Every person should know their blood pH. Acidification of the blood leads to illness and poor health. Severe alkalization - loose skin, dry and brittle hair, nails.
Every liquid has its own level of acid-base balance, including human blood. If there is a disorder in the functioning of the body or a malfunction of a specific system or organ, a PH blood test is done.
- The term blood pH is the level of hydrogen content in the body and general acidity. If the balance of alkalis is maintained, then all systems and organs function normally.
- The acid-base balance is in a normal state if the liver, lungs and kidneys function well and harmoniously. These are real “compensators” that remove harmful substances from the body.
- Therefore, every person should monitor their blood PH level to prevent the development of serious diseases.
Blood PH level of a healthy person: normal
PH level of the blood of a healthy person: normal
The level of alkaline indicator in the blood is the basis for doctors to prescribe treatment if they have large deviations from the norm. Thanks to these indicators, it is possible to monitor the condition of the body, and if malfunctions occur in the functioning of organs or systems, such an analysis should be done.
The normal PH level of the blood of a healthy person is no less than 7.35 and no higher than 7.45. All indicators that differ from the norm to a lesser or greater extent are deviations that are incompatible with life and require urgent medical intervention.
pH of different human blood systems
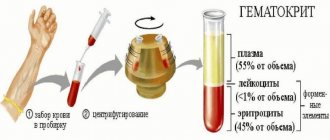
The acid-base indicator of arterial blood, saturated with oxygen, is 0.01-0.02 units higher than the same indicator of venous blood, which contains excess carbon dioxide.
The acidity of blood plasma, which has a balance of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions, corresponds to the acidity of the blood as a whole.
The pH value of other media (serum) may have a small range of values. Blood plasma removed from the hemostatic system is devoid of fibrinogen. Its acidity is of practical importance when plasma is used to determine blood group using hemagglutinating sera.
Blood pH level during acidosis
Blood PH level during acidosis
If the acidity in the body is normal, then the PH readings will be at the level of 7.4 units. If this indicator decreases significantly, a diagnosis of “acidosis” is made. The pH level of the blood during acidosis is 7.0 or less.
Mild acidosis does not manifest itself in any way. But, if the indicators decrease to critical limits, which can only be recorded in laboratory conditions, then the person experiences the following symptoms:
- lack of oxygen;
- a feeling of shock at the primary stage of many diseases - diabetes and others;
- nausea;
- vomiting or urge to vomit;
- breathing problems.
Acidification of the body occurs for the following main reasons:
- nervous tension;
- obesity;
- against the background of cardiovascular diseases;
- when eating sweet and meat foods in large quantities.
When a severe form of acidosis is detected, it is necessary to establish the causes of this disease. You should definitely consult a doctor who will correctly prescribe treatment, diet and tell you about all the consequences if you do not control your blood PH level.
Alkalosis
The causes of metabolic alkalosis, in which the body is oversaturated with alkali, are:
- Intense vomiting, in which a lot of acid and gastric juice are lost,
- Oversaturation of the body with certain plant or dairy products, leading to alkalization,
- Nervous stress, overstrain,
- Overweight,
- Cardiovascular diseases occurring with shortness of breath.
Alkalosis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Poor digestion of food, feeling of heaviness in the stomach,
- The phenomena of toxicosis, since substances are poorly absorbed and remain in the blood,
- Skin manifestations of an allergic nature,
- Deterioration of the liver, kidneys,
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases.
During treatment, elimination of the causes causing alkalization is indicated. Inhaling mixtures containing carbon dioxide will help normalize acidity.
Solutions of ammonium, calcium, potassium, and insulin, prescribed by a doctor in a therapeutic dosage, are also effective for normalizing pH. This treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a physician in a hospital setting.
Blood pH level in alkalosis
Blood PH level during alkalosis
Alkalosis, unlike acidosis, appears immediately as soon as the blood PH readings become above 7.45. When the body becomes strongly alkalized, the skin becomes flabby and dry. A person takes on the ugly appearance of a “dried wooden knot.”
