A little about platelets
We need blood cells such as to maintain normal blood clotting. These are anucleate cells that are produced by the bone marrow.
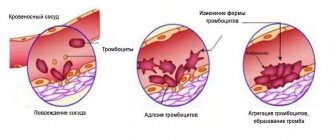
It is thanks to platelets that a blood clot forms at the site of a ruptured vessel. This clot (thrombus) clogs the lumen of the vessel, and the bleeding stops.
Important
: The lower acceptable limit for platelet levels in adults is 100 g/l, the upper limit is 400 g/l.
If the number of these blood cells exceeds the upper norm, then thrombocytosis is noted.
This means that the blood “thickens” and blood clots can form in the vessels, which narrow the lumen of the veins and arteries.
With low platelets (), blood clotting worsens, bleeding increases, and bruises often form at the slightest impact.
What does abnormal blood test mean?
Indicators of platelets and hemoglobin are often considered in combination, because they are related and indicate the state of the hematopoiesis process.
The most common abnormalities are high platelets and low hemoglobin.
Why does the platelet count increase?
- Malfunction of the bone marrow
- Side effect of taking certain medications
- Complication after an infectious disease,
- Autoimmune processes.
Causes of drop in blood hemoglobin
- Long-term course of diseases
- Bleeding
- Problems in the gastrointestinal tract,
- Toxicosis,
- Dehydration of the body
- Women are in the postmenstrual period.
High platelets in combination with low hemoglobin most often indicate not just iron deficiency anemia, but the presence of a chronic disease.
However, it should be taken into account that in women during menstruation, the amount of hemoglobin decreases due to blood loss.
At the very end of menstruation, platelets increase. This is a normal reaction of the body that stops bleeding.
What to do with high platelets and low hemoglobin
If a deviation from the norm is detected in a patient for the first time, and there are no obvious reasons to suspect a pathological condition, the test must be repeated.
Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia, a sign of which is most often an imbalance such as low hemoglobin, may be a cause for concern.
Symptoms of anemia
- lethargy,
- Drowsiness,
- Noise in ears,
- Pale skin
- Deterioration of the condition of nails, hair and skin,
- Dizziness.
Since low hemoglobin with high platelets may indicate problems in hematopoiesis, the patient is referred for consultation and examination to a hematologist. If no pathology is identified in this area, then an examination by other specialists is prescribed.
Possible causes of high platelets with low hemoglobin
- Infectious or autoimmune diseases,
- Treatment with hormonal drugs, antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,
- Liver failure.
Thus, if a person has recently suffered some kind of infection, then a change in blood counts may be a consequence of it. In this case, the results must be taken into account as a whole.
What is blood?
First you need to answer the question, what is blood? Blood is a kind of liquid connective tissue that circulates within the volume of blood vessels, which can be graphically compared to a closed system of “tubes.” Blood contains a liquid intercellular substance - plasma, as well as morphological elements. Blood is made up of elements that include: red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets - all of which are produced in the bone marrow of the human body. Both plasma and the structural elements of blood perform many and clearly defined functions.
The blood distributes oxygen throughout the body and releases carbon dioxide in the lungs. It transports electrolytes, hormones, proteins, nutrients, metabolic products, has the ability to coagulate, and participates in the defense of the body (immune cells are also carried by the blood).
Blood has a strictly defined composition; it is far from a random mixture of various chemical compounds. Moreover, every substance in the blood, every electrolyte, chemical compound, protein, hormone is contained in a strictly defined quantity: normally from - to; no more, no less. Consequently, the doctor, having examined the patient, based on the clinical picture of the disease, performing a blood test, can easily assess deviations from the norm and associate them with specific pathologies. To illustrate: too low hemoglobin level and red blood cell count (with a clinical picture) - anemia. Of course, sometimes a number of other tests and examinations are necessary to make a diagnosis.
Low hemoglobin and platelet counts
Important
: Low hemoglobin with high platelets may be a temporary condition of the body and a normal reaction to a previous illness.
