Many people have heard about the connection between iron and hemoglobin. It is a structural element of this protein. There is even a misconception that a lack of hemoglobin in the blood is necessarily associated with iron deficiency. This is not true. There can be a lot of reasons. Hemoglobin may be low despite normal iron levels. The opposite case is also possible - low iron in the blood with normal hemoglobin. There are explanations for this.
The role of iron in a woman’s body
Iron is important for the proper functioning of all cells in the body. About 70% of it is found in blood cells, red blood cells containing hemoglobin, and in muscle cells - myoglobin. Part of the mineral, no more than 6%, is found in proteins necessary for respiration and energy production, and part is in enzymes involved in collagen synthesis.
The human body has an intracellular depot where iron is stored in the form of ferritin. The male body contains 1000 mg of iron, while the female body contains only 300 mg. When its reserves decrease, the level of hemoglobin decreases.
Main functions of iron:
- Forms hemoglobin. When interacting with proteins, it creates hemoglobin in the blood, the main function of which is to transport oxygen from the lungs to the tissues.
- Increases energy through the production of myoglobin. This hemoprotein, found in muscle fibers, receives oxygen from hemoglobin and distributes it throughout the muscle cells. A decrease in myoglobin leads to fatigue and weakening of the body.
- Supports brain functions. The brain uses 20% of the oxygen contained in the blood. Since iron is responsible for creating proteins that transport oxygen, brain function depends on iron stores.
- Supports metabolism. Metabolism may slow down to adjust to low oxygen levels, leading to fatigue and weakness, two signs of iron deficiency. But when a sufficient amount of iron is supplied, metabolism functions normally.
- Supports immunity. The human body requires iron for the proliferation of T cells, which drive immune system responses against cancer cells. Its lack makes a person susceptible to infections.
- Supports the endocrine system. Iron is an important component of many enzymes. These are complex proteins that serve as catalysts in chemical reactions. A body deprived of iron will suffer from endocrine disruption, including high cholesterol and thyroid dysfunction.
A few facts about iron and its role:
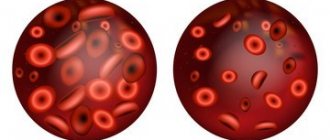
- The female body has 4.7 million red blood cells per 1 cubic meter. ml of blood. Their production occurs in the bone marrow.
- Each red blood cell contains 280 million hemoglobin molecules.
- The lifespan of an erythrocyte is from 90 to 120 days. When old cells are destroyed and removed by the liver and spleen, iron is returned to the bone marrow to form new cells.
- Additionally, iron accumulates in the liver and bone marrow for the synthesis of hemoglobin.
Why do you need iron?
Iron is one of the main components of the hemoglobin protein, which plays a vital role in the metabolic processes of the body. It is he who delivers oxygen throughout the body, nourishing every cell. And if the iron level decreases sharply, then the proportion of hemoglobin itself decreases.
In fact, this is a rather dangerous condition, since all the muscles and tissues of the body do not receive sufficient oxygen. This leads to their discord and disruptions in their work. Doctors call this iron deficiency anemia.
Causes of iron deficiency in women
Lack of iron in the body (symptoms in women are expressed primarily in iron deficiency anemia and frequent infectious diseases) causes a number of other problems. General fatigue, lethargy, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, and dizziness appear. Blood loss leads to severe iron deficiency.
Heavy periods
During heavy and long menstrual periods, iron consumption increases. At the same time, the number of building blocks - red blood cells, which the body cannot replace with anything, decreases. Severe blood loss during menstruation, menorrhagia, is abnormal uterine bleeding.
This is one of the reasons why women often turn to doctors. Prolonged heavy bleeding, hypermenorrhea, in which the menstrual cycle lasts up to 2 weeks, leads to anemia if the losses are not compensated by increased doses of iron.