The blood pH level during alkalosis is normalized if the causes that caused this deviation are eliminated. The treatment process can begin with breathing exercises. This will help saturate the blood with carbon dioxide and oxygen compounds in the correct proportion. Read more about acidification and alkalization of the body in this article.
Important: Do not self-medicate! It may be dangerous. Never make even rough diagnoses for yourself or your loved ones.
Analysis transcript
Decoding of the received data should be carried out by a medical specialist.
Based on the digital values, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- If the indicator is 7.4, this indicates a slightly alkaline reaction and that the acidity is normal.
- A condition in which the pH level is higher than normal is associated with the accumulation of alkaline substances and is called alkalosis.
- If the indicator is below normal, this indicates an increase in acidity, and this condition is called acidosis (acidic blood).
Any deviations from the norm of this indicator require close attention and urgent treatment. Both acidification and alkalization of the blood are harmful to the body. Normalization of pH levels with the help of special preparations should only be carried out under the supervision of a physician.
Blood pH level in cancer: comparison
Blood PH level in cancer: comparison
A person's blood PH level fluctuates throughout life. But there are critical indicators when chronic diseases and even cancer can occur. It is bad for the human body when the body is highly acidified, that is, PH values are below 7.45 units, and when a sharp alkalization occurs. If the indicator is below 6.0 units, then the alarm should be sounded.
Blood pH level in cancer is below 6.0. With such indicators, a person has a poor complexion, pale lips, no blush, hair and nails break. We can say that a person has a sick appearance.
Remember: Only a doctor should make a diagnosis! Don't do anything on your own. If you have any doubts about your health, get examined and take the necessary tests. You can only sound the alarm in a timely manner if you feel unwell or other symptoms that interfere with your normal life.
Only a doctor should compare blood pH levels in cancer. He will be able to correctly prescribe treatment and take emergency measures that will be a salvation for your health.
Blood pH: normal and abnormalities
The acidity and alkalinity of human blood is assessed on a pH scale of 0-14 (strongly acidic - strongly alkaline). A neutral pH level is 7.0 (corresponding to distilled water), which is in the middle of this scale.
Blood is usually slightly alkaline, its normal value falls within a certain range of 7.35–7.45. Interestingly, the pH of human blood is normally different for venous and arterial blood:
- venous - 7.32-7.42;
- arterial - 7.37-7.45.
Only at such values do the systems work harmoniously, removing excess hydrogen and bases. When the values on the scale shift to the right of the permissible interval, alkalosis develops, and to the left, acidosis develops.
The body tries to keep the blood pH within 7.40. This is ensured by the functioning of the respiratory system, kidneys, and buffer systems.
Weakly acidic carbon dioxide is a byproduct of the metabolism of oxygen, which is needed by all cells. Cells constantly produce it, and then “dump” it into the bloodstream, along with other by-products. From there, carbon dioxide is transported to the lungs, from where it is expelled when you exhale. As carbon dioxide accumulates in the biofluid, its pH level decreases and acidity increases.
The brain regulates the amount of carbon dioxide exhaled by controlling the rate and depth of breathing (gas exchange). As breathing becomes faster and deeper, the volume of carbon dioxide exhaled increases and the blood pH value also increases. By regulating the rate of breathing, the brain, along with the lungs, continuously regulate the pH level.
The kidneys influence the acidity of the blood by removing excess acid or alkali. However, the process is slower than in the lungs, so it takes several days to correct the balance.
pH buffer systems protect the body from sudden changes in acidity and alkalinity. There are 4 of them in total:
- Bicarbonate.
- Hemoglobin.
- Protein.
- Phosphate.
Interesting! The most important pH buffering system in the blood consists of carbonic acid (a weak acid formed from carbon dioxide dissolved in the blood) and bicarbonate ions (a corresponding weak alkali). Its share of all buffering abilities is 53%.
