general information
Immunoblot - what is it? In order to recognize HIV infection in a person, it is necessary to undergo a laboratory test of blood serum for the presence of antibodies. The immunoblotting technique is also called Western blot. It is used to detect human viral infections as an additional expert method. It is necessary to confirm ELISA - a laboratory test that allows you to determine the presence of HIV antibodies in the blood. A positive ELISA test is double-checked by immunoblotting. It is considered the most sensitive, complex and expensive.
The importance of clinical diagnosis of HIV
In the understanding of many people, an HIV-infected person looks sick and exhausted. He coughs, sneezes, itches, groans, everything hurts... In fact, this is not so! The problem is that after HIV infection and during the subsequent incubation period, there are no symptoms at all. Then comes the acute phase, during which there are symptoms reminiscent of ARVI or flu. But they soon pass, and the so-called latent period begins - a long period of time when HIV infection does not show itself in any way. From the moment of infection to the pre-AIDS stage, about 10 years can pass, during which neither the patient himself nor his environment even suspects about the disease. And when it already declares itself at full capacity, it is very difficult to control it. It is difficult to resist the complications of HIV and maintain the practically destroyed human immune system.
It is very important to understand that, although there are risk groups - homosexuals, drug addicts and girls of easy virtue - for the most part, patients with HIV infection are ordinary people. They study, go to work, visit public places, meet people on the Internet - in general, they live like everyone else. Unfortunately, no one is immune from HIV. Unprotected sexual intercourse in a fit of passion, a treasured tattoo without maintaining sterility, a half-price manicure from a novice artist, a street fight - all these and many other everyday situations can result in HIV infection.
Only those who do not live do not make mistakes! We cannot know everything in advance, we cannot correct mistakes that have already been made, but we can take simple steps to correct their consequences - go to the nearest dermatovenerology clinic, a local clinic or a specialized AIDS center for testing and early diagnosis of HIV.
Purpose
What is an immunoblot? This is a laboratory method for testing blood serum for the presence of antibodies to the virus. During the study, a specialist first separates the viral proteins in a gel and transfers them to a nitrocellulose membrane. The immunoblotting procedure is intended to detect HIV at different stages. At the first stage, the purified virus from its constituent parts is subjected to electrophoresis, and the antigens included in its composition are separated by molecular weight.
The human immunodeficiency virus multiplies in a living cell, embedding its genetic information into it. At this stage, a person becomes a carrier of the HIV virus if he has been infected. The specificity of the disease is that it may not manifest itself for a long time. The virus destroys lymphocytes, so a person’s immunity decreases and the body becomes unable to resist infections. If HIV is treated correctly and on time, the patient will live to a ripe old age. Lack of therapy inevitably leads to death. From the moment of infection, but without treatment, the maximum lifespan is no more than ten years.
ELISA finds chlamydia, cytomegalovirus and even parasites
Tests for chlamydia and cytomegalovirus using the enzyme immunoassay method have also gained particular popularity, due to the fact that they make it possible to determine the time of infection, the stage of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment measures.
When chlamydia is introduced, one can also observe the appearance of antibodies of various classes in different phases of the pathological condition caused by the infectious agent:
- IgM can be detected as early as seven days after infection;
- IgA indicates that the infection has been living in the body for more than a month;
- IgG confirms the diagnosis of chlamydia and helps monitor treatment and determine its effectiveness. It should be noted that class G antibodies remain and circulate in the body regardless of the duration of the disease, therefore, to correctly interpret the analysis, you need to take into account the reference values (norms), which, by the way, are different for each CDL: taking into account the brand of the test system and the specificity of the reagents included in the set. The normal values are entered in the form next to the ELISA result.
As for cytomegalovirus (CMV), it is somewhat different: class M antibodies appear after about a month and a half, that is, the positive result (IgM+) becomes positive in the phase of primary infection or during reactivation of a latent infection and remains so from 4 months to six months.