Uterine bleeding
Anemia can be caused by fibroids, benign growths that form in the muscle tissue of the uterus. Fibroids often bleed, which leads to frequent and heavy menstrual cycles and blood loss. Iron deficiency may be a sign of uterine cancer in older women who experience uterine bleeding. But the main cause of anemia in postmenopausal women is gastrointestinal blood loss.
Bleeding of other etiologies and localizations
Slow chronic blood loss causes iron deficiency anemia. It occurs from peptic ulcers, colon polyps, colorectal cancer or hiatal hernia. Stomach bleeding occurs as a result of frequent use of painkillers, especially aspirin.
Poor nutrition
People on a meat-free diet, vegetarians, are especially susceptible to anemia. Additionally, dietary supplements such as calcium taken with iron-rich foods interfere with the absorption of the mineral.
Factors inhibiting the process of mineral absorption
All iron is absorbed from food into the blood in the small intestine. People suffering from an intestinal disorder, celiac disease, cannot fully absorb the microelement. If part of the small intestine has been removed, the ability to absorb micronutrients and nutrients is also affected.
Colitis, stomach infections, and diseases associated with chronic diarrhea interfere with the absorption of the mineral.
Normal functioning of stomach acid is also necessary. Chlorhydria is a disorder in which there is a lack of hydrochloric acid in the stomach. And when its environment is not acidic enough, then substances, including iron, cannot be absorbed. Problems with malabsorption occur as a result of taking medications such as antacids, acid blockers.
Increased iron consumption
Women are at risk of getting excess iron when their periods suddenly stop. Amenorrhea can last 6 months or more. This is associated with menopause, hysterectomy, birth control pills.
Excess iron, increasing its level to toxic, affects the development of:
- premature heart attack;
- diabetes;
- liver diseases;
- osteoporosis;
- hormonal imbalance;
- loss of menstruation.
Pregnancy and lactation
Lack of iron in the body (symptoms in women are expressed by a sharp decrease in hemoglobin) occurs in pregnant women and during breastfeeding. At this time, iron reserves are consumed not only by the woman’s body, but also serve as a source of hemoglobin for the growing child or fetus.
During pregnancy, blood volume increases and it becomes more dilute, which leads to a decrease in red blood cells.
Women who suffer from anemia during pregnancy often give birth to children with severe anemia. The amount of blood lost during childbirth is about 500 cubic meters. cm. Thus, 200-250 mg of iron is lost. In addition, another 500-800 mg of the substance that was originally in the mother enters the blood and tissues of the newborn.
Nutrition rules for deficiency
Depending on age and physical activity, premenopausal women should receive 16-19 mg of iron per day (pregnant women - 26 mg), men - 15 mg, and postmenopausal women - 13 mg.
A well-composed, varied diet will provide this amount. Iron is found in almost all foods. But the problem is that the body of a healthy person can absorb on average only 10 percent of the mineral they contain.
The notorious spinach is not such a valuable source of iron as previously thought. In 100 g of spinach there is only 2.4-3.9 mg. Most iron is found in liver and meat.
Iron is better absorbed from animal products than from plants. For example, the body absorbs only 1 percent from rice and spinach, 3% from corn, 4% from lettuce, 11% from fish, 12% from liver, and 22% from veal.
This is due to the different chemical structure: products of animal origin contain divalent (heme) iron, while plant products contain trivalent (non-heme) iron.
A lot of iron is found in beans, peas, broccoli and shrimp. The iron contained in vegetables is less easily absorbed, but they contain fewer calories, so you can eat them at your discretion, supplying a lot of this invaluable element to the body. Iron absorption increases vitamin C (up to 2-3 times).
Therefore, in every meal there should be foods that provide it the most, for example, peppers, parsley, tomatoes, strawberries, black currants, citrus fruits. And since it is temperature sensitive, the best sources are raw vegetables and fruits, as well as freshly squeezed juices.
