What is Dopplerography?
Dopplerography is an ultrasound examination of internal organs based on the Doppler effect. The abbreviation for the procedure is UZDG.
The Doppler effect in medicine is used to study the speed of sound in a stationary environment. It is based on the broadening method - the frequency of radiation increases when moving towards the observer and decreases when moving away from him.
This study has several subtypes:
- USDG MAG stands for checking the main arteries of the head;
- Ultrasound Doppler Doppler (BCS) means the study of abnormalities associated with the vessels of the head and neck;
- BCA ultrasound is a scan of large arteries: carotid, vertebral and subclavian.
What is the difference between Doppler and ultrasound?
Ultrasound produces waves at the same time interval, and also receives the signal back. This creates a general picture of the internal organs and their static structure.
Dopplerography differs in that it emits waves at one speed and receives them at another. The difference in such fluctuations shows the movement of blood flow through the vessels and its speed.
When is it prescribed?
Doppler ultrasound is prescribed if a circulatory disorder is suspected, which manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- memory impairment;
- prolonged insomnia;
- nervous and mental disorders.
Other indications for Doppler ultrasound:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebra;
- stroke;
- persistent headache;
- transient ischemic attack;
- visual impairment;
- phlebeurysm;
- arterial hypertension;
- vascular aneurysm;
- vascular malformation;
- encephalopathy;
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- acute cerebrovascular accident.
Are there any contraindications?
Ultrasound ultrasound is a harmless procedure that is prescribed to both pregnant women and infants. It does not have a negative effect on the body and does not disrupt the structure of tissues.
Contraindications occur when the patient cannot remain in a horizontal position due to severe illness, for example:
- bronchial obstruction;
- respiratory failure;
- heart failure.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of Doppler ultrasound examination:
- the procedure does not require special preparation;
- only this diagnostic method will reveal some types of vascular pathology;
- painless for the patient;
- does not emit dangerous rays;
- has no age contraindications;
- the procedure takes from 15 minutes to 1 hour;
- affordable for most residents of the country.
Flaws:
- does not visualize the cause of vascular stenosis;
- does not show the appearance of vascular tissue;
- does not assess the condition of the veins.
Doppler ultrasound cannot replace procedures such as CT and MRI.
What does it reveal?
Dopplerography reveals:
- narrowing of the lumen of the arteries and severity;
- condition of the vertebral arteries;
- blood flow speed in the main arteries;
- causes of headaches, increased blood pressure;
- organ disorder from the consequences of the formation of plaques and blood clots;
- condition of blood vessels and their deformations.
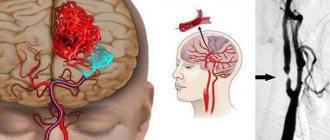
What is transcranial Doppler ultrasound (TCD)?
Transcranial Dopplerography is nothing more than an ultrasound scan of the brain
. Since the vessels of the brain are securely “hidden” under the skull, which does not transmit ultrasound waves well, ultrasound of the brain is done using a special technique in open areas of the skull, and this examination method is called TCD (transcranial Doppler).
When is TKDG prescribed?
TCD, like ultrasound, is indicated for various symptoms: fatigue, dizziness and headaches, attention disorders, frequent fainting, numbness of the extremities. All this may indicate brain damage, including after trauma or surgery. TCD is also prescribed for diagnosed vascular diseases to control their course. TCD is indicated for infants after neurosonography, which gave alarming results.
How is the TCD procedure performed?
To assess the condition of the vessels located in the cranium, the sonologist uses three “windows”: temporal (in the temporal part of the head), suboccipital (in the occipital part) and orbital (in the eye area). Through these areas (the doctor briefly places the probe on them), ultrasound waves can easily reach most of the intracranial vessels. The TCD procedure itself takes about twenty minutes, but it is usually complemented by an ultrasound scan of the neck
to obtain more complete information about the condition of the patient’s blood vessels, therefore it requires more time.
