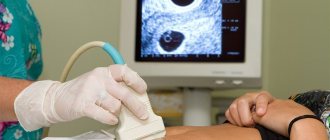
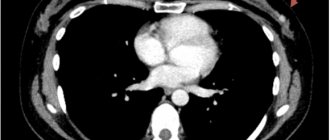
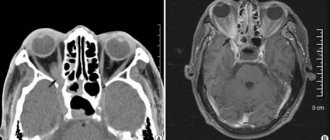
Prostate CT is one of the modern methods for diagnosing diseases of this organ. Under the influence of X-rays that penetrate the human body, a three-dimensional image of a given organ is obtained, the information is converted into a computer image through special sensors connected to a tomograph. The main feature of this method is that it does not require any outside intervention, i.e. is a non-invasive and at the same time highly reliable method that allows you to clearly visualize both the organ itself and the vascular-lymphatic system of this area and the surrounding soft tissues.
What does a CT scan of the prostate gland show?
Computed tomography allows the doctor to evaluate all the structural features of this organ: the density of the gland, the contour of the organ, the nature of the angle, the ratio of prostate parameters relative to other organs. In the image when performing tomography of the prostate gland, you can evaluate the condition of the seminal vesicles and canals, as well as the uniformity of distribution of fatty tissue. The method does not allow assessing the condition of the internal structures of the prostate gland. Typically, CT of the prostate gland is carried out in a complex study with other pelvic organs, for example, CT of the prostate and bladder, ureters, rectum.
The advisability of prescribing a computed tomography of the prostate can only be assessed by a doctor. The most common indications for this type of scan are:
- Decreased quality of sexual life.
- Urinary dysfunction.
- Increased anxiety and worry in men associated with sexual dysfunction.
This diagnostic method allows you to identify diseases and symptoms that are dangerous to human life, such as:
- Various injuries due to traumatic organ damage, foreign bodies.
- Initial signs of prostate cancer.
- Prostate adenoma.
- Inflammatory processes in the prostate gland.
- Complications and lymphadenopathy in men with diagnosed cancer.
- Organ circulatory disorders and bleeding.
- For follow-up or before starting radiation therapy.
- During aspiration biopsy.
Advantages of the method
If you follow the safety instructions, the magnetic resonance imaging method has a number of advantages:
- During a series of images, no invasion occurs and there is no exposure to ionizing radiation.
- During the procedure, it is possible to study the chemical composition of prostate tissue, which is a valuable diagnostic tool in identifying malignant neoplasms in the organ at the initial stages.
- Compared to X-ray examinations using iodine preparations, MRI contrast agents have a low allergenic effect.
- The clarity of the images and their detailed description provide the basis for the primary use of the method when choosing all diagnostic tools during the early detection of malignant changes in the pelvic organs and surrounding soft tissues.
- Bone tissue is not an obstacle when considering the soft tissues located underneath. Other visual methods do not allow detection of pathologies under bone structures.
- MRI makes it possible to differentiate pathologies in the early stages, including inflammatory processes with or without the participation of infectious agents, benign prostatic hyperplasia or malignant changes in the gland.
Contraindications to CT scan of the prostate
Prostate CT does not harm men's health, so there are no strict contraindications. Due to the specific design of the device itself, a person weighing up to 140-150 kg can fit into the tomograph. If the examination is prescribed for patients with impaired coordination of movements, then sedative premedication is administered before the procedure.
If we talk about CT scan of the prostate with contrast, then this type of study has its contraindications: it is not prescribed for men with allergies, because Contrast intolerance may occur, as well as in patients with heart and kidney failure.
Risks, restrictions, contraindications
When examining the prostate using MRI, damage to implants or metal structures of body parts may occur.
Possible low image quality when:
- implants that improve hearing;
- metal prosthetic crowns, pins;
- metal stents in blood vessels;
- joint metal parts;
- surgical plates, screws, staples;
- metal clips for cerebral aneurysms;
- electronic devices containing metals (pacemaker, defibrillator);
- artificial heart valves containing metal;
- nerve stimulants of metallic origin;
- infusion pump for distributing injected fluids in the body;
- Due to the attraction of bullets or fragments by the magnetic field of the device, a change in the static localization of a metal object may occur with consequences of disruption of the structure of soft tissues.
There is a slight risk of a mild allergic reaction that can be controlled and relieved in patients undergoing MRI when using a contrast agent.
In very rare cases, an increased proportion of contrast agent (gadolinium) in combination with the patient’s renal failure leads to systemic nephrogenic fibrosis. To prevent risk, a renal functional assessment is recommended before MRI.
The procedure imposes restrictions on the patient's movement in order to obtain clear images.
The second limitation is that the patient’s too large size does not allow high-field closed examination due to the standard size of the cylinder, so such patients are subjected to non-classical magnetic resonance imaging methods.