It is worth combining vegetables and fruits on your plate, which are a treasure trove of vitamin C, with animal products containing a lot of iron. It’s good to put a few slices of tomato on a sandwich with sausage, and eat the cutlet with sauerkraut salad.
The absorption of iron is hindered by phytic acid contained in bran, oatmeal, as well as oxalic acid, the source of which is sorrel and rhubarb. In their presence, iron salts precipitate and are not absorbed.
The most formidable enemies of iron are tea and coffee, because they contain tannins - compounds that interfere with the absorption of the mineral from the digestive tract. Therefore, it is better to limit them in your daily diet. Their effect can be reduced by drinking these drinks not during, but between meals.
Symptoms of iron deficiency in the female body
Iron deficiency develops gradually, and symptoms of anemia are not immediately visible.
Prelatent stage
At the first stage, the need for iron in the body in women exceeds consumption, causing a gradual depletion of reserves in the bone marrow and liver. This stage often goes unnoticed, since there are no pronounced symptoms and there is no effect on the production of red blood cells. A blood test taken during this period indicates a decrease in ferritin levels.
The accumulation of iron during this period is significantly reduced, and its decrease leads to the second stage.
Latent stage
During this period, deficiency begins to affect hemoglobin production, and symptoms appear:
- chronic fatigue;
- difficulty concentrating;
- irritability.
Symptoms of iron deficiency in the body
Tests performed during the latent stage to evaluate iron deficiency include total iron binding capacity and serum iron testing. Together, these tests are used to assess transferrin saturation, an indicator of iron status. It is very low in people with iron deficiency.
Stage of pronounced deficiency
At this stage, stores are depleted to the point that they cannot produce the hemoglobin needed to produce enough red blood cells. Severe and long-term iron deficiency can cause dysfunction of iron-containing cellular enzymes.
Symptoms, consequences of iron deficiency
As iron stores dwindle, fewer and fewer healthy red blood cells are produced and alarming symptoms appear. The first sign of iron deficiency is usually apathy and constant fatigue for no apparent reason.
The main effect of iron deficiency in the body is anemia. The degree of impairment depends on the degree of deficiency. Not everyone with iron deficiency develops anemia, but it is the result of chronic deficiency.
According to the WHO standard, anemia is detected when the level of hemoglobin in the blood falls below 120 g/l in women and children aged 6-14 years, and in pregnant women - 110 g/l, in men - 130 g/l.
Symptoms of anemia are initially quite subtle and accumulate as iron deficiency increases. It usually begins with chronic fatigue, constant drowsiness, and lack of vitality. Another characteristic symptom of anemia is pale skin and mucous membranes. Thus, pale skin, dark circles under the eyes, brittle nails and hair, and lack of skin hydration may be symptoms of anemia due to iron deficiency.
With anemia, the amount of ferritin (a protein containing iron stores) falls below normal, which is in the range of 12-200 μg/L (normal for men: 15-200 μg/L, for women: 12-150 μg/L). This condition can occur at any age and affects women more often than men.
Symptoms of iron deficiency and anemia:
- Weakness and fatigue, lack of strength;
- Poor concentration;
- Headaches and dizziness;
- Rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath;
- Weakening of the immune system;
- Paleness of the skin and mucous membranes (they are less red than usual);
- Weakening of hair quality;
- Nail changes;
- Dry skin.
Treatment for iron deficiency involves taking iron supplements and following an appropriate diet rich in meat, fresh fruits, greens, nuts, egg yolks, fish, vegetables and legumes.
Possible complications of anemia in women
Lack of iron in the body (symptoms in women can be mild, moderate or severe) leads to decreased endurance and performance. Decreased red blood cell production reduces the body's ability to absorb oxygen. This leads to heart failure and arrhythmias in the long term.
Pregnant women are at increased risk of an adverse birth, especially if they are anemic in the first trimester.
