to 4).
Decoding the results
| Procedure | Confidence level of results | Decoding the research results |
| PCR | High | Positive—Helictobacter pyloriosis has been detected; negative - no type of Helicobacter pylori was detected |
| Bacteriological analysis for sensitivity to antibacterial drugs | Low – for antigen detection High - to determine sensitivity | The number of bacteria is 0 - the result is negative, no bacteria were detected; indicators greater than 0 - helictobacteriosis is determined; R—resistance to a specific antibiotic; I - moderate sensitivity to the antibiotic; S - high sensitivity to antibiotic |
| Immunological methods | Low | Positive—Helictobacter pyloriosis has been detected; negative - no pathogenic bacteria have been identified |
Preparation for the procedure
High-quality preparation requires focusing on 3 key points, namely changing the diet, limiting the use of medications and correct collection of biomaterial. Now about everything in a little more detail.
Diet
To ensure that the final indicators are not distorted, it is necessary to exclude the following types of food 3-4 days before the analysis for Helicobacter pylori:
- drinks: alcohol, soda, strong tea and coffee;
- vegetables: radish, cabbage, beets, radishes, tomatoes, carrots, bell peppers;
- fruits: peaches, apricots, oranges, tangerines, pomegranate, nectarines, persimmons, mangoes, grapefruit;
- spices: curry, turmeric;
- sauces: ketchup, soy;
- first courses: bran, pearl barley, buckwheat or bean porridge.
It is also worth limiting the amount of pickles, spicy and fried foods you eat as much as possible.
It is advisable to boil, bake and steam lean varieties of meat and fish before testing for Helicobacter
When preparing for a test for Helicobacter pylori, it is best to introduce more slimy porridges, fermented milk and dairy products, purees (from fruits and vegetables), and light soups into your usual diet. Preferred drinks include rosehip decoction, green tea, compotes, non-concentrated juices from grapes or apples, fruit drinks and, of course, plain water.
Use of drugs
In fact, a stool test for Helicobacter suggests a complete abstinence from any medications, especially for:
- rectal suppositories;
- antacids (Almagel, Vikalin, Maalox, etc.);
- laxatives;
- antibiotics.
If some medications require regular use, you must inform your doctor about this.
Determination of Helicobacter pylori antigen in feces by immunological method
The patient's feces can be subjected to immunological research, which allows identifying not the microorganism itself, but its parts - antigens.
For this:
Special antibodies are used aimed at detecting a foreign antigen - parts of a bacterium, its metabolic products, genetic material.
Interacting with a foreign agent, antibodies form a specific complex, which is determined by enzyme immunoassay.
This method of studying feces is rarely used in Russia; not many laboratories are equipped with the necessary reagents and necessary tests.
But in the future, it is possible to include this method of detecting Helicobacter as screening tests: studying broad groups of the population for infection with the bacterium.
Collection of biomaterial
First, you should purchase a special container on the eve of the Helicobacter test. A sterile container is purchased either from the doctors themselves or from a pharmacy chain. If this is not possible, you can resort to using a miniature clean glass jar with a tight-fitting lid (it is better to boil such a container before use).
It is worth noting that it is strictly forbidden to collect biomaterial directly from a diaper or toilet bowl, since foreign bacteria may stick to the feces, which tend to distort the results of the study. It is advisable to wash yourself before defecation. Using a plastic spoon attached to the lid of the purchased container, it is necessary to separate several segments of biomaterial taken from different points.
The container should be filled ⅓ or ¼, then screw on the lid. It is advisable to collect stool 1-3 hours before testing for Helicobacter pylori, but if necessary, you can wrap the container in a solid plastic bag and place it in the refrigerator (never in the freezer). The required temperature regime is not higher than 3–4 °C. The sample should be stored in this manner for no more than 48 hours.
Results
- there are several ways to determine Helicobacter in stool using a laboratory method;
- each analysis option has its own advantages and disadvantages;
- To obtain the most accurate results, it is recommended to take several tests of different types;
- feces for analysis are collected taking into account a number of rules;
- a few days before the procedure, coarse fiber, fried, fatty foods, hot spices and seasonings, alcohol and any orange or red fruits are excluded from the diet;
- the container for feces must be sterile (pharmacy containers are the best option).
