Indications for the study
The specialist will recommend a CT scan of the eye orbits and optic nerves when he suspects:
- Traumatic damage to the eye sockets (orbits) of the optic nerve, eye muscles;
- Presence of a foreign body;
- Tumor process in this area;
- Inflammatory changes.
There are symptoms for which you should definitely consult a doctor and have your orbits scanned. These include:
- Significant decrease in vision over a short period of time.
- Pain in the eye area that occurs for no apparent reason.
What you can explore
Optical coherence tomography of the eye allows you to evaluate all parts of the visual organ. However, the most informative manipulation is when analyzing the features of the following ocular structures:
- corneas;
- retina;
- optic nerve;
- front and rear cameras.
A particular type of study is optical coherence tomography of the retina. The procedure allows us to identify structural disorders in this ocular area with minimal damage. For examining the macular zone, the area of greatest visual acuity, OCT of the retina has no full-fledged analogues.
Possibilities of the method in studying orbits
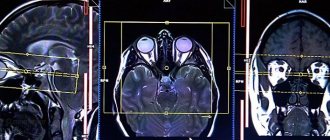
Computed tomography is a diagnostic procedure based on the action of x-rays. Our medical center is equipped with an expert-class Siemens Somatom tomograph, which allows us to improve the quality of diagnostics.
After the scan, the doctor analyzes the resulting images, which visualize:
- Bone structures that form the basis of the orbits.
- Soft tissue lining the orbital cavity.
- Lacrimal glands.
- Eyeballs.
- Part of the optic nerve.
Thanks to the high accuracy of the images and the qualifications of the specialist, CT of the eye orbits shows:
- Neoplasms of this area with determination of the stages of the process (including metastatic lesions).
- Bone fractures caused by trauma.
- Foreign body, its location and affected area.
- Various inflammatory processes with determination of their prevalence and degree of tissue destruction.
If the question of the need for a CT scan of the eye orbits has not been resolved, our call center staff will help you. A telephone consultation is also possible.
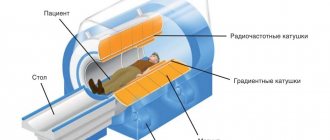
What is the principle of eye CT based on?
CT has revolutionized the treatment of orbital disorders. Tissues in the tomographic plane are assigned a density value proportional to their x-ray absorption coefficient. Based on these measurements, a two-dimensional image is constructed.
Modern helical CT scanners have multiple detector ports, and the scanner and collection tube move in a spiral around the patient, creating continuous data collection. This results in more data being acquired quickly, which, when combined with advanced software, allows for highly detailed reconstructions in all imaging planes.
Contraindications to CT of the eye orbits
Regardless of the examination area, contraindications to computed tomography are always the same. Among them are:
- Pregnancy, since X-ray radiation has a detrimental effect on the actively developing fetus.
- Behavioral disorders accompanied by increased excitability, when the patient cannot remain motionless in the tomograph.
- The technical weight limit applies to patients with high degrees of obesity (more than 150 kg).
Children can undergo this study only if:
- when other reliable diagnostic methods cannot be used;
- mandatory referral from a doctor.
If after a standard CT scan of the eye orbits the eyes should be examined using a contrast agent, then additional contraindications must be taken into account. These include:
- Allergic reactions to iodine and iodine-containing drugs. In this case, allergies of any severity are taken into account: from skin rashes to swelling of the larynx.
- Presence of renal failure. The removal of the contrast agent from the body occurs primarily through the kidneys, which increases the physiological load on them.
- The presence of other diseases that affect the kidneys. These include severe diabetes mellitus, long-term malignant hypertension and atherosclerosis of the renal arteries.
The period of breastfeeding is not an obstacle to CT. However, before the procedure you should pump or prepare formula, as it is not recommended to feed your baby breast milk for 24 hours after the scan.
The decision on the possibility and necessity of performing a CT scan of the eye orbits should be left to the doctor. Only a specialist will be able to correctly assess the situation of each individual patient.
Alternative Eye Exam Options
Computed tomography has the advantage of x-rays over other diagnostic methods. It allows you to identify hundreds of different defects and recognize inflammation at a very early stage.
However, it is contraindicated for some patients. In this case, use alternative eye examination options:
- MRI of the eye;
- ultrasonography;
- OCT (optical computed tomography).
These methods make it possible to identify many diseases that cannot be determined by other contact or non-contact methods. This is not to say that they are better than computed tomography, but they are the best diagnostic methods if CT is contraindicated.
Preparing for the study
There is no need to carry out special preparatory measures for standard tomography of the orbits.
If a contrast study is planned, it is necessary to check the blood creatinine level. Analysis done in advance will be valid for 2 weeks. If it was not possible to determine blood creatinine in advance, some centers provide the opportunity to be tested immediately before scanning using a test strip.
You should not go to a contrast examination completely hungry, as this may lead to nausea and dizziness. Some time before the scan you need to eat lightly.
When planning a CT scan, you need to tell your child in detail about the study in advance. You can also watch a video of the procedure together or play “we are in the CT room.” After this, the child will feel more confident.