Anemia has serious consequences for older women. It increases the risk of falls, reduces physical strength, and increases the severity of heart disease, which includes a decreased chance of surviving heart attacks. Even mild anemia at this age gives impetus to the development of dementia and cognitive impairment.
What is the best blood test to do to detect iron deficiency?
The most appropriate blood test to check if you have iron deficiency is a ferritin test. For the vast majority of people, ferritin is a very reliable indicator. Ferritin concentrations below the lower limit of the reference range indicate iron deficiency. Nothing else leads to a decrease in ferritin concentrations. Normal ferritin levels in patients without inflammation are a reliable criterion that excludes iron deficiency. An ambiguous situation occurs only in patients with systemic inflammation or liver disease. Then finding an iron deficiency is much more difficult.
Diagnostic features
If symptoms indicating the development of iron deficiency are detected, it is suggested to take a blood test, which examines:
- Size and color of red blood cells. With anemia associated with iron deficiency, the red blood cells are smaller than usual and their color is paler.
- Hematocrit The percentage of red blood cells in relation to the blood level. The normal level is between 34.9 and 44.5% for middle-aged women.
- Hemoglobin. A reduced level indicates developing anemia. The normal range for adult women is 13.0-15 g per deciliter.
- Ferritin. Normal protein levels help maintain iron in the body. A reduced amount indicates its low level.
If signs of iron deficiency anemia are detected, the doctor may prescribe additional tests:
- Colonoscopy. To exclude internal bleeding in the lower intestines.
- Endoscopy. The examination checks for bleeding from esophageal hernia, stomach, and ulcers.
- Ultrasound. This method determines the cause of excess menstrual bleeding.
After passing the tests, treatment with drugs with iron supplements is prescribed. When making a diagnosis, one must distinguish between anemia that is caused by internal diseases and anemia caused by iron deficiency.
In some bacterial infections and inflammatory diseases, anemia develops as a secondary cause, so taking glandular supplements is not suitable for a person with anemia caused by a chronic disease. Symptoms of iron deficiency include shortness of breath on exertion, fatigue, restless leg syndrome, and poor coordination.
Causes of iron deficiency
A deficiency of this mineral occurs when its consumption exceeds its intake and absorption - this can occur with:
- Pregnancy (the need increases due to the development of the fetus and placenta, as well as with blood loss during childbirth - they can reach 1700 mg) and breastfeeding.
- A period of rapid growth.
- Uterine bleeding.
Let us remember that abnormal uterine bleeding is any deviation from normal menstruation.
The duration of the cycle should be 24-38 days, menstruation - 4.5-8 days.
Volume of blood released = 5-80 ml/cycle
[Order No. 353 of the Ministry of Health dated April 13, 2016]
- Impaired absorption and parietal digestion in the small intestine - malabsorption syndrome (with tumors, Crohn's disease, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, celiac disease).
As well as gastritis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, the presence of polyps in the gastrointestinal tract - all this negatively affects the absorption of iron.
- Bleeding from the digestive tract is the most common cause of iron deficiency in men.
- Unbalanced nutrition, vegetarian diet.
- Hypochlorhydria is a decrease in the secretion of hydrochloric acid. Hemoglobin contains a protein part - globin, which is why adequate intake of amino acids and proteins from food is so important, as well as well-established work on their breakdown and absorption.
We recommend
“Proper nutrition as a factor in maintaining human health” Read more
Treatment of anemia
Treatment of mild and moderate iron deficiency is carried out in a clinic or day hospital. Severe cases of anemia are treated in a hospital setting. Initial therapy is carried out with ionic salt preparations of divalent iron.
To do this, doses are calculated corresponding to the patient’s weight and the severity of the disease:
- Iron tablets are taken on an empty stomach. If you have an upset stomach, they can be taken with meals.
- Iron supplements should not be taken together with antacids. Medicines that reduce heartburn interfere with the absorption of the mineral. The difference between doses should be at least 4 hours.