Preparing for a prostate CT scan
The preparatory stage before the proposed CT scan requires attention from the patient, because You will have to prepare 2 days before the examination. A couple of days before the tomography, you should eat exclusively dietary foods, completely removing from your diet foods that can cause increased gas formation. In order to completely eliminate the problem of bloating, medications are additionally prescribed that eliminate this problem, for example, Espumisan. 24 hours before the start of the upcoming examination, take laxatives and give a cleansing enema to completely cleanse the intestines. On the day of diagnosis, the patient should refrain from food and drink, because The examination will be carried out on an empty stomach.
Immediate preparation before starting a CT scan involves changing into comfortable, loose clothing without metal rivets or inclusions, in which the patient will feel comfortable, because CT diagnostics is a fairly time-consuming process - from 10 to 30 minutes.
MRI with dynamic contrast
With this method, the contrast agent is also administered intravenously, but not the entire dose in a stream, but in small drops. Thus, the same amount of gadolinium salts enters the prostate, but gradually. At the same time, an MRI examination is carried out, during which the doctor observes the work of the affected organ in real time, as they say in the scientific literature - in dynamics. This technique is indicated for diagnosing functional disorders. Diagnosis using fat suppression
In order to improve image quality, the so-called fat reduction technique is used. Moreover, as a result of the impact on the body of special radio frequency pulses generated by the device in a certain sequence, fat deposits cease to resonate with the magnetic field. Structures, including tumors, containing lipids will appear more intense on MRI images.
How is a prostate CT scan performed?
How is a prostate CT scan done? This question is asked by many patients who are about to undergo this examination. It should be noted that computed tomography is a painless and non-invasive method, so there is no need to worry too much.
After the preparatory stage, the patient takes a supine position on a special table, which the doctor then slides into the tomograph and the working element is activated. During the entire examination, the patient is alone in the room, the radiologist goes into the next room, where he controls the operation of the tomograph and observes the patient through the window, communication is carried out through a loudspeaker. The working element of the tomograph in the form of a ring rotates around the examined area. The tomograph works quite noisily, making cracking sounds, so the doctor should warn the patient about this so that it does not frighten him. If a CT scan with additional contrast is provided, the course of such scanning is slightly different.
Prostate MRI
In the classic version of prostate MRI, the patient is placed on a tomograph couch and secured with special straps. During scanning, it is important to keep your body still, otherwise the clarity of the image will be disrupted. The tomograph resembles a large cylinder into which a couch slides. To obtain clear images of tissue sections of the prostate, magnetic strips are attached to the lower back and lower abdomen.
With endorectal coil
Additional rectal sensors significantly expand the capabilities of prostate MRI. The resolution of the area, the clarity of incoming noise and signals, images and neurovascular bundles increases. The coil in a sheath is coated with gel and inserted into the small intestine using a thin tube. The cavity is then inflated and the balloon is secured in the desired position. The rest of the process follows the classic version. After the scan is completed, the balloon is deflated and removed.
With contrast
Before scanning, a contrast solution is injected intravenously. The coloring agent can also be administered orally or by injection. Contrast helps evaluate blood flow in the gland, distinguish between tumors and inflammatory processes. After administering the substance, the patient may feel coolness or a slight burning sensation, which is normal.
The usual examination time is 15-30 minutes. If a rectal coil or contrast is used, another 15 minutes are added. MR spectroscopy is performed during the study.
Prostate CT scan with contrast
The use of contrast enhancement makes it possible to accurately determine the features of the anatomical structure of a given organ, vascular network and regional lymph nodes, and to identify possible pathologies. For example, CT diagnosis of prostate cancer is best done with contrast, because such a substance stains the vascular network of a given organ, and the contours become clearly defined, clearly conveying all the structural features and possible inclusions in the form of various cysts, neoplasms, etc. The contrast agent is non-toxic to the human body and is completely eliminated from the human body naturally within 36-48 hours.
When is the procedure prescribed and indications?
In most cases, MRI is prescribed to identify the degree of development of prostate cancer, its localization in the organ, and assess the risk of metastases spreading beyond the lining of the gland.
In the absence of a malignant neoplasm, this method detects congenital pathologies of the prostate, benign tumors, complications after pelvic surgery in men, inflammatory and purulent processes in the gland.
POPULAR WITH READERS: Treatment of prostatitis with herbs, 10 basic recipes
The method is well suited for diagnosing prostate adenoma.
Features of this procedure and possible risks during CT diagnostics
Considering the peculiarity of the operation of a computed tomograph - exposure to X-rays, the main danger in such a diagnosis is radiation exposure. However, do not worry unnecessarily; the dosage received during scanning is small and not dangerous to human health. The risk appears only in the case of multiple repeated scans, since radiation can accumulate in the body and thereby provoke the growth of tumors in the body. Therefore, in cases where repeated examination is recommended, for example, when monitoring over time or before and after surgery, you should pause for at least 3-4 weeks or use, if possible, other alternative diagnostic methods without x-ray irradiation, this may There can be both laboratory examination methods, for example, biopsy, smears, and instrumental ones - ultrasound, magnetic resonance diagnostics.
