The spinal cord is the most important part of the central nervous system, responsible for many functions in the human body. Without proper functioning of the spinal cord, normal life activity and the functioning of all organs and systems are not possible. Its structure is specific. The spinal cord is cylindrical in shape and runs through all parts of the spine. It is located in a special spinal canal and has an unequal width along its entire length: in the neck and lumbar region it is slightly thicker than in other areas.
Due to injury to the spinal cord or compression of it, a person can develop various health problems from paralysis of the limbs to difficulties with breathing and digestion. The genitourinary and excretory, circulatory and cardiovascular systems will also suffer from damage. Moreover, this can become a threat not only to the health, but also to the life of the patient.
MRI is the only non-invasive method that allows detailed visualization of the spinal cord.
Basic anatomy and physiology of the spinal cord for understanding MRI
The spinal cord is surrounded by three membranes and is located in a special bone canal. It is formed by many vertebrae, between which there are articular discs and nerve roots.
The spinal cord has two main tasks:
- Reflex - communication with internal organs, tendons, mucous membranes, skin and ensuring autonomous operation, performing a protective function.
- Conductor - nerve fibers pass through the spinal cord to the cerebral cortex.
In some diseases (hernias, injuries), the spinal cord or its roots are compressed.
Sometimes tumors, cavities or cysts form in the tissues, and inflammation occurs. MRI scans show these conditions.
Indications and contraindications for MRI
To undergo an MRI, you will need a referral from a doctor - a neurologist or orthopedist. The study is prescribed if the following conditions are suspected:
- spinal injuries;
- osteochondrosis;
- arthritis or arthrosis of the facet joints, damage to the spinal ligaments;
- intervertebral hernia;
- cavities, cysts in the spinal cord;
- inflammation in soft tissues;
- oncology.
MRI is prescribed to monitor patients after surgery on the spine and surrounding tissues - the spinal cord is located in close proximity, so it is important to carry out timely diagnosis to exclude damage.
Patients are often referred for examination on their own initiative if they have pain and limited mobility in the spine.
We list the contraindications for the examination:
- pacemakers - they fail during the procedure;
- metal implants - create interference with image projection and cause pain;
- convulsions, increased activity - during the examination, complete immobility is required for a long time;
- severe obesity - there are restrictions on weight and size for the hardware capsule.
Relative contraindications for which MRI is prescribed with caution and under medical supervision:
- claustrophobia;
- 2-3 trimester of pregnancy;
- mental disorders;
- metal-based ink tattoos;
- the patient has an insulin pump.
Indications for testing
MRI of the spinal cord is prescribed to identify the smallest pathologies and anomalies. The method is accurate, allows you to obtain high-quality images and make a diagnosis. It is often used when other research methods have failed or are contraindicated.
When is an MRI of the spinal cord prescribed?
- to assess the condition of the spinal cord after injury;
- if there is a suspicion of malignant neoplasms;
- when there is periodic pain between the shoulder blades;
- for congenital pathologies of the spine;
- for back injuries;
- to assess compression of the spinal cord roots;
- for assessing the spine after surgery;
- chronic myelopathy.
MRI is often prescribed to clarify a diagnosis made using other diagnostic methods. Since the study is safe, it can be carried out several times in a row without harm to health. Thanks to magnetic resonance imaging, it is possible to correctly recognize the nature of the pathology and carry out appropriate treatment.
How is the examination carried out?
After preparing for the study, the patient comes to the MRI diagnostic room on the appointed day. The procedure consists of the following steps:
- the subject changes into special pajamas and shoes, removes metal jewelry;
- instructions are provided and a special button is issued, which is used in an emergency;
- the torso and limbs are fastened with belts, the patient puts on headphones and moves into the apparatus tunnel;
- Within 40-60 minutes, pictures are taken and the procedure ends.
MRI of the spinal cord using contrast agent
If an MRI with contrast is prescribed, an allergy test is performed, which involves administering a substance in a minimal amount.
If there are no skin rashes and heart problems, the patient’s well-being is not impaired - the test is considered passed.
The procedure is performed on an empty stomach, the contrast agent is administered intravenously immediately before the examination. During the injection, the patient feels cold or slightly warm, which is considered normal.
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine is a safe procedure that can be repeated many times if necessary. However, there are a number of contraindications:
- The presence of ferromagnetic and electronic implants in the human body. Under the influence of a magnetic field, the likelihood of metal objects moving and heating increases. Electronic devices may stop working.
- Claustrophobia. When you are in a closed tomograph tube, panic attacks may occur. This problem has been solved in open-type tomographs.
- Excess body weight (over 130 kg) does not allow examination in closed devices. This limitation is due to the characteristics of the device. There are modern tomographs for which this limitation exceeds the specified figure.
- MRI with contrast should not be performed on pregnant women or patients suffering from renal failure.
- The patient's condition is severe and requires physiological monitoring. In a powerful magnetic field, it is impossible to monitor and provide hardware support for patients.
Interpretation of results
Let us note the conditions that are determined from MRI images and their distinctive features.
- Compression of the spinal cord - this group includes hernias and protrusions, joint diseases. In the first case, the images will show a bulging of the disc towards the spinal canal. With arthritis, arthrosis and osteochondrosis, curvature is observed in the corresponding section, which causes painful damage to the spinal cord.
- The presence of cavities - this group also includes cysts, which are defined as dark spots with pink borders.