Each system is represented by a combination of weak acids and weak alkalis present in the body. They exist as equilibrium pairs at normal pH levels. Buffers at the chemical level minimize changes in the pH level of a solution by regulating the proportion of acids and bases.
How to measure blood PH at home with a device, test strips?
How to measure blood PH at home with a device, test strips?
Of course, if you have any health problems, you should go to the clinic to see a doctor. But it often happens that we don’t have time to go to the hospital - don’t be upset. You can measure blood PH at home with a device or test strips.
A special device is sold at a pharmacy or any medical equipment store. It is inexpensive, but very useful for measuring blood PH at home. If you can’t find such a device, use test strips. They are sold in every pharmacy and cost pennies. If you don’t find any strips or a tester at the pharmacy, you can order everything you need online.
How to measure blood PH at home with test strips - tips:
- Prick the finger of your right hand with a scarifier, which is also sold in pharmacies.
- Squeeze some blood into a small container. It's good if you have a laboratory test tube.
- Dip the test strip into this blood, hold it for a few seconds, remove it from the tube, and evaluate the result.
- The scale for determining the alkaline reaction in the body is on the package with strips. Compare the color and find out the result.
When measuring PH values using the device, it is faster, easier and more convenient. You do not need to pierce your finger, the device will do everything on its own: puncture, sampling and give the result.
pH (acidity) of blood: what is it, the norm in a blood test, how is it regulated, when it changes
© Z. Nelly Vladimirovna, laboratory diagnostics doctor at the Research Institute of Transfusiology and Medical Biotechnology, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
Usually an indicator such as pH or blood acidity (hydrogen indicator, acid-base balance parameter, pH), as patients are used to calling , not noted in the referral for hematological tests for the purpose of examining the patient.
Being a constant value, the pH of human blood can change its values only within strictly designated limits - from 7.36 to 7.44 (on average - 7.4).
Increased blood acidity (acidosis) or a shift in pH to the alkaline side (alkalosis) are conditions that do not develop as a result of exposure to favorable factors and in most cases require immediate therapeutic measures.
Blood cannot withstand a pH drop below 7 and a rise to 7.8, so extreme pH values such as 6.8 or 7.8 are considered unacceptable and incompatible with life. In some sources, the high limit of compatibility with life may differ from the listed values, that is, equal to 8.0.
Blood buffer systems
Products of an acidic or basic nature constantly enter the human blood, but for some reason nothing happens? It turns out that everything is provided for in the body; buffer systems are “on duty” around the clock to guard the constancy of pH, which resist any changes and do not allow the acid-base balance to shift in a dangerous direction. So, in order:
- The bicarbonate system opens the list of buffer systems; it is also called the hydrocarbonate system. It is considered the most powerful, since it takes on a little more than 50% of all blood buffering abilities;
- The second place is taken by the hemoglobin buffer system, it provides 35% of the total buffer capacity;
- The third place belongs to the buffer system of blood proteins - up to 10%;
- In fourth position is the phosphate system, which accounts for about 6% of all buffering capabilities.
These buffer systems, in maintaining a constant pH, are the first to resist a possible shift in the pH value in one direction or another, because the processes that support the vital activity of the body are ongoing, and at the same time, products of either an acidic or basic nature are constantly released into the blood. Meanwhile, for some reason the buffer capacity is not depleted. This happens because the excretory system (lungs, kidneys) comes to the rescue, which reflexively turns on whenever there is a need - it removes all the accumulated metabolites.
buffer system
The activity of the bicarbonate buffer system, which includes two components (H2CO3 and NaHCO3), is based on the reaction between them and bases or acids entering the blood. If there is a strong alkali in the blood, then the reaction will follow this path:
NaOH + H2CO3 → NaHCO3 + H2O
The sodium bicarbonate formed as a result of the interaction does not stay in the body for a long time and, without having any special effect, is removed by the kidneys.
The second component of the bicarbonate buffer system, NaHCO3, will react to the presence of a strong acid and neutralize the acid as follows:
HCl + NaHCO3 → NaCl + H2CO3
The product of this reaction (CO2) will quickly leave the body through the lungs.
