January 20, 2020 Admin Home page » MRI and CT scan of the brain Views: 9230
MRI of a brain tumor is a study of tumors located in the intracranial cavity, which are formed through abnormal cell division. These tumors appear both in and around the brain. They are called primary. It is also possible for them to be transmitted from cancer cells that have affected other organs, and they are called secondary tumors or metastases.
MRI of a brain tumor is the most accurate and safe imaging method today. In the magnetic resonance imaging method there is no technology for using x-ray irradiation, which accordingly does not cause absolutely any harm to the body.
An MRI study of the brain makes it possible to visualize the presence of a brain tumor as accurately as possible; therefore, if no neoplasms were detected during the study, then oncology can be automatically excluded.
MRI: how the research procedure is carried out
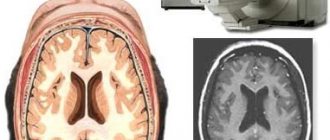
Magnetic resonance imaging is a highly informative research technique that helps obtain a layer-by-layer image of the affected area of the brain.
Detects structural changes, structural anomalies, traumatic lesions, pathological neoplasms. Progress of the procedure:
- the patient removes metal jewelry (including piercings), takes a horizontal position, and puts on protective headphones;
- communication with the doctor remains throughout the procedure;
- if necessary, a contrast agent is administered intravenously;
- duration of the study without contrast agents is up to 20 minutes, with contrast up to 40 minutes;
- the procedure does not cause pain or discomfort.
The radiologist deciphers the image. The doctor determines the presence and structure of the formation, its boundaries, and the pathological effect on neighboring tissues.
Are there any contraindications to this examination?
This study has several contraindications related to the specifics of the process:
- MRI of the head is not performed on patients in a terminal, unconscious state or mentally unstable, violent patients, as the procedure can take up to half an hour.
- MRI of the brain is not performed on patients with claustrophobia, since the machine is a closed cylinder in which the patient is placed.
It is not performed on patients with metal elements in the body, since the magnetic field attracts metal and injury is possible.
No special preparation is required for an MRI of the brain. The patient is warned about the procedure and contraindications. They explain that you need to remove all metal objects and warn about the presence of any metal implants. An allergy history is ascertained to prevent an undesirable reaction to the contrast used in magnetic resonance imaging.
With the help of MRI, it is possible to detect malignant brain tumors in a timely manner and carry out the necessary therapy in a timely manner.
Classification of tumors
A primary brain tumor develops from cells and is not as common as a secondary one. Depending on their origin, neoplasms are classified into:
- astrocytic: astrocytomas, astroblastomas;
- ependymal: ependymomas;
- oligodendroglial: oligoastrogliomas, oligodendrogliomas;
- pineocytomas, pineoblastomas - lesions of the pineal gland;
- ganglioneuroblastomas, gangliocytomas;
- neoplasms are embryonic and poorly differentiated.
Gliomas are the most common, diagnosed in more than 40% of cases. Depending on the type of cells included in the composition, gliomas are classified into:
- astrocytomas - consist of glial stellate cells, affect the anterior part, cerebellum, brain stem;
- ependymomas - formed from the cells of the ventricles; children, adolescents, and young adults are at risk;
- Oligodendrogliomas are produced from cells that contain fat that protects the nerves. They affect the forebrain and grow slowly. People of middle age groups are at risk.
Astrocytoma
Ependymoma
Patients are also diagnosed with:
- medulloblastomas—form from the cerebellum and occur in childhood;
- Schwannomas are tumors of cells that surround the nerves of the inner ear;
- meningiomas - formed from the meninges, grow slowly;
- germinomas are tumors of germ cells.
Secondary tumors are said to occur when a pathological process spreads to the brain area from another organ.
Metastatic tumor spreads to the intracerebral hemispheres of the brain. Cancer metastases form in the GCA, affecting the gastrointestinal tract and genital organs.
To distinguish one type of tumor from another requires a comprehensive diagnosis and consultation with an experienced doctor.
Symptoms
The initial period of the disease, as a rule, proceeds latently. Such patients may experience minor disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, which in most cases do not indicate the existence of a tumor. Further growth of the tumor is accompanied by the development of specific symptoms, the nature of which is associated with the location of the pathology.
Common signs of meningeal benign tumors include:
- disorders of the sensitive functions of vision, smell or smell;
- impaired coordination and sense of balance;
- pathology of processes of higher nervous activity. For example, patients with a brain tumor report decreased attention and concentration. At the same time, the memory and articulation of the cancer patient during a conversation also suffers;
- convulsive syndrome, which is manifested by the presence of sudden convulsions and loss of consciousness;
- abnormal contractions of skeletal muscles;
- intoxication of the body, accompanied by nausea and vomiting;
- local or general paresis of the facial facial system;
- chronic migraines;
- loss of sensation in the upper and lower extremities.