When can the procedure be done after a biopsy?
Typically, MRI is performed before transrectal biopsy of the prostate, if the organ is intact.
If necessary and as prescribed by the doctor, a repeat MRI after the biopsy is performed no earlier than 20-30 days. During this time, local hemorrhages after needle insertion are eliminated naturally.
POPULAR WITH READERS: Why pay attention to urine during prostatitis
After the biopsy, it is recommended to perform magnetic resonance imaging using a high-field device with a magnetic field strength of more than 1 Tesla.
It is advisable to conduct the study with images taken in two perpendicular directions; additional contrast is used in dynamics.
Peristaltic activity of the intestine is inhibited by the preliminary administration of hyosnip butylbromide intravenously.
Where to get a prostate CT scan?
After your attending physician has given you a referral for this type of diagnosis, you can independently choose the place where you will have it performed, taking into account your preferences, wishes and capabilities. Computer diagnostics of the prostate gland is carried out both in public medical institutions and in private offices and clinics. In state medical institutions you can even undergo such diagnostics for free, because this is included in the compulsory health insurance policy. However, the waiting period for your turn is completely unexpected and can range from several weeks to several months; this, as a rule, is a matter of chance. Therefore, in cases where an immediate CT examination is necessary, you will have to use the services of commercial medical institutions. Some private diagnostic centers operating around the clock offer discounts for their patients when conducting such examinations at night, so it is worth paying attention to this. CT scan of the prostate gland with contrast in St. Petersburg and Moscow is performed in the same place as CT scan without contrast.
Prices
You can get an MRI of the prostate in any clinic that has this equipment and specialists of a certain profile. The cost of diagnostics will depend on the method and scope of the study, the power of the equipment and the rating of the clinic.
| Clinics in Moscow | Price in rubles |
| On the street K. Zetkin | 8600 |
| LDC Kutuzovskaya | 6500 |
| Scandinavian Health Center | 11000 |
| Medskan, st. Nizhny Novgorod | 7500 |
| Research Institute of Urology named after Lopatkin | 3750 |
Magnetic resonance equipment may differ in the strength of the magnetic field, and therefore in the quality of tomographic images. Based on the radiation power, MRI machines are divided into:
- Low-floor - 0.23–0.35 Tesla.
- Mid-field -1 Tesla.
- High-field - from 1.5–3 Tesla.
For diagnostic purposes, radiation from 1 Tesla is relevant. There are devices with radiation of 5 Tesla used for scientific purposes.
What is better for prostatitis: MRI or CT
The prostate gland is an organ of the male reproductive system responsible for the production of sperm. The organ is composed of parenchymal tissue, making visualization using computed tomography (CT) difficult. X-ray diagnostic methods show hard tissue structures, so the prostate is better visualized by MRI.
Special modes have been developed to track prostatitis, adenoma, malignant and benign tumors. Magnetic resonance imaging qualitatively monitors the condition of the surrounding lymph nodes. Cancerous lymphadenitis occurs when affected by metastases. Tomograms show enlarged nodes measuring over 5 mm.
Damage to the prostate gland in men provokes three common diseases:
- Acute and chronic prostatitis;
- Adenoma;
- Cancer.
Differential diagnosis of pathology is carried out using magnetic resonance imaging. The examination helps to distinguish chronic inflammation from the acute version. An additional method, MR angiography with intravenous administration of gadolinium salts, verifies vascular changes, congenital and acquired anomalies, and tumor capillaries. The study of layer-by-layer sections allows you to track the smallest details, detect small cancer nodes and metastatic foci. Secondary lesions appear not only in the prostate, but also in nearby and distant lymph nodes.
High-field MR imaging has high resolution, allowing differentiation of tumors several millimeters in size.
Early stages of oncology do not manifest clinical symptoms. Common screening for prostate disease using the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test may be false-positive. Prostatitis is accompanied by an increase in tumor markers. If you do a magnetic resonance scan, you can distinguish prostatitis from hyperplasia and cancer. Contrasting provides more detailed information. The information content of the combination of native scanning and subsequent enhancement exceeds 96%. The effectiveness of the examination is sufficient to study changes in the prostate parenchyma, surrounding tissues, arteries and veins.
Computed tomography allows one to distinguish between benign and malignant prostate tumors. The best quality is offered by multispiral units (MSCT). The devices are equipped with several groups of radiation sensors, allowing simultaneous examination of large areas through 1 mm. Due to the weak reflection of rays from soft tissue parenchyma, scanning is complemented by CT angiography.
Oncology requires the most thorough research.
It is necessary to take into account the impossibility of initial detection of small lesions using CT. A computed tomography scan is prescribed to study previously identified tumors (by other clinical means). X-ray methods are not used to screen for malignant tumors. Computer scanning does not detect metastases. Visualization is enhanced by using the Gleason score to detect cancerous pelvic lymphadenitis.