The hydrocarbonate buffer system is the first to “feel” a change in the pH value, so it is the first to begin its work.
Hemoglobin and other buffer systems
The main component of the hemoglobin system is the red blood pigment - Hb, the pH of which changes by 0.15 depending on whether it currently binds oxygen (pH shift to the acidic side) or releases it to tissues (shift to the alkaline side). Adapting to circumstances, hemoglobin plays the role of either a weak acid or a neutral salt.
When bases arrive from the hemoglobin buffer system, the following reaction can be expected:
NaOH + HHb → NaHb + H2O (pH remains almost unchanged)
And with acid, as soon as it appears, hemoglobin will begin to interact as follows:
HCl + NaHb → NaCl + HHb (pH shift is not very noticeable)
The buffering capacity of proteins depends on their basic characteristics (concentration, structure, etc.), therefore the buffer system of blood proteins is not as involved in maintaining acid-base balance as the previous two.
The phosphate buffer system or sodium phosphate buffer does not produce a special shift in the blood pH value. It maintains pH values at the proper level in the fluids that fill the cells and in the urine.
pH in arterial and venous blood, plasma and serum
Is the main parameter of acid-base balance – pH in arterial and venous blood – somewhat different? Arterial blood is more stable in terms of acidity. But, in principle, the pH norm in oxygenated arterial blood is 0.01 - 0.02 higher than in blood flowing through the veins (pH in venous blood is lower due to excess CO2 content).
As for the pH of blood plasma, then, again, in plasma the balance of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions, in general, corresponds to the pH of whole blood.
pH values may vary in other biological media, for example, in serum, but plasma that has left the body and is deprived of fibrinogen is no longer involved in maintaining vital processes, so its acidity is more important for other purposes, for example, for the production of sets of standard hemagglutinating serums, which determine a person's group affiliation.
Acidosis and alkalosis
A shift in pH values in one direction or another (acid → acidosis, alkaline → alkalosis) can be compensated or uncompensated. It is determined by the alkaline reserve, represented mainly by bicarbonates.
Alkaline reserve (ALR) is the amount of carbon dioxide in milliliters displaced by a strong acid from 100 ml of plasma. The norm of SH is within the range of 50 – 70 ml of CO2.
Deviation from these values indicates uncompensated acidosis (less than 45 ml CO2) or alkalosis (more than 70 ml CO2).
There are the following types of acidosis and alkalosis:
Acidosis:
- Gas acidosis - develops when the removal of carbon dioxide from the lungs slows down, creating a state of hypercapnia;
- Non-gas acidosis – is caused by the accumulation of metabolic products or their entry from the gastrointestinal tract (alimentary acidosis);
- Primary renal acidosis is a violation of reabsorption in the renal tubules with the loss of a large amount of alkalis.
Alkalosis:
- Gas alkalosis – occurs with increased release of CO2 by the lungs (altitude sickness, hyperventilation), forms a state of hypocapnia;
- Non-gas alkalosis - develops with an increase in alkaline reserves due to the intake of bases from food (nutritional) or due to changes in metabolism (metabolic).
Of course, it will most likely not be possible to restore the acid-base balance in acute conditions on your own, but at other times, when the pH is almost at the limit, and the person does not seem to be in any pain, all responsibility falls on the patient himself.
Products that are considered harmful, as well as cigarettes and alcohol, are usually the main cause of changes in blood acidity, although a person does not know about it unless it comes to acute pathological conditions.
You can lower or increase the pH of the blood with the help of diet, but we should not forget: as soon as a person switches to his favorite lifestyle again, the pH values will return to their previous levels.
Thus, maintaining the acid-base balance requires constant work on oneself, recreational activities, a balanced diet and proper regimen, otherwise all short-term work will be in vain.
© 2012-2020 sosudinfo.ru
Sources
Display all posts with the tag:
Source: https://sosudinfo.ru/krov/ph/
Where can I get a blood PH test?