The presence of class G antibodies is characteristic of the onset of a primary acute infection or reinfection. The analysis states that the virus is present, but does not provide information on what stage the infectious process is at. Meanwhile, determining the normal IgG titer also causes difficulties, since it depends entirely on the immune status of a particular person, which, however, is established by identifying class G immunoglobulins. Given this behavior of antibodies, when diagnosing CMV, there is a need to assess the ability of class G antibodies to interact with CMV, in order to later “neutralize” it (AT avidity). At the initial stage of the disease, IgG binds very poorly to viral antigens (low avidity) and only then begins to show activity, therefore, we can talk about an increase in the avidity of antibodies.
Algorithm for ELISA studies for suspected CMV
What parasites are is hardly worth telling, because they haunt a person starting from childhood and, in the full sense of the word, poison his life (the waste products of parasites are very poisonous). They can be impressive in size (helminths, or simply worms) or small (amoebas, Trichomonas, Giardia).
Before the advent of the enzyme immunoassay method in clinical laboratory diagnostics, it was very difficult to find parasites, but now, as they say: “No problem!” And all because there is an ELISA that will find the parasite, no matter what form it is in (cysts, larvae, eggs or an adult) and no matter what part of the human body it is in. To do this, you just need to take blood from a vein and find the antibodies with which the body has already responded to foreign antigens.
We can talk a lot about the advantages of enzyme immunoassay, because this method has managed to solve many diagnostic problems using only venous blood. There is no need for long waits, worries and problems with collecting material for research. In addition, test systems for ELISA continue to be improved and the day is not far off when the test will give a 100% reliable result.
Peculiarities
Immunoblot analysis is a reliable method that allows you to determine the presence of antibodies to HIV antigens of the first and second types. If a person is infected, antibodies appear within two weeks, which can be detected much later. The peculiarity of HIV is that the amount of antibodies quickly increases and remains in the patient’s blood. Even if they are present, the disease may not manifest itself for two or more years. The ELISA method does not always accurately determine the presence of the disease, so confirmation of the results is required using immunoblotting and PCR if the enzyme immunoassay shows a positive result.
About HIV
The causative agents of the disease are types 1 and 2. For a long period of time, their presence in humans goes unnoticed; then, first of all, the immune system is affected, then other human systems.
The main method of laboratory diagnosis of the immunodeficiency virus is to detect antibodies to HIV. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is the basis of the method; it is sensitive (99.5% and above) and specific (99.8% and above). In addition, when diagnosing HIV, p24 antigen is determined using ELISA.
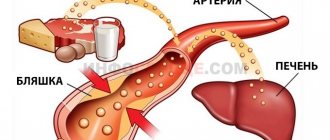
Each test system has different indicators; therefore, they determine different protein structures of viral shells. The causative agents of HIV come in two subtypes: 1st and 2nd or HIV-1 and HIV-2. Viral particles appear as a spherical shape with an outer phospholipid shell. For subtype 1, it has the following molecular weight: gp120, gp41, gp160. The 2nd subtype contains gp105, gp36, gp140. For the inner shell of the virus, the molecular weight is also known. For subtype 1, these are p55, p17, p24. For the 2nd - p16, p25, p55.
For each test system to detect a virus, there are three main sets of proteins.
In general, the ELISA result can be:
- negative;
- false positive;
- false negative;
- doubtful or uncertain.
Diagnostic methods identify antigens and antibodies.
Indications for use
What is an “immunoblot” has already been found out, but who is this study prescribed for? The reason to get tested for the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) using the immunoblotting method is a positive ELISA result. It is necessary to undergo an enzyme immunoassay for patients who will undergo surgery. In addition, women planning a pregnancy, as well as anyone who is promiscuous, should be tested. Immunoblotting is prescribed to patients with HIV if the ELISA results are in doubt. The following alarming symptoms may be a reason to consult a doctor:
- sudden weight loss;
- weakness, loss of performance;
- intestinal upset (diarrhea) that lasts for three weeks;
- dehydration of the body;
- fever;
- enlarged lymph nodes on the body;
- development of candidiasis, tuberculosis, pneumonia, toxoplasmosis, exacerbation of herpes.