If low hemoglobin and low platelets are detected, the situation is much more serious.
Accompanying such indicators with a low number of leukocytes means that the body is weakened and is unable to resist negative factors.
If platelets and hemoglobin are very low, total pathological processes have occurred in the body.
This blood condition is observed in severe poisoning, after certain courses of chemotherapy, in the presence of irreversible changes or metastases in the bone marrow, as well as in renal failure.
Based on the results of the examination, treatment and measures to normalize blood counts are prescribed.
In addition to iron-containing medications, experts also prescribe folk remedies, as well as lifestyle optimization.
How to increase hemoglobin
- Taking iron supplements
- A sufficient amount of meat and liver in the diet,
- Walks in the open air,
- Strong physical activity
- Adequate sleep and rest.
Reducing hemoglobin
How to reduce hemoglobin in women and men? This can be done using dietetics and folk remedies, as well as medications.
Dietetics
It would be logical to assume that increased hemoglobin in women and men can be reduced by those foods that cannot be eaten if you are anemic.
It is forbidden:
- meat, offal (tongue, liver), game, smoked meats;
- beets, red vegetables and fruits, radishes;
- caviar;
- fast foods;
- full-fat milk, butter;
- cereals: buckwheat, rolled oats;
- soda;
- sweets;
- drink and drink;
- smoke.
Conclusion: you should not eat any foods that contain large amounts of iron and vitamin B12.
Can:
- seafood;
- lean fish;
- legumes;
- salads and vegetables with green fruits;
- cottage cheese;
- sour cream, kefir and other fermented milk products;
- chicken;
- drink more clean water (you remember about the water diet).
Dishes should not be fried, only boiled, raw, stewed or baked.
The table will help you navigate through foods containing iron. We choose those that contain less of this mineral.
Folk remedies
It is useful to know how to reduce hemoglobin in the blood of men or women using folk remedies, and not just food.
- A long time ago, they practiced a method such as bloodletting (by the way, it is still used quite actively now - there was an article about hijama on the website). In this case, you can contact him. You can also use leeches. They not only thin the blood, but also normalize hemoglobin levels. Just don't go to the swamps. This procedure can be done safely in clinics or medical centers.
- There are also good reviews about the effect of mumiyo, a resin that is mined in Central Asian caves. Dosage – 10 days, one tablet before bedtime.
- Become a donor. Regular donation of blood for the benefit of medicine will also benefit the sufferer.
- Salads of woodlice, squash and fireweed. We take one part of each plant, cut them and season with natural yogurt or kefir. For variety, you can also put white meat (breast) or cottage cheese there.
Official medicine
If you are wondering how to quickly lower hemoglobin in the blood, then there is only one answer - you need to consult a doctor for medical help. Drugs that thin the blood and bring its clotting back to normal will help:
Electrophoresis is very rarely prescribed. Under the influence of current, excess red blood cells are broken down and removed from the body.
It is difficult to say what is more dangerous – increased or decreased hemoglobin. But in both cases it needs to be normalized in order to live, work and enjoy life.
Increased hemoglobin and decreased platelets
A slight increase in hemoglobin levels, as a rule, is not a cause for concern, but too high levels indicate possible problems in the heart or blood vessels, and may also be a sign of a developing malignant neoplasm.
For this reason, if high hemoglobin is detected, consultation with a cardiologist and oncologist is necessary. Also, increased hemoglobin levels in the blood occur in patients with diabetes.
High hemoglobin and low platelets are uncommon and indicate the presence of concomitant pathologies in the bone marrow.
A routine blood test always requires careful attention, because it allows you to quickly notice problems in the body if there are deviations from the norm and take the necessary measures in a timely manner.