Video on the topic: Why is the Helicobacter pylori bacterium dangerous?
What is the reliability of diagnosis for Helicobacter?
Much depends on the diagnostic method used by specialists when identifying Helicobacter. Cultural and immunological methods are considered imperfect types of research, since each of them does not take into account a number of nuances associated with the detection of pathological bacteria.
For example, the first method cannot always provide a suitable nutrient medium for colonial Helicobacter parasites. An equally important point is that as they move through the intestinal tract, single-celled representatives of Helicobacter pylori are exposed to the negative effects of juices coming from the pancreas and gall bladder, which forces them to take the coccal (spherical) form that was discussed earlier.
If flagellated parasites are in protective capsules (and this is where they stay when they get into the feces), only PCR, based on the artificial duplication of bacterial DNA, can reliably detect them. This method is considered the most truthful.
A type of jar for collecting feces
There is only one “but”: Helicobacter DNA can be detected even within a month after treatment, so additional medical research will be required to clarify the patient’s physiological condition. If laboratory personnel did not neglect precautions when working with biomaterial, avoiding accidental mixing of different samples, then the final indicators will correspond to the real state of affairs.
How to take the test correctly?
Carrying out the procedure for examining stool for the presence of pathogenic bacteria requires following certain rules. If preparation for analysis or collection of biological material is done incorrectly, the test results may show a false result. Feces have a certain shelf life. If the material is delivered to the laboratory late, the testing may also become unreliable.
Preparing for the test
Preparatory measures for stool analysis for Helicobacter pylori include recommendations for following a certain diet, as well as adjustments in drug therapy (if any). If it is not possible to temporarily stop taking the prescribed medications, then this nuance must be reported to the doctor.
Substances contained in antibiotics and other categories of medications may cause incorrect interpretation of study data.
Recommendations:
a few days before the procedure you should stop taking laxatives or antacids;
- within a month before the test, the patient should not take antibacterial drugs;
- You should not eat foods containing coarse fiber (beets, cabbage, radishes, radishes) for several days;
- for three days before the procedure, strong tea, coffee, hot spices and seasonings, red or orange vegetables and fruits are excluded from the diet);
- It is recommended to prepare dishes within three days before analysis only by cooking, stewing or steaming;
- You should not drink alcoholic beverages for several days.
Preparing containers
A sterile container for collecting biological material can be purchased at a pharmacy. When purchasing such a jar, the presence of contamination is excluded. As an alternative, you can use other container options (for example, baby food containers). An important nuance is their sterility. Containers must be as clean as possible from any type of contamination.
Collection of material
It is prohibited to collect feces from a diaper or toilet. The ideal option is to collect biological material from a pot or from a plastic bag. The container for storing feces should be one third full. The filled direction must be attached to the container.
How and for how long can the material be stored?
The container with stool is delivered to the laboratory as quickly as possible. If it is not possible to quickly send material for analysis, you can use two storage options. In the first case, the feces are frozen once. In the second, they are stored for no more than two days at a temperature no higher than 4 degrees.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of a group of intestinal infections include:
- loss of appetite;
- general weakness;
- excessive gas formation;
- discomfort in the stomach - heaviness, bloating;
- headache.
After some time, more dangerous signs of the disease appear. The patient suffers from severe abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea. In some cases, body temperature rises, chills and sweating appear.
Symptoms of the disease may appear within 6 to 48 hours. One of the most dangerous consequences can be dehydration, since the patient loses a large amount of fluid along with vomiting and loose stools. As a result, an imbalance of sodium and potassium occurs in the body.
Causes of infectious disease
The risk of infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori increases with age. Moreover, if one of the family members has this microorganism, then, most likely, other relatives living with him are also infected with it. Determination can occur using PCR (polymerase chain reaction) analysis.
The bacterium lives in the stomach due to the fact that this is due to the peculiarities of its survival in the environment. For its life, it requires constant nutrition and a certain temperature. Otherwise, the bacterium dies within two weeks. Humans are the main carrier, but Helicobacter pylori can also be found in dogs, pigs and cats.