The patient does not need to prepare before donating venous blood. You should not eat food 8-10 hours before the test. The day before donating blood, it is not recommended to drink alcoholic or coffee drinks, engage in strenuous physical exercise, or experience anxiety.
When is an HIV immunoblot test prescribed?
Immunoblot analysis for HIV is done exclusively after ELISA if its result is positive or doubtful. In addition, patients before surgery, donors, and women during pregnancy or planning pregnancy are required to undergo a mandatory HIV test. Once every 6 months, the test is recommended for people who often change sexual partners, as they are at risk.
You can become infected with HIV through sexual contact and through blood, including from non-sterile medical or cosmetic instruments. If the HIV-positive status is confirmed, the immunoblot will be positive in any case. Therefore, you should consult a doctor if you have the following symptoms:
- Sharp loss of body weight
- Constant weakness, decreased performance
- Diarrhea for more than 3 weeks
- Fever
- Dehydration
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Development of tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, pneumonia
- Exacerbated herpes for a long time
All this may indicate the presence of a virus. Blood for HIV testing is taken from a vein. It should be taken on an empty stomach. During the day, it is not recommended to drink coffee and caffeinated drinks, alcohol, or experience excessive physical activity.
Where can I get tested?
An HIV test can be taken at a regular clinic, a private clinic, or at special HIV centers. ELISA and immunoblot results are issued within 24 hours. If desired, an urgent analysis can be done.
Those who have been diagnosed with HIV as a result of tests are wondering: can an immunoblot be false positive? This is practically impossible, but it happens in 1% of patients. This happens when the test reacts to other antibodies. And often, this mistake occurs in people with other serious chronic diseases.
An immunoblot falsely positive for HIV often implies a different medical formulation - undetermined status. In this case, the test reacts to individual proteins, identifying them as HIV. This happens with autoimmune diseases, oncology, and even during pregnancy. In this case, additional tests are required at intervals of 1, 3 and 6 months.
Can an immunoblot be false positive ? Yes, it can, but extremely rarely. Additional research is required that can confirm or refute the disease. A number of people who suspect the virus are tormented by doubts about whether they need to take the test after 4 weeks, if after 12 it needs to be done again. You don’t have to take the test, but doctors strongly recommend doing so; if the status does not change, then it will be easier to wait for the next diagnosis. If you see the immunoblot formulation false positive for HIV, then most likely the status is questioned.
How is the research conducted?
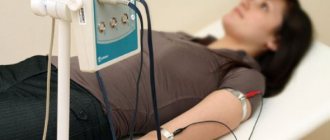
How is ELISA analysis performed? Positive/negative immunoblot confirms or refutes the results of the enzyme immunoassay. The research procedure is quite simple. The specialist takes venous blood, which takes no more than five minutes. After taking samples, the injection site should be disinfected and covered with a band-aid. The sampling is carried out on an empty stomach, so after the procedure it will not hurt to eat a bar of dark chocolate or drink a sweet hot drink.
In order to receive a referral for a free test at a public medical institution, you must visit a general practitioner. In general, immunoblotting does not differ from other blood tests in terms of the sampling method. The research methodology is simple. If there is a virus in a person’s blood, the body begins to produce antibodies to destroy it. Each virus has its own set of antigen proteins. The detection of these antibodies is the basis of the immunoblotting technique.
ELISA results using the example of syphilis
Enzyme immunoassay is suitable for detecting all forms of syphilis , and, in addition, is used in screening studies. To carry out the analysis, the patient's venous blood taken on an empty stomach is used. The work uses tablets with a certain specificity (AB classes A, M, G) or total antibodies.
Considering that antibodies in syphilis are produced in a specific sequence, ELISA can easily answer the question of when the infection occurred and at what stage the process is, and the interpretation of the results obtained can be presented in the following form:
- IgM indicates the duration of the infectious process (may appear during exacerbation of chronic inflammatory diseases);
- IgA states that the infection occurred more than a month ago;
- IgG indicates that the infection is in full swing or that treatment has recently been carried out, which is easily determined by taking an anamnesis.
