The X-ray method has been used to diagnose gastric pathology since the beginning of the 20th century. It belongs to the oldest achievements of medicine. But, despite the fact that, thanks to the development of medicine, specialists have wide diagnostic capabilities, they continue to use X-ray examination to identify stomach tumors.
True, modern radiography is no longer what it used to be. Today these are large series of high-quality x-ray photographs, made with very short exposures and characterized by fairly good resolution. But is this test recommended for all patients with suspected stomach cancer? And is it possible to trust its results ? We will try to answer these questions in our article, and also consider:
- Why does stomach cancer occur?
- how does he manifest himself ?
- What types of tumors exist and what do they look like on an x-ray ?
- What stages does the disease have?
- What capabilities does X-ray examination have?
- Do you need any preparation for it?
- What can a stomach x-ray show?
- what to do if cancer is detected during the examination?
- What diagnostic methods exist that can confirm or refute the diagnosis?
Causes
Gastric cancer is one of the most common cancers in the world, characterized by a long asymptomatic course and high mortality. The exact causes of the tumor are not known, but scientists have identified the prerequisites for its development:
- hereditary predisposition;
- unhealthy diet (violation of its regime; eating large amounts of animal fat, carcinogenic foods; low content of fresh vegetables and fruits in the diet);
- occupational hazards;
- bad habits (smoking doubles the risk of developing gastric dysplasia);
- Helicobacter pylory infection;
- the presence of background precancerous processes (chronic gastritis, especially with atrophy of the mucous membrane, polyps, Ménétrier’s disease, pernicious anemia);
- operations on the stomach.
Help Stomach cancer does not occur against a background of complete health. Its development is preceded by many years of exposure to unfavorable external and internal factors.
Diagnosis and treatment of stomach cancer
Return to section:
Oncological diagnostics
Over the past 5 years, 40 thousand people are diagnosed with stomach cancer in Russia every year. In terms of general statistics on cancer incidence, malignant neoplasms of the stomach occupy fourth position after breast cancer, respiratory cancer and skin cancer.
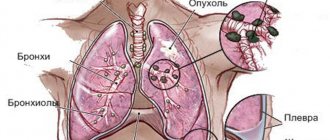
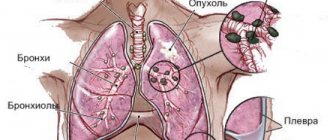
Where does the tumor occur in the stomach?
A tumor in the stomach can occur in various parts - in the junction of the esophagus and stomach, in the fundus of the stomach, in its main part (body), in its outlet section. Depending on the location of the tumor, different symptoms occur.
How dangerous is stomach cancer?
A tumor in the stomach can disrupt digestion and prevent food from passing into the underlying parts of the digestive tract. A cancerous tumor grows into the wall of the stomach and can spread to other organs - grow into the colon, pancreas. If the tumor is located near the esophagus, it can spread to it and interfere with the passage of food into the stomach. As a result of all this, weight loss occurs, even to the point of exhaustion. The tumor can spread through the lymphatic and blood vessels to other organs (liver, lungs, brain, bones, etc.), where it produces foci of growth. As a result of disruption of the body's functioning, death occurs.
CAUSES OF STOMACH CANCER
Leading oncologists around the world are looking for the answer to this question, but reliable reasons for the appearance of malignant tumors of the stomach have not yet been found. However, to date, the conditions affecting the appearance of cancer cells in the gastric mucosa have been well studied.
The first three factors in the development of gastric cancer can be combined into the concept of “ lifestyle ”:
- unhealthy diet
- smoking tobacco,
- alcohol abuse.
According to some data, smoking tobacco increases the risk of developing stomach cancer by 2 times. There is no such information about the effect of alcohol, but there is an opinion that strong alcohol damages the gastric mucosa, which in turn provokes the appearance of cancer cells in place of the damaged ones. The risk of stomach cancer is much higher if your diet is dominated by salted, smoked, pickled foods and foods high in nitrates and nitrites. For an adult, the maximum allowable amount of nitrites per day is 2 mg per 1 kilogram of weight, and nitrates - 5 mg per 1 kilogram.
The next group of factors is precancerous diseases .
Doctors refer to such diseases as:
- pernicious anemia , which develops due to vitamin B12 deficiency;
- stomach ulcer;
- hypertrophic gastropathy, otherwise Mentrier's disease ;
- stomach polyps.
