Transferrin is a protein in the blood plasma that binds iron ions and transports them throughout the body. When your body contains enough transferrin, you can effectively use the iron you get from food. The presence of iron in the body dictates the production of transferrin, but its levels are also affected by inflammation, liver and kidney health. Below in the article we will talk about high and low transferrin levels, and ways to normalize them.
The article is based on the findings of 56 scientific studies
The article quotes the authors:
- Department of Pathology, Children's Hospital Boston, USA
- Fernando Bermejo, Digestive Service, University Hospital of Fuenlabrada, Spain
- University of Utah, USA
- Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Medical University of Wroclaw, Poland
- Medical University and University Hospital of Innsbruck, Austria
- and other authors.
Please note that the numbers in parentheses (1, 2, 3, etc.) are clickable links to peer-reviewed scientific studies. You can follow these links and read the original source of information for the article.
What is transferrin
Transferrin is a blood plasma protein that binds iron and transports it throughout the body. It is the main carrier of iron in the blood. If you have enough transferrin, then your body can effectively use the iron you get from your diet. [, ]
The characteristic patterns of changes that occur in the blood plasma through the concentration of certain acute phase proteins after moderate inflammation are shown. Pay attention to the duration of fibrinogen production (simultaneous increase in ESR).
Transferrin levels increase with increasing iron deficiency. When iron is low, your body will try to compensate by increasing the amount of transferrin to increase the availability of iron in tissues. [] On the other hand, the amount of transferrin decreases with increasing iron content. [, ]
Acute phase reaction. The inflammatory stimulus leads to the activation of monocytes and macrophages, which release cytokines. Cytokines act on the liver to stimulate the production of acute phase proteins. Cytokines, together with acute phase proteins, produce a systemic response with neuroendocrine, metabolic, hematological and biochemical changes. (www.researchgate.net)
Transferrin protein is produced in the liver, so its levels are also associated with overall health and general inflammation in the liver and in the body as a whole. Transferrin is a negative acute phase protein. This means that as inflammation increases, and as the liver produces more inflammatory proteins (eg, C-reactive protein , ferritin), transferrin production decreases. [,]
Scheme of iron homeostasis (iron metabolism). The central part of the figure depicts the entry of iron into the body (via the small intestine), its attachment to transferrin (TF), movement to the main site of disposal (erythroid bone marrow), attachment to circulating red blood cells, to tissue macrophages, which phagocytize red blood cells and recycle iron levels to spleen, movement for storage in hepatocytes. (www.researchgate)
Other functions of the transport “vehicle” for iron
Transferrin not only transports Fe to tissues and organs for storage “in reserve” or delivers it to the bone marrow so that iron participates in the synthesis of hemoglobin. It also does:
Identification of young red blood cells.
Transferrin, which belongs to the acute phase proteins, is a participant in the body’s immune response programmed by “hereditary memory”. Residing in the mucous membranes and binding “detected” iron, it does not allow pathogenic microorganisms to take advantage of this element. This prevents all kinds of microbes from multiplying.
Normal transferrin level
The unit of measurement for transferrin when taking tests is g/l.
Transferrin reference values (normal range)
Age, gender | Transferrin, g/l |
| up to 2 months | 0,99 – 2,18 |
| 1 month – 1 year | 1,02 – 3,17 |
| 1 – 14 years | 2,14 – 3,30 |
| >14 years old | 2,0 – 3,6 |
| Pregnant women 1st trimester | 2,54 – 3,44 |
| II trimester | 2,2 – 4,41 |
| III trimester | 2,88 – 5,3 |
Serum transferrin concentrations are approximately 10% higher in women than in men. A high concentration of transferrin in the blood serum is observed during pregnancy (especially in the third trimester) and when using estrogens.
Transferrin test
A study of the level of transferrin in the blood is necessary for a more detailed study of iron metabolism in the body. This in-depth consideration is necessary to:
- iron metabolism assessments (along with iron testing) to determine how much iron the blood carries
- estimates of iron stores in the body
- identifying the cause of anemia - iron deficiency, chronic diseases or vitamin B12 deficiency
- liver health assessments.
Transferrin saturation coefficient (TSR)
After the synthesis of transferrin in the liver, it is saturated with iron. This saturation depends on the level of iron in the body, which comes with food. The main location of transferrin is the mucous membrane , where this protein captures iron ions from food and prevents harmful microorganisms from also using the iron. With a lack of iron, pathogens on the mucous membranes are inhibited, which allows a very small list of bacteria to multiply. In addition to iron, transferrin is capable of binding cobalt and zinc.