#!UZIseredina!#
Types of research
Doppler ultrasound is performed in three modes:
- B-mode. This is a black and white picture that allows you to assess the thickness of the vessels, the condition of the valves and the presence of tumors.
- Color mapping - tissue Dopplerography. This is a multi-colored image that shows the relief of the fabric: its indentations and bulges. It can also estimate the speed of blood flow.
- Spectral - echo or D-mode. It is a graph of changes in blood flow in the vessels over time.
Doppler echography is divided into two types:
- pulse-wave - makes it possible to see changes in blood flow in one section of the vessel;
- constant wave - allows you to study blood speed of 5-20 m/s.
Also distinguished:
- three-dimensional scanning;
- duplex;
- triplex.
three-dimensional
Three-dimensional scanning is a three-dimensional image that is obtained by converting a computer signal from a sensor. It allows you to see the organ from different sides and evaluate its size.
Most often, this mode is used in perinatal medicine, studying the norms and pathologies of the fetus. Thanks to three-dimensional imaging, some problems of a conceived baby can be solved even before birth.
3D photo
Duplex
Duplex ultrasound scanning (USDS) is a diagnostic method that combines the Doppler effect and B-mode (two-dimensional). This diagnostic allows you to examine an organ in real time, monitoring changes in its frequency indicators.
Advantages of the method:
- visualizes veins;
- allows you to study the condition of tissues of organs and veins.
A photo taken using the duplex method
Triplex
Triplex research is a combination of the duplex method with color mapping, that is, working simultaneously in three modes.
This type of diagnosis allows you to study:
- blood flow speed;
- direction of blood flow;
- vein patency;
- the structure of the vessel and its walls;
- degree of tortuosity of veins.
Triplex mode snapshot
Diseases that can be found
Dopplerography of the vessels of the lower extremities of the main blood flow allows you to diagnose the following diseases of the veins and arteries:
- Obliterating endarteritis, if the diagnosis is confirmed, urgent treatment is required.
- Obliterating atherosclerosis, the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, the degree of their development, as well as the effect of existing formations on blood flow are assessed.
- Vascular aneurysms occur when pathological stretching of the vessel wall leads to its thinning. The risk of rupture of a damaged vessel during stress and the need for surgical intervention are assessed.
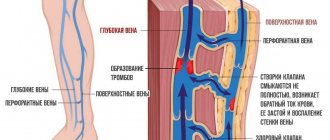
- Varicose veins of the legs. A sedentary lifestyle and excess body weight contribute to the development of the disease. Overfilling of the vascular network leads to dilation of the veins, and subsequently to the formation of blood clots, which pose a danger to life if they rupture.
- Venous insufficiency of the legs is determined by incomplete collapse of the vein; during the contraction phase, part of the blood is thrown back, which leads to the accumulation of blood in the vein cavity and stretching of the vascular wall. This later manifests itself in insufficient nutrition of the tissues of the lower extremities.
- Thrombosis is a complication of varicose veins; when a thrombus is detected, its location, the degree of filling of the vessel, a young or old thrombus and the risk of its rupture are assessed.
In addition to making a diagnosis, ultrasound of the arteries allows you to assess the degree of blood supply to tissues and identify violations of the patency of deep veins.
How is Doppler sonography done?
The Doppler ultrasound procedure is done as follows:
- The patient should lie down on the couch and take a comfortable position. The position can be changed at the request of the doctor, it depends on the area being studied.
- The desired area of the body must be left without clothing.
- The doctor applies a special gel to the ultrasound sensor. In paid clinics, the client is offered napkins to wipe it off; in free clinics, most often you are required to bring your own.
- The device is applied to the patient’s skin, and the necessary organs are viewed.
- The ultrasound specialist may require the patient to change the breathing rate and tension of certain muscles. This is necessary for analyzing the blood flow of peripheral vessels and large arteries.
- The readings received through the sensor are recorded by a specialist and deciphered for the patient.
