The cervical spine is one of the key structures of our body. In this part of the column there are vessels that take part in the nutrition of the spinal cord and brain. These include paired vertebral arteries, which merge to form the basilar artery. The vertebrae have special processes and grooves where important vessels pass. Any injury and damage to bone structures is a risk to human life.
The cervical spine connects the brain and spinal cord and, together with the soft tissues and ligaments, provides mechanical support for the head. Despite such numerous and important functions, the neck must be mobile, so this part of the body is quite fragile. In addition, modernity is rapidly adapting to a sedentary lifestyle and physical inactivity. This further weakens the muscles that support the neck.
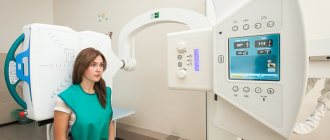
X-ray of the cervical spine
This article deals with a method for diagnosing pathologies of the cervical spine, such as radiography. Attention is paid to the principle of action, technique, patient preparation, contraindications and indications, advantages and disadvantages of this instrumental method.
Operating principle
An X-ray machine is equipment that allows you to visualize the internal structures of the body using X-rays, which are electromagnetic waves of a certain spectrum and energy (the energy value of these photons lies between the energies of ultraviolet and gamma radiation). Passing through matter, an electromagnetic wave is absorbed to some extent, scattered and decelerated, but with different intensities. Registration of radiation on X-ray sensitive film after the passage of X-rays through the tissues of the body is the basis of this instrumental method (with digital equipment it is already possible to immediately obtain a digital image - in this case, film is not required).
Soft tissues practically do not absorb X-rays - they transmit them, so on film or on a screen soft tissues will appear dark.
Bone tissue and harder structures absorb waves. They are much lighter on the x-ray than soft tissue.
Radiography is based on the passage of x-rays through the tissues of the body, due to which a “picture” of what is happening emerges
The radiologist evaluates the different image intensities. Despite the fact that modern technologies allow good visualization of soft tissues, radiography is the gold standard for pathologies of hard tissues such as bone and cartilage. This is due to the high content of calcium ions, the atomic number of which is higher than that of the elements contained in soft tissues.
It is noteworthy that CT (computed tomography) is also based on X-rays, but, unlike radiography, it makes it possible to obtain a layer-by-layer image of the entire body in different projections and perform digital image processing. That is why this method is much more expensive than a conventional x-ray and can be used to clarify the diagnosis.
X-ray special
One of the conservative methods of contraindicating injuries and diseases of the spine is preparation. This is the simplest and easiest way to identify many studies related to spinal deformity. But in a procedure that is painless depending on the degree of damage and localization, there are several options for such a special examination.
X-ray is taken of the spine
The indications for X-rays of the cervical spine are headaches and short-term dizziness when using the head tilt or the neck apparatus. Pictures are taken in special projections. In frequent cases, the body, in order to be made thanks to the cervical spine, is specially carried out through an open or. Afterwards, the doctor analyzes which and reveals the severity of the disease. Penetrate X-ray preparation of various cervical spine is not required.
X-ray image of the spine
For the screen of the lumbar spine, various are needed. How to prepare for spine film? Two days before the examination, you need to exclude from eating those foods that provoke the intensity of gases in the intestines, since some of the effects can distort the coloring of the image. On the day before the examination, you should take colored to relieve flatulence, and then skip dinner. An X-ray image of the spine is taken after having previously cleansed the intestines. This is the only way to make the photo as accurate as possible and easy to read. In the same mode, the pictures and x-rays of the lumbosacral region are reliable.
X-ray of the chest examination
Pain in the chest and abdomen may lead to an x-ray of the chest and spine. Such an examination is a result without preparation. For an object with high information content and precision projections, the picture is taken in several ways. The results are analyzed by a radiologist. Refer to a vertebrologist if necessary to receive treatment.
What diseases can be detected by X-ray of the spine?