The transferrin saturation coefficient (TSC) is the ratio of iron bound in transferrin (iron in serum) to the total iron binding capacity (TIBC) or total transferrin, measured as a percentage.
KNT = iron / OZhSS * 100
Normal CST values for adults are: 15-50%
High values of CST (transferrin saturation coefficient) are determined with increased iron content in the body and are inherent in the following conditions: megaloblastic anemia, sideroblastic anemia, hemochromatosis. A decrease in CST indicates the following possible problems in the body: iron deficiency anemia, chronic infections, malignant tumors, tissue inflammation, uremia and nephrotic syndrome.
What is the essence of the analysis for the determination of siderophilin in the blood?
One of the main, more accessible methods for determining siderophilin in the blood is turbidimetry .
This method requires blood serum. To obtain it, donated by the patient centrifuged For this purpose, venous blood is most often taken.
A reagent containing antibodies to human transferrin to the patient's blood serum If transferrin is present in the serum, antibodies will specifically bind to it . This to become cloudy . Based on this turbidity, the concentration of siderophilin will be calculated.
According to the calculated indicator, which is proportional to the degree of turbidity, the concentration of transferrin in the blood is determined.
The turbidity of the solution with the test serum is compared with a blank sample, in which the absence of siderophilin is known.
High transferrin levels
Causes of elevated transferrin levels:
- The most common cause of elevated transferrin is iron deficiency anemia. [,, ]
- Pregnancy, especially its third trimester. Normal condition.
- Birth control pills. In a study of 117 women who took birth control pills (oral contraceptives) for at least 2 years, transferrin levels were higher than in women who had never taken them. []
- Obtaining a significant amount of fluorides (fluorine compounds).
Reasons for the increase
An increase in transferrin is less typical and occurs with a lack of iron, so the main cause is iron deficiency anemia due to large blood loss, constant prolonged feeding, low iron content due to insufficient consumption of foods rich in microelements, and pregnancy.
A physiological excess of the transferrin norm is possible after severe physical or psycho-emotional stress, due to the growth of estrogens in the body, or taking medications: Mestranol, Carbamazepine, Danazol.
Ways to reduce transferrin
Eating foods high in iron can help prevent iron deficiency. Iron-rich foods include red meat, liver, poultry and fish. []
Iron supplements will iron intake, but should only be taken if your iron deficiency cannot be corrected through diet. [, , ]
Reduce consumption of drinks such as coffee , cocoa , green and herbal tea , as they reduce the absorption of iron from food. [, , , , , ] Or postpone their consumption 1-2 hours before meals. alcohol consumption , which completely destroys heme iron in animal foods, but not in plant foods. []
Vitamin C increases iron absorption []. It is a good practice to add sources of vitamin C to iron-rich foods (dried rose hips, lemon juice, sauerkraut, etc.).
FOOD RICH IN IRON AND FOODS WITH VITAMIN C TO IMPROVE IRON ABSORPTION
It is worth noting that night shift work disrupts circadian rhythms and there is a disagreement between the “internal clocks” in the liver and brain. If, in the evening or at night, you eat food that contains a lot of iron (for example, sausage, hamburger, steak), then an even greater mismatch occurs between the circadian rhythms in the liver cells and in the brain. This disorder increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. []
Heme and non-heme iron
Heme is part of hemoglobin, myoglobin, and some enzymes (cytochromes, catalase, lactoperoxidase). The iron included in these compounds is commonly called heme iron .
Heme iron is much better absorbed by the body.
SOME FOOD PRODUCTS ARE SOURCES OF HEME AND NON-HEME IRON
Iron compounds found in plant foods are classified as non-heme iron . It is much less absorbed than heme iron, and its absorption is influenced by many additional factors.
Substances that reduce iron absorption
- Solubility of various non-heme iron compounds
- Integrity of the intestinal mucosa (healthy intestines absorb better)
- polyphenols in food – grains, vegetables, spices and drinks
- Calcium (cow's milk, calcium supplements)
- Phytic acid – bran, wheat, rice, legumes, nuts (can reduce absorption by 50-60%).
- Zinc supplements . It is better to take separately from food.
- Oxalic acid – found in spinach, cabbage, beets, nuts, chocolate and tea. Reduces the absorption of heme iron.
