An x-ray of the heart helps determine its location in the chest, configuration and size, as well as detect changes in the aorta and pulmonary vessels. To accurately identify deviations from the norm, three projections (sometimes four) are used, as well as filling the esophagus with barium to contrast the boundaries. The method is considered accessible and relatively safe when used no more than 2 times a year.
What does a heart x-ray show?
An X-ray examination of the chest organs can identify the shadow of the heart; it resembles an oval, obliquely located in the left half. With a dense physique, it tends to a horizontal line, and in thin people it takes a more vertical position. The great vessels are located closer to the head. Between them and the oval, indentations are created that form the waist.
X-ray of the heart (contours of the heart and blood vessels)
The muscular layer of the heart contains a dense shadow, it is uniform in structure, and the outlines are clear and even, they have an arched shape. Each arc is a representation of the chamber of the heart. If part of it becomes straight, then this is a sign of myocardial pathology.
In addition to the shadow of the heart, the following may be visible on the x-ray:
- areas of calcification of blood vessels, valves;
- an increase in the size or anomaly of the structure of the aorta, pulmonary artery;
- manifestations of heart failure in the form of changes in the pulmonary pattern;
- diaphragm location.
If pericarditis is present, it can be defined as an expansion of the pericardial sac.
We recommend reading the article about coronary angiography of the heart vessels. From it you will learn about indications and contraindications for cardiac coronary angiography, as well as preparation, recommendations and possible negative consequences of this procedure.
And here is more information about the accumulation of non-inflammatory fluid or hydropericarditis.
Signs of cardiomegaly
The symptoms of bovine heart are no different from diseases accompanied by heart failure.
Noteworthy changes in well-being:
- shortness of breath during physical exertion - going up to the second floor,
- palpitations,
- difficulty breathing when lying down,
- arrhythmia,
- increased sweating,
- heaviness over the left hypochondrium,
- pain in the heart area,
- swelling of the veins of the neck, legs,
- arterial hypertension.
A person with cardiomegaly changes as a person for the worse. Addiction to alcohol deprives him of his usual social circle. Next to him are the same dependent people. Under the influence of alcoholic beverages, cognitive abilities gradually weaken and memory deteriorates.
Why is radiography needed?
Examination of the heart using X-rays is carried out using two methods - radiography (taking pictures) and fluoroscopy (the doctor sees the work of the heart in real time). Diagnosis also involves several projections and contrasting the esophagus with barium.
Diseases for which a heart x-ray may be prescribed include:
- myocardial aneurysm;
- congenital and acquired defects;
- cardiomyopathy – primary and secondary, hypertrophic, dilated;
- myocarditis, pericarditis;
- cardiosclerosis;
- pericardial cyst, mediastinum;
- hypertonic disease;
- tumor of the pericardium or heart;
- myocardial dystrophy;
- heart failure;
- pulmonary heart.
In three projections
Direct projection involves examination with the patient facing the screen. It is needed to determine pathology in the following departments:
- aorta in the ascending part;
- left ventricle;
- border between the atria;
- both angles between the diaphragm and the cardiac shadow;
- pulmonary artery.
In the right oblique position, the patient stands with the right shoulder forward at an angle of 45 degrees to the screen. The X-ray tube is always positioned behind the patient. This position helps to explore:
- space behind the sternum;
- cone formed by arteries;
- contours of all parts of the heart;
- pulmonary fields.
For the left oblique position, the patient is asked to rotate the left shoulder toward the screen at the same angle as in the right oblique position. It is possible to clearly examine all parts of the aorta and the posterior wall of the left ventricle; all other parts, the trachea, are also visualized.
With esophageal contrast
The esophagus is located behind the heart. If any chamber enlarges, it is pushed towards the spine along arcs of different radii. To diagnose changes, this arc is measured.
X-ray of the heart with contrast of the esophagus in an oblique projection (A – normal, B – mitral valve disease with predominant stenosis, C – mitral valve disease with predominant insufficiency)
If there is a displacement along a small radius arc in the right oblique position, then this is a sign of narrowing of the mitral orifice. When valve insufficiency predominates, the esophagus deviates along an arc with a large radius. This method also helps to establish the right location of the aortic arch, abnormal branches of vessels from it, and expansion of the pulmonary trunk.
Contraindications for examination
Diagnosis using X-rays is contraindicated in pregnant women. Before the widespread introduction of ultrasound into cardiological practice, patients were asked to cover their abdomen with a lead apron.
Currently, such an examination is considered too great a threat to the formation of organs in the fetus, so it is not prescribed, replacing it with alternative methods.
The study is contraindicated in the following patients:
- in the presence of malignant tumors;
- after radiation therapy;
- in serious condition;
- under the age of 14 (unless absolutely necessary).
During lactation, an X-ray of the heart can be performed, as this does not affect the composition of breast milk and does not harm the baby’s health.
