Tumor formations, benign and malignant, are found quite often in the mammary glands. If the pathology is detected at an early stage, a complete cure can be achieved. Breast ultrasound plays an important role in early diagnosis. That is why every woman should carefully monitor her health and undergo all examinations on time.
How is breast ultrasound performed and how to prepare for mammography? What does an ultrasound scan show? How to interpret mammography results? You will find answers to these and other questions in our article.
Ultrasound examination of the breast
Ultrasound (sonography) of the mammary glands and its lymph nodes is scanning of breast tissue with ultrasound at a frequency of up to 19 MHz (megahertz). During the examination, the sensor is applied to the skin. The echo signal passes through the liquid unhindered and is reflected from the ribs and hard tumors. Ultrasound waves are absorbed differently by healthy and altered glandular tissue.
The echogenicity of the structures appears on the sonographer’s monitor in the form of a black and white picture. The denser the fabric, the lighter the area. The accumulation of liquid is colored black. Inhomogeneous (heterogeneous) lesions contain two colors, shades of gray.
Types of ultrasound for examining the mammary glands:
| Types of sonography | Features of the method |
| Doppler ultrasound, sonography with color Doppler mapping | In Doppler ultrasound, standard ultrasound is combined with Doppler: it allows you to assess the condition of the mammary glands and blood vessels, the nature of the tumor |
| Ultrasonic elastometry | The sonoelastography method helps to identify the boundaries of benign or malignant formations and perform a targeted biopsy. On the monitor, hard areas are highlighted in blue, healthy tissue is colored green, and changed tissue is colored red, orange, yellow |
| Duplex (UZDS) | Combines Doppler and AB ultrasound mode. The image on the monitor is two-dimensional |
| Triplex (UZTS) | This type of ultrasound combines the capabilities of duplex scanning and color mapping (CDC). The image is 3-dimensional, allows you to see differences in the direction and speed of blood flow |
There are portable models of sonographs: a doctor can be called to your home. This medical service is inexpensive and is useful for examining the mammary glands of people with disabilities.
Ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound) of the breast is done in the late follicular phase of the ovary, and in emergency cases - on any day of the menstrual cycle. Sonography of the mammary glands is performed for the purpose of preventive research, determining the type of pathology, and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
Ultrasound is prescribed before medical or plastic surgery. In the first case, the severity and localization of changes are clarified; in the second, they are used more often for the selection of female breast implants. It is mandatory to evaluate the mammary glands using an ultrasound at the stage of preparation for IVF.
To watch a video of how ultrasound diagnostics are performed before mammoplasty:
Features of the procedure for children
Children (boys, girls) have the same diseases as adult women, plus the likelihood of birth defects and chromosomal disorders. A child can have a breast ultrasound at any age, including the neonatal period. There are no differences between the preparation and procedure for performing the procedure for children and adults.
How to prepare for the procedure
The preparation process only involves choosing the right day. Since a woman’s breast is a hormonal-dependent organ. Consequently, it undergoes multiple changes during the menstrual cycle. These changes can affect the final result. No other preparation is required for the procedure.
Ultrasound is recommended in the first half of the menstrual cycle
Indications and limitations of breast sonography
You can do breast ultrasound for children, during pregnancy, during breastfeeding, for patients with installed implants, and for neoplasms. Ultrasound is absolutely safe for the body, does not provoke the development of oncology, and does not damage endoprostheses. After 40 years, glandular tissue is coarser, so women are shown digital mammography rather than ultrasound diagnostics.
There are no contraindications to breast sonography. A temporary limitation for ultrasound is deep skin damage or acute inflammation of the mammary gland tissue.
Emergency ultrasound diagnostics are prescribed by a doctor if cancer is suspected (enlarged regional lymph nodes) or signs of the disease appear. This rule also applies to immature girls, women during lactation, pregnancy, and after childbirth.
Direct indications for unscheduled breast ultrasound:
- premature growth of mammary glands in girls under 8 years of age;
- swelling, redness, peeling of the skin, areola;
- discharge from the nipple, its retraction;
- compaction in glandular tissue;
- change in sensitivity, shape, size, contour line;
- asymmetry of the mammary glands, nipples or areola;
- chest pain;
- bruise, intramammary hematomas;
- sign of damage/displacement of the implant;
- symptoms of the disease in boys.
Reproductologists or gynecologists prescribe sonography of the mammary glands during pregnancy planning and IVF. Ultrasound is done to identify life-threatening pathologies and timely treatment. If cancer or metastases are discovered after conception, treatments are harmful to the fetus. Due to the risk of congenital deformities, abortion will be necessary.
For women of childbearing age, emergency ultrasound can be done at any time of the day, regardless of what day of the menstrual cycle it is.