- Iron is better absorbed together with vitamin C, so you can take the medications with orange juice.
- Iron supplements cause stool upset and change its color.
The effect of taking iron-containing medications appears after a week of treatment. If the use of drugs does not increase iron levels, then the cause of the anemia is caused by bleeding or an absorption problem, which must be treated.
Iron supplements
| Drug name | Operating principle |
| Sorbifer Durules | In 1 tab. Contains 100 mg of 2-valent iron and 60 mg of vitamin C. Take 1 tablet. 2 times a day. |
| Ferretab | The drug is in capsules containing 152 mg of iron and 540 mcg of folic acid. Prescribed 1 drop. Per day. |
| Totema | Available in liquid form. 1 ampoule contains 50 mg of iron, 700 mcg of copper, 1.3 mg of manganese. Before eating, the contents of the ampoule are dissolved in water. Daily dose – 2-4 ampoules. |
| Ferrum Lek | Chewable tablets containing 400 mg of iron. |
| Maltofer | It is used for prevention in a group of elderly women, pregnant women, and those on strict diets; it is used in the form of drops; 1 ml contains 176 mg of iron. Tablets taken after meals - 1 pc. 1 time per day. Pregnant women - 1 tablet. 2-3 times a day. |
| Fkrro-Foil | Contains ferrous sulfate and folic acid. In mild forms of anemia, take 1 capsule 3 times a day, the course of treatment is 4 weeks. In subsequent stages of anemia, the dose is increased. |
Folk remedies for improving blood composition
You can increase hemoglobin with vegetables. Beets contain a lot of iron, folic acid, fiber and potassium.
- Bake 2-3 washed tubers in the oven or place in the microwave for 10-20 minutes. at a power of 750-800 W. Before placing in the microwave, wrap the vegetables in a baking sleeve, making holes to allow steam to escape.
- After baking, cool and use as intended: adding to salads, or eating as an independent dish.
- You can use fresh beet juice by adding carrot or apple juice.
Daily consumption of pomegranate or its juice is the best way to increase iron levels and strengthen the walls of blood vessels.
- Drinking the juice daily in the morning will increase your mineral levels.
- Dry the pomegranate seeds and grind them in a coffee grinder to a powder. Every morning drink a glass of milk with 2 tsp pre-soaked. dry powder.
Nettle is a good source of iron, vitamins B and C. It also stimulates hair growth, controls blood sugar levels, and removes water from the body.
- Add 2 tsp. dried leaves into a cup of hot water.
- Brew for 10 minutes.
- Strain and add a little honey if desired.
- Drink herbal tea 2 times a day.
Dates contain iron and vitamin C.
- Soak 5-6 dates in a cup of milk and leave overnight.
- In the morning, eat berries and drink milk on an empty stomach.
Fenugreek seeds contain large amounts of minerals that help produce red blood cells.
- Boil 150 g of rice.
- Add fenugreek as a spice.
- Eat for breakfast, adding a little salt to the rice.
Fenugreek leaves can be added to salad. You can make tea based on the seeds. For this, 2 tbsp. l. seeds are brewed in 0.5 liters of water and boiled. After cooling and straining, drink 50 ml 3-4 times a day.
What to do with additives
Sometimes diet is not enough, and you need to support the body with iron supplements. However, dietary supplements, especially those that contain the mineral itself, should not be taken without consulting a physician.
They are recommended in special cases, for example, pregnant women and the sick, but only if the level of the element in the blood cannot be leveled with diet. Usually it is enough to eat more liver, and to quickly increase the level of the element, add a bunch of parsley and dill to your dishes every day.
If the doctor detects anemia, then it is necessary to know its cause and undergo a course of treatment.
Taking supplements on your own can make it difficult to identify the true cause of anemia, such as stomach ulcers.
Taking iron supplements can sometimes lead to an overdose.
The body that receives them from food carefully regulates the concentration of the microelement, absorbing it as needed.