- Eggs contain a compound called phosvitin, which impairs iron absorption. One boiled egg can reduce the absorption of iron in food by 28%.
Substances that increase iron absorption
- Vitamin C – can increase absorption 4 times
- Beta-carotene – increases absorption and reduces the effect of phytic acid and tannins.
- Betaine hydrochloride is an acid that is present in the stomach and it helps with the breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients.
Table of examples of iron absorption from various foods
| Iron-rich foods | Iron type | Suction |
| Veal, beef | Heme | 22-25% |
| Fish, kidneys, liver | Heme | 11% |
| Eggs | Heme | 3% |
| Soya beans | Non-heme | 7% |
| Apples, pomegranates, buckwheat | Non-heme | 3% |
| Rice, spinach | Non-heme | 1% |
Functions of transferrin in the body
As you know, all microelements important for human life enter the body with food. Iron is included, but in order to be absorbed in the intestines, it must be processed by enzymes, vitamin C and intestinal microflora.
The transport protein, or it is also called siderophilin, has different forms of attachment to its molecular structure of iron ions:
- Polyglandular form of transferrin A.
- Polyglandular form of transferrin B.
- Apotransferrin.
- Diferric transferrin.
Siderophilin, encountering a cell with a transferrin receptor on its way, gives it iron molecules for its further participation in the functioning of the human body.
A molecule with different forms of metal attached to it serves specific organs. For example, the polyglandular form of transferrin B saturates the liver, and the polyglandular form of transferrin A saturates the placenta and regulates erythron.
By its nature, transferrin is a glycoprotein. It has a molecular weight of about eighty kilodaltons.
When conducting
electrophoresis
Serum proteins transferrin will be located in the zone of beta-fraction globulins.
Transferrin is a protein, that is, the monomers for its synthesis will be amino acids. The formation of this protein occurs in the liver and reticuloendothelial system.
The structure of transferrin has two regions that can bind to iron. That is, the main function of this glycoprotein is the transfer of this trace element to organs and tissues.
Fe2 enters the body with food. Next, it is oxidized to Fe3. So, the carrier protein is capable of binding only the oxidized form of this trace element.
Normally, the microelement binding centers in the transferrin molecule are not completely saturated; the rest remains in reserve. In the case of low Fe content, the amount of transport protein in the body increases and all binding centers are filled.
Interesting Facts
The following are interesting facts about this indicator and more:
- Transferrin is also called siderophilin, which literally stands for iron-loving.
- 1 gram of transferrin is capable of binding 1.4 milligrams of Fe.
- Iron has a positive charge, so to bind it in the siderophilin molecule, a negatively charged bicarbonate is additionally required.
- If the body does not have this trace element (iron), then this protein can also bind Cr2, Mn3, Cu2.
- There is a polymorphism of siderophilin that can be detected by electrophoresis. For example, Caucasians have type C, and Africans have type D.
- There are other indicators that characterize iron metabolism in the body and have some relation to transferrin: the ability of serum to bind iron, the percentage of transferrin saturation, etc.
- Fe plays an important role in our body. This element is involved in the formation of another transport protein molecule - hemoglobin. For those who don’t know, hemoglobin transports gases between different tissues. In addition, iron is part of the myoglobin found in muscles, acting as an oxygen depot there. Proteins such as cytochromes also contain this microelement. Their main function is to provide cells with energy, as well as to neutralize toxic compounds.
- The body should receive 10 - 15 micrograms of Fe per day. In some conditions, the need for this microelement increases, for example, during pregnancy.
- If there is an insufficient amount of amino acids in the body, then the processes of transferrin synthesis will be reduced.
- Free Fe ions can contribute to the formation of radicals, which will lead to damage to cell membranes.
Decreased transferrin levels
Iron overload
The most common cause of low transferrin is iron overload (excess iron). [, ]
Protein food deficiency
To produce proteins, the liver needs resources. To do this, the liver requires amino acids, which you get from your diet. When there is not enough protein in your diet, then your liver cannot produce enough transferrin. []
In studies of over 80 children who were malnourished, transferrin levels were significantly reduced. [, ]
Inflammation
As mentioned above, transferrin is a negative acute phase protein. When the liver increases the production of proteins associated with inflammation (eg, C-reactive protein , ferritin), there is a decrease in transferrin production. [,] A number of diseases, such as infections and cancer , which are characterized by an inflammatory process, can reduce transferrin levels. []
PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL MECHANISMS OF CHRONIC ANEMIA WITH INFLAMMATION (www.scielo.br) The anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 regulates the expression of the transferrin receptor, enhancing its binding to iron, mediated by the monocyte transferrin receptor.