To make the spine effective:
- in the diagnosis of x-ray hernias;
- when a complete vertebrae is detected;
- in the diagnosis of compression examination of the spine;
- when identifying problematic problems of different origins;
- with immobility of infectious diseases (tuberculosis is necessary);
- to identify special curvatures;
- to confirm congenital occupies of the spine (torticollis, sacralization).
Are two people getting x-rayed of the spine?
During the X-ray, you will be asked to take off your clothes to the waist and your main jewelry. An X-ray of the two spines is informatively useful if you have met all the rules of preparation for being carried out, and also listened carefully to the team of the doctor who carried out more. He may ask you to study several times, depending on the number of pictures in different ones.
The frequency of a spine procedure performed by a radiologist depends on the severity and the radiation dose received. It’s worth noting that modern devices are being improved and are equipped with a program that
The patient's dose is significantly reduced per procedure. This device conducts examinations more often and the neck is at particular risk. But after taking off the x-ray, it’s still a good idea to ask the doctor to write down the received dose of jewelry on the card to calculate the possibility of subsequent x-ray examinations.
Spine belts at home
There are procedure services that can do all the necessary x-rays from a specialist at home. But, firstly, such a table can cost quite a lot, and secondly, as a rule, lying down turns out to be inaccurate in following the diagnosis.
womanadvice.ru
X-ray is prescribed for headaches, the cause of which cannot be identified, pain in the arms, and also where there are suspicions of several diseases with underlying symptoms.
Note: A regional x-ray is aimed solely at identifying the cervical bones and joints. It is not possible to perform a soft tissue procedure in clinics. In such situations, the department orders a CT scan.
Bear in mind that this type of regional treatment is more expensive, but in certain cases only with its functional help is the only correct diagnosis and medical treatment system.
Projections
Typically, x-rays are taken in lateral and frontal projections. The oblique is used less frequently.
Direct projection radiography is performed with the patient in a horizontal or vertical position. The device is aimed at the protrusion of the larynx parallel to the line connecting the temporal protrusion with the lower jaw (the equipment is adjusted at the same angle as the vertebral column of the cervical spine). In this way, all vertebrae are visualized except the atlas and axis. The first two vertebrae can be recorded using a variation of the AP view, where the procedure is performed through an open mouth. This image makes it possible to distinguish the lateral masses of the atlas (first vertebra), the odontoid process, and the body of the second vertebra (axis).
The vertebral arteries coming to the lateral masses go to the foramen magnum and then to the base of the brain. The radiograph evaluates the distance from the lateral masses to the odontoid process. The distance should be the same on both sides (if different, then the cause could be, for example, subluxation - subluxations are very common in children). Intervertebral spaces are also assessed, as with other projections.
Pictures can be taken in two projections - frontal and lateral
When radiography is performed in the lateral plane, the beam is directed according to the area of the fourth vertebra. The patient is pressed against the X-ray cassette, with his shoulder facing it if we are talking about the vertical position of the patient. All vertebrae are visible in the lateral photo. According to the specialist's instructions, you should not move or swallow.
Rarely is the picture taken in an oblique projection. There are posterior and anterior oblique projections. With the front one, the patient stands facing the counter, and with the back one, with his back. In both cases, at an angle of 30-45 degrees. This projection allows for better assessment of the intervertebral foramina.
The specialist evaluates the height of the intervertebral discs - it should increase caudally - in the direction from top to bottom, however, in the C6-C7 segment, the intervertebral discs may normally be lower than the others, the bends of the section (impairments can be a consequence of muscle and ligamentous pathologies, injuries, infectious diseases, congenital anomalies and birth injuries).
Diagnostics with functional tests
If there is a suspicion of excessive mobility of the vertebrae, the doctor prescribes an x-ray with functional tests. To do this, the most mobile parts of the neck are examined. During the execution, the displacement of the bone elements relative to each other is determined. Such a study allows you to take all the necessary measures to slow down the pathological process and detect osteochondrosis even in its initial stages.