How to do an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the lower extremities
The procedure can be performed with the patient lying or standing. Naturally, you need to free your legs from clothing, then the doctor applies a special gel and moves the ultrasound sensor over the skin of the legs in the examination area.
The ultrasound examination procedure is performed in a lying or standing position.
Before starting the procedure, the doctor conducts various tests to determine the area with possible violations, in which visualization is carried out with the greatest attention. Doppler ultrasound reveals a fundamentally altered type of blood flow and allows the doctor to determine the amount of treatment required.
The following veins are accessible to the Doppler method:
- lower hollow;
- thigh vein;
- subcutaneous large and small;
- ileal;
- deep shins;
- popliteal;
- fibula;
- and sural veins.
The diagnostician sees the speed of filling and strength of the veins with blood in real time in the form of noise and graphic effects.
If necessary, the doctor will ask you to perform simple actions, such as getting off the couch or holding your leg up. This is necessary to assess the behavior of the vascular network in a changed position and evaluate the work of the veins under load.
The ultrasound procedure of the lower extremities takes from 10 to 15 minutes of pure research time, maybe longer. During this period, the sonologist will fully assess the functionality of the veins and identify foci of pathology. At the end of the procedure, the patient is given a study protocol, which must be shown to the attending physician. Some indicators can be deciphered and you can understand on your own what is written there, but you don’t need to draw your own conclusions.
Doppler ultrasound examination during pregnancy
Doppler ultrasound examination during pregnancy (DPM) is carried out twice:
- at 18-21 weeks;
- at 32-34 weeks.
If necessary, additional research can be carried out if the following abnormalities are suspected:
- gestosis;
- multiple pregnancy;
- deviation in the structure of the umbilical cord;
- kidney diseases;
- maternal autoimmune diseases;
- fetal death;
- Rhesus conflict.
Before diagnosis, doctors do not require special preparation from the patient. But according to reviews from pregnant women and young mothers, it is better to refrain from eating fried and spicy foods before an ultrasound scan and not to overeat the day before.
The following characteristics are studied on Doppler ultrasound:
- blood flow in the umbilical cord and fetal circulatory system;
- the state of the baby's heart;
- picture of the mother's circulatory system.
Ultrasound ultrasound does not affect the health of the mother and child.
Ultrasound specialist Maria Medvedeva on the channel of the Clinic for Reproductive Medicine named after. Academician V.I. Grishchenko talks about Dopplerography during pregnancy.
TCD and USDG - what is the difference?
The main difference between TCD and ultrasound is their purpose. Ultrasound Dopplerography is not only a common name for all methods of sound Dopplerography, but also a way to assess the condition of the vessels of the extremities and other accessible parts of the body using indirect signs of blood flow. Due to the complexity of its implementation, TCD is a separate examination technique, but there is no other difference between it and ultrasound, since the same problems are solved, and the principle of both diagnostics is based on the Doppler effect.
Examination in children
Ultrasound with Doppler is prescribed to babies at the age of 1 month to identify disorders associated with blood supply to the brain. Usually this procedure is carried out in the maternity hospital. There is no need to re-examine if no problems were found during the first examination.
Indications for ultrasound examination for children:
- prolonged headaches;
- poor sleep;
- dizziness;
- causeless tearfulness;
- restlessness and overexcitability;
- delayed speech development;
- memory and school performance disorders;
- fast fatiguability;
- vascular pathology;
- diabetes;
- other diseases associated with impaired blood circulation in the brain.
Children tolerate Doppler sonography well, since it is a painless research method that is performed only on the surface of the skin without penetration.
TCD or ultrasound ultrasound - which is better?
If you understand the difference between TCD and ultrasound, the question of which is better will not arise in the future. For pathologies of the lower extremities, TCD will not be prescribed, while for problems with brachycephalic vessels, an additional ultrasound of the neck vessels
. Thus, these two methods are complementary and cannot replace each other. The importance of ultrasound research methods in modern medicine is very great, since they are completely safe even for pregnant women and newborns.