The main element of the human body, which is considered one of the most important and ensures many metabolic processes, is blood. It has a complex multicomponent structure consisting of hemoglobin, red blood cells and platelets. Depending on age characteristics, each has its own standards, and deviation from them is fraught with the development of serious diseases and pathologies. Thus, increased hemoglobin in children is a reason to seriously concern themselves with their health and undergo related tests.
Systematic monitoring of the state of the blood is necessary, because having discovered a negative process in its very inception, it will be much easier to deal with it than with an advanced one.
The main component of hemoglobin, and it itself supplies oxygen to all human organs and cells of the body. The norm for children is considered to be a hemoglobin level of 89-220 g/l, and differs in different age categories. In children under 12 months, this figure is the highest, but over time it normalizes and stops at 110-150 g/l. However, it is not a good sign in a child and confirms the development of some pathological processes. But what does it mean?
Did you know that in the waters of Antarctica there is an Ice fish, it is the only animal in the world with a backbone, whose blood completely lacks the declared components.
An increased level of hemoglobin in the blood of children reveals a disruption in the functioning of the hematopoietic system. In addition, problems may be in the heart or lungs, insufficiency may develop, or congenital abnormalities may be detected.
And also the problem of increased hemoglobin can be detected in insufficient intestinal permeability, or with very severe burns, when an increase in the oxygen content in the tissues is necessary for regeneration. The most dangerous thing is that this high hemoglobin level in a child may indicate cancer.
What reasons could there be and what is the reason for the increase in hemoglobin in the child’s blood? And with the fact that in case of anomalies in the body, children’s immunity is extremely active.
One of the alarm bells when you should definitely consult a doctor and take blood tests will be increased fatigue of the child, a constant desire to sleep, tearfulness, unnatural pallor or, conversely, redness of the skin.
They play a huge role in the activities of the entire human body. These red blood cells transport oxygen and amino acids throughout all systems, and also help remove carbon dioxide. Their work is directly related to hemoglobin. In children, normal red blood cell counts range from 3.4-5.4 * 1012/l; in newborns, this figure is increased and decreases over time.
Simultaneous hemoglobin levels in the blood detected during diagnosis indicate problems in blood circulation.
The growth of red blood cells and an increase in hemoglobin in the blood may indicate due to a lack of water in the tissues, problems with the lungs, or heart defects. They can also increase during the adaptation of the child’s body to new conditions.
Experts distinguish between total and relative growth of red blood cells and hemoglobin. If complete, Vex disease may develop, followed by chronic disease. But the relative increase also occurs due to a decrease in the total amount of plasma.
Necessary diagnostics
The main method of diagnosis is a detailed blood test. One study will not be enough; it will have to be repeated a couple more times. This is done to eliminate errors and omissions. They rent it out at intervals of several days. The doctor should prescribe additional diagnostic tests.
Great importance is attached to the amount of serum ferritin. This protein contains iron, its content increases in the presence of inflammation. A hematologist will most likely refer such a patient for an ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs. Women will have to visit a gynecologist, and men - a urologist. A colonoscopy may also be required. It is done when there is a possibility of pathologies in the intestines. The patient will need to monitor their temperature for a week. After receiving all the results, the doctor will be able to make a final diagnosis.
Simultaneous increase in hemoglobin and platelets
Another equally important component is that cells without nuclei are small in size. In children, depending on age, the norm should be 100-450 units/μl. A simultaneous increase in hemoglobin and platelets in children should also convince parents to consult a pediatrician as soon as possible.
Usually marks an increase in hemoglobin. This happens when an infection, pathogenic microorganisms enter the child’s body and negative processes begin. The growth of a pair of these indicators is affected by developing tumors, including malignant ones. However, platelet growth may be affected by certain medications, such as hormones used to treat autoimmune diseases.
To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor needs to take these two indicators into account. Indeed, against the background of this clinical picture, thrombocytosis can still develop; it occurs due to dehydration of the body, which thickens the blood.