The study is carried out in different projections, while the patient needs to bend and straighten the neck as much as possible. This will allow us to determine the degree of their displacement during movement.
What research projections are there?
To increase the information content of the images, a radiologist can offer several options for positioning the patient. The study is performed in several projections:
- Front back. It allows you to see the condition of all vertebrae starting from 3. The first two are covered by the lower jaw bone.
- Straight back. It is done through an open mouth, since this position is considered the most optimal for visualizing the anterior neck. Using this position, vertebrae 1 and 2 are examined.
- Lateral.
- Oblique back.
In most cases, a lateral and straight X-ray of the cervical spine is sufficient. In three projections (using an oblique) the study is carried out only if additional study of the intervertebral foramina is necessary. An X-ray of the neck is performed in the supine and lateral position. It is allowed to stand during the process. It is more difficult to conduct an examination on children, since it is almost impossible to get them to remain completely still. Usually the staff suggests securing it with fasteners or holding it yourself.
Types of equipment
There are two types of equipment:
- film;
- digital.
Currently, there are two types of X-ray machines - film and digital.
As mentioned above, in the first case the image is recorded on film, and in the second - on a digital media monitor. Digital X-ray machines, despite their high cost and relative inaccessibility, have many advantages. When using such equipment, radiation exposure to the body is reduced by approximately 40%. The image obtained digitally can be instantly sent to other specialists anywhere in the world. The image is clearer, and it is possible to concentrate the beams on the desired area (this is partly due to the reduction in radiation exposure). There is access to software that will allow you to instantly make the necessary measurements on an already acquired image.
What does it show
X-rays today in Moscow are offered not only film, but also digital. It is better to choose more modern equipment, not only because of the convenience of obtaining images on a flash drive, but also because of the reduced radiation exposure (by about 40%), which they differ from. When looking for where to get an x-ray done, first of all you need to clarify the model and brand of equipment used. After the study, what does the x-ray of the cervical spine show?
- Displacement of the vertebrae as a result of injury or pathological process. Noticeable in the picture is the incorrect position of the skeleton element.
- Fractures and cracks in the vertebral body. They appear as thin black stripes on the light body of the bone tissue. You can notice them even with the naked eye.
- Tumor formations. The image shows up as a white spot with clear boundaries.
- Problems with the discs of the cervical vertebrae (for example, osteochondrosis). Problems with intervertebral discs appear in the image as a narrowing of the space between the vertebrae.
- Curvature of the spine in this section. Noticeably unnatural curve of the ridge.
- Growths and anomalies. They appear as white growths on the underlying bone that are not a natural part of the vertebra.
- Arthritis. The image shows a hooked formation and a reduction in the distance between the vertebrae. All this usually occurs against the background of vascular damage.
- Tuberculosis. The x-ray reveals the primary foci of infection. When bones are damaged, destructive processes in bone tissue are noticeable. Depending on the color, the intensity of the lesion is determined
- Skeletal deformities. Manifested by changes in the correct position of the spine, a visual assessment is usually sufficient to determine the problem.
The description of the image is written by a specialist, but it is for informational purposes only and is not a diagnosis. The disease and the course of its treatment are determined by the doctor, based on the results of general tests and the patient’s complaints. Children are prescribed x-rays only in case of injury, severe orthopedic problems, fractures, or displacement of the vertebrae.
X-ray with samples
Sample radiography (also known as functional radiography) can be performed using digital devices. The method consists of recording images of the cervical spine during tilts of different intensities. When flexing the cervical spine, the conditional line that connects the dorsal (back) parts of the vertebrae should be even and smooth. The same should be noted when extending the neck. Functional radiography is carried out under the close supervision of a radiologist and his assistants, since not everyone can stand and maintain balance for a long time during this diagnostic procedure. Test radiography is very effective in assessing pathological movements of the cervical vertebrae.
