Patients are often frightened by the mere mention of words such as “gastroscopy” or “colonoscopy.” The reasons are clear - these procedures are very unpleasant and even painful for the body. At the same time, painless procedures, such as ultrasound, are not always quite effective. How to check the stomach and intestines without swallowing a probe, is there an alternative to gastroscopy and colonoscopy? Yes, now it exists; it is quite possible to examine the stomach and intestines without gastroscopy. Video capsule endoscopy is the name of this diagnostic method. During this procedure, the gastrointestinal tract is examined without an endoscope. Instead, you just need to swallow a special capsule, with the help of which the research will be carried out.
In addition to non-invasiveness, capsule endoscopy of the stomach and intestines has another important advantage: it allows you to examine not only the upper and distal parts of the intestine, but also the middle sections - the jejunum and ileum, which is much more difficult to achieve with other procedures. First of all, it is precisely when it is necessary to examine the middle sections of the intestine that capsule endoscopy is used.
Both doctors and reviews of patients who have undergone the procedure speak about the effectiveness and painlessness of the technique. We will talk in detail about capsule endoscopy in this article, from which you will learn how to prepare for it and how it goes, about its advantages and disadvantages, contraindications and possible complications.
What it is?
The procedure is a method for studying the small and large intestines, differs from others in its lack of invasiveness , and is extremely informative. This requires a special capsule with a built-in camera.
The patient swallows it, and the device moves sequentially through the gastrointestinal tract and records images after a certain period of time ( from 1 to 35 images per second ). All this is recorded on the device (receiver) thanks to the presence of sensors that are located on the patient’s body. The doctor then works with the images, analyzing the results of the study. The capsule is often used instead of FGDS with an endoscope, which helps to avoid complications and fear of the procedure.
Capsule price
The cost of capsule endoscopy is often a major barrier to testing, forcing patients to turn to more painful but cost-effective options. Prices can vary greatly depending on the capsule manufacturer, starting from 20 thousand rubles and reaching several hundred thousand.
In general, capsule endoscopy can be characterized as a much easier way to examine the gastrointestinal tract than procedures such as colonoscopy or retoromanoscopy, and is usually quite useful and informative. If necessary, capsule endoscopy can be supplemented with other procedures - CT or MRI.
For diagnosing diseases of the large intestine, colonoscopy is more preferable in terms of information content, and for the duodenum, FGDS. This is due to the fact that by the time the capsule enters the colon, the battery is usually low, and it is usually not possible to conduct a detailed study of it. In addition, capsule endoscopy is not recommended if a suspected tumor is being tested due to the impossibility of performing a biopsy with its help.
Sometimes patients ask how to check the colon without using a tube, whether there is a capsule colonoscopy, trying to avoid this painful procedure. Alas, no, if you are prescribed a colonoscopy to examine the large intestine, then you will have to do just that, without any capsules, but in many cases, capsule endoscopy can be used to examine the intestines.
How is FGDS performed using a tablet with a camera?
The patient comes to the medical facility on the appointed date. installs special sensors in the abdominal area necessary for the procedure. They connect the abdominal area to the recording device. The receiver remains with the patient throughout the entire procedure: he wears it on his belt or slings it over his shoulder.
After all the preparatory stages, the person swallows the capsule: this is done in the presence of a doctor who specializes in endoscopic examinations. The procedure is not over yet: the patient is sent to the day hospital, where he is observed for 8 to 12 hours (this is the approximate time during which the endoscopic capsule passes through the entire gastrointestinal tract). 3.5 hours after swallowing the capsule, the patient is allowed to eat.
Help During the time the patient is in the hospital, it is recommended to walk and
change body position : this prevents the capsule from stagnating in the intestinal loops.
After 9-12 hours, the receiver gives a signal that the recording of information from the capsule has stopped. The doctor removes touch sensors from the patient’s body along with the receiver, after which he downloads all the information onto an electronic device and subsequently analyzes it. If there are no complaints, the patient is sent home, warned that the capsule endoscope does not need to be removed: it will come out on its own in the stool.
Decoding the study takes a lot of time , because the procedure lasts about 10 hours. With the help of special programs, this time can be reduced; pictures are viewed in accelerated mode, and if necessary, the playback of information can be slowed down. You can simultaneously place several images on the computer screen and compare them with each other; the zoom function allows you to evaluate the intestinal structures in more detail.
What does the capsule consist of and how does it work?
Viewing and analyzing information takes the doctor approximately 1.5-2.5 hours : this depends on the experience of the specialist and the equipment used. The results of capsule endoscopy are delivered to the patient: most often it is a disk containing images and short videos.
