Indications for studying ASL-O
Beta-hemolytic streptococcus is a spherical bacterium that causes pharyngitis, sore throat, scarlet fever, erysipelas, and endocarditis.
Complications of streptococcal infections often include rheumatism, vasculitis, and glomerulonephritis. After penetration into the body, microbes release toxins that damage the tonsils, heart, kidney tissue and skin, and massive hemolysis (destruction) of red blood cells also occurs. After 10 - 20 days from the moment of infection, cells of the immune system produce antibodies (ASL-O), which reduce the activity of toxins.
Based on the degree of change in the titer of these protective compounds, one can determine the relationship with streptococcal infection of the following symptoms:
- recurrent pain in the knees or elbow joints;
- labored breathing;
- new long-term pain in the heart;
- swelling in the ankles and under the eyes;
- arterial hypertension in children, adolescents, young people;
- violation of urine excretion, the appearance of blood in it;
- elevated body temperature of unknown origin (37.1 - 37.5 degrees);
- sudden onset of fever up to 39 degrees or higher;
- burning or bursting pain in the legs, facial skin, redness, swelling, blisters and ulcers in this area;
- twitching of limbs in children with nervousness, tearfulness;
- circulatory disorders (shortness of breath, tachycardia, swelling of the extremities) with myocarditis and heart defects.
Culture for group B beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
Characteristic manifestations of streptococcal infections usually do not require confirmation by ASL-O testing, but atypical forms of the disease are also common. If antibacterial therapy is not carried out in a timely manner, autoimmune inflammatory processes occur, since streptococcal antigens are very similar to the components of vascular cells, cardiac muscle tissue, articular surfaces, and neurons.
A referral for analysis can be issued by cardiologists, nephrologists, dermatologists, otolaryngologists to select a treatment method, determine its effectiveness, and indications for surgery. The examination is usually prescribed over time (for example, every week) along with the determination of rheumatoid factor, C-reactive protein, and ESR.
If there are no clinical manifestations, no increase in acute phase indicators of inflammation, and the titer remains stable, then this indicates that the person is a carrier of streptococcus; he can infect others without showing signs of illness.
Causes of high ASL-O levels
The brain, trying to protect organs and tissues from pathological processes, when streptococci penetrate, sends a signal to begin the synthesis of protective antibodies - antistreptolysin-O molecules. They are distributed in the body and eliminate the negative consequences after the attack of emerging toxins.
But their disadvantage is that these molecules are not able to fight streptococci. To confirm the fact of penetration of microorganisms and their vigorous activity, the patient is sent for detailed diagnostics to make an accurate diagnosis.
Routes of transmission of streptococci:
- airborne;
- food;
- sexual;
- domestic.
Airborne is the spread of infection through sneezing or coughing. Food route - transmission through food that has not been subjected to sufficient heat treatment.
In the household method, spread occurs through personal belongings, shared utensils, and saliva remaining on them. An important feature in this case is the fact that streptococci remain viable for a long time, without having a constant source of food.
Reasons to conduct an analysis
Streptococcus, belonging to group A, is responsible for the development of the following pathologies:
- Sore throats;
- Pharyngitis;
- Inflammatory processes in the lungs;
- Scarlet fever;
- Myositis.
A dangerous microorganism also causes the development of rheumatism and glomerulonephritis.
However, in this situation, “surprises” of bacteria, which manifest themselves as complications of streptococcal pathologies, pose a particular danger:
- Otitis and sinusitis, accompanied by purulent discharge;
- Development of sepsis;
- Manifestations of shock of the toxic variety;
- Endocarditis;
- Progression of meningitis and osteomyelitis;
- Neurological disorders in children.
Developing rapidly, streptococcus “hosts” the body: actively multiplying, it releases a large amount of toxins that the human immune defense cannot cope with.