How to reduce
However, general recommendations for reducing hemoglobin in the blood would be to minimize the intake of an abundance of meat protein - chicken, liver and offal, plentiful consumption of clean drinking water for, reducing iron-fortified foods in the diet - pomegranates, buckwheat and others, adding fish and plant products that reduce hemoglobin - dairy and fermented milk products, pasta, milk chocolate.
It is necessary to eat less fatty foods, as they provoke the formation of blood clots in the blood vessels. Seafood is very useful for such conditions, as it strengthens the walls of blood vessels and helps dilute the blood. However, for the normal functioning of the body, obtain protein from legumes and dietary white chicken meat.
No matter what age the child is, it is important to regularly visit the treating pediatrician and sometimes take blood tests to determine the level of hemoglobin, including platelets and red blood cells.
If you identify problematic indicators in time, you can avoid dangerous consequences in the near future. Parents must remember that they are responsible for the health of their children.
Video - Dr. Komarovsky about the causes of increased hemoglobin:
When examining your blood, you should definitely pay attention to high platelets and low hemoglobin - the reasons can be either the most trivial or very serious. Every person donates blood at least several times in their life. This is necessary to determine the state of his health and identify possible violations. Without blood tests, a correct diagnosis is impossible. And sometimes analysis is necessary to monitor the treatment being carried out.
High hemoglobin. Happiness or danger to health
Those suffering from anemia will say: “Lucky guys, your hemoglobin is elevated. This means your head is not spinning, you have enough strength to turn the earth over even without a support point.” Is it so? Is it possible to be jealous? If hemoglobin in the blood is increased, what does this mean?
The level of red blood cells in the blood cannot be constant even in a healthy person. If you get injured or your monthly cycle begins, your hemoglobin drops. Everything has healed and ended - he can return to normal again. We dealt with this in the previous article. But something else is surprising: every third person has increased hemoglobin. What is the danger or is it not worth worrying about?
As a result of an increase in hemoglobin over a long period, deterioration in many parameters is observed:
- disorder in the functioning of the kidneys and genitourinary system: colic, pain, cystitis, etc.;
- visual acuity decreases;
- the skin becomes pale, in some even yellowish;
- a person gets tired quickly and wants to sleep all the time. This has already been discussed somewhere, hasn’t it;
- complete or partial lack of appetite.
But all these consequences are superficial. But the real danger is much more serious. High hemoglobin - why is it dangerous? Increased red blood cells make the blood thicker. In case of wounds, it stops quickly, and this is a definite plus. If you look at it from a different angle, the circulation of viscous blood is slowed down, which means that the heart and internal organs are not receiving enough oxygen. And low speed means plaque settles on the walls of blood vessels, causing blood clots to form. The result is a heart attack, heart attack, stroke, thrombosis.
When and why do blood counts change?
In some cases, even in infants, a general blood test reveals high platelets and low hemoglobin - the reasons may lie in a systemic, infectious or functional disease. Platelet levels may increase in women during pregnancy or before the start of monthly menstruation, and a decrease in hemoglobin will be noted. This condition is physiological and should not cause concern if after some time the indicators return to normal.
In all other cases, reduced hemoglobin with high platelets requires a more thorough examination.
Especially if you experience symptoms such as:
- weakness, dizziness, lethargy;
- tachycardia;
- sweating;
- pale skin;
- sudden weight loss;
- brittleness of hair and nails;
- fainting.
If, with two or more of the listed signs, a general blood test shows high platelets and low hemoglobin, there is every reason to consult a doctor and begin an examination.
Thrombocytosis - what is it?
If, according to a blood test, a patient has low platelets, then they speak of the development of a pathology such as thrombocytopenia. This is evidence that there are not enough cells in the blood responsible for its clotting. As a rule, hemoglobin is also reduced, that is, the causes of this condition are anemia. High hemoglobin is much less common, which, in principle, is no less dangerous and also indicates serious problems in the body.