Patient opinions
Those who have encountered the need to perform an ultrasound of the mammary glands note a low level of discomfort and a fairly high effectiveness of the procedure. The fact that the breast ultrasound protocol is given to the patient almost immediately after the examination also creates a positive impression.
Depending on the results, the specialist refers the subject to a consultation with a mammologist.
To ensure a high-quality procedure, according to patients, you should choose a clinic with good modern equipment and qualified doctors. Many private medical centers offer their clients no queues, individual approach and friendly attitude.
Preparing for breast sonography
There is no need to change the diet of children or adults during preparation for an ultrasound examination of the mammary glands. It is enough to follow the recommendations regarding the day of the menstrual cycle. You are allowed to eat and take medications. The need to interrupt the course of hormones and oral contraceptives is agreed with the doctor.
Before the procedure you cannot:
- sunbathe;
- visit the sauna, solarium, baths;
- supercool;
- take a hot bath;
- lactating women should feed the baby and express milk before the procedure;
- It is forbidden to heat the space-occupying lesion (it may cause deterioration).
You can eat any food, drink coffee, sparkling water before the ultrasound. They do not distort the result of breast diagnostics. In preparation for a preventive study, there is no need to submit biomaterial for laboratory tests.
You need to go for the procedure after cleansing the breast skin of medicinal or cosmetic products; do not use soap or gel during the shower. Because of them, the echo signal penetrates the epidermis less well.
During what period and how often is breast ultrasound done?
It is better for women of reproductive age to undergo routine ultrasound diagnostics of the mammary glands annually. Over 40 years of age, ultrasound or digital mammography is recommended once every 6 months. It is advisable to go to a doctor for a medical examination with an ultrasound protocol.
For teenage girls or women of childbearing age, it is recommended that ultrasound be performed between the 4th and 11th day of the cycle. It is advisable to examine the mammary glands in the first days after the end of menstruation. If there are no periods during lactation, sonography is performed at any time.
Regardless of the phase, breast cancer is examined urgently if breast cancer, metastases, or other dangerous diseases or injuries are suspected. An ultrasound can be done any day for children, women during menopause/menopause, girls after menarche (first menstruation) until the cycle stabilizes.
Not the best days for a planned ultrasound:
- during full menstruation or when smearing;
- ovulation + days before/after egg release;
- before the onset of menstruation 0.5–1 week.
This is due to the fact that in the ovulatory period and in the second half of the cycle the concentration of progesterone is increased. The functions of the reproductive organs, including the breasts, are reconfigured for pregnancy. As menstruation approaches, hormonal levels change again. These fluctuations can distort the validity of the survey. After ovulation, ultrasound is prescribed only if hormone-dependent diseases are suspected.
Ultrasound can be done frequently, even daily, during breast examination/therapy. Ultrasound is safe, helps the doctor to see deviations in a timely manner and adjust the treatment method.
Differences between ultrasound and x-ray
It is not possible to choose between these procedures because they are both an important part of breast cancer screening. Due to their differences, radiography and ultrasound allow one to obtain high-quality diagnostic results, since they complement each other.
Only mammography can accurately detect mutations in cells . But due to radiation, it is prescribed only in cases of urgent need and only to patients over 40 years of age.
In this sense, ultrasound diagnostics is more harmless, but it is often unable to diagnose a tumor, since the latter merges with the surrounding tissue in the image.
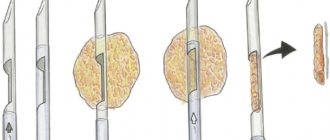
Patients at risk alternate between these two examinations. X-ray reveals the location of the tumor, but sometimes there are errors in interpretation. Ultrasound diagnostics is indispensable when it is necessary to control the taking of a puncture or biopsy.
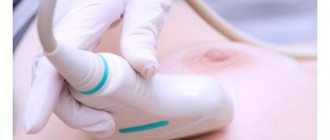
How is breast sonography performed?
In the ultrasound room, a woman undresses to the waist, takes off her bra, voluminous beads, and necklace. Watches, rings, glasses or contacts do not interfere with the diagnosis. The couch is covered with a disposable diaper or a large towel.
Rules for performing breast ultrasound:
- The subject lies down with her stomach up, placing her hands behind her head.
- The diagnostician applies the gel to one breast or sensor and places the device against the skin.
- First, one breast is examined (in case of diseases, the healthy one), then the second, the lymph nodes around the glands.
- The nipple area is immediately scanned. Then the surface of the mammary gland is visually divided into 4 parts, each segment is examined in turn.
- An ultrasound scan lasts up to 15 minutes if there are no echo signs of disease.
- After the procedure, the gel is wiped off, and the diagnostician prints out the protocol.
The ultrasound technique is the same when examining the mammary glands by any method: ultrasound, with elastometry, Doppler, Color Doppler. Sonography with contrast (intravenous, oral drugs) is not performed.