When testing for syphilis, negative wells (and the negative control) will remain colorless, while positive wells (and the positive control) will show a bright yellow color due to the color change of the chromogen added during the test. However, the color intensity does not always coincide with the control, that is, it may be slightly paler or slightly yellowish. These are dubious results, which, as a rule, are subject to re-examination with mandatory consideration of the quantitative indicators obtained on the spectrophotometer, but in general, the color is directly proportional to the number of immune complexes (associated Ags and ATs).
Price
How much does the analysis cost? Immunoblot for HIV is not a cheap test. On average, a screening examination using enzyme immunoassay methods costs from 500 to 900 rubles. Immunoblotting is a verification study, the cost of which is from three to five thousand rubles. More complex methods are much more expensive. For example, for a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis you will need to pay about 12,000 rubles.
What is immunoblot for HIV?
The immunoblot for HIV has the international name western blot. This laboratory diagnostic technique detects antibodies to HIV in blood serum. World Health Organization protocols prescribe its use as an additional examination in cases where ELISA shows the presence of antibodies. This is the order because this analysis is more accurate, specific and expensive.
HIV immunoblotting was developed in the American laboratory George Stark, which is located at Stanford Research University. In addition to medicine itself, the technique is used in genetics, biochemistry, molecular biology and is particularly accurate.
Interpretation of the result
The most common methods for diagnosing HIV infection are enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunoblot. They are used to determine antibodies to the immunodeficiency virus in blood serum. The presence of infection is usually confirmed by two tests: screening and confirmatory. The interpretation of the study results should be carried out by a doctor, who also makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment. If the immunoblot is positive, this means that a virus is present in the human body.
A positive result should not be a reason for independent treatment, since each patient may have a different picture of the disease. Qualitative analysis includes screening and verification. If the patient does not have a virus, the result is indicated as “negative”. If detected by screening, an additional verification study is carried out. An immunoblot is an analysis that confirms or refutes the screening. If darkening appears on the test strip in certain areas (locations of proteins), a diagnosis of HIV is made. If the results are in doubt, tests are carried out within three months.
You can prevent infection with the immunodeficiency virus if you follow certain rules: avoid casual sex, use a condom during contact, do not take drugs. If the disease is detected in a pregnant woman, it is important to strictly follow the recommendations of the attending physician and do not forget to undergo examinations for the presence of the virus.
FAQ
What stages does immunoblotting include?
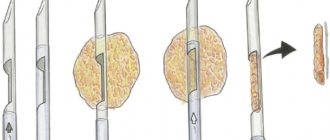
- Strip preparation. The immunodeficiency virus (HIV), previously purified and destroyed into its constituent components, is subjected to electrophoresis, and the antigens that make up HIV are separated by molecular weight. Then, using the blotting method (analogous to squeezing out excess ink onto a blotting pad), the antigens are transferred to a strip of nitrocellulose, which now contains a spectrum of antigen bands characteristic of HIV, which is still invisible to the eye.
- Sample examination. The test material (serum, blood plasma of the patient, etc.) is applied to the nitrocellulose strip, and if there are specific antibodies in the sample, they bind to strictly corresponding (complementary) antigenic bands. As a result of subsequent manipulations, the result of this interaction is visualized - made visible.
- Interpretation of the result. The presence of bands in certain areas of the nitrocellulose plate confirms the presence in the tested serum of antibodies to strictly defined HIV antigens.
- Lane A – Positive Control
- Lane B – Weak Positive Control
- Lane C - Negative Control
- Lane D – Positive sample (antibodies to HIV-1 detected)
How to decipher the analysis?
If the ELISA showed the presence of all or almost all antibodies to the antigens according to this test system, this means a positive test for HIV. If the answer after the second serological enzyme immunoassay is positive, then immunoblotting must be performed. Deciphering its results will be more accurate. If the enzyme immunoassay gave a positive result, the next immunoblot analysis also showed the presence of HIV, then the final result is given.
When the tests are deciphered, you need to know that a positive HIV test is determined by:
- 60% to 65% 28 days after infection;
- in 80% – after 42 days;
- in 90% – after 56 days;
- in 95% - after 84 days.