But there is also a condition opposite to this, when the level of platelets, on the contrary, is increased - this is thrombocytosis. In this case, blood clots form in large veins and arteries, which can partially or completely block the lumen of the vessel. This condition is considered very dangerous: if the clot breaks off, travels along with the bloodstream to the coronary artery and blocks it, the patient will die.
Why does thrombocytosis develop?
The reasons may be as follows:
- Dysfunction of the bone marrow, which produces platelets.
- Acute stage of autoimmune diseases.
- Side effect of certain medications.
Platelet levels may be elevated after a severe infection. In this case, you need to wait some time and take the test again. If the result is the same, measures should be taken to.
Platelets (PLT)
platelets in the blood
The third group of morphological composition of blood is platelets. These cells, at the right time (for example, after an injury), connect with each other and form a blood clot, which prevents the flow of blood from the damaged area of the blood vessel.
The standard is 150,000 to 400,000 platelets per mm3 of blood.
More often, thrombocytopenia (thrombocytopenia) is associated with thrombocytopenia caused, for example, by damage to the bone marrow in which platelets are produced (due to the adverse effects of certain drugs on the bone marrow, infections or cancerous infiltrates).
In addition to the indicated number of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets, there are other names on the computer printout. These are hemoglobin (HGB) and hematocrit (HCT), as well as MCV, MCHC and MCH.
What do these letter abbreviations mean?
What does low hemoglobin mean with high red blood cells?
Such indicators are a typical sign of iron deficiency anemia. If they occur periodically (in women under certain conditions), then no special treatment is required to increase hemoglobin. It is enough to adjust the diet by including protein foods and vitamins, as well as normalize the daily routine (you need to get proper rest).
If this condition is constant, we are talking about the development of a chronic disease. To determine which one, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination and a series of tests. First of all, the patient should be examined by a hematologist. If he does not find any abnormalities in hematopoiesis, the patient is referred to other specialists.
The causes of low hemoglobin and high platelets can be the following diseases:
- Chronic gastritis and pancreatitis.
- Phlebeurysm.
- Chronic vitamin deficiency.
This condition is typical for patients who have recently undergone major surgery. In women, thrombocytosis combined with anemia is a reason to consult an endocrinologist. The fact is that during menstruation a woman always loses blood, hemoglobin decreases - this is natural. To protect the body from further blood loss, platelets begin to be actively produced, which is why thrombocytosis develops. But all these are temporary phenomena, and deviations from normal indicators should not be significant. Otherwise, hormonal disorders may be suspected, so intervention by an endocrinologist is needed.
In what cases are platelets elevated? What does it mean? Such questions arise in every patient who has received a test that shows elevated platelets.
When an increased level of platelets in the blood is detected, the shape of the platelets is first assessed. Most of the bodies of men and women contain mature cells, and only a percentage are young. Elevated levels of platelets in their juvenile form usually appear after severe blood loss or surgery.
However, an increased number of platelets in the blood may indicate various blood diseases, including tumors. A sharp increase is observed in diseases of the housing and communal services, liver or joints. The indicator is slightly lowered or increased due to inflammation. There are even a number of medications that can increase the rate in men and women.
When platelet levels are low in men or women, this is perceived as an alarming symptom.
The normal level in men should not be below 200 × 109 per liter of blood. Women, unlike men, may experience a lower rate during menstruation, and this will also be considered a variant of the norm.
When the reading is low, men and women are at risk of bleeding. Many cases of leukemia have been identified in conjunction with a reduced platelet count. Cancerous tumors in the bone marrow also cause these cells to shrink. This is due to improper functioning of the bone marrow. The rate may be reduced in case of cirrhosis of the liver, chronic and acute viral hepatitis, malfunction of the thyroid gland, or viruses.
Normal leukocyte level during pregnancy
norm of leukocytes, erythrocytes and leukocytes
Pregnancy is a special condition of a woman associated with dramatic changes in the body. Changes affect many vital systems, especially the circulatory system. It is worth noting the change in the level of leukocytes contained in the blood. It fluctuates throughout life, increasing in accordance with increasing age. The same thing happens during pregnancy.
