In what cases is it necessary to do an ultrasound for ovulation?
Any diagnostic procedures are prescribed if there are complaints or suspicions of a certain disease. Ultrasound for ovulation is indicated for those women who are faced with problems conceiving. Most often, the procedure is prescribed a year after the start of pregnancy planning. This is exactly how much time is given to a healthy couple to conceive naturally. The method of determining ovulation by ultrasound is considered the most effective. Indications for the procedure are as follows:
- Irregular menstruation;
- Preparatory activities for IVF;
- Long absence of pregnancy;
- Amenorrhea;
- Ailments accompanied by hormonal disorders.
Does ultrasound show ovulation? Ultrasound for ovulation is done over several cycles, since 1-2 anovulatory cycles per year are considered normal. You can talk about infertility only after long-term observation of follicle growth. Research helps not only to identify the problem, but also to determine the nature of its origin. Ovulation on ultrasound is determined by certain signs.
Indications for the procedure
There are many methods you can use to track ovulation. The maturation of the egg is determined by scheduling basal temperature measurements or by counting days on a calendar. But the above methods are not always informative for a woman who has an irregular cycle or has problems with hormones and metabolism.
An ultrasound aimed at determining the ovulation cycle gives an accurate result, which in the future is necessary for girls who want to become mothers.
Research is also necessary in the following cases:
- control over follicle maturation in case of unsuccessful conception, after miscarriage or spontaneous abortion;
- preparation for IVF;
- find out the reason for the absence of menstruation (with amenorrhea);
- infertility therapy when trying to get pregnant after several years of trying with a partner;
- irregular periods due to late ovulation or due to problems with the reproductive system;
- detection of hormonal imbalances.
Additionally, read the article: what is folliculometry.
Corpus luteum on ultrasound after ovulation
The corpus luteum is located in the uterus, and not, as some girls and women think, in the fallopian tubes or anywhere else outside the ovaries. It always strictly develops exclusively on the ovary where ovulation occurred. A woman has two ovaries. Follicles grow on both at the very beginning of a new cycle, but there is usually one dominant one, the rest undergo reverse development. The dominant follicle is located either on the right or left ovary.
Sometimes a woman develops two corpora lutea at once. Due to double ovulation, two dominant follicles burst at once, so there is a possibility of multiple pregnancy. The phenomenon of double ovulation is not a common phenomenon, because the body saves the follicular reserve, since it is not replenished and renewed in a woman.
The corpus luteum is visible in the area of the ovaries and looks like a small sac, an anechoic formation. There is no echogenicity because there is a certain amount of liquid inside the temporary gland. The gland is formed immediately after ovulation, but it can be seen on an ultrasound only 3-4 days after it, since the size of the corpus luteum at the initial stage of formation is very small.
Anechoic formation - description
The doctor measures the diameter if there is a temporary gland in the right or left ovary. The diameter indicator shows how well the corpus luteum corresponds to the stage of its development. To assess the performance of the gland, the thickness of the endometrium is measured.
Endometrium - description
results
On the scanogram of the ovaries obtained during the first ultrasound, you can see several small anechoic formations - follicles. By the time of the study, the dominant follicle has already been determined, standing out among others in its larger size, reaching 0.8–1.2 cm. Simultaneously with the examination of the appendages, the thickness of the endometrial layer of the uterus is assessed, which normally should be 0.6–0.8 cm .
The second scan allows you to evaluate the growth rate of the dominant follicle, the daily growth of which is about 2 mm. Depending on the time interval between procedures, the diameter of the follicle reaches 1.6–1.8 cm. The thickness of the endometrium at the time of the second examination should be 1.5–1.7 cm. Evidence of ovulation by ultrasound during the third scan is the disappearance from the field vision of an anechoic formation and the appearance of fluid in the retrouterine (Douglas) space.
At the site of the follicle, the corpus luteum is determined, and the ultrasound characteristics of the endometrial layer also change. If it was possible to visualize the dominant follicle immediately before ovulation, then, first of all, its size is assessed, which is one of the indicators of the usefulness of a mature egg. The normal size of a preovulatory follicle should be 2.0–2.4 cm.
