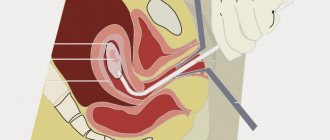
Breast biopsy is the most reliable method of differential diagnosis between benign and malignant neoplasms in the mammary glands.
The importance of having a reliable diagnostic method is invaluable. Breast cancer is one of the most common malignant pathologies in women. This diagnosis accounts for about twenty-eight percent of all malignant diseases in the world.
Attention! Currently, there is an increase in the incidence of breast cancer. This is due, first of all, to frequent hormonal imbalance (hyperestrogenism or hypoestrogenism), a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, alcohol abuse, etc.
The main method of screening for breast cancer is palpation of the mammary glands (self-examination and examination by a mammologist) and mammography.
To confirm the diagnosis, when signs of a neoplasm are detected, a biopsy of the mammary glands is mandatory.
Indications for the procedure
Pain in the mammary gland, lumps and redness, which can be noticed at home during an examination, become the reason for going to a mammologist.
Reasons for performing a biopsy:
- lumps are felt in the chest;
- The pictures show various spots;
- there was discharge from the nipples, including bloody ones;
- ulcers on the breast epithelium;
- inverted nipples, pain around the nipple;
- various peelings, swelling of the breast;
- lack of any other way to diagnose the disease;
- suspicion of cancer.
Read also
- How not to die from breast cancer
- What is the relationship between high cortisol levels and breast cancer?
- Millions of healthy women have undergone aggressive cancer treatment
- Mammography is a cruel medical hoax
- Aggressive surgery and business are coming!
- Statements by an oncologist surgeon that make your hair stand on end
- Cancer prevention is a business with fear
- The main cause of cancer is cancer treatment
- We reveal all the cards: the connection between Angelina Jolie's breast removal and corporate profits
- The world is in shock! An oncologist surgeon made incorrect diagnoses and removed women's breasts
- Study: Eating more fiber may reduce risk of breast cancer in young women
- Breast cancer: three main causes
Does breast biopsy hurt?
Regardless of the method of taking biomaterial, the study is quite unpleasant. Depending on the type of biopsy, your doctor will administer anesthesia.
Painfulness of biopsy types:
- Needle method. According to patient reviews, the needle biopsy method is the most painless. It is carried out without anesthesia (if the patient is ready to endure the injection), or an anesthetic gel is applied to the area of the skin where the needle will be inserted.
- Trephine biopsy. The procedure is similar to the needle method, only samples are obtained using a special gun into which a biopsy needle is inserted. It is quite voluminous, which allows you to obtain a whole section of tissue for analysis. Before inserting the needle, a small incision is made in the breast. The intervention is performed under local anesthesia.
- Surgical method. Operation. It is carried out under local anesthesia, and if the patient is very worried and worried, the doctor will suggest full anesthesia to avoid increased blood pressure and other negative consequences. After surgery, you may experience mild pain from tissue damage.
Summary
Biopsy and lumpectomy are both considered breast-conserving procedures, but carry the risk of serious complications.
A breast lumpectomy consists of removing the mass itself (i.e. the tumor itself) and usually some healthy tissue surrounding it. This operation is often called a partial mastectomy.
Every time there is physical interaction with a cancerous tumor during surgery (including biopsy), the integrity of the natural barriers that would normally limit the tumor occurs. This may allow cancer cells to move beyond the tumor and metastasize to other parts of the body.
Surgery causes immune suppression and can initiate an inflammatory response, which in turn can stimulate cancer cells to proliferate (further grow). It also suppresses the production and activity of the cellular portion of the immune system (Natural Killer Cells), whose main function is to seek out and destroy harmful pathogens (including cancer cells).
There are alternatives to biopsy that are practically safe for a woman's health and can provide additional information about the type of breast cancer. These include the ONCOblot test and thermography.
If you do have major surgery such as a mastectomy, lumpectomy, or biopsy, consider taking the following supplements to speed recovery and strengthen your immune system:
- Modified Citrus Pectin;
- Medicinal mushrooms, garlic, glutamine, IP-6 (inositol hexaphosphate);
- Genistein, milk thistle, EGCG, curcumin.