They received the name “precancerous” because stomach cancer often develops against the background of precisely these pathologies. Also, the likelihood of a tumor occurring is higher in patients who have undergone gastric resection .
The causes of a tumor largely depend on the person. In order to minimize the risk of getting stomach cancer, you need to monitor your habits, especially in nutrition. If your medical history contains “precancerous” diseases, undergo regular preventive examinations and medical examinations. These precautions will not take much time: in St. Petersburg City Hospital No. 40, consultations are carried out by specialists with many years of experience, and all diagnostic procedures are performed within the walls of one institution.
SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS OF STOMACH CANCER
Stomach cancer does not have noticeable first symptoms in the early stages. Signs of stomach cancer are mistaken for manifestations of other diseases, such as gastritis. But exacerbation of gastritis brings few people to the doctor, more often to the pharmacy. Unpleasant sensations are removed with available medications and hope that the illness will recede. But if you notice that you begin to get tired quickly, have lost a lot of weight and constantly experience discomfort in your stomach, consult an oncologist; you need to check your stomach for the presence of tumors.
The question often arises whether the manifestations of stomach cancer differ in men and women. The first symptoms of stomach cancer in women are no different from the first signs of stomach cancer in men. But women are less susceptible to stomach cancer, perhaps this is due to a more attentive attitude to their health and the desire for a healthy lifestyle.
The manifestations of advanced stomach cancer depend greatly on the location of the tumor. If in the upper section at the transition of the esophagus to the stomach, dysphagia and difficulty swallowing appear. If in the lower part, when passing into the duodenum, vomiting of food just eaten.
Severe heartburn and persistent abdominal pain also become constant companions .
If you or your loved one starts vomiting “coffee grounds” or the stool turns black and tarry, consult a doctor immediately - these are signs of possible gastric bleeding caused by stomach cancer!
Even if it seems to you that “it doesn’t hurt much,” or “you can be patient, it will go away,” don’t take risks, and if the following symptoms appear, consult a doctor immediately:
- Increased fatigue;
- Sudden unintentional weight loss;
- Constant discomfort in the stomach and abdominal area;
- Difficulty swallowing food;
- Constant abdominal pain;
- Frequent vomiting;
- Constant severe heartburn.
HOW IS STOMACH CANCER DIAGNOSED?
Based on the results of a consultation with an oncologist at St. Petersburg City Hospital No. 40, a patient with suspected stomach cancer may be prescribed a set of diagnostic tests, both laboratory and instrumental.
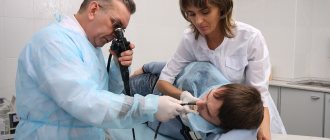
Fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy (FEGDS) is an endoscopic procedure that is usually primarily prescribed for diagnosing gastric cancer. To examine the inside of the organ, the doctor uses a flexible tube with a high-definition video camera at the end, the video is displayed on the screen in real time. If during the examination the endoscopist sees pathological changes in the walls of the stomach, he will take samples of suspicious tissue for further laboratory analysis.
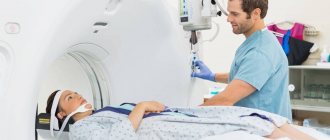
In addition to endoscopic examination, radiography with a contrast agent, laparoscopic diagnosis and various types of tomography are used to confirm the diagnosis. Computed tomography and MRI for stomach cancer allow you to get a complete picture of the development of the disease and the ways of its metastasis; when performing positron emission computed tomography (PET CT), the doctor receives information about cancer cells at the molecular level. In St. Petersburg State Budgetary Institution “City Hospital No. 40” they perform all types of tomography: two CT and MRI machines operate around the clock, and PET CT is performed by appointment.
Based on the research results, a commission of leading oncologists at the hospital determines further treatment tactics for the patient.
TREATMENT OF STOMACH CANCER
Stomach cancer, like any cancer, requires an integrated approach to treatment. But the main method of treating stomach cancer is surgery.
Depending on the size and extent of the tumor, doctors perform operations of varying volumes: complete or partial removal of the organ and surrounding tissue.
In St. Petersburg City Hospital No. 40, in addition to traditional methods of surgical treatment, high-tech methods of intervention are widely used. Most high-tech operations are performed with the help of the Da Vinci robotic surgeon. Robotic surgeries for stomach cancer that are performed in our hospital:
- Gastrectomy;
- Distal subtotal gastrectomy;
- Partial gastrectomy;
- Proximal gastrectomy.