#!UZIVRA4!#
Doppler of vessels of various organs
To examine various organs with Doppler, the specialist asks the patient to take one of several positions:
- sitting;
- standing;
- lying on your stomach;
- lying on your back.
Vessels of the brain and neck
Diagnosis of the brain and neck takes place in a lying or sitting position. Before the procedure, it is necessary to expose the areas of the neck and shoulder blades and take the correct position.
During Dopplerography of blood vessels, the doctor will evaluate the condition of the veins and large arteries, and the structure of the surrounding tissues. The patient may be required to briefly hold their breath or change their body position.
When studying cerebral vessels, it is often necessary to apply the gel directly to the hair.
Heart vessels
Cardiologists send people for ultrasound examination if the patient complains of pain in the chest and heart area. This method detects cardiovascular pathologies at an early stage of development, allowing the doctor to begin treatment on time.
During the procedure, the patient must lie on his back and completely expose his chest. The ultrasound specialist directs the transducer at different angles, which helps assess the whole picture of the chest area.
Vessels of the lower extremities
Ultrasound scanning of the vessels of the legs and veins is carried out in different positions:
- lying on your stomach, with your legs spread shoulder-width apart;
- standing.
Changing the position allows you to assess the condition of the veins and blood vessels at rest and during exercise. To check for blood clots, your doctor may press on veins that are close to the skin.
There is also a method that is used only for varicose veins:
- squeeze the patient’s calves;
- press on the forearms;
- The patient is asked to exhale with the mouth closed and the nose pinched.
This is called the Valsalva method. It gives an estimate of the speed of blood movement in the legs.
Abdominal vessels
To diagnose the abdominal cavity, preparation is required:
- you should not eat gas-forming foods the day before the test;
- You need to take enterosorbents for 2-3 days;
- 2 hours before the diagnosis, do a cleansing enema;
- come to your appointment on an empty stomach.
The specialist will ask the patient to expose the stomach and, if necessary, inflate it. When a patient complains, they look at a separate area, but during a general check, they look at everything in a complex: the abdominal aortas and renal arteries.
Male reproductive system
During ultrasound examination of the male reproductive system, the following is examined:
- scrotum;
- testicles;
- appendages;
- penis;
- seminal vesicles;
- prostate gland;
- vas deferens.
The patient is asked to lie on his back and expose the groin area. If necessary, you need to help the doctor and hold the penis so that the Doppler has access to all study areas.
Indications
Ultrasound scanning of the vessels of the lower extremities is prescribed to patients with the following symptoms:
- swelling of the legs;
- constantly cold feet;
- feeling of numbness in the legs;
- pain and cramps in the calf muscles;
- vascular “networks”, “stars”, protruding veins;
- heaviness in the legs when walking for a long time or that occurs for no reason;
- numbness and changes in sensation in the limbs (for example, goosebumps);
- when determining asymmetry in the patient’s legs (one may be thicker than the other);
- the formation of bruises with minor damage, abrasions that do not heal for a long time.
In addition to complaints, the procedure is prescribed for people suffering from such diseases as:
- thrombosis;
- atherosclerosis;
- thrombophlebitis;
- trophic ulcers;
- arterial aneurysms;
- vasospasm (arterial spasm);
- obliterating endarteritis;
- varicose veins of the legs;
- arteriovenous malformations.
Decoding the results
Indicators for deciphering ultrasonography:
- systole size;
- diastolic blood flow velocity;
- the ratio of the above indicators;
- resistivity index.