Is it possible to determine ovulation by ultrasound?
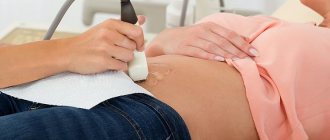
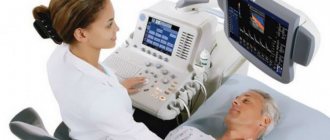
Of course, ultrasound is one of the most accurate methods for determining ovulation. Typically, a transvaginal or ultrasound probe is used during the procedure. Both methods are painless. The transvaginal method significantly expands the boundaries of diagnosis and gives more accurate results. When using a transvaginal sensor, ultrasound occurs. Before the procedure, care should be taken to clean the external genitalia to prevent pathogenic microorganisms from entering the vagina. The procedure is performed with an empty bladder. If you have bloating, you need to take a drug that reduces gas formation. It is not advisable to have sex before the procedure.
How is it carried out?
Folliculometry is performed transvaginally, so the sensor can be brought as close as possible to the ovaries. The device is lubricated with gel and inserted into the vagina. The data is displayed on the monitor - the doctor is interested in the largest follicle in which a viable egg should mature.
The research involves several stages. As a rule, during one cycle a woman should undergo an ultrasound scan for ovulation 2-3 times.
- With a regular menstrual cycle, it is easier to plan the first visit: you can clearly visualize the dominant follicle (its size is about 1.5 cm) 4-5 days before the middle of the cycle (with a standard cycle of 28 days, this is 8-10 days after the start of menstruation) . If menstruation is irregular, ovulation may occur either earlier or later. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo the first folliculometry on the 3rd day of the start of menstruation, which will provide an opportunity to assess the dynamics of the process and prescribe the next procedure.
- The second monitoring is carried out 3 days after identifying the dominant follicle. This time it is necessary to determine whether it is developing and how correctly this process is proceeding. Normally, the follicle should grow to at least 2 cm. If it stops developing or decreases, then the next ultrasound is scheduled for a new menstrual cycle.
- If the follicle develops, another test is usually done to make sure that ovulation (the rupture of the follicle and the release of an egg into the fallopian tube, which carries it down to the uterus) has occurred. This time, the doctor must make sure that the corpus luteum remains in place of the follicle, and that there is a small volume of fluid in the uterine cavity.
| No. | Service name | price, rub. |
| 1 | (Uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, ovaries, retrouterine space). Transvaginally. // With Doppler analysis. | 1500 // 2100 |
| 2 | Ultrasound of the pelvis. (Ovaries (appendages), uterus, bladder). Transabdominal. // With Doppler analysis. | 1100 // 1700 |
| 3 |
Ultrasound of the pelvis. (Uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, ovaries, retrouterine space, bladder). Complex - transvaginal and transabdominal. // With Doppler
Folliculometry - 1 study Monitoring follicle maturation.
Hysterosalpingoscopy with recording on DVD. Ultrasound of fallopian tube patency - ultrasonic echohysterosalpingoscopy.
When is the best time to do an ultrasound for ovulation?
The gynecologist prescribes several sessions, each of which is carried out 2-3 days after the previous one. The study reveals everything from the maturation of the follicle to the formation and development of the fertilized egg. Usually 4 procedures are done. Let's look at the example of a 30-day cycle:
- 10th day of the cycle. The first procedure is carried out 3-4 days before the expected rupture of the follicle. During this period, the dominant follicle is already visible.
- 12-13 days. Ultrasound shows the presence of a dominant formation in the ovary.
- 15-16 days. The onset of the ovulatory phase. The phase lasts only a day, after which the egg can no longer be fertilized.
- 18-19 days. Confirmation of the release of the egg into the uterine cavity. A formation with blurred contours—the yellow body—will be clearly visible on the monitor.