The bacteria is detected, most often when an antigen test or PCR is performed in the stool.
It can stay in the body for a long time and not cause any inconvenience. But there are several favorable conditions for the appearance of disease due to this bacterium. These include:
- weak immunity;
- non-compliance with diet;
- eating unhealthy foods;
- frequent exposure to alcohol on the stomach.
Preparation
Preparation for collecting biomaterial is carried out 2-3 days before visiting the laboratory. It is necessary to correct the diet with the exclusion of foods that cause diarrhea.
It is recommended to avoid the following types of food:
- whole milk;
- kefir;
- beans;
- sweeteners;
- broccoli;
- mint;
- hot spices.
If 1-2 days before the expected date of the test there is loose stool, you should add low-fat broths, crackers, dried bread, low-fat omelet, tea, bananas to the menu. It is allowed to take loperamide according to the regimen recommended by the developer of the drug (2 tablets at once and 1 tablet after each act of defecation).
Take the h test. pylori is possible 1 month after completing the course of antibacterial agents and 2 weeks after discontinuation of proton pump inhibitors or bismuth preparations. Otherwise, there is a high risk of obtaining a false negative result.
Note: liquid masses are also suitable for research. A sample of this consistency is more difficult to collect and place inside the container.
What does a stool test show?
When analyzing stool for intestinal infections, the following microorganisms are detected:
- bacterial origin;
- viral etiology;
- specific infectious forms.
The causative agents of dysentery and salmonellosis are bacterial in nature. They often enter the body due to poor hand hygiene and after eating unwashed vegetables/fruits. Pathogens of viral origin are, as clinical experience shows, most often rotaviruses, adenoviruses and enteroviruses.
Specific infections are caused by too active proliferation of opportunistic microorganisms. The trigger for their development can most often be dysbiosis or other digestive disorders. The doctor will determine the exact cause only after conducting a complete examination of the patient.
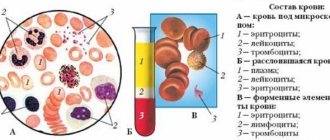
Helicobacter pylori: blood test, normal
To identify this bacterium, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is used. Its essence is to determine the concentration of antibodies in plasma to Helicobacter. When a pathogen enters the internal environment of the body, complex immune processes occur that are aimed at removing a genetically foreign protein compound, which is Helicobacter.
In cases where the infectious agent has already entered the body, but the immune system has not yet had time to respond to it, laboratory testing can produce false negative results. Also, when the bacteria is eliminated, antibodies to it may still be detected for some time (pseudo-positive reaction). Taking into account this pattern, a fractional determination of the level of immunoglobulins is carried out:
- Ig M are the largest, but make up only 10% of the total number of immunoglobulins. These antibodies can be detected earlier than Ig G.
- Ig A - they are detected not only in the blood, but also in gastric juice or saliva, which indicates significant activity of the pathological process.
- Ig G is a class of immunoglobulins, which makes up 75% of all types.
These protein substances appear a month after the infection enters the stomach. The concentration of igg is directly proportional to the activity of Helicobacter pylori infection. In addition, weakly positive results occur a month after treatment and complete recovery from helicobacteriosis.
The standard of analysis is the absence of Helicobacter pylori infection in the body. When the level of all immunoglobulins increases, an active infectious process is indicated. In this case, when assessing the results, total antibodies are taken into account.
Determination of giardia lamblia antigen in feces
Each immune cell contains a molecule that attracts the antigen of a foreign cell. It transmits information to the immune system. If she cannot identify a foreign cell, she directs efforts to destroy it. This complex process in the body can be identified using an analysis for antibodies and antigens.
The procedure consists of several components:
- enzymatic reaction;
- immune response.
Initially, the laboratory assistant adds AT Giardia to the feces. Their task is to attract protozoan antigen. After a while, reagents are introduced to remove cells that have not reacted. Wash off unbound enzymes. A special stop solution is added to slow down the reaction. It also changes the color of the material being tested and is used for diagnostics. If the reaction to the antigen is positive, the test material turns dark.