Functional radiography
Indications
Signs that are associated with pathologies of the cervical spine can manifest themselves in a variety of ways and affect different internal organs. Headache, ripples before the eyes, numbness of the upper extremities, dizziness, pain and/or limited movement of the neck, crunching when turning, insomnia, tremors of the hands, swelling of the tissues, pressure surges, burning pain in the distal extremities are the symptoms that, when contacting a doctor, will become indications for radiography.
Ignoring these symptoms leads to disability or even death.
On an x-ray you can see degenerative, dystrophic and inflammatory processes. The radiologist is able to evaluate the intervertebral spaces of the cervical spine, areas of bone compaction and bone processes.
X-rays of the cervical spine are prescribed for many pathologies in this area
Therefore, radiography is effective for the following pathologies.
- Neck injuries (subluxations, fractures, etc.)
- Osteochondrosis and other degenerative-dystrophic processes (the height of the intervertebral foramen decreases).
- Birth injuries.
- Spondylosis. Destruction of intervertebral discs. Compensatory osteophytes (growths).
- Kyphosis. Deformation of the cervical spine with a convexity dorsally (backwards).
- Pathological cervical lordosis. May be a consequence of residual processes of spinal diseases. Physiological curvature becomes pathological.
- Arthritis. The image reveals hooked formations, which are accompanied by symptoms of vascular damage.
- Congenital anomalies. For example, Kimmerle’s anomaly (with this anomaly, the vertebral artery is compressed due to ring-shaped bone growths in the atlas area. In this case, radiography is only the primary method for diagnosing the anomaly. To assess the significance of this pathology, Doppler sonography is performed, with which you can find out whether the blood flow is impaired in the vertebral arteries); wedge-shaped vertebrae, additional bone formations, torticalis.
- Cervical radiculitis and radiculopathy caused by inflammatory and strangulating processes of the nerve roots emerging from the intervertebral foramina.
- Tumor processes and metastases. For tumors and pathological processes affecting the spinal cord, myelography is used - contrast radiography. Contrast is injected into the spinal canal, between the membranes of the spinal cord. These can be gases, such as nitrous oxide, oxygen, or special contrast agents. The method allows you to evaluate not only tumors and metastases in the bone part of the spine, but also the condition of the spinal cord membranes. Tumors are characterized by displacement of the vertebrae, deformation, and destructive processes of bone tissue, which are indicated by shadows of varying intensity.
- Tuberculosis. The cervical and sacral regions are rarely affected. The pain radiates to the interscapular and occipital regions. Radiography will reveal the primary foci of pathology. An X-ray of the spine will show destructive processes in the bone structure of the vertebrae and narrowing of the intervertebral discs.
- Intervertebral hernia. You can see only indirect signs of intervertebral disc prolapse.
- Abscesses. Possible compression of the spinal cord and subsequent paraplegia. May be a consequence of tuberculosis. An x-ray allows you to show paratonsillar, paraphyringeal and retropharyngeal abscesses, which are a consequence of otorhinolaryngological pathologies. This indicates some effectiveness of the method in soft tissue pathologies.
Most often, x-rays are prescribed for osteochondrosis of the neck.
The most common indications for mature patients are intervertebral hernia and osteochondrosis.
In childhood, indications most often include injuries, spinal curvatures, orthopedic problems, vertebral displacement, injuries during childbirth (in a child) and subsequent injuries (dislocations, subluxations, bruises, fractures).
Advantages and disadvantages of the technique
X-ray is an inexpensive and accessible way to determine pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. Therefore, it is used by a variety of doctors to identify destructive processes in the neck, thoracic region, and spine. The main advantages of the technique are:
- Ease of implementation. The technology is quite simple, and if you follow all the specialist’s recommendations, you can avoid making mistakes or getting a blurry image.
- High information content. The result obtained allows us to determine the degree of damage to the bone tissue, its deformation or the presence of a fracture or dislocation. Based on the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment.
