Women's health requires attention, which is why doctors recommend visiting an ultrasound room for a gynecological examination at least once every six months. Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages is an absolutely safe, modern and very informative diagnostic method, which makes it possible to identify potential problems of the female genital area. On what day of the cycle should I do an ultrasound of the uterus? What is preparation for diagnosis? Answers to these questions can be found in our article.
Diagnostic methods
It is possible to obtain reliable information about the condition and anatomy of the internal genital organs thanks to high-frequency ultrasonic waves. Using ultrasound, you can evaluate the organs being examined in real time and check the blood flow in the vessels. The duration of the procedure is short.
Examination of the pelvic organs using ultrasound allows you to evaluate the structure and condition of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. This study is carried out for fibroids, cysts, inflammatory diseases and other pathologies of the pelvic organs. Ultrasound is performed in three ways:
- Transvaginal examination. An ultrasound scan through the vagina will help diagnose the presence of genital pathology as accurately as possible. Thanks to the introduction of a special sensor into the vagina, clear visualization of all parts of the examined area is ensured. Transvaginal examination allows for a procedure such as folliculometry, which is a method of performing ultrasound of the ovaries in women. It becomes possible to assess the degree of maturation of follicles in the ovaries. Considering the physiological characteristics of the female reproductive system, be sure to discuss with your doctor on what day the procedure should be performed. In order to diagnose infertility, using the transvaginal method it is possible to assess the patency of the fallopian or, as they are also called, fallopian tubes.
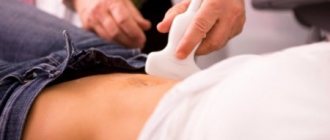
- Transabdominal examination is carried out by guiding the sensor along the surface of the anterior abdominal wall, that is, non-invasively, without penetration of the sensor into the patient’s body. With this method, ultrasound is allowed during menstruation.
- Transrectal examination, which is an alternative to transvaginal examination, can be performed on virgins by inserting a probe into the rectum.
Methods of gynecological ultrasound examination
Norms for ovarian size
One ovary in a woman is always slightly larger than the other - this is due to the peculiarities of their work. The dominant organ is large due to the constant production of eggs, the second in most cases is responsible only for the production of hormones. Therefore, identifying different sizes of appendages should not frighten the patient.
Normal ovarian size on ultrasound in adult women:
- length – 20-37 mm;
- width – 18-30 mm;
- thickness – 16-22 mm;
- volume – 4-10 cubic meters. cm.
During menopause, the maximum ovarian volume is 4 cubic meters. see - this is due to the natural cessation of their functionality.
Minor deviations can be considered normal. If the appendages are excessively large, their inflammation, the presence of neoplasms and other pathologies are diagnosed. Small ovaries are not the norm - such organs most often have low functionality, cause infertility or signal the onset of menopause.
Indications for testing
For preventive purposes, a gynecological examination is recommended to be carried out at least once a year for all women. The frequency of examination in the presence of chronic diseases, for example, fibroids or cysts, can be increased. Also, the gynecologist may prescribe an unscheduled and sometimes emergency examination if the patient has the following symptoms:
- Painful menstruation;
- Delayed or absent menstruation (amenorrhea);
- Irregularity of menstruation (cycle failure when there are less than 20 and more than 35 days between menstruation);
- Sudden spotting or bleeding between periods;
- Pain during sexual intercourse;
- Suspicious vaginal discharge;
- Atypical enlargement of the uterus, which is detected when examining the uterus in speculum or two-handed examination;
- Pregnancy;
- Infertility.
Optimal timing
If you delve into the physiological characteristics of the female body, you can figure out on your own what day of the menstrual cycle to do a gynecological ultrasound. The favorable time for an ultrasound is the first 3-5 days after menstruation, counting from the very first day of the onset of menstruation. However, it is not recommended to conduct the study later than 8-10 days of the menstrual cycle. The appointment of gynecological ultrasound exclusively in the first phase of the menstrual cycle is not accidental.