Diet for illness
The use of such a diet is indicated for the treatment and prevention of diseases such as bovine heart. Here are the basic principles of such nutrition:
- For breakfast you need to eat cereals, and for dessert you need to eat fruit.
- For lunch you need to eat dishes containing protein and plant foods.
- It is necessary to have dinner with low-calorie foods. As a rule, these are freshly squeezed juices, low-fat yogurt, kefir, vegetables, and fruits.
The carbohydrates obtained from these products do not turn into excess weight. At the same time, such nutrition allows you to get the necessary elements for the normal functioning of the body throughout the day;
As a rule, these are vegetables, fruits, fish and meat dishes, low-fat dairy products, and hard cheese. Meat and fish must be dietary.
The Mediterranean diet in the treatment of a syndrome such as ox heart also involves eating seafood, and you should not give up first courses;
Snacks are not prohibited with this diet, which is used in the treatment of an ailment such as bovine heart syndrome, but they can consist of low-fat yoghurts, vegetables, and fruits.
But you should give up canned food, sugar, and animal fats. You can use sesame, olive, soybean, and peanut oil as fats. You need to eat food in small portions.
How to do radiography
The duration of the procedure is several minutes. The patient enters a special chamber and faces the screen. Your arms need to be bent at the elbows and raised up so that they do not obscure the chest. If contrast is needed, the patient first drinks a barium suspension. Then the data in the images is quickly recorded, and the subject is asked to turn at different angles to the screen and hold his breath on command.
Radiography
There is no unpleasant or painful sensation during the examination. At the end, the resulting images are processed, developed and dried, after which the radiologist describes the identified changes.
What the results will tell you
Based on the combination of signs of changes in shape, location, and size, one can judge the presence of diseases or abnormalities in the structure of the heart.
heart shadow
Normally, the heart occupies the anterior lower part of the left half of the chest. When the body moves, it can shift by 1 - 2 cm. On an x-ray, you can detect the following variants of the heart shadow:
- location on the right;
- shift due to effusion into the pleural cavity;
- displacement by a diaphragmatic hernia or tumor;
- movement when the lung shrinks.
Configuration of the heart with defects
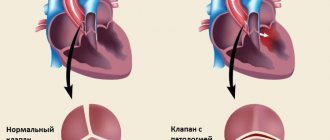
Depending on the damage to the valve apparatus, heart configurations are distinguished:
| Heart configurations | Description |
| Mitral | The pulmonary artery arches are long, the waist is smoothed, the right angle between the atrium and the vessels is shifted upward, and the arc radius of the left ventricle is increased. It occurs with congenital and acquired anomalies of the structure of the mitral valve, narrowing of the pulmonary trunk. |
| Aortic | The waist is pronounced, the left ventricle is large, the aorta is wider than normal. It occurs with Fallot's disease, aortic stenosis, wetting of the aortic valve cusps, and hypertension. |
| Globular or trapezoidal | The right atrial and left ventricular arches are enlarged, the waist is defined, the outlines are smoothed. It occurs with dystrophy and inflammation of the myocardium, expansion of the chambers with cardiomyopathy, disruption of the structure of the septum, effusion into the pericardial sac. |
Organ enlargement
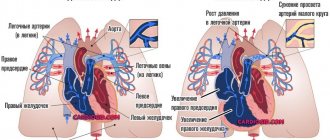
When the cavities of the heart and large vessels expand, an increase in the size of the heart occurs. Depending on the location of such pathological changes, the following diseases can be suspected:
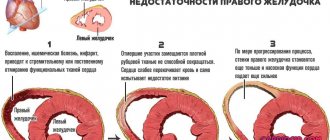
- Left atrium - the esophagus deviates posteriorly to the side, the appendage enlarges, there is an additional arch below along the right border. Sign of mitral valve defects.
- Left ventricle – the apex is rounded, later the arc increases. Occurs with valvular insufficiency in the left half of the heart, arterial hypertension, and cardiomyopathy.
- Aortic arch – the first arch along the right contour is expanded. It occurs with hypertension, open ductus Botall, aortic insufficiency, and aneurysm.
- Right atrium - indirect signs of enlarged arch, expansion of the vena cava. Indicates tricuspid valve defects and pulmonary hypertension.
- Right ventricle - the pulmonary trunk is elongated and expanded, the apex is round and directed upward (the shape of a wooden shoe), the diameter of the heart is increased, the retrosternal space is not defined. Occurs with congenital anomalies of the septum, right valves, and cor pulmonale.
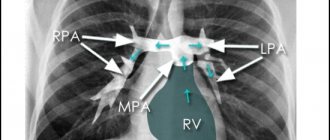
X-ray of the heart with enlargement of the left atrium. Mitral configuration of the heart. Direct projection. The arches of the left atrium (arrow) and pulmonary artery (short arrow) are enlarged. On the right, against the background of the shadow of the right atrium, the shadow of the edge of the left atrium is visible.