CT scanning for prostate cancer is performed before surgery to determine the progress of surgery. The modern method - PET/CT involves the introduction of a radionuclide agent that can be quickly eliminated and accumulate excessively inside the prostatic parenchyma. A cancerous tumor intensively “collects” the substance, which makes it possible to guarantee (about 100%) detection of oncology.
The preparatory stage for CT and MRI of the prostate does not cause any particular difficulties for the patient. Before prescribing X-ray examinations, it is necessary to calculate the harm from the procedure and the diagnostic benefit. If there is no suspicion of a cancerous tumor, there is no particular rationale for a CT scan. Detection of prostatitis by tomography is of no practical use. A PSA test and examination by a urologist can confirm the diagnosis with high certainty. There is no need for excess radiation in this situation.
Magnetic resonance scanning is carried out in the absence of metal objects in the area of study. Ferromagnets are ways to move or heat up under the influence of a magnetic field. Titanium implants are not dangerous.
Features of preparation for MRI:
- Elimination of fear of enclosed spaces;
- Examination of the patient's outpatient card;
- Analysis of allergy history, hypersensitivity to gadolinium;
- Consultation with specialists if necessary (taking pills, removing a pacemaker during the examination);
- Studying the possibility of a person maintaining a stationary position when scanning on a diagnostic table.
A list of manipulations to cleanse the intestines of gas and feces helps older patients properly prepare for a prostate examination. The attending physicians prescribe fortrans, espumizan, and activated carbon. A cleansing enema with clean boiled water is prescribed to remove feces from the rectum. The organ is located next to the prostate gland. Fecal stones and gas create signal distortion and provoke additional noise.
Next to the prostate is the bladder and seminal vesicles. If you plan to study the condition of these organs, you will need to first take about 2 liters of water. Filling the bladder ensures stretching of the walls, which improves the visibility of the mucous membrane and the thickness of the walls of the organ.
Magnetic resonance examination is characterized by high information content. Diagnosis becomes better after preliminary ultrasound. Ultrasound examination verifies pathological changes. Detection of a suspicious node allows for a targeted magnetic resonance scan with projection onto the area of unknown pathological foci.
Determines what is best to do - CT or MRI of the prostate gland, a radiation diagnostics doctor. The specialist will analyze the outpatient card, medical history, and determine the indications for the required diagnostic method.
Suspicion of oncology requires obtaining a number of important information:
- Study of the localization of the outbreak;
- Determining the depth of location;
- Assessment of the condition of distant and nearby lymph nodes;
- Differential diagnosis of changes in surrounding tissues;
- Verification of metastatic nodes.
It is important to diagnose changes early in development. The high reliability of radiation methods suggests the appointment of both studies if oncology is suspected.
Computed tomography is prescribed according to indications:
- Diagnosis of acute conditions (bleeding from the pelvic organs);
- Inflammatory processes;
- The occurrence of lymphadenitis in patients with cancer;
- After heavy blows to the abdomen, perineum;
- Exclusion of foreign bodies;
- Presence of perforations (through defects).
The test is carried out before planning radiation therapy to accurately determine the tumor site. Before taking material from the pathological area, positioning is required to accurately insert the puncture needle.
CT scan does not show structural changes in the prostate parenchyma, which is an indication for MRI.
A benign tumor (adenoma) is accompanied by an increase in the size of the parenchyma. A large node leads to compression of the urethra. The situation leads to certain clinical symptoms:
- Difficulty urinating;
- Painful sensations after urge;
- The appearance of blood in the urine;
- Sexual problems;
- Decrease in sperm count during spermogram analysis.
On magnetic resonance imaging using a high-field apparatus, prostate adenoma is diagnosed by detecting an area of increased intensity against the background of normal prostate tissue.
The essence of an MRI examination is the registration of the changed radio frequency of hydrogen atoms of liquid tissue under the influence of a magnetic field. Obtaining tomograms is achieved by placing a person inside a tunnel with a signal source and receiver. The duration of the procedure is 20-30 minutes.
If you find out how magnetic resonance scanning is carried out in St. Petersburg, clients of diagnostic centers are offered tomography with open and closed tomographs.
The device creates noises and clicks. Noise effects are suppressed by wearing headphones and earplugs. Some clinics offer video broadcasts of films and cartoons so that patients can remain still during the procedure.
It is better to diagnose oncological processes with intravenous contrast. Improves visualization of the arteries of the pelvic organs during CT of an iodine-containing drug. MRI enhancement is performed through an injection of gadolinium. The paramagnetic shows the condition of the vessel wall, helps to detect atherosclerotic narrowing and blood clots.
Before the procedures, a provocative test is done. A small dose of contrast is administered and the person’s health status is monitored. If allergic reactions do not appear after the injection, an MRI with contrast is performed. The basal-bolus method of enhancement is common. The substance is supplied sequentially by injection with syringe dispensers. Continuous scanning allows you to observe the distribution of the substance through the blood supply.