All these operations, except for partial resection, include mandatory lymph node dissection. Lymph dissection for stomach cancer is the removal of fatty tissue surrounding the stomach, which contains lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels. This procedure is performed regardless of the presence or absence of metastases in the lymphatic system.
Residents of St. Petersburg and the Leningrad region can receive high-tech medical care for FREE! All information on quotas for surgical treatment of oncology at St. Petersburg City Hospital No. 40 will be provided to you by calling +7-911-823-28-84.
In addition to robotic operations, the hospital performs intraluminal endoscopic, X-ray endoluminal and laparoscopic operations as part of surgical treatment.
Radiation and drug antitumor therapy for stomach cancer is used both before and after surgical treatment. And in cases where surgical intervention is not possible, these treatment methods act as palliative care.
STOMACH CANCER: FIVE-YEAR SURVIVAL RATE
The success of treatment in oncology is assessed in terms of five-year survival. This figure shows what percentage of patients remain alive five years after diagnosis.
As with any statistical data, the five-year survival rate has errors associated with the individual characteristics of each patient. But it still reveals general trends in treatment results.
For example, the five-year survival rate when treating stage 1 gastric cancer is 80% of patients, and when treating the disease at stages 3-4 - only 10%.
Only one in a hundred patients is diagnosed with stage 1 gastric cancer, and 6 out of 100 are diagnosed with stage 2.
This is due to the lack of pronounced symptoms, hence late diagnosis.
The solution to this problem can be regular medical examinations and basic attention to one’s own health.
← Back
Signs
The initial phase of the tumor process is often hidden and asymptomatic . Moreover, patients often do not pay attention to their condition (attributing poor health to fatigue, gastritis, etc.) and do not seek medical help for a long time. The first signs of the disease include:
- general weakness, fatigue, decreased performance (for several months or even years);
- vague dyspeptic disorders (nausea, belching, lack of satisfaction after eating);
- poor appetite;
- selectivity in food and aversion to certain types of food (for example, meat);
- discomfort in the stomach (feeling of heaviness, fullness after eating), less often - pain;
- weight loss for no apparent reason;
- persistent decrease in hemoglobin level in the blood;
- pale skin;
- apathy, indifference to what is happening around.
In some cases, these symptoms are absent, and the disease manifests itself with bloody vomiting or sudden dysfunction of the digestive tract.
In the later stages, patient complaints become more pronounced:
- dull pain in the stomach area after eating or at night, not related to the nature of the food;
- nausea, vomiting of gastric contents, such as “coffee grounds” (due to the presence of blood);
- belching, heartburn;
- increasing weakness;
- lack of appetite;
- weight loss.
Classification
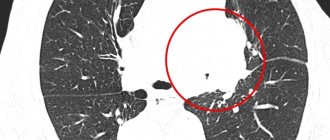
Before proceeding with the classification of stomach cancer, it should be noted that it can grow into the lumen of the organ (exophytic growth) or spread deep into its wall (endophytic growth). These features determine the clinical picture of the disease and the possibility of its detection by various diagnostic methods. For example, with endophytic growth, a tumor may not cause any symptoms for a long time and is more difficult to detect during endoscopy. In such cases, X-ray diagnostics is especially important.
Currently, there are several classifications of stomach cancer. Let us dwell on those of them that are important in the process of primary diagnosis.
Table 1. Main types of cancer according to the classification of A. S. Holdin.
| Tumor types | a brief description of | X-ray changes |
| Fungiform and polypoid | Tumor nodes on a narrow stalk or wide base. | Round filling defects with clear, even contours. They are difficult to distinguish from each other and from a simple polyp. |
| Cabbage-shaped | Lumpy neoplasms resembling cauliflower in appearance. | They are manifested by a filling defect with bumpy contours, which is clearly demarcated from the intact mucous membrane and protrudes deeply into the lumen of the organ. |
| Cup or saucer shaped | Tumors with raised edges and a disintegrating central part. They have a tumor-like shaft that separates the neoplasm from the healthy mucous membrane. | Filling defects are oval or round in shape with smooth and clear contours; in later stages, the tumor may ulcerate in the center, which creates a depot of barium suspension with uneven outlines. |
| Ulcerative-infiltrative | Partial infiltrative germination of all layers of the stomach with ulceration. | Uneven contours of the organ; weakening of peristalsis; malignant relief of the mucous membrane - shapeless accumulations of contrast, alternating with structureless zones |
| Diffuse | They affect the wall of the stomach over a large area and disrupt its motor activity. | Thickening and rigidity of the stomach wall; its deformation and change in size; narrowing of the lumen of the organ. |
Of these, the first 3 options relate to limited growing forms of cancer (exophytic), and the last 2 – to infiltratively growing tumors (endophytic). There are also mixed forms that combine features characteristic of its various types.