Watch how an appointment with an ultrasound specialist goes:
Diagnosis of mastitis at the Naran clinic
Tibetan medicine does not ignore the results of traditional Western diagnostic methods, but takes them into account when making the final diagnosis of interest to the patient. However, the main attention at the Naran clinic is paid to the original Tibetan methods; they help to establish the true causes of the disease and prescribe the most effective treatment.
Doctors at the Naran Clinic use the following methods in diagnosing diseases:
The main key to successful treatment in Tibetan medicine is the cooperation between the doctor and the patient, which begins from their first meeting. Doctors of Tibetan medicine conduct a detailed survey and find out all the patient’s complaints. The occurrence of any disease has its own causes and prerequisites. Naran doctors, during a conversation, find out what could be the cause of the disease, find out what kind of lifestyle the patient leads, what food preferences are. The doctor examines the patient, palpates the mammary gland and lymph nodes.
Pulse diagnostics is of great importance in diagnosing the disease. Pulse examination allows you to determine what diseases the patient has had in the past, what she is currently suffering from, what is the degree of development of the disease, and also to prevent the problems that may await her in the future if she does not pay attention to her health. Based on the characteristics of the pulse, the state of the internal organs is determined, and the degree of disturbance of a particular constitution is revealed.
Interpretation of protocols
The results are interpreted by a mammologist, gynecologist or oncologist. At the conclusion of the ultrasound, a healthy mammary gland is considered a sample of the individual norm, if there are no deviations from the medical standard.
The breast is one of the hormone-dependent organs. In each phase of the menstrual cycle there are characteristic changes that are not related to pathologies. During decoding, the doctor compares the mammary gland with the corresponding physiological norm of the MC.
Breast sonogram in women in the absence of pathologies:
| Type of fabric | What does normal look like? |
| Glandular | Fine-grained, cell-shaped, light gray, with black dots and tubes of milk ducts |
| Fat | Hypoechoic (dark), sometimes layered: alternating with light areas |
| Connective | Hyperechoic, in the form of light threads, stripes |
Normally, expansion of the mammary ducts on the sonogram occurs in pregnant, lactating women and in the 2nd half of the cycle after ovulation. Intramammary lymph nodes are not visible.
What a healthy mammary gland looks like on an ultrasound:
Pathological echo signs
Ultrasound signs are often the same for diseases of the same group. It is advisable to obtain a second medical opinion. Interpretation of the ultrasound report and further examination of the mammary glands can be done in another diagnostic center.
What pathologies does a sonogram show:
- cyst of any type;
- false/true gynecomastia;
- Poland syndrome (pathology of the pectoral muscle);
- breast hypertrophy (macromastia);
- wen, hamartoma, benign lipomas;
- cancer, metastases;
- fibroadenoma;
- mastitis, mastopathy;
- intrathoracic hematoma;
- intramammary (inside the glandular tissue) lymphadenitis;
- neoplasms, tumors;
- lactating adenoma;
- intraductal papilloma (papillomatosis);
- pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia;
- foreign body, bone (after injury).
In mammology, cysts inside the mammary gland, inflammation, neoplasm, and cancer are more common. Enlarged lymph nodes or dilated ducts accompany many breast diseases.
What does a cyst look like:
- the shell is round, hyperechoic (light);
- intracavitary fluid is anechoic (black spot);
- There may be gray inclusions in the cavity.
The shell of a benign cyst is normally not penetrated by vessels, and if the description indicates vascularization, this indicates malignancy. When developing into oncopathology, increased blood supply also occurs in the intracavity space.
Description of echo signs of breast cancer:
- the malignant area is motionless;
- does not have a clear boundary;
- the contour line of the seal is uneven;
- in the area of nodule formation, blood supply has increased;
- the cancer zone is hyperechoic (light);
- there are white spots (microcalcifications);
- An acoustic shadow (dark stripe) is visible behind the seal.
Focal benign changes inside the mammary gland with a smooth border, easily displaced, less rigid (lighter than healthy tissue). Intramammary lymph nodes are not enlarged. Control ultrasounds show a slow growth of the compaction.
Echo signs of other pathologies:
- inflammation - the milk ducts are usually dilated, the glandular tissue is darker in comparison with healthy areas (hypoechoic);
- breast lipoma - an oval gray spot with a light shell, a wavy contour;
- breast adenosis - the lymph nodes in the mammary gland are enlarged, a cord/densification is formed from the growing glandular tissue, resembling cancer in color and shape.
If the anatomical indicators in the protocol are abnormal, there are echo signs of the disease, the diagnosis is made taking into account the results of other studies.
Classification of bi rads during ultrasound of the mammary glands
BI-RADS – ultrasound analysis system and coding of ultrasound results. It was created for standard logging.
Formations that can be detected:
- An abscess is a cavity in the soft breast tissue filled with purulent fluid. It manifests itself as a complication of mastitis or a separate disease with elevated body temperature, pain and tension in the chest.
