Both CT and MRI have become safer over time. Previously, the harm caused by these procedures was much greater. However, they have not become absolutely safe, although more modern equipment is used. You need to figure out which is more harmful and worse for the body - CT or MRI, and which causes more radiation, which tomography is more dangerous.
The essence of MRI
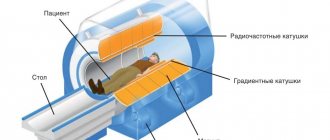
Magnetic resonance imaging is a procedure during which the patient is placed on a couch so that a special scanner, inside which the part of the patient’s body to be examined, is placed, determines the state of health of the person, including the child.
A referral for an MRI is not always a bad sign. The doctor just wants to make sure you're okay.
Most often, patients who need to check the condition of the central nervous system (central nervous system), soft tissues, and musculoskeletal system are referred for an MRI. This procedure is used to diagnose cancer. Using MRI, specialists obtain information about organs in three projections.
MRI diagnostic room
Magnetic resonance imaging scanners produce significant noise during operation (like a hammer working on metal), so the patient may be asked to use special sound-proof headphones.
People who have tattoos on their body should inform their radiologist. The fact is that some dyes contain metal compounds, including titanium dioxide. This may negatively affect the operation of the tomograph.
Limitations of MRI
Is MRI harmful to health if performed during pregnancy? You should focus on the health status of the expectant mother. One thing is clear: it is not advisable to undergo the procedure in the first trimester.
Magnetic tomography is contraindicated for people with metal implants. Therefore, before the procedure, the patient must remove all metal objects.
Considering the existing ban on MRI for patients with implanted pacemakers, manufacturers have released a new generation of pacemakers, the presence of which is not a contraindication for MRI.
Scanning may also be difficult if the patient is claustrophobic. And if the patient has a mental illness that affects his ability to lie still during the procedure, then it is better not to do magnetic resonance imaging. The fact is that during the procedure you need to remain motionless for about 30-40 minutes while the device scans the necessary organs.
Indications
Quite often, CT and MRI are prescribed for similar diseases with identical symptoms, and perform equally well. But some pathological phenomena force a specialist to make a choice between studies, based only on their strongest aspects. Using X-rays, it is possible to conduct a detailed examination of structures such as bone tissue, parenchymal elements (adrenal glands, pancreas, etc.), as well as hollow internal organs (ureters, bladder, lungs, stomach and intestinal tract).
MRI accurately records disorders related to the body’s vascular system, so this procedure is often prescribed for damage to arteries and veins
Therefore, the main indications of CT include the following ailments:
- deformation of the vertebrae in the neck;
- arthrosis of the hip joint;
- inflammatory process;
- increased frequency of epileptic seizures;
- various mechanical head injuries;
- oncology;
- bloody discharge in the urine;
- chronic heartburn and nausea;
- dysfunction of the thymus gland (thymus);
- throbbing and squeezing headaches;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- the process of suppuration in the bronchopleural tree;
- causeless shortness of breath;
- thrombophlebitis of the heart, etc.
MRI cannot read complete information from bones, since their composition is characterized by the content of a relatively small number of hydrogen atoms, which supply data to “magnetic field scouts.” But scanning muscle tissue, tendons, joints, blood vessels, the central and peripheral nervous system, MRI is more than good.
For this reason, it is prescribed to people who suffer from:
Difference between MSCT and MRI
- meningitis;
- aneurysms and cysts;
- otitis media or inner ear;
- encephalitis;
- narrowing of the spinal canal;
- intervertebral hernia;
- multiple sclerosis;
- vasculitis;
- encephalomyelitis;
- spondyloarthrosis;
- synovitis;
- consequences of a stroke;
- osteomyelitis;
- abscesses;
- mastitis of the mammary gland;
- cirrhosis;
- endometriosis;
- migraines, etc.
The essence of CT
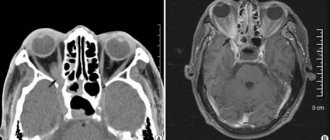
Computed tomography, like MRI, obtains a three-dimensional image of the examined organ in a section. The main distinguishing feature is the use of X-rays. At first glance, both methods are in no way different: in both the first and second cases, the computer independently processes the data so that the output is a three-dimensional image, on the basis of which doctors write a conclusion.
It is believed that computed tomography is an almost ideal way to examine fresh injuries, bleeding, damage to bone tissue, teeth, joints, and the spine. That is why CT is often prescribed for suspected osteochondrosis and complications in the form of intervertebral hernia are also well shown by computed tomography.