A blood test for ASLO is prescribed in the following situations:
- Confirm the type of infection of streptococcal origin;
- Assess the likelihood of complications occurring after an illness;
- Compare the symptoms of streptococcal infection with developing defects of internal organs and joint tissue;
- Conduct a differential diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Assess the effectiveness after treatment of rheumatism and glomerulonephritis.
Getting ready for analysis
In order for the results of a biochemical study to correspond to the truth, you need to know about the rules for conducting them:
It is better to donate blood in the same laboratory
It is especially important to follow this rule if deviations from the norm were recorded during the first study. The test requires blood from a vein. However, if necessary, biological material can be collected from a finger. The analysis is done exclusively on an empty stomach
In this case, the duration of food refusal should be at least 8 hours. In the morning, you are allowed to drink water without gases. Biological material for research must be received no later than 11 a.m. Three days before the biochemical study, fatty, smoked and spicy foods should be excluded from the diet. Limit physical activity and active sports. Avoid drinking alcohol. Do not smoke immediately before the procedure. During the period of preparation for the analysis, stop taking medications. The exception is drugs that are necessary to maintain vital functions. In this case, the names of the medications and the purpose for taking them must be reported to the doctor before the test. Eliminate nervous tension, stress and psychological fatigue.
It should be noted that in some pathologies it is not practical to use a biochemical analysis to determine the level of ASLO. These include the following pathologies:
- Streptococcal skin diseases;
- Scarlet fever;
- Streptococcal endocarditis;
- Osteomyelitis.
It should be noted that increased ASLO levels can also be observed in the following specific cases:
- In patients with liver disease;
- In healthy people who are carriers of streptococci;
- In patients with developing tuberculosis;
- In persons with elevated lipoprotein levels.
It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that there is a risk of distortion of laboratory test results. They are influenced by the following factors:
- Breakdown of red blood cells;
- Presence of liver pathologies;
- Use of antibiotics or glucocorticosteroids before taking tests.
Preparation and progress of analysis
In order for the results of a biochemical study to be as reliable as possible, it is better to donate blood in the same laboratory not throughout the entire dynamic examination of the patient. Blood is most often taken from a vein, but capillary blood is also suitable for research. The test is carried out on an empty stomach, no later than 11 am.
There is no special pre-preparation, the algorithm of actions is standard: for three days, exclude everything fatty, smoked, spicy, alcohol from the diet, and minimize physical activity. You should not smoke before the procedure. Taking medications is agreed with your doctor. They take the test in a state of complete rest, having ruled out all psycho-emotional breakdowns and overwork the day before.
In some pathologies, it is useless to take an ASLO test: scarlet fever, streptococcal dermatoses, endocarditis of streptococcal origin, osteomyelitis.
In addition, a priori, ASLO may be increased in liver pathologies, carriers of streptococcal infection, in patients with tuberculosis, obesity or atherosclerosis. Data distortion is possible due to the breakdown of red blood cells, taking antibiotics or hormonal drugs. All this must be taken into account when deciphering ASLO indicators within the framework of standard blood biochemistry.
The procedure is carried out as follows: the latex test is carried out in the morning (usually at 7-9 o’clock), on an empty stomach, blood is taken from a vein, less often from a finger in the amount of 5 ml, the tube is labeled, sent to the laboratory for routine assessment of the peak of streptococcal toxins, which indicates about whether a person is currently infected, how long ago the infection occurred. In addition, ASLO allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy and monitor rheumatic tissue damage.
Sometimes a turbidimetric titration is performed, where the amount of antibodies is measured with a photometer or spectrophotometer. Many doctors are confident in the greater reliability of such results. We emphasize that a single study of ASLO is not enough to make a diagnosis or predict the risk of complications; dynamic testing is needed.
What the analysis shows
The level of antistreptolysin and its deviations from the norm are determined using a blood test.
In the laboratory, a vein sample is taken on an empty stomach. The result of the study provides information about how long a person has been ill with an infectious disease. Knowing the time of growth, peak and decrease of antistreptolysin, the doctor determines:
- Is the person currently infected?