Where can I get a blood PH test?
Laboratory tests are much more accurate than those obtained at home. If you decide to take a blood PH test in a special laboratory, you can go to the clinic at your place of registration or to any private clinic. The analysis will be ready on the day of blood sampling. The doctor himself may suggest that you take a test during a routine examination or preventive procedures if there are deviations in your health.
What does blood PH depend on?
What does blood PH depend on?
If the pH level becomes too low - less than 7.35 (acidic) or too high - more than 7.45-8 (alkaline), then the cells of our body begin to poison themselves with toxic emissions and die. Slags and toxins appear in large quantities. In this case, many people begin to remove these harmful substances from the body. But you just need to bring the PH levels of blood, urine and saliva back to normal. What does blood PH depend on?
This indicator depends on the following factors:
- Nutrition - you need to learn the basics of proper nutrition. Our body must maintain a balance of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
- Stress resistance - constant nervous tension leads to acidification of the body. Learn to be calm and not get nervous over trifles.
- Obesity - When the body is acidic, it begins to accumulate fat. If you alkalize, you will immediately begin to lose weight, which means your well-being, skin and hair condition will improve.
The acid-base balance in the body depends on maintaining the correct proportions between intercellular and intracellular waters in the tissues. If the acid-base balance of liquids is not maintained constantly, it will be impossible to preserve life and the normal functioning of all organs and systems.
What does PH depend on?
pH: what is it?
The concept of pH was first formulated in Denmark at the beginning of the 20th century. Physicists introduced the concept of the degree of acidity of a liquid, defining it on a scale from 0 to 14. For each human liquid environment there is its own optimal pH, including blood.
A value of 7 on this scale indicates a neutral environment, values less than this indicate an acidic environment, and higher values indicate an alkaline environment. What makes an environment acidic or alkaline is the concentration of active hydrogen particles in it, which is why this indicator is also called hydrogen.
The blood hydrogen index, if a person has normal metabolism, is stably within certain limits. In other cases, the balance of the body's systems is disrupted, which provokes health problems.
To keep the pH value stable, the body operates special buffer systems - liquids that ensure the correct concentration of hydrogen ions.
They do this with the help of the liver, lungs and kidneys, which, with the products of their activity, regulate the physiological mechanisms of compensation: they increase the pH concentration or dilute it.
The body can function smoothly and smoothly only if the acid-base reaction of the most important body fluid is normal.
| Buffer system | Share of all buffering abilities |
| Bicarbonate system | 0.53 |
| Hemoglobin buffer system | 0.35 |
| Protein buffer system | 0.1 |
| Phosphate buffer system | 0.02 |
The main role in this interaction belongs to the lungs, since it is their structures that produce the overwhelming amount of acidic products, which are excreted from the outside in the form of carbon dioxide and affect the functioning of the entire organism.
The kidneys play the role of binding and producing hydrogen particles when the released sodium ions and bicarbonate are returned to the blood. The liver utilizes unnecessary acids entering it from the body, which forces the acid-base balance to move towards alkalization.
Alkaline balance of different liquids
The level of pH constancy also depends on the digestive organs, which also do not stand aside, but actively influence the level of acidity by producing a huge amount of digestive juices that change the pH level.
Negative factors affecting pH levels are:
- Bad ecology,
- Bad habits,
- Unbalanced diet
- Psycho-emotional stress,
- Violations of the work and rest regime.
How to reduce acidity and raise blood pH?
How to reduce acidity and raise blood pH?
Acid-base balance is our indicator of health. The more “sour” a person is, the faster he begins to age and get sick more. For the normal functioning of all organs and systems, the PH level in the body must be alkaline at least 7.35 units. How to reduce acidity and raise blood pH? Some tips:
- Eliminate meat products from your diet. You can fish, but in small quantities.
- It is important to make your nutrition correct. Get the right ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Use boiled and steamed dishes, exclude everything fried. Eat more fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Stop being nervous. Reconsider your attitude towards life - eliminate stressful situations.