Pregnancy is usually divided into 3 stages. In medicine they are called trimesters. For each of these trimesters, leukocytes and red blood cells should be normal. Any significant deviation from the norm indicates the appearance of some kind of inflammation in the body.
Combination with other indicators
Often an increase in platelets is combined with an increase in ESR. Among the reasons that simultaneously increase both the number of platelets and the ESR indicator are pregnancy, diseases of inflammatory and infectious nature, problems with the liver and kidneys. An increase in ESR is observed after poisoning, trauma, surgery, and chronic diseases. A number of drugs can also increase ESR. There are many cases where platelets increase along with ESR in bone marrow diseases.
First of all, when the analysis reveals an increase in platelets and ESR, it is necessary to identify the cause. By and large, treating high platelets and ESR means treating the pathology that provoked the high number in the analysis. In most cases, the platelet count returns to normal faster than the ESR. Such conditions can be treated with antiviral drugs and antibiotics. Other medications that correspond to the identified pathology are also used.
You can often observe a condition where, along with platelets, leukocytes also increase. In most cases, this means the presence of an inflammatory process. When the analysis shows white blood cells above normal, it is necessary to conduct additional examinations to help determine the cause.
Most often, the analysis reveals an increase in platelets and leukocytes in infectious diseases. Quite often, many cells are formed during ARVI and other inflammatory processes in the body. A large number of leukocytes may be present in extensive burns, infarctions of internal organs, and severe blood loss.
Hemoglobin and red blood cells
Another important blood indicator is hemoglobin. There are cases when hemoglobin decreases along with platelets. Often the analysis shows deviations during pregnancy and childbirth. Hemoglobin in such cases becomes lower, which is explained quite simply. A large amount of iron and folic acid is sent to the baby’s body, so the mother’s hemoglobin inevitably decreases. That is why during pregnancy, proper nutrition with additional amounts of various microelements and substances is of great importance.
Reduced or increased hemoglobin may be a sign of a serious illness. In particular, when the analysis revealed low hemoglobin, it is necessary to exclude thalassemia, aplastic anemia, and blood diseases.
Quite often, hemoglobin is reduced in diseases of the bone marrow, which cannot function correctly. Accordingly, blood cells are produced in insufficient quantities. As a result, not only hemoglobin decreases, but also:
- red blood cells;
- leukocytes.
Red blood cells are also an important component of blood. Normally, the analysis of an adult should show an indicator of approximately five million red blood cells per 1 mm³ of blood. Red blood cells in the body carry oxygen and carbon dioxide. When red blood cells are elevated, this often means the presence of leukemia, congenital heart defects or chronic pulmonary diseases.
A decrease in red blood cell count means the risk of developing anemia. It is worth noting that if the reason for the decrease or increase is not determined by general tests, you should consult a gemologist who will prescribe specialized studies. Since the function of red blood cells is very important in the body, there is no point in delaying such studies.
A significant increase in red blood cells may be a sign of acute poisoning, impaired metabolism, dehydration, long-term lung or cardiovascular diseases. An increase in red blood cells is also observed in people living in high mountain areas. In this way, the body adapts to the insufficient amount of oxygen in the air.
Red blood cells (RBC)
red blood cells, red blood cells and leukocytes
Red blood cells are “carriers” of oxygen.
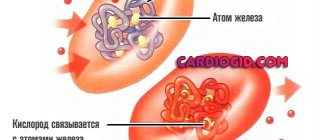
The name comes from the fact that these blood cells are red in color, due to the hemoglobin they contain. Hemoglobin binds and releases oxygen at the right time thanks to the iron it contains. It is red blood cells that give blood its red tint. Oxygenated (arterial) blood is bright red; after oxygen is released, the color of the blood changes to dark red (venous blood).