An observational study of 297 patients with active inflammatory bowel diseases ( Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis ) found significantly lower transferrin levels. Increased disease activity and inflammation were associated with decreased transferrin levels. []
Another similar study compared 20 patients with chronic periodontitis (gum inflammation) and 20 healthy people. It has been found that people with chronic gum disease have lower levels of transferrin. Three months after treatment of inflammation, the level of transferrin in the blood increased to the values that were in healthy people. []
Preeclampsia , a condition that causes high blood pressure during pregnancy, is associated with inflammation. Women with preeclampsia often show decreased transferrin values. [, ]
Other chronic diseases leading to an increase in inflammation and a decrease in transferrin: systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis , tuberculosis, bacterial endocarditis.
Liver disease
In liver disease, this organ cannot effectively produce transferrin. [] This happens when liver function is impaired by inflammation or alcohol consumption. []
Patients with liver disease , including cirrhosis, have significantly lower transferrin levels than healthy people. [, ]
Kidney disease
Nephrotic syndrome is a kidney disorder that causes too much protein to be excreted in the urine. Transferrin is one of the proteins that is excreted from the body in urine. This is why nephrotic syndrome, especially in diabetes, can exhibit significant transferrin losses. [, ] Glomerulonephritis is another inflammatory kidney disease, possibly autoimmune, leading to a decrease in transferrin values.
Genetic predisposition
Transferrin may be low due to genetic reasons. In these cases, transferrin values were in the range of 10-20 mg/dL. [, ]
Other reasons for decreased transferrin levels
- Use of corticosteroids and testosterone
- Thalassemia
- Hereditary hemochromatosis
- Loss of protein in burns
- Malabsorption syndrome
- Serum hemolysis
Other indicators of iron metabolism
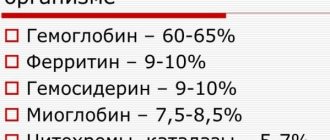
Ferritin is a protein molecule in the form of which Fe is stored in cells and tissues. Its quantity directly reflects the content of this microelement. That is, if the body lacks it, then this indicator will be lower than normal values.
The results of determining this indicator in the blood will be influenced by increased physical activity, consumption of alcohol and certain medications.
When diagnosing conditions accompanied by iron deficiency, transferrin iron saturation coefficient . This coefficient is calculated as follows:
Siderophilin saturation Fe = serum Fe/TJSC * 100%, where TJSC is the total iron-binding capacity of the serum .
Normally, this coefficient is 15 – 45%. If there is a deficiency of this microelement in the body, this indicator will be reduced.
OZHSS is an indicator that shows the amount of Fe that is able to contact siderophylin. That is, this is the maximum that is able to contact the transport protein siderophilin.
Normally, this characteristic of Fe metabolism is 40 – 62 micromol per liter in males, and in women – 40 – 75 µmol/l.
There is also the concept of latent iron-binding ability of serum . This indicator shows how much of a trace element can be associated with other proteins, not necessarily siderophilin. This serum indicator is calculated as the difference between the THC and the serum iron content.
45–60% is allocated to the latent ability of serum to bind Fe.
The doctor must understand all these complex and confusing indicators. Based on them, on examination data, complaints, instrumental research methods, a diagnosis is made. For the doctor to do everything right, the patient must trust him and not hide anything from him.
Ways to increase transferrin levels
In order to increase your transferrin levels, you must make sure that your blood does not contain large amounts of iron. An iron blood test will help you answer this question.
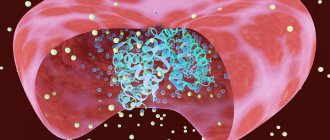
DISTRIBUTION OF IRON IN THE BODY OF AN ADULT.