Author of the translation: Boris Grinblat Source (English): www.thetruthaboutcancer.com
How is a breast biopsy done?
The procedure takes place under sterile conditions. The doctor must wear disposable gloves.
The patient can sit, lie on her back or on her stomach. The breast can be in a natural position or be clamped into a special device. In most cases, the woman is on the couch facing the doctor.
The procedure goes as follows:
- At the puncture site, the skin is treated with an antiseptic.
- Afterwards, an anesthetic gel is applied to the chest, or local anesthesia is given. In certain cases, at the request of the patient, general anesthesia can be given.
- Next, the needle is inserted; during this, under no circumstances should you move.
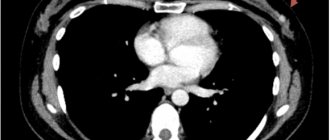
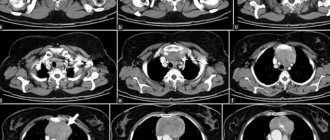
- The process of cell collection occurs quickly and is controlled visually by a specialist, using an ultrasound machine, mammograph or x-ray control.
- After completing the procedure, the doctor treats the injection site and stops the bleeding using a pressure bandage or an ice compress. It should be kept for no more than 10 minutes, then take a break and apply cold ice again to the injection site.
- When the bleeding has stopped and the patient’s condition has stabilized, a bandage is applied and compression garments may be used.
- The woman remains in the hospital for another half hour, after which she can go home.
The tissue obtained during analysis undergoes a number of studies. Samples are cut into thin layers, 5*10*5 millimeters in size. If the tissue is contaminated, it is washed in saline solution; after treatment, the biomaterial is filled with a 10% formaldehyde solution.
Having achieved the purity of the material, they begin to study it. It is performed under a microscope or binocular loupe. The specialist works on a number of symptoms, which are markers for diagnosing a neoplasm.
After the procedure
Recommendations on personal hygiene are mandatory: after the procedure, the breasts should not be wetted for 48 hours, and visits to the bathhouse and sauna should be avoided. You should especially avoid any physical stress on your arms and pectoral muscles. If the condition worsens, the patient should immediately consult a doctor.
How often can I do it?
The decision on the need for repeated studies is made by the attending physician. Samples are taken every 1-1.5 months so that the breast tissue is completely restored. As a control, it is recommended to conduct the study once a year.
Preparation
There is no special preparation for performing a biopsy. There are several recommendations that should be followed before the procedure.
Preparing for a biopsy:
- alcoholic beverages for 2-3 days before the examination
- before the procedure, do not take medications that affect blood clotting (Aspirin);
- on the day of diagnosis, do not use body cosmetics
- Before starting the examination, remove all jewelry, glasses and dentures.
Before the procedure, it is necessary to warn the doctor about allergies to certain drugs (before anesthesia) and electronic devices in the body (if MRI is also used).
When going for a biopsy, it is advisable to take a loose bra with you. After the procedure, you can put an ice pack in the cup to stop the development of edema and hematoma at the injection site.
After the biopsy, if there are no contraindications, you can go home. The woman is weakened after the procedure, so it is necessary that a loved one accompany her to the doctor. If this is not possible, it is advisable to return home by taxi after the biopsy.
What does a biopsy reveal and its types?
The object is examined for:
- nodules, vitreous and psammoma bodies;
- areas of necrosis and calcification;
- compaction boundaries;
- glandularity, granularity, homogeneity of glandular tissue;
- shape and size of cells.
There are the following types of breast biopsy:
- puncture;
- fine needle aspiration;
- thick needle puncture;
- stereotactic;
- trephine biopsy;
- vacuum aspiration.
puncture
It is one of the most gentle research methods and is carried out with minimal trauma. Biomaterial is obtained using a manual syringe. The diameter of the needle varies depending on the purpose of the study: thin needles are for liquid, thick needles are for collecting cells.