Attention! An experienced radiology doctor will be able to detect cancer inside the pancreas without contrast. The localization of the tumor inside the capsule cannot be verified using computed tomography. MRI helps resolve the issue.
A qualified specialist can choose what is best for the prostate. If necessary, after a native examination, tomography with contrast is prescribed. Over 500-700 images are obtained in one procedure.
Features of microcirculation of the pelvic organs require knowledge of the anatomy of the organs. After enhancement, the distinct contours of the prostate are not visible. The procedure is aimed at increasing the visibility of newly formed capillaries of the pathological node. Tumors have their own network of vessels, which are clearly visible on photographs even when the tumor is small.
The main advantages of MR examination:
- A small list of indications;
- Low price;
- No harm from radiation exposure (compared to CT);
- Obtaining clear informative images of the prostate gland.
Contraindications to CT and MRI exist. If the study is performed with contrast, it is necessary to exclude hypersensitivity reactions to the enhancing agent.
X-ray examination methods are carried out after alternative examinations have been performed, in which there is no harm. Computed tomography results in a high exposure dose of radiation, so it is performed strictly according to indications.
Methods of alternative diagnosis of the prostate:
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- Multislice tomography (MSCT);
- Laboratory urine analysis;
- Spermogram;
- Endoscopy.
The price of computed tomography of the prostate gland in St. Petersburg and Moscow is from six to twelve thousand Russian rubles. The cost includes the main service, wages for medical personnel, costs for optical discs and other storage media. By analyzing reviews from regular customers of our partner clinics, readers will be able to choose the optimal diagnostic center, taking into account the features of the tomograph and the qualifications of doctors.
Call us by phone from 7:00 to 00:00 or leave a request on the website at any convenient time
Based on materials from mrt-kt-malogo-taza.ru
To differentiate disorders, various types of instrumental diagnostics are used. PET, CT, magnetic resonance imaging for prostatitis are different in their information content and have their own characteristics, disadvantages and advantages.
The study of the pelvic organs is associated with certain difficulties associated with their anatomical location. The prostate gland is surrounded on all sides by muscles and protected by the male skeleton.
To determine the condition of the prostate, the digital rectal method is traditionally used, in which the results of the study largely depend on the qualifications of the doctor and his experience.
Examination of the pelvic floor is also carried out using modern types of instrumental research. During the initial examination and suspicion of prostatitis, an ultrasound is often prescribed. MRI, CT, PET-CT are used to clarify the diagnosis.
Medical practice has shown that although ultrasound diagnostics can quickly determine deviations in the size and structure of the prostate gland, for the most part it leaves many questions open. TRUS and ultrasound do not make it possible to determine the nature of the changes or detect the initial signs of the disease.
In modern urological clinics, tomography is increasingly recommended for diagnosing prostatitis. There are three main types of instrumental research, differing in information content and methodology.
At the moment, magnetic resonance imaging for prostatitis is done for two reasons:
- Identify inflammation at an early stage of development.
- Rule out the malignant nature of the changes.
An MRI image not only shows the presence of inflammation in the prostate gland, but also allows us to identify the causes of disorders:
- Congestion associated with deterioration of venous outflow.
- Results of exposure to pathogenic organisms.
In modern practice, MRI of the prostate for prostatitis is considered one of the most effective and informative diagnostic methods. An additional advantage is the absolute safety of the study and the almost complete absence of contraindications.
Computed tomography for inflammation of the prostate gland is performed with contrast. The study is less informative than MRI, but has an important advantage: speed of results.
Based on the images obtained, the acute and chronic forms of the disease are differentiated, and you can also see the prostate abscess and the direction of growth of the purulent sac, for timely surgical removal.
The information content of CT is significantly inferior to magnetic resonance imaging. Research for prostatitis is carried out with contrast. Spiral computed tomography can compete with MRI in terms of the results obtained, but has certain contraindications:
- Contrast causes allergic reactions and is not prescribed to patients with kidney problems.
- During a CT scan of the pelvis, the patient is exposed to a dose of radiation. Repeated examination is allowed no earlier than after several months.
Computed tomography of the prostate gland for prostatitis is prescribed to clarify the localization of inflammation and internal disorders, in cases where there are time restrictions: the patient’s serious condition, the need for surgical intervention, etc.
Positron emission tomography is an innovative diagnostic method designed to assess tissue metabolism at the cellular level. The main purpose of the study is to diagnose cancer in the early stages of development. During the examination, it is possible to detect a malignant tumor up to 0.5 mm.
The main task and purpose of positron emission tomography is to identify oncology. Additionally, PET-CT shows malfunctions in the functioning of internal organs.
For the study, contrast enhancement is carried out: choline, gallium, methionine, fluorodeoxyglucose - radionuclides. After accumulation in tissues, a scan of the human body is performed.
Signs of prostatitis on PET-CT will be shown in the form of malfunctions and insufficient functionality of the gland. Positron emission tomography is performed only if there are reasons to suspect cancer.