international classification TNM
To assess the extent of the process, the international TNM classification is used, where T- characterizes the condition of the tumor itself:
- The neoplasm affects the wall of the stomach to the submucosal layer (T₁).
- The tumor grows to the subserosal layer (T₂).
- This formation grows into the serosa, but does not spread to the surrounding structures (T₃).
- The pathological process involves nearby organs (spleen, liver, pancreas, intestines, adrenal gland) or the walls of the abdominal cavity (T₄).
- In the event that the primary focus is not determined, the stage of the process corresponds to T₀.
- There is also a concept called TIS, which means “carcinoma in situ” or “cancer in situ” (occurs inside the epithelium and does not spread, can only be detected by biopsy).
Please note: If cancer is detected at stage Tіs, then with adequate treatment, patient survival approaches 100%.
N – damage to regional (where lymph flows from the stomach) lymph nodes:
- are not involved in the pathological process (N₀);
- affected in quantities of 1-2 (N₁);
- metastases in 3-6 lymph nodes (N₂);
- pathological change in 7 or more lymph nodes (N₃).
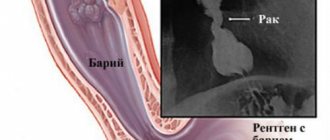
What will a barium stomach x-ray show? will cancer show?
Barium X-ray of the stomach
In 1895, the German physicist W. K. Roentgen discovered X-rays, which were later called X-rays. A year later, the scientist discovered that the rays are capable of leaving an image on photographic film if the human body is transilluminated. This property of X-ray radiation is used in medicine today, being the most common diagnostic method.
X-ray examination allows you to examine all organs, but some require additional contrast. These are the hollow organs of the abdominal cavity, in particular the organs of the digestive tract. Without additional staining with barium sulfate, it is impossible to clearly see pathological changes in the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
Preparing for the study
X-ray
Before an X-ray of the stomach with barium, the doctor should warn you that the study is carried out strictly on an empty stomach. To increase effectiveness, 3 days before the intended procedure, you need to exclude gas-forming foods from your diet - rich pastries, carbonated drinks, fresh milk, legumes, etc.
They should also explain to you that barium suspension is absolutely safe, it is not absorbed into the body, is not destroyed by digestive enzymes, but, as it were, “coats” the walls of the esophagus and stomach for a while for better diagnosis.
During the examination, the radiologist will ask you to change your body position several times. Gastrography with barium is carried out in several positions - standing, lying, etc.
What does the doctor see in the pictures?
In an X-ray of the stomach with contrast, each position of the patient's body shows different parts of the digestive tract.
State of the gastrointestinal tract
Direct projection of the body:
- At the first sip of barium sulfate suspension, the doctor examines the folds of the duodenum and evaluates their structure. This is where the ulcer is most often detected.
- After several sips, the doctor clearly sees the relief of the mucous membrane of the esophagus and the antrum of the stomach.
- Direct projection allows you to evaluate on an X-ray image the condition of the grooves and folds of the organ, as well as the functionality of the gastrointestinal junction.
Lateral and oblique projection of the body:
- Allows you to determine the displacement of organs. For example, cancer of the stomach or other parts of the abdominal cavity can change the location of organs.
- In the lateral projection, the functions of the pylorus are assessed, and the presence of reflux is determined.
Lying position:
- The condition of the lesser curvature is assessed.
Lying position with the leg end elevated (Trendelenburg position):
- Allows you to identify the esophageal opening.
When is an examination ordered?
X-ray process
An X-ray of the stomach with contrast is indicated for the patient if he complains of epigastric pain, heartburn, belching, and various digestive disorders. An X-ray with barium is also necessary if the patient has lost a lot of weight, has bloody stools, or is anemic.
X-ray with a barium suspension helps diagnose cancer and organ polyps. Any ulcer localized in the digestive tract is clearly visible. Hernias, functional disorders and tissue defects are also visible.