Side effects of the medications may include stomach problems such as constipation.
By interacting with certain medications, such as antibiotics, they interfere with their absorption. Therefore, you should always inform your doctor about the use of iron tablets.
Enriching your diet with foods high in iron
The lack of iron in the body (symptoms in women are sometimes reflected in the condition of the hair) is compensated by vitamin supplements and foods high in the mineral:
- Meat (beef), fish.
- Liver.
- Bean products.
- Buckwheat.
- Pomegranate juice.
- Eggs.
- Dried fruits: dates, figs.
- Broccoli, spinach, kale.
- Green bean.
- Nuts and pumpkin seeds.
- Peanut butter.
- Spirulina.
- Cheese, cottage cheese.
One apple eaten at night will help maintain iron and hemoglobin levels.
Additional reasons for decreased hemoglobin
Sometimes normal iron levels cannot prevent developing anemia.
The reason for this is a problem with a lack of red blood cells. They are the carriers of hemoglobin throughout the body. The faster the number of red blood cells decreases, the stronger the anemia. This problem occurs with congenital or acquired inferiority of red blood cells. In the case of congenital, a child is born with a mutation of the HBB gene. In this case, the red blood cells are sickle-shaped and cannot carry hemoglobin. This is why sickle cell anemia occurs. However, a person will not always suffer from anemia. Usually, under normal conditions, this does not manifest itself in any way. But with temporary hypoxia, symptoms appear.
Red blood cells can be destroyed under the influence of certain snake venoms or special substances that have a destructive effect. Therefore, an unprepared person will not be able to cope with such problems on his own.
An insufficient number of red blood cells can occur due to pathologies in the hematopoietic system. Such diseases can be congenital or acquired. In diseases of the myeloid tissue of the bone marrow, where red blood cells develop, their reduction is possible. This can happen with minor problems or blood cancer.
In this case, pathological cells develop faster and take up more and more space, leaving no space for red blood cells and other blood cells.
What should vegetarians do?
People who have consciously given up animal products containing iron should consider using vitamin complexes and biological supplements. Taking additional vitamins is an effective way to eliminate iron deficiency. They should include not only iron, but also vitamins A, C, E, D, all groups of vitamin B, as well as manganese, copper and zinc.
Iron-containing foods suitable for vegetarians:
- spinach;
- tofu;
- Bell pepper;
- cauliflower;
- fenugreek leaves;
- beans;
- pomegranate, watermelon;
- grapes, persimmon,
- apricots, apples.
To prevent symptoms of iron deficiency from bothering women, it is necessary, in addition to foods of animal and plant origin, to consume mineral supplements. For better absorption of vitamins, you should move more, as physical activity helps saturate the body with oxygen.
Serum iron is below normal and hemoglobin is normal
Sometimes situations arise when a patient has low iron with normal hemoglobin. Everyone knows that iron deficiency leads to the development of iron deficiency anemia, but this is not always the case.
Quite often, iron deficiency occurs not only when a patient has a normal amount of hemoglobin, but also when its levels are elevated.
This situation is observed both in well-equipped cities, where approximately 20% of residents suffer from a deficiency of this element, and in areas endowed with low medical indicators. Here the situation is much more serious and about 80% of the population already suffers from iron deficiency.
Symptoms and signs of iron deficiency
Currently, the problem of lack of this substance in people is not given too much attention. In fact, this is a rather serious health condition, which is characterized by painful and severe symptoms, especially noticeable in the late stages of the disease.
However, it often happens that patients who have a lack of iron in the body are treated for completely different diseases, such as vegetative-vascular or neurocirculatory dystonia.
This is due to the fact that at the initial stage the symptoms of a deficiency of this chemical element are not specific, so it can be difficult to diagnose this pathology in a timely manner and correctly assess the possible consequences.