- Practice separate meals. This will help the body quickly reduce acidity and normalize digestion. Products consumed separately will be better digested.
You can use special drops that are sold in pharmacies to alkalize the water. Alkaline water will help reduce acidity levels, and the kidneys, stomach and intestines will begin to work well. If your body is highly acidic, switch to a raw food diet.
But remember! Conducting experiments on your own is dangerous! Consult your doctor before following an alkaline diet or drinking alkaline water.
How to increase or decrease acidity through nutrition
With the help of proper nutrition, you can not only diversify the menu and make the diet more balanced, but also use them to maintain the required pH level. Certain foods, during assimilation processes, contribute to increased alkalinity, while when consumed, others, on the contrary, increase acidity.
Foods that increase acidity:
- Meat, fish and seafood;
- Eggs;
- Sweets;
- Bakery and pasta products;
- Beer;
- Fermented milk products;
- Carbonated drinks;
- Cereals, legumes;
- Salt;
- Antibiotics.
If the diet is oversaturated with these products, then a person will inevitably, over time, begin to experience immune disorders, malfunctions of the digestive system,
Such nutrition leads to failures of the reproductive system in both men and women: for normal synthesis, sperm require an alkaline environment, and when they move through the vagina of a woman with too high acidity, they die.
Foods that help alkalinize the blood:
- Citrus;
- Melons;
- Celery;
- Mango;
- Papaya;
- Grape;
- Greens (parsley, spinach, celery, asparagus);
- Fruits (pears, apples, apricots, bananas, avocados, peaches)
- Absolutely all vegetable juices;
- Ginger;
- Garlic;
- Simple drinking and mineral water.
When a person abuses animal fats, alcohol, coffee, sweets, smokes and is exposed to stress, the body undergoes “acidification.” The toxins formed in this case are not removed from the body, but settle in the blood, joints, and blood vessels, becoming disease provocateurs. Along with a set of cleansing and therapeutic procedures, doctors advise regularly drinking alkaline mineral water.
The high efficiency of mineral water lies in the fact that it not only normalizes the acid-base balance, but also has a beneficial effect on the entire body - removes toxins, heals the stomach, improves blood structure and strengthens the immune system. Recommended dose: 3-4 glasses per day.
A pH value within normal limits is an indispensable condition for the healthy functioning of human organs and systems, since all tissues are extremely sensitive to its fluctuations and prolonged disturbances can lead to the most disastrous consequences. Every individual who is responsible for their health should check and monitor their acid-base balance on their own from time to time.
How to increase acidity and reduce blood pH?
How to increase acidity and reduce blood pH?
It is bad for the body when the alkaline balance of the blood is greatly increased and has high levels. How to increase acidity and reduce blood pH? Adviсe:
- Eat acid-containing foods - grains, legumes, protein foods (meat, eggs).
- Eat foods rich in dietary fiber.
- Three times a day you can take 1 tablespoon of apple cider vinegar with honey.
- Vitamin C lowers pH levels.
- Do breathing exercises with deep breaths.
- If there are no medical contraindications, you can use dietary supplements - food enzymes and others.
- Correct the vitamin status in the body by taking multivitamin complexes.
Also, to increase acidity, it is necessary to carry out prevention and adequate treatment of the genitourinary system.
How does calcium affect blood pH?
How does calcium affect blood pH?
Calcium is an alkaline substance. How does calcium affect blood pH? Our body is a smart “system”. In order to prevent critical indicators of the acid-base balance, with strong acidification, it begins to extract calcium and magnesium from our bones and teeth.
When the body is acidified, it will be useful to take a course of calcium. But this substance is well absorbed if taken along with magnesium and vitamin D3. The pharmacy sells special vitamin complexes with calcium. There is a lot of magnesium in fresh herbs and green vegetables.