The puncture is carried out in close connection with the woman’s menstrual cycle. The study is most informative from days 7 to 10 of the cycle. When menopause occurs, the calendar indicator becomes unimportant.
Contraindications, in addition to the main ones:
- purulent and inflammatory processes in the mammary gland;
- large neoplasms located next to blood vessels;
- bleeding disorders.
Fine needle
The most gentle method for examining non-palpable tumors found in the mammary glands. Allows you to recognize both a cyst and a tumor. Glandular tissue or liquid is drawn from the neoplasm into a syringe. The disadvantage of the procedure is that only neoplasm cells can be obtained. To test for cancer, tissue is also needed.
In addition to cancerous diseases, fine needle biopsy diagnoses benign changes:
- tumors consisting of dead adipose tissue;
- intraductal papilloma;
- mastitis;
- mastopathy;
- cystic formations in the mammary gland;
- fibroadenoma.
thick needle
It is carried out in the case when the seal can be felt with the fingers, but the boundaries of the area being examined are not entirely clear and more material is required for testing. It is carried out using a large-diameter biopsy needle with a special cutting tip. After pain relief, the specialist makes a small incision on the chest, approximately 0.5-0.7 centimeters, to insert the equipment. This method is used to diagnose breast cysts.
Vacuum
Vacuum aspiration biopsy (VAB) is an advanced method for detecting benign and cancerous breast diseases. The breast being examined is gently fixed, numbed, and an Encor vacuum gun is inserted. Tissue samples are lifted under pressure into a special container for analysis collection. It is possible to obtain from 8 to 10 samples from different areas, while the needle itself is not removed from the chest, it only changes the angle of inclination.
Aspiration takes 30 minutes and is performed under local anesthesia. After the intervention, a small red dot remains, which disappears after two to three weeks. The shape of the breast does not change after VAB.
Vacuum is successfully used when:
- removal of cysts;
- ductal papillomas;
- breast fibroadenomas.
The modern method allows a robotic needle to be inserted into an incision with a diameter of up to 5 millimeters, minimizing blood loss and without compromising the integrity of the milk ducts. Alternative methods of treatment lead in the future to the formation of mastitis during pregnancy; a vacuum eliminates these consequences.
Mammography-guided biopsy
This type of biopsy is considered targeted. The essence of the procedure is that the path of the biopsy needle is monitored using a mammograph. It's called a stereotactic breast biopsy.
This procedure is prescribed if the tumor is located very deep, or if there are pockets of microcalcifications after operations. Before the procedure, the patient undergoes an X-ray examination in different planes, which allows choosing the optimal path to the biopsy object.
It also differs in technology. The woman lies down on a special couch with holes for the breasts, and a compression device and mammograph sensors are attached to the mammary gland. The procedure is similar to TAB; depending on the indications, needles of different diameters are used. The diagnostic accuracy is not inferior to the surgical method, but is less traumatic. After the intervention, there are no scars left on the chest, the shape does not change.
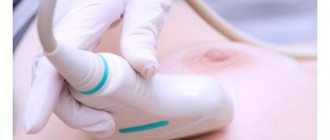
Ultrasound-guided examination
This method is similar to a biopsy under the control of a mammograph, only the movement of the needle is monitored using an ultrasound diagnostic device. During the procedure, the patient is in the classic position, lying on her back or side. The specialist conducts diagnostics, notes the location of the tumor, and the site of tissue puncture. An ultrasound sensor is placed on the chest throughout the procedure. The monitor displays the movement of the biopsy needle to the surface of the tumor.
It is worth remembering that the use of ultrasound, MTP and mammography in biopsy is accompanied by a certain amount of radiation and has a number of contraindications, including pregnancy. The procedure under ultrasound guidance is considered the safest.
Excision
In fact, this method is a full-fledged operation. This procedure has not only diagnostic, but also therapeutic functions. It is carried out under anesthesia. During such a biopsy, the doctor completely removes the tumor, and if there is an indication, then the organ where it is located. Tumor tissue is sent for examination, which allows us to determine the type of tumor and its possible consequences for the body.