Regardless of the chosen examination method for prostatitis, it is necessary to properly prepare for the examination session:
- MRI - if the study is performed using a rectal coil, a cleansing enema will be required. In other cases, preparation for an MRI includes psychological assistance to the patient to overcome the fear of being in the confined space of a tomograph. You will need to remove all metal objects.
- CT scan - one day eliminates all foods that contribute to flatulence. Contrast is administered on an empty stomach. Preparation for computed tomography includes determining allergic reactions and contraindications in the patient.
- PET-CT - there are no special measures intended to prepare the patient for the examination. It is necessary to introduce a radioisotope substance in advance. You can remain in your clothes during the PET-CT scan. You will have to remove all jewelry, removable dentures, and glasses.
Preparing for a CT scan is not difficult. The study takes from 5 minutes to half an hour, depending on the chosen technique. The results are deciphered within a few hours.
Ultrasound has long remained an almost indispensable method for studying inflammation of the prostate gland. This was facilitated by several factors: the speed of the survey, information content. Ultrasound helped identify abnormalities. The results were used to make a differential diagnosis.
There were several disadvantages:
- Impossibility to exclude cancer.
- A little information.
Modern techniques are more informative and are gradually replacing ultrasound. MRI or PET-CT data accurately determine not only the presence of an inflammatory process in the prostate gland, but also help differentiate cancer or refute its presence.
With computed tomography, it is more difficult to determine prostatitis, but it is also possible. The technique is used for patients in severe conditions. Although medical practice has shown that often repeated MRI or PET scans refute the diagnosis made by CT.
Ultrasound will remain the most popular diagnostic method for a long time. Not all hospitals and urological centers have the necessary equipment to perform tomography of the gland, but an ultrasound device is present in almost every clinic.
But if you have a choice to diagnose genitourinary disorders, it is better to undergo an MRI or CT-PET study.
Based on materials from ponchikov.net
Prostate CT is one of the modern methods for diagnosing diseases of this organ. Under the influence of X-rays that penetrate the human body, a three-dimensional image of a given organ is obtained, the information is converted into a computer image through special sensors connected to a tomograph. The main feature of this method is that it does not require any outside intervention, i.e. is a non-invasive and at the same time highly reliable method that allows you to clearly visualize both the organ itself and the vascular-lymphatic system of this area and the surrounding soft tissues.
Computed tomography allows the doctor to evaluate all the structural features of this organ: the density of the gland, the contour of the organ, the nature of the angle, the ratio of prostate parameters relative to other organs. In the image when performing tomography of the prostate gland, you can evaluate the condition of the seminal vesicles and canals, as well as the uniformity of distribution of fatty tissue. The method does not allow assessing the condition of the internal structures of the prostate gland. Typically, CT of the prostate gland is carried out in a complex study with other pelvic organs, for example, CT of the prostate and bladder, ureters, rectum.
The advisability of prescribing a computed tomography of the prostate can only be assessed by a doctor. The most common indications for this type of scan are:
- Decreased quality of sexual life.
- Urinary dysfunction.
- Increased anxiety and worry in men associated with sexual dysfunction.
This diagnostic method allows you to identify diseases and symptoms that are dangerous to human life, such as:
- Various injuries due to traumatic organ damage, foreign bodies.
- Initial signs of prostate cancer.
- Prostate adenoma.
- Inflammatory processes in the prostate gland.
- Complications and lymphadenopathy in men with diagnosed cancer.
- Organ circulatory disorders and bleeding.
- For follow-up or before starting radiation therapy.
- During aspiration biopsy.
Prostate CT does not harm men's health, so there are no strict contraindications. Due to the specific design of the device itself, a person weighing up to 140-150 kg can fit into the tomograph. If the examination is prescribed for patients with impaired coordination of movements, then sedative premedication is administered before the procedure.
If we talk about CT scan of the prostate with contrast, then this type of study has its contraindications: it is not prescribed for men with allergies, because Contrast intolerance may occur, as well as in patients with heart and kidney failure.
The preparatory stage before the proposed CT scan requires attention from the patient, because You will have to prepare 2 days before the examination. A couple of days before the tomography, you should eat exclusively dietary foods, completely removing from your diet foods that can cause increased gas formation. In order to completely eliminate the problem of bloating, medications are additionally prescribed that eliminate this problem, for example, Espumisan. 24 hours before the start of the upcoming examination, take laxatives and give a cleansing enema to completely cleanse the intestines. On the day of diagnosis, the patient should refrain from food and drink, because The examination will be carried out on an empty stomach.
Immediate preparation before starting a CT scan involves changing into comfortable, loose clothing without metal rivets or inclusions, in which the patient will feel comfortable, because CT diagnostics is a fairly time-consuming process - from 10 to 30 minutes.
How is a prostate CT scan done? This question is asked by many patients who are about to undergo this examination. It should be noted that computed tomography is a painless and non-invasive method, so there is no need to worry too much.