This is due to the fact that it is during this period of time that the mucous membrane of the uterus, the so-called endometrium, has a minimum density. And with a reduced endometrial layer, pathologies of the uterine cavity such as fibroids, hyperplasia, cysts and polyps are quite easily visualized. Therefore, only a qualified specialist can correctly set the date for an ultrasound scan.
In the second phase of the menstrual cycle, a significant thickening of the endometrium occurs, therefore, the smallest pathologies may be hidden in its layers, which will go unnoticed in a given time period.
It is noteworthy that during the period from the middle and in the second phases of the menstrual cycle, small cysts with a diameter of about 2 cm can alternately form in the ovaries. As a rule, this is either a follicle that should ovulate in the near future, or a kind of corpus luteum cyst that forms on the spot ruptured follicle and can last up to two weeks. Both formations are physiological structures characteristic of the female body. Therefore, when performing an ultrasound in this phase, it can be difficult for gynecologists to determine exactly what structure these formations have.
The indication for an ultrasound before menstruation is the diagnosis of the formation and development of the follicle to ascertain the completed phase of ovulation. Typically, this procedure is performed to evaluate and treat women with infertility or in preparation for in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages, as well as the fallopian tubes, must be performed within the above-mentioned periods, namely, on days 6-8 of the menstrual cycle. But there are circumstances in which the doctor needs to assess the functionality of the ovaries, namely the development of the follicle and the subsequent formation of the corpus luteum. In such cases, the question arises when is it better to do an ultrasound of the ovaries. It should be noted that this examination must be carried out several times throughout the menstrual cycle, for example, the first time on days 8-11 of the cycle, the second time on days 15-18, and the third time on days 23-25.
If a patient who consults a gynecologist complains of pain in the lower third of the abdomen, purulent discharge or excessively heavy menstruation, then on what day of the cycle an ultrasound is performed is not significant. If menstruation is delayed, the procedure is carried out upon request to exclude serious pathological processes.
Ultrasound diagnostic device
Monitoring folliculogenesis
All stages of egg development, from the follicle until the release of a mature egg (ovulation), are called folliculogenesis. Using ultrasound, you can monitor the evolution of the follicle and determine the presence and quality of ovulation. In addition to monitoring the growth of the egg, a general assessment of changes in the woman’s reproductive organs and their compliance with all phases of the cycle is made.
To carry out monitoring, ultrasound must be done at least 4 times during 1 cycle, and the procedure must be repeated at least 2 cycles in a row. So, the first study is carried out on days 7–10 (with a 28-day cycle). If menstruation is not regular, then the count starts from the first day of menstruation, performing diagnostics 3 days after their end. With a regular cycle, however, which has a longer or shorter time period, the time of the first diagnosis is considered 5 days earlier than the established mid-cycle.
Further sessions are performed at intervals of 2–3 days until pregnancy or the final formation of the corpus luteum. Simultaneously with the ultrasound examination, it is necessary to take a blood test for hormones, while the doctor analyzes the correspondence of the hormone levels to the data obtained using ultrasound.
The use of transvaginal ultrasound makes it possible to diagnose ectopic pregnancy in the early stages
Ultrasound during menstruation
Before going to the doctor, many patients wonder whether it is possible to do an ultrasound during menstruation? The answer to this question is quite ambiguous. It is not recommended to carry out a routine examination in the presence of bloody discharge, as this can create additional discomfort and pain for the woman, and existing blood in the uterus can significantly complicate the examination, interfering with the review, and making the procedure insufficiently informative. In general, this is not a contraindication and an ultrasound can be done during menstruation, for example, in case of emergency.
Common diseases
As a result of the study, many diseases can be identified, for example:
- Uterine fibroids are a benign neoplasm in the muscular layer of the uterus. The use of ultrasound for fibroids is a mandatory diagnostic method. This disease is characterized by symptoms that depend on the size of the tumor and its location: periodic aching pain in the lower abdomen, prolonged menstruation and uterine bleeding in the middle of the cycle. On the monitor, in the presence of fibroids, an increase in the volume of the uterus and the formation of a myomatous nodule are noted. Ultrasound of uterine fibroids can detect even small nodes, up to 1 cm in diameter.