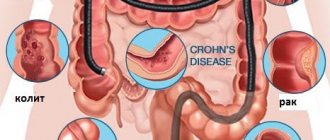
What diseases can be detected during diagnosis?
Using capsule endoscopy, you can evaluate the condition of all parts of the gastrointestinal tract, but the greatest diagnostic value is found when examining the small intestine . Diseases of other parts of the digestive tract (stomach, esophagus, large intestine) can also be detected in this way, but it is still inferior in information content to the conventional endoscopic technique and colonoscopy.
The small intestine is quite difficult to access for other research methods, but is perfectly visualized in pictures taken by the capsule camera. Each organ has its own capsule, and devices have also been developed that can record images from all parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Capsules vary in size: the smaller it is, the greater the safety of the procedure. The speed of recording images and the viewing angle of the camera are of - the diagnostic value of capsule endoscopy depends on these indicators.
Many companies produce capsules. Some of them are Given Imaging (Israel), IntroMedic Co. (Seoul, South Korea).
Given Imaging capsule
Using the capsule, you can detect polyps in the intestines, neoplasms, hidden bleeding, Crohn's disease , establish celiac disease and other changes in the gastrointestinal tract that are difficult to see with other research methods.
Capsule
Previously, only with the help of procedures such as colonoscopy and endoscopy was it possible to conduct a complete diagnosis of the gastrointestinal tract. During their course, the doctor observed the large and part of the small intestine, stomach and esophagus. Of course, the special probe introduced into the body, with the help of which the observation was carried out, caused certain painful sensations.
To eliminate this problem and be able to check the stomach without swallowing a probe, a high-tech endoscopic capsule was developed, with which everything has become much simpler: it is enough to just swallow it, like a regular medicine, especially since it is comparable in size to ordinary capsules. Moreover, it is an electronic device that contains a mini-camera, a light source, an electromagnet for data transmission and microcircuits.
Once in the gastrointestinal tract, the capsule sequentially passes through all its sections and transmits a signal directly from there to the doctor’s monitor. It is completely sealed, which makes it resistant to the aggressive environment of the gastrointestinal tract.
There are different types of capsules: the Israeli Pillcam is aimed at diagnosing the small intestine, the Swiss Bravo is intended primarily for the esophagus, the American SmartPill examines the entire gastrointestinal tract. Finally, the domestic AES-GTI (the famous “Kremlin pill”) can act on the intestines using electrical impulses, thereby preventing constipation.
Possible complications
There are practically no negative consequences after capsule endoscopy. The method differs from other endoscopic examinations in its simplicity and ease of portability. But sometimes it happens that the capsule does not leave the body naturally for a long time , that is, it lingers in the intestines. This is practically the only complication that can occur after swallowing the capsule. The frequency of its occurrence is no more than 5%, it depends on the most likely pathology in the patient.
Can the capsule get stuck inside?
If the capsule does not leave the intestine within two days (48 hours) , then it is said to be stuck. This occurs infrequently and retention of the endoscopic capsule requires close attention from medical personnel. The frequency of capsule retention in the gastrointestinal tract depends on the existing pathology: in healthy people it always comes out, in 5% of cases it gets stuck in patients with suspected Crohn's disease . With intestinal obstruction, the patient's capsule is retained in 21% of cases .
Important If a capsule gets stuck, you need to take measures to remove it from the body.
It can block the intestinal lumen, thereby provoking the development of acute obstruction.
This situation cannot be left to chance; there are several methods for getting it out:
- The capsule can come out on its own , it just takes a little longer. It is advisable to be under the supervision of a doctor to prevent the development of complications.
- Drug therapy - the patient is prescribed medications that relieve the inflammatory process in the intestines and improve motility. As a result, the intestinal lumen expands and the capsule is removed.
Endoscopic method - used when previous methods are ineffective ; it also depends on the cause of capsule retention. It is removed using a colonoscope or enteroscope. The advantage of this method is that it is possible to simultaneously treat the disease that caused the capsule to get stuck.
- Surgical intervention - preference is given to the laparoscopic technique: the patient recovers faster, the risk of complications is lower. At the same time, the cause of capsule retention can be eliminated.
Indications
Most often, this method is used when pathology of the small intestine . Experts recommend conducting the study only if other methods have not given the desired result: this is due to the high cost of capsule endoscopy.
Indications for the procedure are as follows:
- intestinal bleeding of unknown etiology ;
- abdominal pain, the cause of which cannot be determined by other methods;
- suspicion of an oncological process in the small intestine ;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis ( Crohn's disease );
- blood in the stool of unknown etiology;
- diagnosis of polyposis nodes in the intestines - especially with a family history;
- suspicion of celiac disease.