- Has the infection been developing in his body for a long time, or has the infection occurred recently?
Doctors recommend taking a blood test for rheumatic tests if you have a sore throat, otitis media or other infectious disease, and such a test must be done at the very beginning of the development of the disease (when you felt the first signs of illness) and after drug therapy.
If you already suffer from rheumatism, then such tests are required. They allow you to track how the disease develops, how correctly the treatment regimen is drawn up, and whether the prescribed drugs are effective.
How is the analysis done? To determine the level of antistreptolysin O, a latex analysis, or latex test, is done. This test is quite quick and inexpensive.
It is used to determine:
- actual antibody concentration;
- antibody titer (dilution of blood serum that allows detection of antibodies).
Sometimes they resort to turbidimetric titration when it is necessary to carry out quantitative measurements using a photometer or spectrophotometer. Some experts tend to trust this type of research more.
Such a test, done once, will not help in making a diagnosis or predicting the further course of the disease. Therefore, to study the dynamics of the pathological process, it is carried out once a week and, based on the data obtained, the nature of the disease and how much it is progressing are accurately determined.
Interpretation of clinical blood test
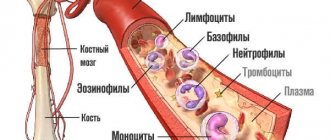
After receiving the results of a laboratory test, the question arises of how to decipher the blood test. For this purpose, hematological determinants are used, the range of which is 24 different parameters. Among them are the hemoglobin concentration, the number of leukocytes, the volume of erythrocytes, the average level of hemoglobin concentration in an erythrocyte, the average volume of platelets, the size distribution of erythrocytes and others.
Automatic decryption involves precise determination of the following parameters:
- WBC – white blood cells, leukocyte content in absolute values. The normal amount is 4.6 – 9.0 cells/l, necessary for recognizing and destroying foreign agents, stimulating the body’s immunity, and eliminating dead cells.
- RBC - red blood cells, the content of erythrocytes in absolute value at a norm of 4.4 - 5.8 cells/l in elements that include hemoglobin, which is a transporter of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- HGB is the level of hemoglobin in the blood at a normal level of 133-174 g/l. The analysis is carried out using cyanide. Measurement is in moles or grams per liter.
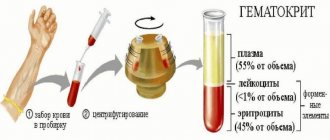
- HCT is hematocrit, which determines the ratio of the volumes of blood elements in plasma: leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets.
- PLT - blood platelets, platelet content in absolute value at a norm of 151-401 cells/l.
Streptococcal infection: what is it, why is it dangerous?
- Streptococcal infection is infection of the body by pathogenic microbes streptococci
- Streptococci are spherical bacteria that cause many human diseases.
Today, 21 groups of streptococci are known (A, B, C, G, V...)
The causative agents of most human streptococcal diseases are group A hemolytic streptococci (in particular the β-hemolytic streptococcus Streptococcus pyogenes)
Penetrating into the body, streptococci release toxic extracellular enzymes into the human blood, causing poisoning, acute inflammation, cell destruction and tissue damage.
Toxic factors of group A streptococcus
| Substance released | Harm |
| Streptolysin-O (hemolysin) | Destroys red blood cells under anaerobic conditions (without oxygen) |
| Streptolysin-S | Destroys red blood cells under aerobic conditions |
| C5a peptidase | Suppresses protective immune responses |
| Pyrogenic toxins | Indirectly stimulate the development of acute inflammation and fever. Cause cytotoxic effects with damage to vascular walls, myocardium, and other connective tissues |
| Cardiohepatic toxin | Damages the myocardium and diaphragm. Causes the appearance of giant cell granulomas in the liver |
| Streptokinase (fibrinolysin) | Indirectly induces the dissolution of fibrin fibers of connective tissue |
| Streptodornases (DNases) | Promote the breakdown and dissolution of DNA structure |
| Hyaluronidase | An enzyme capable of breaking down mucopolysaccharides of connective tissues, including hyaluronic acid |
Indications for analysis
There are several reasons for scheduling an event. If we talk about them in more detail:
- Development of typical diseases. Those that are usually formed under the influence of streptococci. This includes two main processes: pharyngitis and, more often, tonsillitis. In either case, we are talking about damage to the pharynx, throat.