Diagnosis of malignant neoplasms
Diagnostics
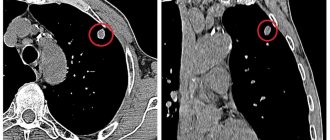
X-ray examination with contrast can detect cancer. To do this, use the technique of tight filling of the gastric cavity. The patient drinks the suspension, after which the stomach must be lightly massaged so that the entire organ cavity is well covered with barium.
Often an ulcer degenerates into a malignant tumor. This study shows rebirth.
The first sign by which a doctor may suspect cancer is the formation of an additional shadow in the gastric cavity. Cancer changes the movable tissue of the gastric wall to a denser one, which does not participate in the peristalsis of the organ.
Gastric cancer with the technique of tight barium filling bends and thickens the contour of the gastric wall, narrows the lumen of the organ.
By analyzing the set of signs, the doctor may suspect cancer, but to clarify, an additional method is used - FGDS.
Who should not be examined?
X-ray - the study is not indicated for the following conditions:
- Pregnancy.
- The patient's condition is extremely serious.
- Suspicion of internal bleeding.
- Individual intolerance to drugs containing barium.
Digestive problems occur to everyone from time to time. If they are systematically repeated, do not delay the examination. It is painless and very effective.
Source: //MojZheludok.com/zheludok/chto-pokazyvaet-rentgen-zheludka-s-bariem.html
Possibility of the technique
X-rays are used to detect stomach cancer along with other diagnostic methods. It allows you to detect a tumor in the early stages, thanks to its good resolution and spatial perception. To increase its information content use:
- double contrast;
- studying the state of the organ during tight filling;
- special positions and projections.
During the procedure, the doctor is able to assess:
- location of the stomach;
- its shape and contours;
- organ size;
- displacement and motor activity;
- the condition of its inner surface;
- wall thickness.
However, X-rays alone cannot accurately diagnose cancer . His conclusion only suggests the presence of the disease in a person. In addition, there is always the possibility of missing this process, so a negative result of one test cannot exclude the diagnosis .
Indications and contraindications for fluoroscopy
Using fluoroscopy, the condition of organs and tissues is examined if diseases such as hernia, gastric ulcer, other pathologies of the stomach or esophagus, intestinal obstruction, and the occurrence of various types of neoplasms are suspected.
In this case, the patient may be bothered by abdominal pain in the navel area, impaired swallowing reflex, sudden anemia of unknown etymology, the appearance of bloody spots, and significant weight loss.
Barium, as a contrast agent, is intended to enhance the visualization of organs examined by x-rays of the stomach. This procedure has a number of limitations. The examination cannot be carried out if:
- allergies to contrast agent components;
- internal gastric or esophageal bleeding;
- pregnancy;
- the patient's serious condition.
Sometimes fluoroscopy of the stomach is prescribed during pregnancy if there is no threat to the life of the mother and child.
If it is impossible to perform fluoroscopy, which is a more gentle diagnostic method, an alternative study is prescribed - fibrogastroscopy. A tube with an endoscope equipped with a camera is inserted into the esophagus. The tube is gradually advanced towards the stomach. Sometimes barium endoscopy is performed for greater visualization.
Preparation
To obtain reliable information during the study, proper preparation is needed, aimed at reducing the accumulation of gases and preventing congestion in the stomach cavity. Its most important part is limiting food and water intake, since the procedure is always carried out on an empty stomach. More information about this and other features of preparing for an x-ray examination can be found in the article of the same name.
Procedure for preparing for an X-ray examination of the stomach
Before fluoroscopy, you must follow a diet.
For three days you should not eat:
- legumes;
- black bread;
- fruits;
- vegetables;
- dairy products;
- flour products;
- fried and smoked foods;
- sparkling water.
You can include in your diet:
- boiled lean meat;
- fish;
- white stale bread;
- porridge cooked in water;
- boiled eggs.
X-ray of the stomach is performed on an empty stomach, that is, 6-8 hours before the examination the patient should not be allowed to drink or eat.
In case of constipation, an enema is performed. If the patient has pyloric obstruction, barium probing is performed before fluoroscopy. Before the procedure itself, you need to get rid of jewelry, removable dentures, and other things.