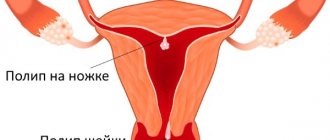
- Endometriotic polyps are uneven growth of the inner mucous membrane of the uterus. This disease is most often asymptomatic and the main study in this case is ultrasound. Sometimes individual pathological symptoms are observed in the form of infertility or spotting in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
- Endometriosis is a pathological process of proliferation of the inner mucous membrane of the uterine body, lining its cavity (endometrium). The disease is characterized by extremely painful periods, an unpleasant odor of vaginal discharge and the occurrence of bleeding in the middle of the cycle. Ultrasound examination for endometriosis, unlike ultrasound of uterine fibroids, is not a reliable method of examination, but helps to prescribe additional diagnostic measures to make a diagnosis.
- Ovarian cysts are round formations filled with fluid and located in the ovarian cavity. Common symptoms include menstrual irregularities, pain in the lower abdomen, and infertility. If you have this disease, you can do an ultrasound even during menstruation.
What does the examination show?
During the study it is possible to determine:
- the structure, size and position of the reproductive organ, as well as the thickness of its walls;
- the number of follicles and their exact sizes;
- proliferation of tumors in the ovaries and uterus.
Any deviations from the norm indicate the presence of violations. Among the pathological signs that are detected during ultrasound are:
- thickening of the fallopian tubes. Indicates an increased risk of onset of a malignant process;
- oval or round objects. Most likely these are fibroids or cysts;
- reduction in the size of the reproductive organ and enlargement of the appendages. As a rule, such changes indicate polycystic disease;
- change in echogenicity. Fixed for endometriosis and uterine fibroids.
Preparing for the study
Despite the fact that the patient can undergo examination at her own request, it is still worth first consulting with a doctor on which day of the cycle is best to do an ultrasound.
Before the procedure, you should empty your bladder, undress to the waist and lie down on the couch. Before a transvaginal examination, the doctor puts a special attachment on the transvaginal sensor and treats it with a gel that improves the passage of ultrasound waves. There is no discomfort when inserting the sensor.
Thanks to ultrasound, the level of diagnosis of gynecological diseases has improved significantly, and the number of accurate and timely diagnoses has increased. Only the treating gynecologist can say with confidence on what day it is worth doing an ultrasound of the uterus. By following the recommendations for conducting an ultrasound gynecological examination taking into account the menstrual cycle, the doctor will be able to correctly and accurately make a diagnosis and begin timely treatment.
Preparatory activities
Diagnosis using ultrasound does not require any special preparatory measures. But some actions can improve the quality of the picture on the monitor screen, which will make diagnosis easier.
- 3 days before the date of the ultrasound examination, it is recommended to exclude foods that cause increased gas formation from the diet. A swollen intestine is an obstacle to a full diagnosis during external examination of the uterus and other genital organs.
- If you cannot go on a special diet, in order to put your intestines in order, 2 days before the ultrasound diagnosis, drink 3 tablets of activated carbon per day, or take Espumisan according to the instructions.
- On the eve of the diagnosis, you should cleanse your intestines - go to the toilet. If you have to do rectal ultrasound diagnostics, you need to do an enema.
- External ultrasound examination must be done with a full bladder. It is necessary to drink tea, coffee, mineral water half an hour before the diagnosis. Such drinks are diuretic and will quickly fill the bladder. If transvaginal diagnostics are to be done, the bladder, on the contrary, should be empty. Before performing an ultrasound examination, simply carry out the washing procedure.
There is no need to do any other preparatory procedures. The entire diagnostic procedure takes from 5 minutes to half an hour. During the process, pictures are taken, the computer provides information about possible pathologies of the uterus, endometrium, other organs of the reproductive system, etc. After diagnosis, no measures need to be taken.
The basic rule of a full-fledged study is a specific day of the cycle, a correctly selected method. The rest depends on the qualifications of the doctor and the quality of the equipment. If you have health problems, you should not wait until the right day of your cycle arrives; you should immediately go to see a gynecologist. All further actions will be controlled by the doctor.