To provide complete information about the patient’s health and the rationale for the prescribed procedure, you must bring:
- medical referral for CT scan of the eye orbits;
- conclusions from previous studies in this area (not just CT).
In the absence of medical documentation, research is also possible.
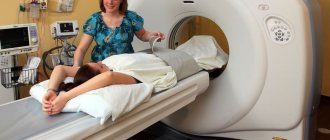
Methodology for CT scanning of the eye orbits
After all the documents have been completed, the nurse will tell you and show you what to do next.
The room with the tomograph and the medical staff's office are two adjacent rooms. Such separation is necessary due to the effect of x-ray radiation.
The nurse will guide the patient to the machine and help him lie down on a special table. It drives into the annular part of the tomograph to the level of the orbits.
Next, the nurse returns to the nursing office, where the doctor and other staff can observe the patient through the window. A special device is provided for voice communication.
A couple of minutes after turning on the device, the painless procedure will be completed. When contrast is administered, the examination time increases by 15 minutes.
You should remain still during the scanning process, as any movement will significantly degrade the image quality.
Diagnostic result
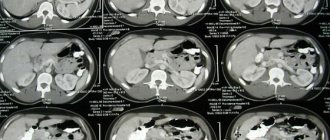
At the end of the scan, the doctor receives many cross-sectional images. After analyzing them, the specialist makes a conclusion and recommendations. Waiting times vary by center but can usually be spent in the medical center or on a walk-in basis. If you don’t have time to wait, you can receive the result by email or arrive on any other day.
Depending on the purpose for which the CT scan was done, the result may be as follows:
- medical center paper form;
- printouts of the most revealing photographs;
- writes all images to disk.
Electronic media in the form of a disk is provided free of charge in most clinics.
Also, after diagnosis, the radiologist will answer all questions regarding this study. This consultation will help the patient more accurately understand the CT scan result.
CT scan
The principle of the method is based on the interaction of body tissues with x-ray radiation. Some tissues absorb Rg - the rays are better than others (bone tissue), and fluid accumulations, on the contrary, do not interact with them.
However, in tomographs it is possible to regulate the “hardness” of the radiation, thanks to which any structures of the human body can be examined.
CT has many advantages, including:
- Non-invasive or minimally invasive with intravenous contrast.
- High accuracy of the results obtained.
- Credibility. Often they are sent for testing to clarify the diagnosis.
- The procedure takes little time, despite its complexity. This is especially important when you need to quickly choose a treatment strategy.
- Possibility of re-examination with image intensification (if necessary).
- Availability.
How does the procedure work?
If it is necessary to examine the fundus, the specialist will first instill the patient’s eyes with a special solution that dilates the pupil. The patient changes into cotton clothing without metal zippers, fasteners or buttons. Any detail can cause signal distortion, leading to image separation and incorrect results. After preparation, you should sit comfortably on the extendable table.
After preparation, the scanner apparatus begins to work, moving towards the person’s head. It slowly reads the information, instantly presenting it to the monitor screen. Therefore, if it is necessary to examine the consequences of an injury, the doctor can see the results during the procedure and decide on emergency surgery or hospitalization. For diseases associated with loss of visual acuity, glaucoma or retinopathy, careful decoding is required.
In difficult situations, specialists prefer to conduct a preliminary examination of the eye without a contrast agent. This allows you to get a picture of the disease. If a tumor is suspected in the fundus or optic nerve, a decision is made to administer contrast. After distributing the composition over the veins, the scanner operation is repeated. This allows you to get dynamic results and make an accurate diagnosis without additional examination or tests.
Some modern eye CT scanners are more compact in size compared to standard equipment. They allow examination in a sitting position and do not require changing clothes, which makes the procedure more comfortable for the patient. In this case, the person must briefly focus his gaze on a special lens through which the X-rays enter. Just a few seconds are enough to get maximum information about the problem or pathological process. After the examination, the patient can return to the usual rhythm of work and rest.
Eye CT findings are slightly different from conventional tomography. In addition to black-and-white images of inflamed or injured areas obtained as a result of CT, the diagnostician must process many graphs, informative diagrams and examination protocols. Using quantitative indicators, it is possible to detect hidden pathologies, but this requires time to decipher the signals.
Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI is based on recording the “excitation” of protons in the body after exposure to an electromagnetic pulse. In this case, the person is in a magnetic field.
Using this diagnostic method, soft tissue pathology is better visualized.
The scanning time for MR diagnostics exceeds that for CT. This factor causes some inconvenience, especially in patients with difficulties in maintaining immobility.
One of the contraindications to MRI is the presence of implants that contain ferromagnets (metals that can be magnetized).
Advantages of the method
First, the main advantage of retinal computed tomography
is non-contact, since the eyes are highly sensitive to any touch and interference. Secondly, the procedure takes no more than a minute (provided that no contrast is used). Thirdly, the diagnosis is absolutely painless (due to the fact that there is no physical intervention). Retinal OCT allows doctors to obtain detailed and clear information about the patient's eye condition, which is a definite advantage. Finally, this diagnostic method is quite inexpensive, its cost can reach 3000-4500 rubles.