- Narrowing of the spinal canal - normally the diameter varies depending on the sections, reaching a maximum in the lower back, ending blindly in the sacrum. There will be a decrease in the clearance between the corresponding vertebrae.
- Vascular pathologies and their consequences are detected when a contrast agent is administered. The risk group includes strokes and heart attacks, which are reflected by increased signal in the affected area.
- Sclerosis - the images show round plaques, characterized by increased signal and accumulation of contrast agent.
- Tumors look like growths where they shouldn't be. Benign formations have smooth and clear boundaries, while malignant ones have blurred outlines.
The above describes the signs of conditions on MRI for informational purposes. Remember that the patient sometimes makes mistakes - the final conclusion is made by the doctor.
Side effects
The procedure is not without its drawbacks. During the examination, due to the use of contrast agents, side effects may develop, which are extremely rare:
- itching and rashes on the skin;
- dyspnea;
- headaches, dizziness and tremors of extremities;
- tachycardia or slow heart rate;
- nausea and vomiting, dry mouth, increased salivation.
The doctor monitors the condition during the entire study and guarantees complete health safety even if undesirable effects occur.
Making a diagnosis based on symptoms
MRI is prescribed based on symptoms. Most often, photographs are taken of the thoracic or lumbar regions, sometimes of the cervical region. After the examination, the following diseases are detected:
- strokes and heart attacks;
- damage to the membranes of the spinal cord;
- multiple sclerosis;
- narrowing of the spinal canal;
- inflammatory diseases of the paravertebral muscles;
- lesions of the nerve roots;
- combined pathologies of the brain and spinal cord.
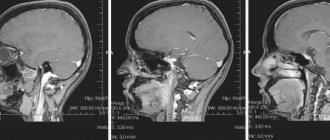
MRI of the cervical spine
Cervical spine, sagittal projection
Cervical spine, frontal view
Cervical spine, axial projection
It should be noted that diseases of the cervical spine and lumbosacral spine are noted by experts as the most common.
Indications for MRI of the cervical spine:
- deforming spondylosis, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- protrusion and herniation of intervertebral discs of the cervical spine;
- metastases of various tumors in the cervical spine;
- spinal canal stenosis;
- injuries of the cervical spine (fracture, dislocation, displacement of vertebral bodies);
- short neck syndrome (Kliepel-Fayle syndrome);
- the presence of various pathological changes in the cervical spinal cord.
CT or MRI scan of the spinal cord
Both methods detect diseases of the spine, but differ in the principle of action:
- - gives a high dose of radiation, therefore it is prohibited for children and pregnant women. The images do not show changes in soft tissues, but they clearly show the condition of bone structures that could injure the spinal cord. It is carried out quickly, the procedure takes a few seconds.
- MRI is safe and detects changes in soft tissues with high accuracy. An indispensable study for inflammation, tumors, hernias, the presence of cysts and cavities. It does not detect fractures well; the procedure requires a long stay in a confined space.
Differences between CT and MRI
How is an MRI performed?
During the test
You lie down on a movable table that slides into the MRI machine. The technologist is watching you from another room. You can talk to a person through a microphone.
If you have a fear of closed spaces (claustrophobia), you may be given a sedative. Most people tolerate the procedure easily.
An MRI machine creates a strong magnetic field around you, and radio waves are directed towards your body. The procedure is painless. You don't feel a magnetic field or radio waves, and there are no moving parts around you.
During an MRI scan, the inside of the magnet makes repetitive tapping, banging, and other noises. Modern devices have a built-in noise reduction system.
In some cases, a contrast material, usually gadolinium, will be given intravenously. Contrasting material enhances certain details. Gadolinium rarely causes allergic reactions.
An MRI can take anywhere from 15 minutes to an hour. You should not move so that the image does not turn out blurry.
During a functional MRI, you may be asked to perform a number of small tasks, such as moving your thumb or answering simple questions. This helps pinpoint the parts of your brain that control these actions.
After the test
You can resume your normal activities immediately after the scan.
Prices for MRI of the spinal cord
The average cost of the procedures is: 6,000-7,000 rubles for examination of one department, 14,000 rubles for a comprehensive MRI of the spine.
MRI is a harmless and effective method that does not require careful preparation. Before the examination, it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations and remain still during the procedure.
When the rules are followed, clear images are obtained that help identify diseases of the spinal cord and the conditions that provoked the damage.
When is it necessary to do an MRI of the spine?
The human spine is the support of the whole body, so its health must be taken very seriously. Advanced diseases of this organ tend to worsen, and if incorrectly diagnosed or without proper treatment, spinal diseases can lead to disability.
Indications for MRI of the spine:
- severe pain in the neck, shoulder blades, lower back, sacrum;
- periodic painful sensations in the heart area of unknown etiology;
- diagnosed intervertebral hernia;
- tingling and numbness in the hands and feet;
- lack of positive dynamics after a course of conservative treatment of such pain syndrome;
- inflammatory processes in the spinal cord and spine (myelitis, spinal abscess);
- suspicion of demyelinating diseases (multiple sclerosis, etc.) myelopathy; dynamic monitoring of their course and response to treatment;
- back and spine injuries;
- Tumors of the spinal cord, intervertebral discs, etc.
- congenital malformations of the spinal cord;
- herniated intervertebral discs;
- disorders of spinal circulation (acute and chronic) and suspicions of them;
- monitoring the results of previous spinal surgery;
- spinal tuberculosis;
After falls, blows, bruises and other mechanical injuries, it is imperative to do a tomography to exclude serious injuries that could lead to the patient’s disability.