Benign and malignant formations: what they look like, what’s the difference
Tumors are formations of a benign or malignant nature. To understand what the pathology looks like, you need to look at the picture of the patients in whom it was detected and receive the accompanying comments from the doctor.
| Benign neoplasms | Quite smooth boundaries are often visible: in the absence of clear boundaries between the brain tissue and the tumor tissue, radiation examination with the use of contrast agents is recommended; |
| there are no malignant cells; | |
| the tumor does not spread to surrounding tissues and organs; | |
| compresses sensitive areas of the brain: intracranial pressure increases, edema forms; | |
| in rare cases, transformation into a malignant process is possible; | |
| Malignant neoplasms | consist of malignant cells; |
| grow quickly, penetrate surrounding tissues, and compress the brain; | |
| cause metastasis; | |
| in severe cases, germination begins into surrounding tissues, followed by destruction. |
Astrocytic gliomas
Astrocytic gliomas are malignant neoplasms affecting the frontal and temporal lobes.
There is no clearly defined boundary and they have a low MRI density compared to healthy areas of the brain.
The contrast agent does not accumulate in such a tumor; small, hollow formations are visible. Astrocytomas are:
- pilocytic - grow slowly, penetrate into surrounding tissues;
- fibrillary - grow slowly, diagnosed in people under 30 years of age;
- anaplastic malignant - rapid growth, penetration into surrounding tissues.
Anaplastic astrocytoma (with contrast, before/after)
Cysts
According to MRI results, the following cysts are diagnosed:
- Arachnoid - vesicular accumulations filled with fluid. They are formed in layered tissue membranes and on the surface of the brain.
- Colloidal - liquid spheres, visible in embryos. It is detected by chance during a routine examination with complaints of epilepsy or headache.
- Dermoid - formed from foreign tissues, diagnosed in infants. For detection, devices with a power of at least 1 Tesla are used.
Arachnoid cyst of the cerebellopontine angle on the right (with contrast, before/after)
Arachnoid cyst of the posterior fossa
Oligodendroglial tumors
They affect the frontal and parietal regions and are formed from glial tissues. Clear boundaries, sometimes merging with nearby edematous tissues. Uneven decrease in MR density of oligodendroglial tumors.
Oligodendroglioma (with contrast)
Ependymal neoplasms
Embryonic neoplasms in the cerebral ventricles. They are characterized by a round shape, clear contours, and increased density of the MR area. Does not affect surrounding tissues and is not accompanied by edema.
Choroid plexus tumors
A rare tumor that forms from vascular structures localized in the ventricles of the brain. They affect the ventricular system and impede cerebrospinal fluid circulation. Classified into:
- papillomas - formations of benign origin that do not spread to surrounding tissues;
- Carcinomas are malignant tumors with the potential to spread to the ventricular system. In patients with hereditary genetic mutations.
Choroid plexus papilloma (with contrast, before/after)
What tests show oncology?
In addition to instrumental examination methods, one of which is MRI, the development of cancer can be predicted by abnormalities in various laboratory tests.
Let's look at what changes in tests can occur during cancer:
- Complete blood count - increased ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate), decreased hemoglobin levels, imbalance in the number of mature and immature cells.
- Changes in the biochemical blood test - a decrease in the amount of total protein, an increase in the level of urea in the blood.
- Blood test for the presence of tumor markers - levels of specific proteins increase. For example, for cancer of the liver parenchyma - AFP, for prostate cancer - PSA, for stomach cancer - CA19-9. There are more than 300 special indicators recorded for a particular cancer disease. Of these, about 30 are widely used in medicine.
- General urine analysis - there may be an increase in the level of protein, ketone bodies, glucose. The urine becomes cloudy and streaks of blood may appear.
- Histological or cytological analysis - these methods help to differentiate the type of cancer. Material for research is most often taken during a biopsy.
Tests prescribed by a doctor if cancer is suspected must be taken into account in combination with other methods.
Benefits of MRI
MRI is a non-invasive procedure, the integrity of the skin and bone elements is preserved. Helps to obtain a high-quality image and monitor pathology over time.
To improve the quality of the study, contrast agents are used, which reveal the initial stages of tumor formation. Other benefits of MRI include:
- safety;
- There are no radiation exposures;
- determination of the type of formation: malignant, benign;
- assessment of the results of conservative therapy and surgical intervention;
- determination of the exact localization of the tumor, degree of spread;
- examination of the cortex, blood vessels, lining of the brain, gray and white matter, nerves.
MRI is not hampered by bone tissue. They examine parts of the brain in several planes at once, and examine the cerebrospinal fluid system in detail.
MRI for a brain tumor determines how far the pathological process has spread and analyzes the degree of damage to surrounding tissues.
An effective technique for identifying gliomas that do not accumulate contrast agent. Modern software converts MRI into a 3D model in Dicom format.
If MRI does not show a tumor, but there are objective indications of formations, additional research methods are prescribed, PET/CT
At the first symptoms of the disease, it is recommended to refrain from self-medication and consult a doctor. The earlier a tumor is detected and therapy is prescribed, the more favorable the prognosis.
Organs of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space
Resonance imaging allows you to examine the following parenchymal organs for the presence of neoplastic processes in them:
- liver;
- pancreatic (pancreas) zone;
- spleen;
- kidneys;
- adrenal glands;
- The lymph nodes.
MRI of the peritoneum is usually performed with contrast. Before the study, it is advisable to fast for 4-5 hours.
Detection of cancer of hollow organs (stomach, intestines) with MRI is impossible. For this, the CT method is used.