As a result, patients suffering from iron deficiency are prescribed treatment with drugs that are not highly effective. These include different types of dietary supplements with iron, where the level of this substance will be low for rapid treatment and prevention of the disease.
As mentioned above, iron deficiency in humans has quite severe symptoms that affect the patient’s health, these include:
- dizziness and headache;
- weakness and constant feeling of fatigue;
- shortness of breath even after a slight load on the body;
- hair loss;
- pain in the lower part of the tongue and atrophy of its papillae;
- tachycardia - rapid heartbeat;
- bluish tint of the eyes, namely the whites;
- tired leg syndrome, in which the discomfort that is observed in a calm state goes away during movement.
Sometimes patients suffering from iron deficiency experience a distorted taste, which is expressed in the following:
- the desire to eat crumbs and paper - the disease is called amylophagia;
- the desire to eat raw clay, earth - this phenomenon is called geophagy;
- the desire to constantly eat only ice - this phenomenon is called pacophagia.
The relationship between iron and products
Almost all foods contain iron, but it is absorbed well from some ingredients, and much worse from others.
This is due to the fact that “animal” products contain heme iron, which can be well absorbed by the body, unlike plant products containing non-heme iron.
It is worth remembering that plant (non-heme) iron is absorbed by only 1-6% of its actual weight.
The main function of heme iron is the formation of a certain substance (hemo), capable of binding oxygen in the lung cavity and delivering it to internal organs and systems.
The sources of this element of animal origin are:
The non-heme element, as mentioned above, is absorbed somewhat worse by the body and this process is directly related to how much iron is already present in the body.
With its deficiency, non-heme iron is absorbed better than with its normal amount.
Also, the absorption of non-heme iron found in plant foods is directly related to how this element is dissolved in the intestines, which depends on the food consumed.
Main causes of iron deficiency
Doctors divide all the reasons for the lack of this element into several groups:
- Blood loss
- Poor absorption and assimilation of iron from the gastrointestinal tract
- Lack of iron from food
- Other factors
Also, a combination of several of the above factors can cause iron deficiency.
The main causes of blood loss are:
- donation;
- period;
- trauma, operations performed;
- bleeding resulting from hemorrhoids, stomach and duodenal ulcers.
Poor absorption of the component in the gastrointestinal tract is influenced by the following reasons:
- chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa;
- infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- gastritis.
Diagnosis of iron deficiency
If, during a medical examination, the doctor suspects a patient has an iron deficiency, he must prescribe an additional medical examination, which will confirm or refute the suspected diagnosis.
Since the initial symptoms of iron deficiency are non-specific, a blood test is first prescribed to assess hemoglobin levels.
Since a deficiency of an element is not always anemia, this condition can occur at any hemoglobin level.
Thanks to the OAC, it will be possible to eliminate the risk of developing anemia, as well as to identify the cause of anemia with low hemoglobin - this will allow us to determine the correct further examination method.
To confirm iron deficiency, the doctor prescribes to patients:
- ferritin, which can reflect the amount of iron in the patient;
- OJSS;
- determination of the amount of iron in the bloodstream.
Iron deficiency is treated with medications.
Many of them have their own side effects, which are related to the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract:
- nausea turning into vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- the appearance of constipation;
- metallic taste in the mouth.
If the patient experiences such effects, he should not stop taking the medication on his own. It is necessary to visit a doctor who will adjust the dose of the medication to reduce negative side effects.
It is also worth keeping in mind that iron-containing preparations can give the stool a dark tint, which should not be a concern.
After all, this cannot be called a sign of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, since such a phenomenon is considered only the cause of the interaction of food with this element.
Hidden anemia with normal hemoglobin: how to identify and treat
It is known that a normal level of hemoglobin is important for the full functioning of all organs and systems of the body. If its concentration is below normal, anemia is diagnosed.
This is a pathological process that requires urgent treatment. But it happens that hidden anemia develops with normal hemoglobin. This condition is rarely diagnosed.