The procedure is characterized by high precision, but has a high degree of danger for the patient. After surgery, breast correction is necessary. For these purposes, special quotas are allocated that can be used by women. If you manage to get a referral, then plastic surgery is performed free of charge.
Incisional
This is also a surgical intervention, only more gentle. During surgery, the doctor removes only part of the tumor, or the part of the mammary gland where the tumor is located. As with excisional biopsy, subsequent breast reconstruction may be required.
This type of research is carried out if:
- less traumatic biopsy options did not give an accurate answer, suspicion of a malignant tumor remained;
- identification of the immunohistochemical nature of malignant tumors is necessary;
- before radiation treatment.
Biopsy needles that allow tissue samples to be taken for analysis
How to prepare
The best time for research is from the 7th to the 14th day of menstruation. No special preparation is required, but if you are taking blood thinners, your doctor may want to stop them for a while. In addition, on the day of the procedure it is not recommended to use deodorants or antiperspirants, and cosmetic substances that are applied to the mammary gland area.
If an MRI-guided biopsy is planned, difficulties may arise in patients with pacemakers and metal implants. The doctor must be notified in advance about the presence of such structures.
Preparing for a breast biopsy
No special preparation is required for the biopsy procedure. The doctor will give detailed instructions on what to do before taking the test.
Before the biopsy, you need to inform your doctor about allergic reactions and chronic diseases.
And:
- Avoid aspirin and anti-blood clotting medications;
- do not use antiperspirants;
- remove jewelry;
- give up alcohol.
Before proceeding with the biopsy, an ultrasound is performed. An ultrasound scan shows the location of the tumor.
How necessary is a biopsy?
One can understand those women who want to learn more about the specifics of their disease and a biopsy does this. However, according to experts: “Cancer is cancer.” The cause of cancer remains the same no matter what form of cancer you are diagnosed with.
For a natural holistic treatment protocol that you can use to treat cancer, the specific type of breast cancer will most likely not matter. The reason for this is that when using herbal and other types of “natural chemistry”, detoxification, immunomodulation, restorative natural drugs, lifestyle changes, nutrition and perception of reality, i.e. a comprehensive protocol, the differences in tumor histology are by and large not significant.
There are also alternatives to Biopsy with much lower risk to your health that can provide more information about your cancer. The ONCOblot test and thermography are one of them.
Consequences of diagnosis
Doctors note that the tumor does not change its structure after the biopsy and does not begin to grow more actively. Consequences can only be in the form of complications, which are a marker of tolerability of the procedure.
They can occur during the tissue healing stage:
- breast swelling;
- the appearance of bruises and hemorrhages;
- burning effect;
- discharge from the puncture site;
- bleeding and infections.
Excessive anxiety can cause unpleasant consequences such as:
- headache;
- nausea;
- increase in body temperature.
A doctor from the Moscow Doctor clinic talks about the features of a procedure such as a biopsy.
What is the basis for the research?
Ultrasound is based on the same principle as the sonar systems used by bats, ships, submarines and weather services. When a sound wave collides with an object, it is reflected, that is, an echo is formed. Analysis of reflected waves allows you to estimate the distance of an object, its size, shape and consistency (dense, liquid or mixed).
In medicine, ultrasound is used to detect changes in organs, tissues and blood vessels or to detect pathological formations such as tumors. During ultrasound, the transducer simultaneously sends sound waves and receives/records reflected vibrations. When the sensor is pressed on the skin, small pulses of inaudible, high-frequency sound waves are generated that penetrate the body. When sound waves collide with internal organs, tissues or fluids, the sensitive microphone of the ultrasound sensor detects minute changes in the pitch and direction of the sound. The resulting characteristic vibrations are continuously measured by a computer program and reflected on the display screen, allowing for real-time imaging. Typically, during the examination, the doctor may obtain one or more images of moving structures. In addition, it is possible to record small video fragments in real time.
After determining the location of the node in the mammary gland, the doctor inserts a biopsy needle into it, advances it to the area of pathological changes and removes a tissue sample.