Standards for Doppler ultrasound results for pregnant women:
| Pregnancy time (weeks) | Systole-diastolic ratio | Resistance index |
| 12-13 | 2-3,5 | 0,52-0,71 |
| 14-16 | 1,9-3,1 | 0,48-0,68 |
| 17-19 | 1,7-2,6 | 0,44-0,62 |
| 20-24 | 1,6-2,5 | 0,41-0,61 |
| 25-31 | 1,7-2,4 | 0,4-0,58 |
| 32-37 | 1,6-2,3 | 0,35-0,58 |
| 38-40 | 1,4-2,1 | 0,32-0,55 |
Norms of Doppler ultrasound indicators:
| Index | Group | Norm |
| Vessel diameter | vertebral artery | 3.5 mm |
| carotid artery | 5.5 mm | |
| internal carotid artery | 4.6 mm | |
| external carotid artery | 3.7 mm | |
| Blood flow speed | young | 0,663-0,71 |
| elderly | 0,685-0,73 |
Pathologies:
| Index | Stages of development |
| Narrowing of the lumen of the vessel |
|
| Artery deformation |
|
| Aortic change |
|
| Vascular diseases |
|
Only a specialist in this field can accurately decipher the results of an ultrasound scan.
Decoding
Let's decipher what indicators should be normal in the protocol, and what these or other terms mean.
- The veins are passable, not dilated, the walls are not thickened. The thickness of the vascular wall normally ranges from 0.9 to 1.1 mm.
- Compressive - they have not lost their normal tone, they can shrink.
- The lumens of the arteries are not narrowed.
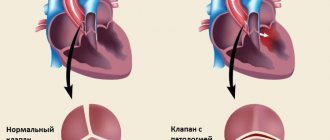
- The valves are healthy, there are no refluxes - the valves are completely closed and there is no reverse blood flow.
- There are no pathological refluxes when performing compression tests and the Valsalva maneuver - blood does not flow in reverse direction when performing tests.
- The movement of blood flow in each individual vessel in different locations (velocity has its own normal values at each site and cannot be measured in only 1 place). Normally, the speed of blood flow in the femoral artery is approximately equal to 100 cm/s, in the arteries of the leg - 50 cm/s.
- No intraluminal structures were identified—there were no atherosclerotic plaques or thrombi.
- There are no pathological connections between the vessels - the norm.
- The blood flow is phasic - it means faster when you exhale and slower when you inhale, which is normal.
Video
Natalya Sergeeva, an ultrasound specialist, talks in detail about Dopplerography on the Rudiamed channel.
Do you have any questions? Specialists and readers of the HROMOSOMA website will help you ask a question
Was this article helpful?
Thank you for your opinion!
The article was useful. Please share the information with your friends.
Yes (100.00%)
No
X
Please write what is wrong and leave recommendations on the article
Cancel reply
Rate the benefit of the article: Rate the author ( 4 votes, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Discuss the article:
What is CDK
Color Doppler mapping (CDC) is an ultrasound examination with an additional assessment of blood flow using the Doppler effect, expressed in a color image of the blood flow of the area under study, superimposed on a black and white picture obtained by ultrasound.
The color flow mode allows you to evaluate additional parameters, namely:
- the direction of blood movement, the speed of its movement and other characteristic features;
- freedom of the bloodstream;
- blood flow resistance;
- the dimensions of the vascular wall and the diameter of the lumen of the venous and arterial network in various parts of the body.
Analysis of this data makes it possible to determine not only the disease and the location of the disorder, but also to predict the further development of the process. This helps to assess the risk to the patient’s life and health even before serious clinical manifestations and take the necessary measures for prevention and treatment.
Preparation, how the procedure is carried out
No special preparation is required for ultrasound examination. The only thing the patient needs is to avoid smoking, alcohol and taking vascular medications on the eve of the procedure , since changes in vascular tone can affect the accuracy of the result.
During a Doppler ultrasound, the patient lies on his back, and the doctor applies a special gel to certain areas and runs an ultrasound probe over them.
During the procedure, you may need to breathe more quickly , hold your breath, or turn your head in a certain way. In this case, the person does not experience any painful sensations, and the only thing that can cause slight discomfort is slight pressure on the neck or head area.