- Mastitis is inflammation of the mammary gland, the initial stage of an abscess. It appears in mothers during lactation.
- A cyst is a tissue cavity filled with fluid. It can be either single or multiple.
- Fibrocystic mastopathy is a dishormonal breast disease typical of middle-aged women (30-40 years old). Symptoms include thickening and discharge of fluid from the nipples.
- Breast fibroadenoma is a formation in the connective and glandular breast tissue.
After the ultrasound, the doctor concludes with a BI-RADS category, which can be used to determine the diagnosis.
BI-RADS 0
The diagnosis has not been definitively established; further examination is required.
The situation may occur due to failures or blurred images, or the inability to perform an ultrasound for other reasons (chest injury). It is recommended to repeat the procedure to obtain a different category. You can also review your previous mammogram results.
BI-RADS 1 negative
No pathological signs.
The patient has no tumor formations, the architecture is not disturbed, there are no calcifications, the mammary glands are symmetrical.
BI-RADS 2
Fibroadenoma with clear, even contours and single linear vascular loci with CDK.
The presence of a benign education.
The category is similar in meaning to BI-RADS 1, as it does not threaten the patient’s health.
Formations that fall under the BI-RADS 2 category:
- Implants.
- Violation of architectonics in connection with operations on the mammary glands.
- Fat-containing formations (cyst).
- Rod-shaped calcifications.
- Fibroadenoma.
If a benign formation is detected in the mammary glands, you need to undergo examination more often.
BI-RADS 3
Fibroadenoma with calcified capsule
Possible benign formation.
The doctor sets this category to observe changes in the patient’s body for a short time, but they most likely will not occur.
Education for this category:
- Group of punctate calcifications (solitary).
- Round formations, unclear from the image.
- Asymmetry, with point compression less dense.
The final examination is carried out six months later, after which category 2 is assigned. If the formation is suspicious, BI-RADS 4 is assigned.
BI-RADS 4
Acute local mastitis
The probability of malignancy is 2-95%.
There are not enough signs of a malignant tumor, but there is a suspicion, the doctor may recommend a biopsy.
Negative signs:
- Abscesses.
- Atypical fibroadenomas.
- Mastitis that cannot be cured.
- Formations measuring 3 cm or larger.
Depending on the percentage of probability of malignancy, the patient is assigned one of the groups: 4A, 4B, 4C.
- 4A. A malignant tumor will not form due to a lack of signs. After 3 months, the woman is recommended to undergo a repeat examination.
- 4B. There is a high risk of developing cancer. Every six months the tumor increases by 5 mm. Complex cysts with internal growths. Abscesses.
- 4C. An incomplete set of cancer signs, but a high probability.
If the percentage exceeds group 4C, the next category is assigned.
BI-RADS 5
Invasive ductal carcinoma: vertically oriented, irregularly oval-shaped formation with blurred contours
The probability of malignancy exceeds 95%.
Used when there is no malignancy on biopsy (contradictory) or most features indicate the presence of malignancy.
BI-RADS 6
The presence of a malignant tumor. Additional examination, treatment or surgery is prescribed.
Cost of breast sonography
Prices for ultrasound diagnostics in mammology range from 500–14,000 rubles. The cost depends on the status of the medical institution and the type of examination.
Average price of ultrasound:
- examination of the mammary glands + regional lymph nodes – 2000 rubles;
- Breast ultrasound – 700 rubles;
- elastography of the mammary glands – 1700 RUR;
- Dopplerography – 1600 rub.
To examine the mammary glands in women and girls, preparation for an ultrasound consists of cleansing the skin before the procedure. No change in diet or interruption of the course of treatment is required. The diagnosis is safe. It can be performed on the same day with X-rays, MRI, CT, pelvic sonography (PSU), examinations with contrast, without an interval between procedures.
Share the article with your friends on social networks. Leave comments and tell us about your examination experience. Best wishes.
Prevention of mastitis in nursing
| “Empty” breasts are the best way to prevent mastitis. To prevent mastitis, a nursing woman needs to express the remaining milk in the breast after each breastfeeding (if the baby has not sucked everything). And if even minor problems appear, start feeding the baby from the “problem” breast: while he is hungry, he sucks better and more actively. The remaining milk must be expressed using a vacuum aspirator, with your hands, with your husband - it doesn’t matter. |
How is ultrasound performed?
Some girls are nervous when going for an ultrasound. Because they think the procedure may be painful. However, it is not. It is completely painless and is carried out quite quickly. Once the patient is comfortable on the couch, the doctor will apply ultrasound gel to the area being examined and begin moving the probe over it. At the same time, he will sometimes ask the patient to change position. For example, lying on your back, put your right hand behind your head. This is necessary to examine the gland from all sides.