Decoding the results
A specialist can suspect the presence of a cancerous tumor in a person based on a combination of radiological signs:
- change in the relief of the mucous membrane in the tumor area (lack of folds, thickening, presence of various outgrowths, erosions or ulcers);
- gastric filling defect;
- the rigidity of its walls;
- the presence of a zone devoid of peristalsis;
- organ deformation;
- the undermining of its contours;
- extension of the lesser curvature;
- narrowing of the lumen and obstruction of patency.
This article will help you analyze the doctor’s conclusion in more detail.
Additional Methods
The final diagnosis of stomach cancer can be established during a comprehensive examination of the patient, which, in addition to radiography, includes other diagnostic procedures:
- endoscopic examination;
- Ultrasound of the stomach;
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- laparoscopy.
These diagnostic methods provide more accurate results in determining tumor lesions of the stomach and surrounding structures. However, they are not always available and are sometimes contraindicated. In such cases, x-ray examination is indispensable.
The scope of additional examination is determined by the doctor in each specific case. The most reliable way to confirm or refute the diagnosis is by EGD with taking a biopsy from suspicious areas of the inner surface of the stomach.
What is fluoroscopy?
X-ray examination of the stomach is performed in the form of radiography or fluoroscopy. Their main difference is in the features of the resulting image. X-ray of the stomach is a diagnostic method in which the affected organ is recorded in the image. It is comprehensively studied by specialists from various fields of medicine. If there is a suspicion of esophageal pathology, an x-ray of the esophagus may be prescribed. The main disadvantage of such diagnostics is that the image is static and does not reflect dynamics. It shows the localization of the inflammatory process, but it is impossible to assess how impaired the function of the organ under study is.
If fluoroscopy is performed, the image is shown on the screen. In this case, not only the place of formation of pathological cells is demonstrated, but it becomes possible to assess the state of the organ in the process of its functioning at the moment. This procedure is usually carried out first. Next, a targeted photo is taken of the place where the lesion was found.
During fluoroscopic examination, the x-ray anatomy of the stomach is of great importance. It may have a different shape in the photograph, shown from three different positions. It all depends on the person’s body type and the tone of the organ’s muscles. This must be taken into account when deciphering the result obtained.
What to do if cancer is discovered?
The reaction of different people who are diagnosed with cancer may be different. Some of them become depressed, others begin to panic, and others refuse to believe doctors. But they all must understand that not a minute of precious time should be lost . After all, the earlier treatment is started, the higher its effectiveness . What should a person do if, based on the conclusion of an X-ray examination, he is supposed to have such a diagnosis?
- Firstly, do not despair , because during the diagnostic process, assumptions may not be confirmed . And if there really is cancer, then with proper treatment you can achieve success.
- Secondly, he needs to undergo a full examination using various diagnostic methods.
- Thirdly, follow all doctor's recommendations .
After a final diagnosis is made, patients with stomach cancer are prescribed treatment with the possible use of:
- surgical methods (radical intervention - removal of part of the stomach or the entire organ with regional lymph nodes; palliative operations aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition, for example, carried out to restore gastric patency);
- chemotherapy (prescribing a combination of drugs from the group of cytostatics);
- irradiation (as an adjunct to other treatment methods);
- targeted therapy (the use of drugs that have molecular properties and can selectively affect cancer cells).
The choice of treatment method is made by the doctor, taking into account the type of tumor , the stage of the pathological process and the general condition of the patient. In this case, surgical intervention is considered the most effective, which can be supplemented with chemotherapy or intraoperative radiation.
Help Inoperable patients in the later stages of the disease are prescribed chemotherapy or radiation therapy to reduce the size of the tumor, slow its growth and alleviate symptoms.
X-ray anatomy of bones.
The presence of calcium salts in bones makes them less “transparent” to X-rays than the surrounding soft tissue; Moreover, due to differences in the histological structure of compact and cancellous bone, the nature of their X-ray imaging is also different. The compact substance of the bone forms an intense “shadow” on the radiograph in the form of light stripes of greater or lesser width, while the spongy substance forms a cellular, network-like pattern.
At the junction of the bones with each other, a dark stripe (“stripe of enlightenment”) is noted - an x-ray joint space, delimited by lighter lines of the subchondral sections of the articulating bones. The width of the x-ray joint space depends on the thickness of the articular cartilage, which is “transparent” to x-rays.
Radiography allows one to identify the “bone age” of a person - to visualize ossification points, replacement of epiphyseal cartilage with bone tissue, fusion of bone sections (formation of synostosis). These age-related features of ossification are the subject of study of clinical x-ray anatomy.