If the response to HIV is positive, this will mean that antibodies to the virus have been detected. To avoid a false positive answer, you need to take the tests again, preferably twice. If antibodies to immunodeficiency are detected when passing two tests out of two, or when passing 3 tests in 2 of them, then the result is considered positive.
The p 24 antigen can be detected in the blood within 14 days from the date of infection. Using the enzyme immunoassay method, this antigen is detected from 14 to 56 days. After 60 days it is no longer in the blood. Only when AIDS forms in the body does this p24 protein grow again in the blood. Therefore, enzyme immunoassay test systems are used to detect HIV in the first days of infection or to determine how the disease progresses and monitor the treatment process. The high analytical sensitivity of the enzyme immunoassay detects p24 antigen in biological material for HIV of the first subtype in a concentration of 5 to 10 pkg/ml, for HIV of the second subtype from 0.5 ng/ml or less.
A questionable result of an enzyme immunoassay means that there was a mistake somewhere in the diagnosis, as a rule, something was mixed up by medical workers, or the person has signs of infection, but the result is negative, which raises suspicion, and the person is sent for a repeat test.
A false positive as a result when blood tests were taken under the following patient conditions:
- pregnancy;
- if a person has hormonal imbalance;
- with prolonged immunosuppression.
How to decipher the analysis in this case? A false positive result is given if at least one protein is detected. Due to the fact that the p24 antigen is very dependent on individual variations, using this method, in the first period of infection, from 20% to 30% of patients are detected.
How reliable is a positive test result?
Sometimes ELISA has false positive results (in about 1% of cases), the cause of such a result may be pregnancy, various viral infections, or simple accident. After receiving a positive result, a more accurate test is needed - an immunoblot, based on the results of which a diagnosis is made. A positive immunoblot result after a positive ELISA is 99.9% reliable - this is the maximum accuracy for any medical test. If the immunoblot is negative, it means that the first test was false positive, and in fact the person does not have HIV.
What is an uncertain (doubtful) result?
If ELISA is positive or negative, then immunoblot can be positive, negative or indeterminate. Indeterminate immunoblot result, i.e. the presence of at least one protein to the virus in the immunoblot can be observed if the infection occurred recently and there are still few antibodies to HIV in the blood, in which case the immunoblot will become positive after some time. Also, an uncertain result may appear in the absence of HIV infection with hepatitis, some chronic metabolic diseases, or during pregnancy. In this case, either the immunoblot will become negative or the cause of the indeterminate result will be found.
How much does the analysis cost?
Immunoblot for HIV is not a cheap test. On average, a screening examination using enzyme immunoassay methods costs from 500 to 900 rubles. Immunoblotting is a verification study, the cost of which is from three to five thousand rubles. More complex methods are much more expensive. For example, for a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis you will need to pay about 12,000 rubles.
Where to do the analysis?
Where can I get tested for HIV? ELISA and immunoblot studies are carried out in city private clinics, the results are given out within 24 hours. Urgent diagnosis is also possible. In public medical institutions, ELISA tests and immunoblotting are carried out free of charge, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation. Pregnant women, as well as patients undergoing hospitalization or surgery, are required to undergo testing for infectious diseases.
Video
Where and how can you get diagnosed with HIV?
Today, testing for HIV infection is not a problem. If the patient wishes, blood can be donated for analysis anonymously and absolutely free. This can be done in medical organizations at your place of residence, in the Sverdlovsk Regional Center for the Prevention and Control of AIDS (Ekaterinburg, Yasnaya St., 46. Registration: (343) 383-30-18 Helpline on HIV/AIDS (weekdays, from 9 to 20 hours).
Diagnosis of HIV is purely voluntary. However, there are four situations for which taking the test is mandatory:
- Donation.
- Employment in a job that involves direct contact with biological material that may contain HIV.
- Foreign citizens.
Persons conscripted for military service who enter military educational institutions.
But even in these cases, testing cannot be carried out forcibly, since any medical intervention requires the voluntary and informed consent of the patient. It is a conscious one, since each of us must understand the importance of timely diagnosis of HIV.