Folk remedies
There is a traditional treatment for an enlarged heart. This therapy helps strengthen the heart muscle, improves its nutrition and cleanses blood vessels. For treatment, healing heart herbs and herbs are used:
- Cranberry. When eaten fresh, this berry is very good for the heart; it saturates the body with essential minerals and vitamins. They eat cranberries grated with sugar. Use 1 tbsp. l. grated berries 3 times a day after meals.
- Blueberry. Young shoots of this plant are used in therapy. They are crushed and simmered over low heat for 10 minutes, then cooled and filtered. For 200 ml of boiling water take 1 tbsp. l. shoots. Use 1 tbsp. l. decoction three times a day.
- Adonis. Steam 1 tsp in 200 ml of boiling water. of this herb, infuse in a thermos for an hour, then filter. Take 1 tbsp. l. drugs three times a day.
- Cornflower. The flowers of this plant are used in therapy. Steam 1 tbsp in 1 glass of boiling water. l. flowers, leave for 1 hour, then filter. Drink 1/3 glass three times a day, a quarter of an hour before meals.
- St. John's wort. For 1 liter of water take 50 g of dried herbs of this plant. Boil over low heat for 10 minutes, then leave for 1 hour and filter. 100 g of natural honey is dissolved in the infusion. Store the drug in a glass container in the refrigerator. Drink 1/3 glass three times a day 30 minutes before meals.
- Lily of the valley. A tincture of the flowers of this plant is prepared. To do this, fresh flowers are poured into a glass container, without compacting, and filled with vodka. Leave in the dark for two weeks, then filter. Take 15 drops of tincture three times a day.
- Rosemary tincture with wine. In moderation, red wine has a beneficial effect on the heart muscle.
- Herbal decoction No. 1. Mix 1 part kidney tea, 2 parts each of dried rosemary and wild rosemary, and 3 parts motherwort. Steam 1 tbsp in 300 ml of boiling water. l. such a collection, infuse in a thermos for 4 hours, then filter. Drink ½ glass of infusion 3 times a day a quarter of an hour before meals.
- Herbal collection No. 2. Mix 20 g of horsetail herb, 30 g of knotweed herb and 50 g of hawthorn flower. Steam 1 tbsp in 300 ml of boiling water. l. such a collection, infuse in a thermos for 1 hour, after which it is filtered. Take 50 ml 6 times a day.
Make a tincture of the leaves in wine. 100 g of dried leaves are poured into 2 liters of red wine, infused in a cool, dark place in a glass container for 30 days, shaken periodically, then filtered. Take 50 ml of the drug twice a day. Treatment lasts a month and a half, then take a break.
Possible complications after
X-ray radiation is ionizing; in large doses it damages DNA, disrupts metabolism, the body's immune defense, and hormone production, destroys tissue and disrupts the functioning of internal organs. Its danger increases as the radiation dose increases. This is not directly related to diagnostic examinations, including cardiac radiography, unless the recommended safe dose is exceeded.
In a year you can receive 1 mSv (one millisievert) without consequences for the body. For one radiography procedure, the radiation exposure is most often 0.3 mSv. Therefore, the maximum number of times an X-ray can be taken per year is 3. In order to leave the possibility of examination for emergency indications, doctors routinely do not prescribe X-ray diagnostics more than 2 times.
We recommend reading the article about dangerous combined heart defects. From it you will learn about the types of combined heart disease, combined heart disease, as well as the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of combined heart disease.
And here is more information about tricuspid valve defects.
X-rays of the heart are performed to determine its size, position, and configuration. This diagnosis is indicated for heart defects, suspected mass processes in the chest, pericarditis, and hypertension. Contraindications include pregnancy, childhood, and the presence of severe pathology. To increase the information content, a study in three projections and additional contrast of the esophagus are used.
Conservative treatment methods
It is important to understand that cardiomegaly is not an independent disease. In this regard, it is initially necessary to get rid of the cause of its development. The goal of treatment is to stop the progression of the disease. At present, it is only possible to prevent further deformation of the heart.
The classic regimen of drug treatment for pathology involves taking or administering the following drugs:
- Antihypertensive drugs.
- Anticoagulants. Active components prevent the formation of blood clots.
- Beta blockers. Drugs belonging to this group normalize the functioning of the heart muscle.
- Diuretics. Prescribed if excess sodium is detected in the patient’s body.
Most patients experience surges in blood pressure. In such cases, additional drugs are prescribed that normalize the indicator. If there are other concomitant pathologies, an appropriate treatment regimen is drawn up.
Antibacterial therapy is indicated only if an inflammatory process occurs in the patient’s body.
Drug treatment will not lead to a positive result if a person does not follow the principles of a healthy lifestyle. Doctors recommend that all patients stop smoking and drinking alcohol. In addition, it is necessary to regularly expose the body to moderate physical activity.