The procedure can last from 20 minutes to an hour.
Ultrasound scanning of extracranial vessels begins with scanning the lower segment of the common carotid artery on the right side, after which the sensor is moved up the neck to the angle of the lower jaw.
This allows you to assess the course and depth of the artery, determine the place where it divides into internal and external, and also identify atherosclerotic plaques.
After this the device switches to color mode to examine the area for areas of impaired blood flow, abnormalities in the structure of the vascular walls, blood clots or plaques.
Next, the vertebral arteries are examined and the main diagnostic parameters are measured (systolic and diastolic blood flow velocity, their ratio, etc.).
Transcranial Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the brain and neck is performed through the anterior and middle temporal windows, located in front of the auricle and above it, respectively. In this way, the main arteries of the brain (posterior, anterior, middle), veins of Galen and Rosenthal, the posterior communicating artery and the straight sinus are visualized. To examine the ophthalmic artery and internal carotid siphon, a sensor is placed on the closed eyelid.
How is the data decrypted?
Interpretation of ultrasound and Dopplerography of the vessels of the head and neck consists of a comparative analysis of the artery with specific standards for a number of parameters: diameter; wall thickness; resistance indices; features of blood flow symmetry; systolic peak velocity. Veins are assessed based on vascular diameter, the nature of blood exchange, and the condition of the vein walls. If the results are normal, then:
- there will be a clearly visible and free gap between the vessels;
- the thickness of healthy arterial walls should be about one centimeter;
- in areas where there is no branching of blood vessels, there is no turbulent blood flow;
- There should also be no arteriovenous malformations;
- if the vessels are compressed together, additional examination will be required;
- if any area is abnormal, the doctor indicates a alphanumeric abbreviation;
- Knowing all the symbols, the neurologist can easily decipher the information received and prescribe appropriate therapy.
Research Modes
The study uses several modes, depending on the specific area:
- scanning of the main arteries, which allows you to study vascular blood flow;
- duplex arterial and venous scanning, which gives the specialist a color two-dimensional sketch, which records the condition of the vessels in the neck, skull, and both lobes of the brain;
- triplex scanning, which complements the first two studies.
To display a comprehensive state of the brain vessels, main veins and arteries that provide blood flow, these modes are used simultaneously. Thanks to TCD of the vessels of the head and neck, a clinical picture is reliably obtained on a computer monitor using the radiation of an ultrasonic wave that penetrates the vessels and is reflected from the blood red cells, depending on the speed and direction in which they move. The reflected waves are caught by special sensors and converted into an electrical signal, which forms a dynamic sketch. If there are blood clots, narrowing of the lumens and spasms, the flow of blood changes. This immediately gets a screen fix. To study the veins and arteries located in the brain, a sensor is installed on the bones of the skull, which have a minimum thickness.
Who needs to be tested?
To understand that there is insufficient nutrition of cells in the brain, you need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- balance problems, unsteady gait, problems while moving;
- decreased hearing and visual acuity;
- violation of speech articulation;
- frequent headaches;
- noise in ears;
- vomiting and attacks of nausea not caused by indigestion;
- dizziness, especially when bending over;
- fainting;
- change in taste sensations;
- insomnia;
- memory loss, difficulty concentrating;
- chilliness, swelling and numbness of the hands and feet;
- decreased sensitivity in certain areas of the body.
Doppler sonography of the head is indicated for patients with certain chronic diseases. A specialist may prescribe an examination for people who:
- suffer from diabetes mellitus and vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- smoke;
- are overweight;
- suffered a heart attack or stroke;
- have osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- feel very tired when walking, running and light physical activity;
- have heartbeat disturbances if there is a possibility that a broken blood clot will block the artery that supplies the brain;
- have a pulsating focus in the neck area.
In addition, the study can be prescribed before cardiac surgery, as well as for children with mental development disorders.
Based on the patient's complaints, the neurologist can determine where the blood flow in the body has been disrupted.