Circulating iron binds to transferrin and is delivered to tissues (black arrows) (openi.nlm.nih.gov)
Reduce iron intake from food
If your transferrin levels are low due to high iron intake:
- Avoid iron-rich foods such as red meat, fish and poultry. []
- Eat more foods that reduce iron absorption, such as fiber and phytic acid (from whole grains) and chili peppers. [, ]
- Drink more coffee, cocoa, green tea and other herbal teas such as chamomile, linden, mint and verbena teas. All of them reduce the absorption of iron from food. [, , , , , ]
Indications for the purpose of the study
If an excess or deficiency of iron in the body is suspected, transferrin is determined. There are many indications for research, the main ones are:
- constant dizziness of varying intensity and duration, which is typical for a whole group of diseases that are accompanied by an increase in free iron in the blood: from brain damage to a banal deficiency of the element with neurological disorders, nausea, weakness, cephalgia;
- weakness, asthenia, encephalopathy due to tissue hypoxia: in this case, transferrin is not always the culprit, but it is necessary to exclude this possibility;
- anemia – insufficient synthesis or poor absorption of iron;
- arrhythmia due to insufficient cellular respiration of the myocardium;
- liver pathology, disruption of the digestive system due to the free circulation of toxic iron ions in the blood;
- hemochromatosis is a disease associated with excess iron in the body, which is clinically manifested by arthralgia, lethargy, decreased libido, arrhythmias, and dry dermis.
Low ferritin levels and its causes
Ferritin is the main indicator of iron reserves in the body and plays an important role in maintaining iron in a biologically useful form. Ferritin contains iron phosphates. Ferritin is found in all cells and fluids of the body.
A blood test for ferritin is used to diagnose iron deficiency anemia and diagnose anemia accompanying infectious, rheumatic and tumor diseases.
The normal level of ferritin in the blood for adult men is 20 - 250 mcg/l. For women, the normal blood test for ferritin is 10 - 120 mcg/l.
Excess ferritin in the blood can be a consequence of the following diseases:
- excess iron in hemochromatosis
- alcoholic hepatitis and other liver diseases
- leukemia
- acute and chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases (osteomyelitis, lung infections, burns, rheumatoid arthritis)
- mammary cancer.
Ferritin levels increase when taking oral contraceptives and fasting.
Low ferritin is a consequence of iron deficiency (iron deficiency anemia).
Treatment for low ferritin is always prescribed only by a doctor: it is necessary to find out exactly what disorders led to a decrease in ferritin in a blood test.
You can always get advice from a professional doctor, undergo an examination and take any tests, including a biochemical blood test, at affordable prices in our medical office. All tests do not require an appointment, are carried out quickly and without queues, using only disposable materials.
When is a test ordered?
There are many indications, given the important role siderophilin plays. If we talk about the reasons for the examination:
- Frequent dizziness. Occurs in diseases for which an increase in free iron in the blood is typical. It is possible that the brain is affected. On the other hand, similar symptoms occur with element deficiency.
Since there is not enough iron, little hemoglobin is produced to carry oxygen to the central nervous system.
These tissues are very demanding on cellular respiration and nutrition. Therefore, neurological manifestations occur immediately.
Additionally, severe, regular headaches develop. Possible nausea and vomiting.
- Weakness. Asthenic syndrome. A natural continuation of the previous phenomenon. Drowsiness, a feeling of exhaustion - these symptoms are almost always caused by disorders of the brain.
Consequently, the cause must be sought in the poor supply of oxygen to cerebral structures. It may well be that transferrin is not the culprit. The doctor prescribes the analysis at his own discretion.
- Anemia. Most often iron deficiency. When the body does not receive enough substance, the production of siderophilin decreases. This is how the body saves energy.
If the element is supplied in sufficient quantity, but is not absorbed, the reverse process occurs. The concentration of free transferrin increases, which should not happen: most of the protein is in a bound state.
This is an informative technique for diagnosing anemia. But for determining its other forms: megaloblastic, etc., the method is not suitable.
- Heart rhythm disturbances. Especially if the reason for this could not be found earlier. We are talking about tachycardia (rapid heartbeat). This occurs against the background of insufficient cellular respiration of the myocardium. Muscle tissue is also extremely demanding of oxygen.
Gas transportation is impossible without hemoglobin. And the synthesis of this, in turn, without a sufficient amount of transferrin. Therefore, any rhythm deviations can occur due to siderophilin deficiency. Although this is relatively rare.
- Errors in other laboratory parameters. Especially if the number of red blood cells is changed.
- Pain in the liver.
- Disorders of the digestive tract. Occurs with excess iron. This is precisely a consequence of the fact that its toxic ions circulate freely throughout the body. Normally, almost the entire element is associated with transferrin. The disease is indicated by an excess amount of iron in the blood.