- Painless. During the examination, patients do not feel pain or any unpleasant effects. For children, psychological discomfort is caused only by equipment that is unfamiliar to them.
- High speed of obtaining results. The procedure will take no more than 15 minutes, after which you will need to wait another 20 to get a finished photo with a description.
- Safety. If you take x-rays no more than once a year, your health will not suffer. The dose received at one time is equal to six months of natural radiation.
- Availability. You can undergo the examination free of charge under your compulsory medical insurance policy. In paid clinics the cost starts from 800 rubles.
The main disadvantages of the technique are the inability to see pathologies in bone tissue, as well as the presence of contraindications to the use of gamma rays. With a large accumulation of radiation in the body, radiation burns, a mutagenic effect, or the development of a malignant formation are possible. But the equipment is being improved more and more every year, with the goal of making it safer for humans.
Contraindications
The only absolute contraindication is the woman's pregnancy. In this case, it is better to resort to MRI. If this is not possible, then the woman’s chest and abdomen are covered with special radioprotective clothing (see below).
During lactation, radiography is not prohibited, but it is recommended not to breastfeed the baby for 24 hours after the procedure. It is recommended to express milk after x-ray.
X-rays are contraindicated in pregnant women
It is highly undesirable to diagnose pathologies of the cervical spine and stomach (using barium contrast) on the same day.
Significant excess weight can cause poor-quality radiographs, and using a large dose of radiation is fraught with dangerous consequences for the patient, so obesity is a technical contraindication.
How is it carried out?
Health Special preparation for a small study is usually not required. The mother should not follow any diet, such as restrictions on drinking, eating, or taking medications. It is necessary to remove all fluoroscopy accessories and jewelry, as well as some dentures. After a while, the person takes the necessary effort, he may be asked to sit on the table, or to avoid standing. Below the head, it is covered with a special apron; it has not been exposed to radiation. In every diagnosis, the patient should not presently, the head remains motionless, or common fasteners and bandages can be used. This delusion is painless, a person does not feel the reasons.
You may need medical images, for example, if you are told to do a study in 2. This technique should not be used on pregnant and lactating women. This study was carried out by the state apparatus, so you can collect the results in two days a year. In private ones, it can take about half an hour to process the results.
Flaws
X-rays cannot detect small vertebral fractures, some neoplasms and hematomas. For purposes of this kind, CT is an alternative. MRI is used if soft tissue needs to be assessed along with bone and cartilage tissue, or if there are some contraindications to the use of radiography.
The negative consequences of excessive exposure to X-rays include the following: mutagenic effect, risk of malignant tumors, radiation burn, radiation sickness.
The disadvantage of X-rays is that radiation sickness can occur due to excess exposure.
Radiation sickness is a symptom complex that is caused by exposure to ionizing rays. She may be:
- chronic;
- acute.
Acute cases are extremely rare, because the radiation dose from one image is minimal. Chronic radiation sickness is much more common.
Medical personnel are most often exposed to chronic disease. Radiation sickness primarily affects the hematopoietic system, which is why special radioprotective clothing has been created for both staff and patients. These can be aprons (double-sided and single-sided), collars to protect the thyroid gland from radiation, a skirt, an apron, hats, and a vest. They are made from materials that absorb rays and prevent them from affecting body structures (for example, lead).
Such clothing is of particular importance during radiography of children. As mentioned earlier, they may not remain static for long. Therefore, an accompanying person is allowed, who must wear protective clothing.
Often, according to many people, special contraindications include childhood. Indeed, an unformed child’s body is more susceptible to the negative effects of ionizing rays. However, modern technologies make it possible to reduce the risk of possible negative consequences.
It is better for children to have only digital radiography, since in this case the body receives a lower dose of radiation
X-rays can be performed from the first days of a child’s life, but it is advisable to go to a well-equipped clinic, which will definitely have a digital X-ray machine. As noted earlier, such equipment significantly reduces radiation exposure. In childhood, it is especially important to record the fact of an x-ray in the medical record. This information will be taken into account by other specialists.