After the preparatory stage, the patient takes a supine position on a special table, which the doctor then slides into the tomograph and the working element is activated. During the entire examination, the patient is alone in the room, the radiologist goes into the next room, where he controls the operation of the tomograph and observes the patient through the window, communication is carried out through a loudspeaker. The working element of the tomograph in the form of a ring rotates around the examined area. The tomograph works quite noisily, making cracking sounds, so the doctor should warn the patient about this so that it does not frighten him. If a CT scan with additional contrast is provided, the course of such scanning is slightly different.
The use of contrast enhancement makes it possible to accurately determine the features of the anatomical structure of a given organ, vascular network and regional lymph nodes, and to identify possible pathologies. For example, CT diagnosis of prostate cancer is best done with contrast, because such a substance stains the vascular network of a given organ, and the contours become clearly defined, clearly conveying all the structural features and possible inclusions in the form of various cysts, neoplasms, etc. The contrast agent is non-toxic to the human body and is completely eliminated from the human body naturally within 36-48 hours.
It is impossible to answer this question unequivocally, because... What to prescribe for a given patient can only be determined by the attending physician who issues the referral for this examination, having studied in detail the history of the disease, the results of additional instrumental and laboratory methods, as well as concomitant pathologies and the individual characteristics of the patient. We can definitely say that if you follow a competent approach when prescribing such an examination, there is no harm observed with a CT scan of the prostate.
Considering the peculiarity of the operation of a computed tomograph - exposure to X-rays, the main danger in such a diagnosis is radiation exposure. However, do not worry unnecessarily; the dosage received during scanning is small and not dangerous to human health. The risk appears only in the case of multiple repeated scans, since radiation can accumulate in the body and thereby provoke the growth of tumors in the body. Therefore, in cases where repeated examination is recommended, for example, when monitoring over time or before and after surgery, you should pause for at least 3-4 weeks or use, if possible, other alternative diagnostic methods without x-ray irradiation, this may There can be both laboratory examination methods, for example, biopsy, smears, and instrumental ones - ultrasound, magnetic resonance diagnostics.
After a CT scan of the prostate, the radiologist interprets all the results obtained and gives the patient a written report, on the basis of which the attending physician assesses the severity and extent of the disease and determines the scope and therapeutic tactics of the upcoming treatment.
After your attending physician has given you a referral for this type of diagnosis, you can independently choose the place where you will have it performed, taking into account your preferences, wishes and capabilities. Computer diagnostics of the prostate gland is carried out both in public medical institutions and in private offices and clinics. In state medical institutions you can even undergo such diagnostics for free, because this is included in the compulsory health insurance policy. However, the waiting period for your turn is completely unexpected and can range from several weeks to several months; this, as a rule, is a matter of chance. Therefore, in cases where an immediate CT examination is necessary, you will have to use the services of commercial medical institutions. Some private diagnostic centers operating around the clock offer discounts for their patients when conducting such examinations at night, so it is worth paying attention to this. CT scan of the prostate gland with contrast in St. Petersburg and Moscow is performed in the same place as CT scan without contrast.
Call us by phone from 7:00 to 00:00 or leave a request on the website at any convenient time
Based on materials from xn—-xtbekk.xn--p1ai
Have you been struggling with PROSTATITIS and POTENTITY for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure prostatitis by taking it every day.
Kidney diseases are steadily increasing every year. Accurate and timely diagnosis is the key to a speedy recovery, which is why MRI of the kidneys is increasingly being prescribed by specialists to make a diagnosis. The examination helps to identify the inflammatory process, associated diseases, the presence of mechanical damage, and also provides complete information about the parameters of the organs. Tomography images are highly accurate and almost 100% error-free. If we talk about MRI of the kidneys with contrast, then, among other things, this type of study helps to identify the difficult presence of a pathological formation, but also provides detailed data on the location of the tumor, the stage of its development, and also shows other parameters that the doctor will rely on when prescribing treatment.
MRI of the kidneys, or in deciphered form - magnetic resonance imaging of the kidneys, is a diagnostic study based on the action of x-rays. As a result, on the monitor the specialist receives not only an image of the organ being examined, but also a section. Thanks to such subtle diagnostics, it is possible to detect even minor changes in the kidneys and urinary tract.
To improve potency, our readers successfully use M-16. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
The procedure itself lasts from ten to thirty minutes. The patient lies down on a table, which is then moved into a special apparatus under the supervision of a specialist. During the procedure, the patient should try to breathe evenly and in no case panic. It is strictly forbidden to move, spin, or talk. This may affect the quality of the image and, as a result, the diagnosis.
The procedure is carried out in two ways:
- using a contrast agent;
- no contrast.
MRI of the kidneys is performed to determine and describe the following data:
- the sizes of organs and information about the departments, up to the determination of exact boundaries;
- anatomical structure of renal tissue and its structure;
- monitoring the dynamics of the development of cysts, tumors, and the size of stones;
- stage of cancer development and its spread;
- degree of damage to the renal vessels;
- the functioning of the organ, that is, excretory and concentration abilities.