Possible violations
It happens that during folliculometry, the doctor discovers pathologies that are associated with ovulation. For example:
- Regression. This is the process of growth of a dominant follicle to a specific size. However, at a certain point the growth stopped and went in the opposite direction. Ovulation never occurred.
- Peristency is the normal development of the follicle, but at a certain point the egg was unable to rupture the follicle and come out. In this case, there will also be no ovulation.
- Follicular cyst. This is a consequence of peristency. That is, the follicle has matured, the egg has not ruptured it, and fluid has accumulated due to the intact follicle.
- Luteinization of the follicle. This is the formation of the corpus luteum, but without rupture of the follicle. This phenomenon occurs due to hormonal imbalance or poor ovarian function.
- There are no follicles. On an ultrasound, the doctor may find that the follicles are not developing at all. Of course, in this case the process of ovulation is impossible.
If such deviations are detected, folliculometry to control conception is postponed until the deviations are eliminated. Then you can start monitoring conception again.
How is ultrasound performed to monitor ovulation?
Ultrasound for ovulation is performed according to a certain algorithm. The diagnosis is made only on the basis of several visits during 1 menstrual cycle. On the monitor, a woman can see with her own eyes what the process of oocyte maturation looks like. When to do an ultrasound to determine ovulation, you need to determine based on the length of the cycle. With the standard duration of the menstrual cycle, the first visit occurs on the 12th day. If the cycle is longer than 28 days, then the ultrasound room must be visited on the 14-15th day. With a cycle lasting more than 35 days, ovulation is late. Therefore, an ultrasound must be done on days 18-19.
More details about folliculometry.
A woman should have an ultrasound scan for ovulation every 2-3 days. During this period of time, the follicles increase by 5-6 mm. In parallel, the increase in endometrial thickness is monitored. Ultrasound for ovulation allows you to detect the dominant follicle. It differs from the others in its volume. The egg becomes mature when the follicle size reaches 18 mm. This means that in 1-2 days the woman will ovulate.
In order to successfully conceive, it is advisable to practice sexual intimacy these days. The endometrium should reach 10-13 mm by the time the oocyte matures. The moment of ovulation on ultrasound looks ambiguous. The dominant follicle disappears, which may indicate its rupture. But such a sign may also indicate luteinization. The follicle deflates, but the oocyte does not come out. In this case, pregnancy becomes impossible. An ultrasound after ovulation will help determine whether the follicle has ruptured.
Methods for determining ovulation
Since the receipt of data on the nature of conception and the regulation of the menstrual cycle, scientists have proposed various ways to control ovulation. To tell the truth, many of them, even very old ones, have not lost their relevance to this day.
- Cervical mucus tension method. Even ancient healers noticed that under the influence of some factors in the middle of the cycle, a woman’s vaginal discharge takes on a special character. This is a profuse, transparent mucous discharge, very similar to the white of a raw egg. The cervical mucus tension method is based on the fact that at the peak of ovulation, the combination of sex hormones determines the maximum viscosity of the mucus - that is, a drop of mucus from the cervix can be stretched between the legs of the tweezers by 5 centimeters or more.
- The “pupil” symptom is based on the same cervical mucus. Considering the large amount and high viscosity of mucus on the day of ovulation, gynecologists, when examining a woman in the mirror, noticed an interesting phenomenon - the cervical canal was stretched by a clot of mucus and looked like the pupil of an eye.
- The symptom of crystallization of cervical mucus was discovered a little later, with the invention of microscopes and magnifying devices. One of the gynecologists came up with the idea to study cervical mucus under a microscope. This is how another interesting phenomenon was discovered - the fern symptom. At the peak of ovulation, under the influence of hormonal levels, the mucus dried on the glass formed a picture resembling a fern branch. When trying to get such a picture on other days of the menstrual cycle, such beauty was not found.
- Basal temperature tests. This is a labor-intensive and discipline-requiring, but extremely accurate method for determining ovulation and the fullness of the phases of the menstrual cycle. Basal (rectal or vaginal) temperature is measured daily with a regular thermometer in the anus or vagina. Measurements should be taken every day in the morning after a night's sleep, without getting out of bed. The obtained data is presented in the form of a graph. Normally, an ovulatory surge is considered to be a temperature difference of more than 0.4 degrees Celsius . Thus, ovulation is the highest peak temperature on the graph.