In a surgical biopsy, ultrasound is used to guide a loop of wire into the tumor, allowing the surgeon to pinpoint the area to remove tissue. By continuously capturing images, the physician is able to see the position of the needle or wire in real time as it moves toward the formation in the tissue.
Up
Interpretation of breast biopsy results
How long you will have to wait for the analysis results depends on:
- laboratories;
- complexity of analysis;
- established regulatory deadlines.
Typically, the study takes from one to one and a half weeks. The doctor will decipher the medical document, and he will prescribe additional tests if necessary.
The laboratory report will show:
- consistency and color spectrum of the samples taken;
- information about the estimated size of the tumor and its location;
- malignancy of the cells of the test material.
If cells have several nuclei, they are large in size, and have an increased chromatin content, then we are talking about tumor tissues.
The morphological and histological conclusion of the biopsy will indicate which cells were found:
- Malignant. The patient is sent for additional tests to determine the type of cancer.
- Benign. There is a tumor, but it does not contain information about cancer cells. Other inflammatory processes and neoplasms.
- Optimal or normal. When all the studied markers are within normal limits or are completely absent.
- Unable to perform analysis. This happens due to poor quality material or insufficient quantity.
Actions to boost immunity and speed recovery after surgery
If you've already had a mastectomy, lumpectomy, or biopsy, here are some things you can do NOW to support your immune system and speed up your recovery:
- Modified Citrus Pectin (MCP) prevents cancer cells from adhering to the walls of blood vessels (some studies indicate a decrease in this activity by 95%). It is recommended to take 14 grams of MCP daily for one year after surgery and biopsy.
- Medicinal mushrooms, garlic, glutamine and IP-6 (inositol hexaphosphate) all have the ability to activate Natural Killer Cells. In addition, mistletoe extract taken before surgery or biopsy can reduce the suppression of these cells.
- Genistein, milk thistle, EGCG/EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate - green tea extract, especially matcha green tea), curcumin - according to a number of scientific works, can reduce tumor vascular growth factors in metastatic cancer. According to some studies, curcumin can reduce tumor weight by 60-80%.
The choice to undergo a biopsy and/or lumpectomy remains with the woman. However, you need to know all the facts so that the decision is informative and contributes to a better outcome for both breast and overall health.
Video
The video from Alexey Aksenov shows a trephine biopsy of a breast tumor.
Do you have any questions? Specialists and readers of the HROMOSOMA website will help you ask a question
Was this article helpful?
Thank you for your opinion!
The article was useful. Please share the information with your friends.
Yes (100.00%)
No
X
Please write what is wrong and leave recommendations on the article
Cancel reply
Rate the benefit of the article: Rate the author ( 4 votes, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Discuss the article:
Stay tuned for new information
- Our channel on YouTube
- Our Facebook page
- Our group in Odnoklassniki
- Our Instagram account
Attention! The information provided is not an officially recognized method of treatment and is for general educational and informational purposes only. The views expressed herein do not necessarily reflect those of the authors or staff of MedAlternativa.info. This information cannot replace the advice and prescription of doctors. The authors of MedAlternativa.info are not responsible for the possible negative consequences of using any drugs or using the procedures described in the article/video. The question of the possibility of applying the described means or methods to their individual problems should be decided by readers/viewers themselves after consultation with their doctor.
Order of conduct
The procedure goes like this:
- The patient should remove clothing from her upper body and lie on her back.
- The doctor administers local anesthesia, after which he examines and palpates the site of the suspected tumor.
- The doctor makes an incision in the problem area and then inserts a needle. The needle can be inserted either automatically or manually.
- A fragment is taken from the area of damaged tissue, after which the needle is removed from the mammary gland.
- The internal space of the area from which the biomaterial was taken is treated with a special anticoagulant, which helps close the blood and lymphatic vessels.
- After the procedure, an ice bag is placed on the chest.
The total duration of the procedure is approximately 20-30 minutes.
This procedure is often used for medicinal purposes - using a trephine needle, it is possible to remove cysts by sucking out the fluid from them. The walls of such a neoplasm subsequently resolve on their own.
This procedure is minimally invasive and painless, which does not require stitches. Trephine biopsy does not leave any scars.