The normal red blood cell count for women is 3.5-5.2 million red blood cells per mm3 (cubic millimeter), and for men it is 4.2-5.4 million red blood cells per mm3 of blood. An increase in the number of red blood cells is called erythrocytosis, and a decrease is called erythropenia. An increase in red blood cells is a rare occurrence. This can be caused by dehydration, cancerous growth of red blood cells, prolonged body hypoxia or increased production of a hormone that stimulates the production of red blood cells (erythropoietin). However, anemia and too low red blood cell levels are more common. Anemia can be caused by blood loss, vitamin B12 deficiency or folic acid deficiency. Anemia also occurs when there are a number of factors that cause the destruction of red blood cells (hemolytic anemia).
Aggregation and distribution width
Platelet aggregation is an important process that determines how quickly the body is able to control bleeding. Aggregation is measured using venous blood as an example. At the same time, in order for aggregation to correspond to true indicators, it is necessary to create conditions in the laboratory as close as possible to the human body. Therefore, when platelet aggregation is assessed, substances are used that are as close as possible in their composition to human ones. They cause the process of thrombosis.
It is worth noting that aggregation can change under the influence of external factors. In particular, high concentration during work can, like heavy physical labor, affect a number of parameters associated with platelets. Certain medications, especially those taken on the day of the test, can also cause abnormalities.
Of course, aggregation can change under the influence of pathologies. In particular, increased aggregation is observed in hypertension, atherosclerosis, stroke and heart attack, and diabetes mellitus.
In addition, deviations from normal values are very often observed during pregnancy.
A reduced level in this case may create an increased risk of bleeding. An increase is observed in the first trimester with toxicosis. This is due to dehydration of the body, the danger of this condition is the likelihood of miscarriage. It is advisable to take an aggregation test at the stage of pregnancy planning.
The width of the distribution is also determined. The width of the distribution helps determine platelet volume. In particular, the width of the distribution is determined by the heterogeneity of the population. The width of the distribution detects changes in cell size. In addition, the width of the distribution shows the percentage of micro- and macroplatelet cells in the total number.
In the previous article we tried to find out and learned how to read it. Today we’ll talk about thick blood: what is the risk, the cause of thickening, symptoms and how to deal with it. Blood is the main source of life and functioning of the body; the health and functioning of all organs, and the entire life support of the body, depend on its quality. Impairments in the quality and consistency of blood, such as high cholesterol, oxidation and thickening, impede blood circulation and lead to oxygen starvation of organs, redox functions of all tissues, brain, liver, kidneys, heart and so on. Blood thickening is the start of the appearance or exacerbation of quite serious diseases; viscous blood stagnates in the vessels, forming blood clots, the breakage and uncontrolled movement of which pose a direct threat to life.
Symptoms indicating a violation of blood consistency:
- increased blood pressure.
- general weakness, fatigue and drowsiness.
- heaviness in the legs, cold fingers and toes.
- absent-mindedness, headaches and depression.
- dry mouth.
- nodules on the veins.
This is not a complete list of possible symptoms; in addition, the disease can occur in a latent form and occur unexpectedly, therefore, to be sure, it is necessary to regularly check the blood for coagulability - a coagulogram, which gives an answer to the quality of hemostasis and the condition of the blood vessels.
Increased hemoglobin. Platelets
- Insufficient consumption of clean water. Water makes up eighty-five percent of the blood and ninety percent of the plasma; even a minimal decrease in these percentages leads to blood thickening.
- Constant exposure to rooms with dry air, which literally draws moisture from the body and leads to changes in blood consistency.
- Severe thermal burns.
- Liver diseases, cirrhosis, pancreatitis and hepatitis.
- Adrenal gland dysfunction.
- , thrombophlebitis, leukemia, hypoxia, myeloma, Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, amyloidosis.
- Varicose veins and pregnancy.
What indicates increased blood viscosity?
- increase in the number of red cells in the blood, red blood cells.
- increased hemoglobin levels (excess iron, globin and protein in the body).