- Ovulation tests. These test strips are freely available in many pharmacies and are relatively inexpensive. The principle of operation of ovulation tests is similar to pregnancy tests, that is, the test reagent evaluates the concentration of certain hormones characteristic of the ovulatory peak in the urine.
- Ultrasound folliculometry or ultrasound monitoring of ovulation. This is a modern, very reliable and indicative method of monitoring ovulation.
Signs of ovulation on ultrasound
An ultrasound after ovulation can show signs that the follicle has burst. They are assessed not separately from each other, but together. Ovulation on ultrasound will be detected in the appendage where the dominant follicle was formed. It is necessary to maintain optimal levels of progesterone in the body if conception occurs. Ultrasound for ovulation allows not only to determine its presence, but also to assess the quality of blood flow. Already at this stage, the doctor can tell how high the probability of conceiving is.
An ultrasound after ovulation will also show a small amount of fluid behind the uterus. It resolves approximately 2-3 days after the follicular membranes rupture. The remaining follicles will begin to regress immediately after visualization of the dominant one. After ovulation they will completely disappear.
Pathologies
Along with stating the fact that ovulation has occurred, ultrasound also helps to see pathological conditions leading to reproductive dysfunction. One of the signs of the presence of anomalies in the development of the follicle is considered to be an increase in its diameter, in the preovulatory phase, by more than 2.5 cm. As a rule, with a large follicle, the ratio of hormones produced is disrupted, which leads to the premature formation of the corpus luteum before ovulation (luteinization of an unovulated follicle) .
Detection of abnormalities leading to ovulation disorders depends on what day the study is carried out. The absence or insufficient size of the dominant follicle detected during the first studies indicates hormonal deficiency (endocrine infertility). If at the third and fourth examination, performed to determine the fact of ovulation, a non-ovulated follicle is still detected, they look at its size, the presence of the corpus luteum and the level of progesterone and estrogen.
Preparation
The only thing recommended before folliculometry is to empty your bladder. Otherwise, the study does not require any preparation.
You can make an appointment for an ultrasound of the follicle, find out the cost of the procedure at the medical office and clarify any questions by calling the phone number listed on the website. Our clinic employs experienced gynecologists who will advise you on the results of the examination.
| 1900 // 2500 | ||
| 4 | (Uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, ovaries, retrouterine space). Transrectal. TRUSY for girls. // With Doppler. | 1900 // 2500 |
| 5 | 1000 | |
| 6 | Folliculometry with measurement of endometrial thickness - 1 study | 1200 |
| 7 | Folliculometry with measurement of endometrial thickness - 4 visits during the cycle (from the 8th day of the cycle, every 2-3 days) | 2900 |
| 8 | Ultrasound of the pelvic vessels (Doppler study of blood flow in the uterus and appendages). Transvaginally. | 1700 |
| 9 | 4900 | |
| 10 | Ultrasound before and after medical abortion for 14 days. (Included in the cost of medical abortion). | For free |
How does the diagnostic process work?
After the attending physician has determined the date of the study, the woman must come on the appointed day. The procedure itself is very simple, it can be carried out in three ways:
- transvaginally. Then the capsules are examined through the vagina. A condom is placed on the sensor, after which it is inserted inside. After a while, the doctor can assess the condition of the internal organs. By the way, this method is not used if the girl is a virgin or pregnant;
- transbdominal, that is, externally. A special gel is applied to the pubic area, and then a special device is moved over it. A little preparation is needed here, because the scan is done on a full bladder. By the way, this method is considered less informative;
- transrectally, that is, through the anus. On the screen, the ultrasound specialist sees the condition of the ovaries. You should immediately warn about the high degree of pain of this method. It is used if the patient is elderly or a virgin.
When a computer analysis is prescribed for the purpose of pregnancy planning, the first method is used.