Indications and contraindications
The method will not always be safe for the patient. If gastrointestinal bleeding is detected, swallowing the capsule may cause additional problems, so this is the main contraindication.
In addition, capsules are not used during pregnancy, in children under 16 years of age and in elderly people after 70 years of age.
Also, electromagnetic radiation, through which the signal is sent and the image is transmitted, can damage the operation of the pacemaker.
Indications for capsule endoscopy are:
- Long-term stomach upset.
- Chronic constipation.
- Weight loss without objective reasons.
- Pain and discomfort in the stomach area.
- Suspicion of colitis, ulcers, polyps or other gastrointestinal diseases.
One indication is to monitor the progress of treatment. In this case, the procedure is more gentle than with traditional endoscopy, but the main obstacle may be the high cost of the examination.
Contraindications
Capsule endoscopy has certain limitations for its use. The procedure is not recommended for a person who has:
- stenosis, stricture in any part of the digestive tract;
- diverticulosis;
- acute intestinal obstruction (high probability of capsule getting stuck);
- pacemaker and other metal structures;
- disturbances in the swallowing process (the capsule simply will not pass);
- epilepsy;
- limited use during pregnancy (insufficient number of studies).
Preparation
Before performing capsule endoscopy, two days of preparation is required. The patient follows a toxin-free diet and takes intestinal cleansing agents. On the day of the study, you should not eat food; you can drink low-fat broth, tea, and water. Read more about preparing for the procedure in this article; it is no different from preparing for a regular FGDS.
Please note The effectiveness of the procedure depends entirely on
the quality of the preparation . This is especially true when considering the cost of gastric capsule endoscopy.
Preparing for capsule endoscopy
In order for the results to be as reliable as possible, all preparation requirements must be met. Their main idea is that the device must pass through the entire length of the digestive system, so the conditions must be adequate.
The study is carried out strictly on an empty stomach. It is required to refuse food no less than twenty-four hours before the diagnostic procedure and before placing the device inside the gastrointestinal tract.
It is also necessary to take laxatives Fortrans and Polyethylene glycol . The night before you need to drink another four liters of solution.
In addition, smoking and drinking alcohol are prohibited.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of this type of endoscopy are:
- There is no possibility of mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of organs. This cannot be said during conventional endoscopy: the tube (endoscope) can injure the mucous membrane, and in severe cases, perforation of the organ may occur.
- Painlessness, psychological comfort of the patient during the preparation and conduct of endoscopy.
- There is no need to use sedation or anesthesia , since the procedure does not cause any discomfort.
- There is no risk of infection through medical devices. The capsule used for research is disposable, which eliminates the transmission of infection to a healthy person.
- High diagnostic value for pathologies of the small intestine - all other diagnostic methods are seriously inferior to capsule endoscopy.
Like any diagnostic procedure, capsule endoscopy has its disadvantages:
- It is impossible to biopsy a suspicious area in the digestive tract. It is only possible to detect some kind of formation or other changes in the tissue, but to take material for histological examination, an additional invasive procedure will be required, in some cases, laparoscopic surgery. The latter allows you to simultaneously eliminate the pathology.
- The cost of the procedure is high , so the procedure is not available to everyone. The price is determined, first of all, by the cost of the video capsule - from 35,000 or more.
- There is a risk that the capsule may get stuck. Sometimes difficulties arise in removing it, which requires surgical intervention. But over time, experts revised their opinion; in some cases, a stuck capsule helps in terms of diagnosis: it is not difficult to find a pathological focus and take measures to eliminate it.
- Not all medical centers offer capsule endoscopy.
Price for gastroscopy of the stomach and small intestine
In Russia, capsule endoscopy is carried out at the expense of the patient himself, that is, it is not paid for under the compulsory medical insurance policy. The cost in Moscow and St. Petersburg varies from 35 to 100 or more thousand rubles. This variation is due to the cost of the capsules, which differ from each other in many respects.
Also, the price of the study may include the work of a specialist to conduct and decipher data, hospital stay and meals. The procedure is not cheap: the reason for this is the high cost of the video capsule.
Cost of the procedure and patient reviews
When it comes to a study such as video capsule endoscopy, its price becomes very important. It is so high that, in a certain sense, it becomes an obstacle to mass use. The cost ranges from twenty to one hundred thousand rubles or even higher, which largely depends on the equipment manufacturer.
Capsule colonoscopy in Moscow most often turns out to be so expensive that its average price reaches forty thousand rubles. Therefore, many patients resort to conventional FGDS or colonoscopy using a probe, despite all the unpleasant sensations that accompany the procedures.
People who have undergone capsule endoscopy note in their reviews that it only requires careful preparation. There are no side effects or discomfort.