Types of blood pH disorders
There are two pathologies of acid-base balance: acidosis and alkalosis. In the first case, there is more acid in the blood than alkali. With alkalosis it’s the opposite. Both conditions are not diseases. They arise as a result of a large number of different disorders.
The presence of acidosis and alkalosis indicates to doctors that a serious problem exists. Depending on their underlying cause, acidosis and alkalosis are divided into metabolic (non-gas) and respiratory (gas).
Alkalosis
Alkalinization is rare. It occurs as a result of a large loss of hydrogen cations in the body or due to the accumulation of alkaline components. A significant decrease in acid levels can occur due to frequent and profuse vomiting (poisoning) or impaired functioning of the kidneys, which regulate balance. The main reasons causing an increase in the indicator on the pH scale:
- Abuse of alkaline foods (green tea, milk and derivative products).
- Overweight, obesity.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Psycho-emotional disorders.
- Taking diuretic medications.
How to maintain a constantly normal blood pH level?
How to maintain a constantly normal blood pH level?
If acidity levels are normal, it is recommended to regularly take tests and check the PH level. How to maintain a constantly normal blood pH level? Adviсe:
- Make it a habit to eat right. Eat at least 5 servings (1 serving - 100 grams) of fresh vegetables and fruits. There are food products that are especially enriched with vitamins, minerals and contribute to the balance of nutrients.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle and exercise. Quit smoking and drinking alcohol - all this strongly and quickly acidifies the body.
- Drink mineral water without gases, freshly squeezed juices, herbal teas.
- Eliminate fatty, high-calorie, smoked foods, coffee, tea from your diet.
Harmful compounds that accumulate during acidification of the body do not leave the body, but are deposited on the walls of blood vessels. To get rid of the effects of acidification, it is necessary to carry out long-term cleaning measures. Therefore, it is better to always keep your blood pH, as well as urine and saliva, normal.
Acidosis and alkalosis: when the analysis differs from the norm
When we are talking about increased acidity, the term “acidosis” is used, from the Latin translation “acidum” - acid. If a shift in equilibrium is observed towards the alkaline side, or towards an increase in pH, then this state is called “alkalosis”, from the corresponding chemical name for alkalis and bases.
Acidosis and alkalosis are a common consequence of various chronic diseases of the heart, blood vessels, and especially the lungs and kidneys, which are involved in maintaining balance and minimizing pH deviations.
In the clinic, it is very important to distinguish between respiratory and metabolic alkalosis and acidosis. Each of us can independently, right now, experience the symptoms of respiratory alkalosis: to do this, you need to breathe very deeply and often for at least 15 - 20 seconds. Unpleasant symptoms of “poisoning” the body with oxygen will appear, and a drop in the partial pressure of plasma carbon dioxide: dizziness, a feeling of numbness in the face and fingers.
But much more often in the clinic a state of metabolic acidosis, or acidification of the body, develops. Free radical oxidation, lipid peroxidation, heart failure, and various chronic diseases may be to blame. The main reasons for pH deviation towards metabolic acidosis are the following conditions:
- chronic hypoxia;
- dysfunction of the liver to neutralize protein breakdown products, and accumulation of acidic compounds - the main disease is chronic liver failure;
- with chronic anemia, and with a pronounced decrease in plasma protein levels. These conditions lead to depletion of buffer systems;
- also the reasons for increased acidosis due to an increase in the concentration of acetone and ketone bodies is observed in patients with severe diabetes mellitus when plasma acidity increases;
- with prolonged fever;
- due to alcohol intoxication;
- for burn disease;
- with massive injuries, especially with crash syndrome, or with prolonged crush syndrome.
In crash syndrome, after releasing the limb from prolonged compression, a large amount of myoglobin enters the central bloodstream, which appears as a result of traumatic rhabdomyolysis, or muscle breakdown. This myoglobin is capable of “clogging” the membranes of the renal glomeruli, and this leads to the development of acute renal failure and impaired excretion of protons into the urine.