What does the diagnostic equipment look like?
Stereotactic breast biopsy uses the same equipment as diagnostic mammography.
A mammograph is a rectangular machine equipped with a tube for producing x-rays. The device is used exclusively for X-ray examination of the mammary glands. In this case, special additional devices ensure that radiation reaches only the gland. A device is attached to the X-ray machine to position and compress (squeeze) the breast, which helps obtain images from different angles.
Most diagnostic departments use special tables equipped with holes for the mammary glands, which hang freely through them while the patient is lying on her stomach. Once the patient is positioned, the table is raised and the biopsy procedure is performed underneath. In other departments, the examination is carried out with the patient sitting on a chair.
During a biopsy, the doctor uses one of the following tools:
- Cutting automatic needle with spring mechanism: consists of an inner needle, which is inserted into a locking cell, covered with a protective sheath and attached to a spring mechanism.
- Vacuum aspiration biopsy device: a tissue sample is taken into a needle under pressure.
Other sterile instruments are also used during the procedure: syringes, forceps, scalpels, sponges and microscopic glasses or tissue containers.
Up
What should you expect during and after the study?
During the examination, the patient is conscious and experiences little or no discomfort. Most women report that the examination was painless or virtually painless, and there was no scarring of the breast skin after the biopsy.
When a local anesthetic is injected to numb the skin, the patient feels a slight prick from the needle. There is a feeling of slight pressure as the biopsy needle is inserted.
The skin remains numb for some time after completion of the study. During the entire examination, you must lie as still as possible. While the tissue sample is being taken, you may hear the tapping or clanking of surgical instruments.
If swelling or bruising occurs after the biopsy, a cold compress (ice pack) and mild pain relievers should be used. Temporary subcutaneous bleeding is normal.
You should contact your doctor if you notice significant swelling, bleeding, or other discharge from the biopsy site, redness, or local warmth in the breast.
The mark left by the doctor to determine the location of the pathologically changed area does not cause pain, changes in the shape of the breast, or other harm.
During the day after the study, you should not engage in intense physical activity, but usual activities are usually allowed.
Up
What are the benefits?
Stereotactic breast biopsy is considered a highly effective diagnostic procedure. Doctors find it very useful when they want to determine whether a suspicious area of the breast is cancerous. This diagnostic method is simpler for women than surgery. In addition, it is associated with lower financial costs.
Compared to surgery, stereotactic biopsy has the following advantages:
- simpler, faster and less invasive;
- usually not so painful;
- leaves behind very small scars;
- detects problems that cannot be detected by ultrasound, such as calcium deposits;
- associated with a shorter rehabilitation period;
- does not require the woman to stay overnight in the hospital;
- costs about a third less;
- associated with fewer side effects.
Interpretation of results
Your doctor may call you by telephone or ask you to return to the clinic to discuss your results. Immediately after the biopsy, you can receive a preliminary report. However, you will receive the final pathological conclusion, as well as the results of additional studies (for example, immunohistochemistry) only after a few days.
Biopsy results may be negative, positive, or inconclusive; in the latter case, a repeat biopsy or other studies are necessary.
The pathological report may contain the following:
- Norm
- Benign breast disease
- Benign breast disease that increases the risk of developing a malignant tumor.
- Preinvasive cancer (lat. carcinoma in situ - cancer in place, intraepithelial cancer or stage 0 cancer) Invasive breast carcinoma.
What are the risks?
Any medical procedure carries certain risks. Risks associated with stereotactic breast biopsy include the following.
- Radiation exposure can be harmful to tissue, so pregnant women should not undergo such procedures.
- Some patients find the biopsy painful, although the discomfort can usually be relieved with painkillers.
- Less than one percent of patients develop blood collections or hematomas after biopsy.
- In one in a thousand cases, an infection develops in the breast due to tissue damage.
- In rare cases, the biopsy needle penetrates the chest wall and causes complications.
- It does not show high effectiveness when applied to areas close to the chest, where calcium deposits are widely distributed, or in cases where the formations are not clearly defined.