Indications for the study are the presence of the following clinical symptoms:
- swelling of the upper and lower extremities;
- colic;
- pain in the lumbar region, which is accompanied by fever, chills and dizziness;
- changes in the general urine test, for example, high specific gravity.
Can children have an MRI? Yes, but the child needs to be adjusted and explained to him how he should behave.
MRI of the kidneys and urinary tract cannot be performed in the following cases:
- pregnancy period;
- renal failure;
- the presence of pacemakers, metal implants;
- epilepsy;
- panic attacks, seizures.
MRI of the kidneys does not require special preparation. The patient must wear underwear made from natural fabrics. Watches, jewelry, hairpins - in general, everything metal must be removed before the procedure.
Preparation does not affect your diet or medications in any way, so you can eat whatever you want and take the medications you need. If you are very impressionable and afraid of confined spaces, then a specialist may decide to prescribe sedatives.
Kidney MRI with contrast is one of the most accurate diagnostic methods. The study can be prescribed not only if there is a suspicion of any pathology, but also when making a diagnosis, to monitor the dynamics of development, and also after surgical interventions.
When is a tomography done? MRI of the kidneys with contrast agent is recommended in the following cases:
- to determine the structure and exact dimensions of not only kidney tissue, but also nearby organs;
- presence of neoplasms;
- disorders of the urinary tract (to determine the general condition);
- the presence of bacterial, infectious or inflammatory disorders;
- determination of performance and functional activity.
There are other contraindications to contrast tomography:
- allergy sufferers. Before the procedure is carried out, specialists do a test that will show the body’s reaction;
- patients with shrapnel wounds;
- presence of implants and prostheses;
- pregnancy. In rare cases, the procedure is carried out as prescribed by a doctor;
- claustrophobia.
In the presence of epilepsy and convulsive syndrome, patients can undergo an MRI, but only after preliminary administration of drugs that are classified as local anesthesia.
What are the advantages of contrast-enhanced tomography? Do I need to prepare in any way for the procedure? No, it does not require any special preparation!
The main advantages of diagnostics include the following:
- the ability to diagnose a disease with contraindications to other types of research;
- indicates the problem and helps determine the effectiveness of the treatment. For example, MRI helps determine the size of the stone and the possibility of removing it in a conservative manner;
- breathing, pulse, heartbeat, amount of adipose tissue - all this does not in any way affect the results of the study and their accuracy;
- All data is processed by a computer, the likelihood of errors is minimized.
Abdominal MRI is an informative diagnostic method that helps in the following:
- visualization of organs, vessels, lymph nodes;
- assessment of the position of the abdominal organs, their shape and size;
- determination of the nature, localization and prevalence of the pathological process.
The main indications for the procedure include the following:
- congenital anomalies and defects;
- injuries;
- circulatory disorders;
- suspected tumors;
- cysts, hematomas;
- disorders of the liver and gall bladder;
- pancreatitis.
So, which is better: MRI or CT? It is quite difficult to answer this question unambiguously, because each of these methods shows great information content in various aspects. Both methods provide complete information about the condition of the kidneys.
MRI is safer and more informative in diagnosing diseases of soft tissues, joints, blood vessels and the nervous system. Whereas CT does not have such a high level of safety, but provides an accurate and complete picture of injuries, diseases of internal organs and bleeding. Depending on the results of preliminary diagnostics, the specialist makes a decision on the advisability of one or another research method!
Patient reviews can say a lot about the benefits of kidney MRI. The study has earned a positive opinion both among ordinary patients and leading specialists.
So, MRI of the kidneys is a modern and highly effective procedure that helps in making a diagnosis. Thanks to innovative techniques such as MRI, kidney diseases can be treated quickly and in a timely manner!
Based on materials from potencya24.ru
Interpretation of MRI diagnostic results
Usually, cynics give the patient pictures, but you should not try to make a diagnosis yourself. The conclusion is made only by an experienced doctor. In addition, in radiology-radiology there is a technique called “double reading”, when at least two doctors evaluate the results of examination of one patient after a certain time. This allows you to avoid mistakes and false positive diagnoses.
The resulting image is interpreted as follows:
- With a healthy prostate gland, the size of the organ corresponds to the age norm; no neoplasms are observed in the prostate and nearby tissues.
- Benign hyperplasia (prostate adenoma) - the contours of the gland are smooth, an increase in its size is observed.
- Inflammatory process - due to weakened blood supply, with prostatitis there is a “blurred”, unclear outline, the gland itself is enlarged.
- Malignant neoplasm - one or more areas are visualized, characterized by a different structure than the tissue of the main gland. They may have unclear contours and grow into surrounding organs.
Rectal suppositories for prostatitis and prostate adenoma
The exact definition of a tumor (malignant or benign) is given by a histologist based on a biopsy, however, based on the image of a magnetic resonance imaging study, the type of process can be assumed.