In the case of metabolic acidosis, the pH of the plasma of arterial and venous blood and the amount of bicarbonate decreases, the concentration of hydrogen ions increases, and as compensation the partial pressure of carbon dioxide decreases.
We have analyzed the conditions in which the pH is below normal. But during the study, one can sometimes notice an increase in pH or a decrease in the concentration of protons. To avoid confusion, remember that the indicator is a negative value of the decimal logarithm, that is, there is an inversely proportional relationship: with an increase in the concentration of protons or hydrogen ions, or with acidification, the pH decreases, and vice versa.
A patient has a high chance of experiencing metabolic alkalosis if he has the following conditions:
- the patient has an excessive loss of acids from the body, or an excessive accumulation of basic compounds. Most often in the clinic, vomiting is encountered, indomitable and repeated, in which protons and chlorine, which are part of the gastric juice, are lost;
- taking large amounts of diuretics;
- loss of potassium with severe diarrhea;
- excessive administration of alkaline solutions in order to compensate for acidosis;
- transfusion of a large volume of donor blood. Its composition for preservation includes lactate or citrate, which lead to the development of alkalization.
Quite often, the condition threatens with alkalosis if there is endocrine pathology, with hyperaldosteronism and Itsenko-Cushing's disease, when taking glucocorticoid hormones.
Unlike acidification, alkalosis has special symptoms for doctors: severe headache, drowsiness, and increased neuromuscular excitability, which is associated with convulsive syndrome. Alkalinization of the plasma and the accompanying decrease in potassium concentration causes a permanent disturbance in heart rhythm, and in elderly patients can lead to atrial fibrillation and other complications.
A complete, comprehensive study and accurate interpretation of acid-base parameters can be challenging. If the patient does not suffer from chronic diseases, leads a healthy lifestyle, and adheres to the rules of a healthy diet, then when testing the blood for acid-base status, you can rest assured that the pH is normal.
But in a patient who feels normally, but has a chronic metabolic disorder, inflammatory disease or metabolic disorders, then there is a risk of a significant worsening of the condition if even minor decompensation develops.
What foods acidify the blood: table
Plan your diet and lifestyle in such a way that you do not have problems with blood alkaline levels. A healthy diet will help you maintain health and youth throughout your life. So, what foods acidify the blood? Table:
What foods acidify the blood: table
If your blood is highly acidified, change your eating habits. Proper nutrition has been in fashion for several years now, but there are still many people in the world who do not know what this term means.
What foods alkalinize the blood: table
If you have health problems, take a blood test to check your PH level. Acidified blood must be alkalized, otherwise failures in the functioning of organs and systems will lead to the most unpleasant consequences. What foods alkalinize the blood? Table:
What foods alkalinize the blood: table
You will see more detailed information about foods that alkalize and acidify the blood in this article on our website. It is important to remember that in a neutral biological environment our body has an amazing ability to heal itself. Therefore, strive to maintain your acid-base balance normal so as not to get sick and stay young for a long time.
Acidosis
Acidosis is a more common manifestation of metabolic disorders than alkalosis - the human body is more resistant to alkalization than to acidification.
Its mild form is usually asymptomatic and is detected incidentally with accompanying blood tests.
In case of a serious form of the disease, the following symptoms appear:
- Increased breathing;
- Nausea;
- Vomit;
- Fast fatiguability;
- Heartburn.
When there is a high level of acidity in the body, organs and tissues experience a deficiency of nutrition and oxygen, which leads over time to pathological conditions:
- Malfunctions of the cardiovascular system
- General weakness;
- Urinary system disorders;
- Tumor processes;
- Pain in muscles and joints;
- Obesity;
- Development of diabetes;
- Decreased immunity.
The causes of established acidosis are:
- Diabetes;
- Oxygen starvation;
- Fright or shock, stress;
- Various diseases;
- Alcoholism.
Treatment tactics involve eliminating the causes of blood acidification. In cases of acidosis and the pathology accompanying this condition, the patient needs to drink plenty of fluids and take a soda solution.