There are many indications. The list is far from complete. The doctor may order an examination for other reasons. This question is best left to the specialist himself.
Etiology of elevated transferrin index
Some pathologies affect the functionality and saturation of Tf, and the fact that its index is elevated in the blood:
- Hypochromic anemia . With this pathology, the analysis shows the color of the blood, which depends on the concentration of Fe in it. Hypochromic anemia responds quite well to treatment and does not pose a mortal danger to a person;
- Chronic blood loss increases the protein index;
- Hepatitis . Tf is directly related to the liver, so any violations in this organ lead to an increase in its coefficient;
- Polycythemia vera is a very dangerous blood pathology. This is a malignant cancer of the blood that makes the blood viscous. This pathology leads to thrombosis of arteries and veins, and is also characterized by blood flow hypoxia;
- Anomalies in the anatomical structure of the body and abnormalities in the absorption of iron by the body , as well as a low percentage of iron intake from food, provoke an increased transferrin index. Comprehensive diagnostics will make it possible to find out the real causes of the disturbance and transferrin concentration.
If Tf in the blood is elevated, this indicates that there is a risk of iron deficiency anemia in the body. If this transferrin index condition is stable, then it is necessary to take preventive measures for anemia.
Red blood cells in iron deficiency anemia
There is also an increase in transfer protein from taking oral contraceptives and during pregnancy. The 3rd trimester of intrauterine development of a child increases the concentration of transferrin molecules.
Decrease and increase in transport protein not corresponding to the norm
When the blood contains a result that exceeds the norm, this can be caused by various factors, for example, pregnancy. In this condition, the amount of transferrin in a woman’s blood will increase and the concentration of iron will decrease.
Hormonal medications, as well as contraceptives, can also lead to an increase in the value of transport protein in the blood above normal. Conditions associated with iron deficiency, as well as various bleeding events, lead to an increase in the transport protein.
Very low transferrin occurs in various disorders and diseases in the human body:
- The use of glucocorticoid drugs and androgens.
- Growth of malignant neoplasms.
- Inflammatory processes that have become chronic.
- Heredity, development of atranferrinemic state and hemochromatosis.
- Pathological liver lesions of various types.
- A large amount of blood transfused.
- Large area of burns on the human body.
- Protein loss by the kidneys.
- Blood diseases.
A decrease in protein in the body occurs not only due to its pathological loss, but also due to burns and kidney disease, a sluggish infectious process, but also diet and fasting with strict limitation of this food component.
Features of preparation for analysis to determine the iron transport protein
In order for the results to reflect the processes that actually occur, the patient must be properly prepared.
The rules are simple, so it will not be difficult for the patient to follow them:
- Blood should be donated in the morning, drinking plain water if necessary. You can't have breakfast in the morning. Since blood must be donated on an empty stomach. This means overnight fasting for 10 hours;
- a couple of hours before blood sampling, it is recommended to refrain from one of the bad habits - smoking;
- the day before submitting biological material, it is important to maintain emotional calm;
- physical rest is also important. There are situations when after a run the indicators change;
- The doctor must be informed about what medications and nutritional supplements the patient is taking. They may contain iron, and accordingly, the reliability of the results will change.
Sometimes patients do not tell the doctor about their medications, resulting in a reading within the normal range. The doctor will not notice real deviations due to the unreliability of the information received. In the future, for example, Fe deficiency may worsen and lead to serious consequences. The patient will regret that he did not inform the doctor about important information.
Decoding the biochemistry result
The norm directly depends on the age of the patient and the condition of his body. In women in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy, this coefficient fluctuates in the direction of its increase.
The standard indicator is:
| Patient's age | Transferrin content |
| children under 10 years of age | 2.030 g/l - 3.60 g/l |
| from 10 calendar years – 60 calendar years | 2.00 g/l - 4.00 g/l |
| from 60 calendar years | 1.80 g/l - 3.80 g/l |
| Patient's age | Transferrin content in % |
| children under 14 years of age | 10,0% — 50,0% |
| from 14 calendar years – 60 calendar years | 15,0% — 50,0% |
| older than 60 years old | 8,0% — 50,0% |
The Tf indicator can also be measured in other units - µmol/l. In this case, the norm of this protein for an adult body will be from 23 µmol/l to 43 µmol/l for men. For women, this figure is 21.0 - 46.0 µmol/l.
Transferrin (TGSS) is 26.850 µmol/l - 41.170 µmol/l