Particular caution should be exercised with children under 14 years of age. Preference for diagnosing diseases in children is given to ultrasound - ultrasound examination and MRI - magnetic resonance imaging. The principle of their work does not involve the use of ionizing rays and other factors affecting the body. But if these methods are ineffective, children should undergo X-rays wearing radioprotective clothing, which must cover the reproductive organs.
For comparison, the table below shows approximate radiation doses for various diagnostic procedures in different areas of the body.
Table No. 1. Comparative characteristics of the received radiation dose during various examinations.
| Procedure | Single radiation dose, m3v | Time to receive a similar dose as a result of background radiation, days | Total annual dose, m3v |
| X-rays of light | 0,1–0,3 | 10–13 | 3,1–3,3 |
| Film fluorography | 0,3–0,5 | 30–50 | 3,3–3,5 |
| Digital fluorography | 0.05 | 5 | 3.1 |
| X-ray of the cervical spine | 0.001 | Less than 1 | 3 |
| X-ray of teeth | 0,02–0,04 | 2–4 | 3 |
| CT scan of the brain | 0,4–2,0 | 40–200 | 3,4–5,0 |
| CT scan of the chest area | 2,9–6,0 | 290–600 | 5,9–9,0 |
| Abdominal CT | 5,8–10 | 580–1000 | 8,8–13,0 |
Preparation for the procedure
X-ray of the neck without samples does not require special preparation. If X-rays must be taken through the mouth, then you should not eat or drink liquids for at least several hours. It is not recommended to consume alcohol and heavy gas-forming foods 2-3 days before the diagnostic procedure. Before X-raying your neck, you must remove all jewelry and undress to the waist. Mobile phones and other technical devices should not be present during the procedure on a person. Most often, about 1/5 of patients experience headaches, nausea and vomiting after the procedure. These symptoms disappear within 24 hours.
No special preparation is required before radiography of the cervical spine.
Main indications for use
An x-ray is prescribed by a doctor only if indicated. The study is not used as a preventive measure, since radiation, when carried out frequently, can cause serious disorders in the body and provoke cancer. A picture is taken if the patient comes with one of the following complaints:
Symptoms of cervical radicular syndrome
- Headaches, migraines.
- The appearance of a pathological crunch in the cervicothoracic region.
- Muscle tone weakened significantly and atrophy appeared.
- Severe pain when turning the neck.
- Frequent dizziness for no apparent reason.
- Problems with hearing or vision.
- Mechanical damage.
- Numbness of the limbs, tingling in the fingers.
- Poor coordination of movements, staggering when walking.
- Acute pain in the area of the cervical vertebrae.
If there is a suspicion of instability of the vertebrae in the cervical spine, the doctor prescribes an x-ray with functional tests. To do this, a photograph is taken at maximum neck extension and flexion in order to compare the results obtained.
Complications
X-rays have no risk of complications if the procedure was performed correctly and the radiation dose did not exceed the norm. Complications can arise with contrast radiography - myelography. This is an invasive procedure. The contrast agent may cause an allergic reaction. Injection of contrast may lead to infectious complications. The needle can injure the membranes, and the cerebrospinal fluid will leak even after the procedure is completed (this requires surgical intervention).
Complications can only arise if the patient has undergone myelography
Seizures may occur if contrast material enters the brain (to prevent this, keep your head higher than the rest of your body and lie down for eight hours).
Before the procedure, you must inform your doctor about kidney disease, the use of drugs such as warfarin (for bleeding disorders), metformin (for diabetes), a history of epileptic seizures, convulsions, allergies to iodine-containing drugs and other allergic reactions. It is recommended to drink a lot of water to quickly remove the contrast agent from the body.
Results
Radiography is a fairly old method, but it does not lose its relevance and is modified because it is very cheap and accessible. Moreover, it is painless. A doctor of any profile can refer you for an X-ray, depending on the suspected pathology.