CT diagnostic room
Limitations of CT
Computed tomography cannot be performed: if the patient is pregnant and if it is necessary to use a contrast agent in the presence of diseases such as renal and/or liver failure, diabetes mellitus of any type, and a number of thyroid pathologies.
And if the woman who is going to have a CT scan is breastfeeding, then she must wait a day after the procedure is completed before she can breastfeed again.
There are also restrictions for people who are overweight. The couch on which the patient lies most often has an acceptable weight limit, so a patient weighing about 200 kg will not be able to undergo a CT scan.
As with MRI, CT requires complete stillness during the scan, although it takes less time - about 15 minutes. Therefore, a person who is in an inadequate state, who has a mental disorder that prevents him from complying with all the requirements of doctors, will not be able to undergo a CT scan.
The examination of the child is carried out only if other procedures turned out to be uninformative. In this case, parents have the right to be nearby during the scan. The only requirement is that they have a special X-ray protective apron.
What is the difference between X-ray and tomography?
Unlike the simplest CT scan, x-ray allows you to obtain images in one plane. X-rays do not always reveal neoplasms, especially at the initial stage, when the tumor is not large in size. X-rays do not allow examining complex organs in real time - for example, fluoroscopy can visualize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, but it is not applicable for studying the brain.
CT is a highly informative method of radiological diagnostics
The advantages of computed tomography, in its various variants, are sufficient:
- tissue resolution is as high as possible - attenuation coefficient is 0.5% for CT and 20% for X-ray;
- there are completely no closed zones - organs do not overlap each other;
- CT allows the doctor to assess the size of organs in the area being examined;
- obtaining additional information through the use of application programs.
In addition, CT does not exclude the possibility of using contrast - it can be intravenous or oral.
Comparison of MRI and CT: which is more harmful?
Above you could get information about what is best for the doctor and the patient in terms of information content. However, not everything is so simple when it comes to harm to the body.
Is CT scanning harmful? It is known that CT has a more negative effect on the body, since X-rays are used for scanning. X-ray radiation is still significant: according to some studies, there is a risk of exposure. Therefore, this procedure must be carried out strictly as prescribed by the doctor and taking into account previously conducted examination sessions.
It turned out that when undergoing a computed tomography scan, a person receives a dose of radiation that is several times higher than the annual radiation! This is why computed tomography is harmful to people's health when undergoing it. It is worth noting that new generation tomographs are currently being used, in which the radiation load on the patient is minimized.
An MRI examination does not harm the patient's health. The benefits of such tomography are greater, but the information content when examining the skeletal system suffers. However, MRI is the gold standard in detecting tumors and diagnosing the brain.
CT scan
CT is a more modern research method that allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer image of any internal organs. CT and X-ray are similar methods, but tomography produces higher-quality images that are of high resolution.
At the same time, x-rays remain safer, since the radiation dose received during the examination is less. Choose - CT or X-ray will be more informative in a particular case, only to the doctor.
Modern complexes for tomography have marked differences from the very first ones, which appeared in the early 80s. Currently, a device characterized by reduced radiation exposure is widely used. The latest generation of tomographs has a huge number of sensors, which have significantly reduced scanning time and reduced radiation dose. This allows this type of diagnosis to be used as often as x-rays.
Computer tomograph
If the most detailed examination of internal organs is necessary, spiral or multilayer (multi-slice) computed tomography is prescribed.
Spiral CT
This scanning technology became widespread in the 90s. Its essence lies in performing two actions simultaneously - rotating the X-ray tube around the patient, and moving the table in the longitudinal direction. Table speed may vary and is determined by specific scanning targets.
Multislice CT
Unlike spiral models, devices for multislice tomography have several detectors located along the Henry's circle, and the emitted beam has acquired a different geometric shape. A feature of modern CT complexes is the ability to scan an entire organ and monitor it in real time. This is relevant when examining the brain, heart or lungs.
Which examination is better in terms of safety?
It is generally accepted that CT causes more significant harm to human health due to the effect of a relatively small dose of radiation on the body. If the patient voluntarily undergoes this diagnosis too often, he may subsequently develop life-threatening illnesses, for example, a malignant tumor.
In many media, MRI is positioned as an absolutely safe procedure, but in fairness it should be noted that there is no official information confirming this hypothesis with calculations and the results of comprehensive studies. Moreover, some doctors argue that a full study of the influence of a magnetic field on a living organism has not yet been completed. Therefore, in the absence of the proper range of evidence, it is impossible to insist with absolute certainty that MRI is safe.
It is best to coordinate the next MRI session with the attending doctor, who will be able to accurately determine the degree of significance and necessity of diagnosis in a particular case.