Until pronounced symptoms arise in the form of dysfunction of internal organs.
How to increase iron in the blood?
You can increase the level of iron in the blood through a balanced diet and medications. The patient should include foods that contain sufficient amounts of iron in their diet. Among the “record-breaking” products are red varieties of lean meat, liver and poultry. The trace element is also found in plant foods - buckwheat, apples and pomegranates.
Often, a diet rich in iron is not enough to replenish it in the body. If necessary, the doctor will select medications, determine their dosage and duration of use. You should not decide this issue on your own, since the wrong dosage can lead to an excess of iron. It is also harmful to the human body, as is its deficiency. Let's take a closer look at the options for drug therapy.
Medicines to restore iron levels
In a situation where a patient has a critically low level of iron in the blood, he requires immediate restoration of hemoglobin. For these purposes, drugs are used in the form of injections. They are also prescribed for the treatment of chronic iron deficiency anemia. Examples of drugs:
- iron hydroxide sucrose complex;
- iron sorbitol complex with citrate in dextrin solution, containing 100 mg of iron;
- iron hydroxide dextran.
If iron deficiency is not critical, then the doctor selects drugs with a prolonged action. These include: ferric chloride, ferrous fumarate or sulfate, as well as its hydroxide polymaltosate. It is acceptable to prescribe vitamin complexes containing the necessary macro- and microelements in their composition. So, in combination with the microelement in question, the patient can take manganese and copper gluconate, ascorbic acid or vitamins B 9 and 12.
Separately, biological food additives should be highlighted. Patients are often interested in the question: does hematogen help maintain normal iron levels? Yes, this healthy product can have a beneficial effect on iron levels in the body. However, its isolated use cannot lead to an increase in the level of the substance. The product cannot be used as an alternative to meat products or medicines. It should be considered a preventive measure, but not a treatment measure.
You should not start using it yourself without your doctor’s permission. Since hematogen contains sugar, which may be a contraindication or limitation for people with diabetes.
How much microelement should there be?
In the male body, the reserves of this microelement are higher than in women, and range from 500 to 1.5 thousand mg. For women, this figure ranges from 300 to 1 thousand mg. At the same time, doctors claim that the vast majority of the population has iron reserves at a minimum. That is why during pregnancy, when the body requires iron in large quantities, iron deficiency may occur, and doctors prescribe vitamin and mineral preparations for prevention.
To find out whether there is a lack of iron in the body, it is necessary to do a biochemical blood test. The material for the study is taken from a vein, then fibrinogen is removed from the plasma (so that the blood does not clot during the study), and serum is obtained. Such a sample is convenient to use when studying the composition of blood.
Thus, the norm of serum iron in the blood of a healthy person should correspond to the following values:
- up to 1 year: 7.16 – 17.9 µmol/l;
- from 1 to 14 years: 8.95 – 21.48 µmol/l;
- in women over 14 years of age, including during pregnancy: 8.95 – 30.43 µmol/l;
- in men after 14 years: 11.64 – 30.43 µmol/l.
In the female body, its amount is less than in men. In women of reproductive age, iron concentration depends on menstruation. In the second half of the cycle, the levels of this microelement reach their highest values; after menstruation, its level decreases significantly, which is associated with blood loss during menstruation.
But at the same time, the body’s need for this microelement increases, and therefore it is necessary to ensure that during pregnancy a sufficient amount of iron is supplied with food. This is due to the fact that not only the mother’s body needs this microelement, but also the baby’s. Therefore, at a certain stage of its development, it begins to very quickly take it in large quantities.
That is why the doctor recommends a special diet during pregnancy and also prescribes the use of special vitamin and mineral preparations. Thanks to this, the body is provided with all the necessary substances during pregnancy. After childbirth, the acute need for iron, as during pregnancy, disappears. But is it worth it to stop taking vitamin and mineral supplements, the doctor must say.