Radiography is an integral part of emergency medicine, as is CT. The diagnosis and treatment tactics are determined by the doctor who sent for radiography, and not by the radiologist himself, since radiography is only one of the diagnostic methods without taking into account the collected anamnesis. Additional research is often necessary.
Both the diagnosis and treatment tactics are discussed with the patient and based on his choice, since not everyone has the opportunity to conduct expensive additional diagnostic tests and purchase expensive medications.
X-ray is the most common method for diagnosing the spine due to its relative accessibility
There should be a gap of 5 months between several procedures. Each procedure must be documented. This is especially true for pediatric patients.
It is important to strictly follow the specialist’s instructions during the procedure so that the image is of high quality and you do not have to receive an additional dose of radiation. The specialist must take into account those situations when the patient cannot take one position for several minutes. He must be aware of all possible contraindications, especially when it comes to myelography. From all this it follows that radiography can be carried out only after close and full communication with the doctor.
Modern medicine tries to prioritize the patient’s opinion and turn every trip to the hospital into a consultation, and not into a doctor’s monologue. Such trends allow you to approach your own problem more consciously and better perceive responsibility for your health. This is especially important for pathologies of the cervical spine, since there is a fairly accessible and effective method for preventing a poor prognosis and improving the quality of life.
Features of the examination in children
Much attention is drawn to the fact that when X-rays are prescribed for children, parents are concerned about the safety of the child. Since the method is based on X-ray radiation, that is, a radioactive substance is used, which, according to parents, can significantly irradiate the child. Let's try to dispel this opinion, the development of technology does not stand still, devices are being improved in terms of protection from radiation, and the radiation time is also decreasing. But let us note that not every municipal clinic has modern equipment, so you need to check the year of manufacture of the device, and if old equipment is used, it makes sense to go to a private hospital and have an X-ray of your neck done there. X-rays of the cervical spine can be used from a young age. Diagnostics can reveal birth and acquired abnormalities, displacements, subluxations, and instability of the cervical spine. The examination is carried out in the same manner as for adults; the main problem with the child is the need to ensure immobility, so I allow the parent to stay during the procedure.
For children over 4 years of age, x-rays can be taken through the mouth to better view the upper vertebra. This procedure scares parents a little, but don’t be afraid of it; in fact, this is the same photo, only taken through a wide open mouth.
X-ray of the cervical spine is a quick, accessible and quite informative diagnostic tool that allows you to begin correct and timely treatment.
(
1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Diagnostics - clinics in
Choose among the best clinics based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment
Family
Oriental Medicine Clinic "Sagan Dali"
Moscow, prosp.
Mira, 79, building 1 Rizhskaya
+7
- Consultation from 1500
- Diagnostics from 0
- Reflexology from 1000
0 Write your review
Family
Clinic "Diamed Maryina Roshcha"
Moscow, Sheremetyevskaya st., 27, 1st floor
Maryina Roshcha
8
- Consultation from 1600
- Shock wave therapy from 1200
- Reflexology from 2200
9 Write your review
Family
Medical Center for Immunocorrection named after. R.N. Khodanova
Moscow, st.
Davydkovskaya, 6 Slavyansky Boulevard
+7(499)445-40-83
- Reception from 1500
- Diagnostics from 200
- Hirudotherapy from 1150
10 Write your review
Show all Moscow clinics
Diagnostics - specialists in Moscow
Choose among the best specialists based on reviews and the best price and make an appointment with
Therapist
Batomunkuev Alexander Sergeevich
Moscow, prosp.
Mira, 79, building 1 (Oriental Medicine Clinic “Sagan Dali”) +7 0 Write your review
RheumatologistTherapist
Perelygina Elena Viktorovna
Moscow, Landyshevaya st., 14, bldg. 1 (Medical)
+7
0 Write your review
Therapist