- violation of the ratio of red blood cells and plasma.
Thick blood needs to be thinned, how to do this? Simple tips
- You need to drink more clean water, two and a half liters daily or more.
- Products that can thin the blood: You need to eat more berries - raspberries, cranberries, blueberries, cherries, strawberries, cherries. Eat more beets, tomatoes and tomato juice, fish and fish oil, oatmeal, garlic, onions, ginger and lemon. Dress salads with olive and flaxseed oil, apple cider vinegar and sunflower seeds.
- Products that help thicken the blood: You need to give up fatty meat broths, jellied meats, smoked meats and sausages, replace white bread with black bread. Also exclude bananas and mangoes, lentils and cream from the diet. Herbs such as St. John's wort, nettle, knotweed, valerian, corn silk and yarrow are not suitable for you. Rosehip and black rowan berries also thicken the blood.
- Blood viscosity is provoked by smoking, alcohol abuse, and a large amount of salty foods and salt on the menu. Contraceptive drugs, diuretics, hormonal and potency-enhancing drugs affect blood clotting.
You are recommended:
- You need to move more, walk, run, do exercises in the morning. More walks in the fresh air, humidify the room.
- Drink more green tea, natural fruit juices, red grape juice is especially good at thinning the blood.
- A menu balanced by a doctor, taking into account the ratio of proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements.
- To lower cholesterol and thin the blood, omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids are needed. You are recommended to drink one tablespoon of flaxseed oil per day, which promotes their synthesis.
- Turanine, which is extremely rich in: fish, especially sea fish, flounder and tuna, shellfish and squid, olive oil, will help thin the blood.
- The enzyme found in seaweed will lower cholesterol levels and thin out thick blood. Eat more seaweed salads.
- Arginine amino acids found in nuts, especially walnuts and cashews, form nitrogen oxides, which help thin the blood. Eating nuts daily will provide you with essential protein, calcium, potassium and magnesium. To reduce blood clotting, you need to eat at least thirty grams of nuts.
Considering all the dangers associated with blood thickening and the risk of blood clots, we recommend that you regularly check its consistency and respond to alarming symptoms. Blood thickening is not only life-threatening blood clots, it is oxygen starvation of your organs, death of body cells and disruption of life processes. Indicators of normal consistency for different ages vary, so the blood of a baby and an elderly person cannot be compared; your doctor will explain all the abnormalities to you.
Why is blood thickening dangerous?
If the blood becomes thicker, this condition is associated with many problems. Its stagnation in organs prevents them from functioning normally. The risk of blood clots increases significantly. Even one blood clot can cause death or disability.
The speed of blood flow slows down, which puts increased stress on the heart and blood vessels. Cells do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients. Radicals are released. Plaques and blood clots form in the vessels. This means that thrombosis has begun to develop. It is the most common cause of strokes and heart attacks. In pregnant women, this problem leads to the birth of an underdeveloped child or a miscarriage.
Important!
Blood thinning is facilitated by an active lifestyle and regular exposure to fresh air.
How to thin thick blood in adults
Treatment for thrombocytosis will depend on its cause. Usually it includes not only taking medications, but also diet. Often, adjusting your diet and increasing the amount of fluid consumed per day gives good results. Thinning medications help make the blood less viscous and thicker. When more effective methods are needed, the doctor may prescribe a course of plateletpheresis. This procedure is carried out using an electrical device. If thrombocytosis was caused by infection or autoimmune processes, appropriate therapy is carried out.
Among the traditional methods, hirudotherapy helps. The substance secreted by leeches during suction is called a natural anticoagulant. At the same time, the blood acquires new physical properties, its composition also changes for the better. It is recommended to eat more berries, beets, onions, garlic and tomatoes. Fish and fish oil are very useful for such patients. Olive and flaxseed oil, ginger and seeds have a beneficial effect. You need to avoid salty and fatty meat dishes. You should eat less bananas, white bread and lentils.