Deviations can be provoked by many other pathogenic microorganisms and viruses. Therefore, it makes sense to prescribe a blood test for ASLO as quickly as possible in order to exclude or confirm the presence of staphylococcus. Further, auxiliary diagnostic measures are carried out as needed.
- Rheumatoid damage to the body with ineffective therapy. Typically, autoimmune diseases, including this one, are caused by bacteria. Most often just streptococci. This is a proven fact.
Without a high-quality and comprehensive elimination of the culprit, there can be no talk of a complete recovery of the patient. Only about relieving symptoms and suppressing acute conditions. A blood test for ASLO confirms the role of infection in the development of the pathological process.
- Glomerulonephritis. In this case, the diagnostic technique is designed to investigate the primary cause of the disorder. This condition in all situations is of an autoimmune nature. However, without identifying the source of the change, the one that encourages the disorder to progress, it is impossible to talk about full-fledged treatment.
If a pathogenic microorganism is detected, measures are taken to correct the condition to ensure that the main therapy for kidney damage is sufficiently effective.
- GABHS or group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus often causes asymptomatic disease, although it actively multiplies and harms the body. As a preventive measure, ASLO analysis is prescribed and taken less often.
The list of reasons for this is not rigid, including contact with an infected person in the recent past, acute lesions that have already been treated, and others. There are plenty of options. The issue is decided at the discretion of the infectious disease specialist or therapist.
- Prolonged fever. For at least a week without visible symptoms. At 37-38 degrees Celsius. We are talking about a group of violations. Including, possibly, caused by an infectious streptococcal process.
- Joint pain of unknown origin. Apparently, the lesion is of rheumatoid origin. A blood test alone for ASLO is not sufficient, although the results may indicate the likely nature of the disorder.
- Diseases of the heart, kidneys, and others, when there is reason to believe that the disorder is caused by pyogenic flora.
A diagnostic test is prescribed to study the effectiveness of the treatment.
ASLO norm in blood test
If the result obtained in adults or children is 0, this is a completely normal result. The main thing is that the upper limit of the standards is not exceeded. ASL O norm depends on the age of the child. The table below shows the limit values:
| Age (years) | Antistreptolysin is normal. Maximum permissible limit (U/ml) |
| Up to 7 | 100 |
| 7-14 | 250 |
| From 14 | 200 |
For women, as well as for men, the upper limit of the standard is 200 U/ml. There is a slight increase in the norm in children, which corresponds to the age of various streptococcal infections - childhood sore throats, and so on, so there are methods by which in children from 7 to 14 years old the upper limit of the norm is higher than in adults.
Complete blood count in adults
A general blood test in adults is mandatory whenever you visit a doctor due to illness or deterioration in health. It allows you to assess the general condition of the body and make the correct diagnosis. Women during pregnancy take the OAC upon registration, at 12, 20, 30, 36 weeks of pregnancy.
For an accurate interpretation of the results of the CBC, the age of the person is important, since the norms of some blood parameters differ somewhat in accordance with this factor
| Indicators | Hemoglobin | Red blood cells | ||
| age | women | men | women | men |
| 20-30 | 110-152 | 130-172 | 3,5*1012-5,0*1012 | 4,2*1012 -5,6*1012 |
| 30-40 | 112-150 | 126-172 | 3,5*1012 -5,0*1012 | 4,2*1012 -5,6*1012 |
| 40-50 | 112-152 | 128-172 | 3,6*1012 -5,1*1012 | 4,0*1012-5,6*1012 |
| 50-60 | 112-152 | 124-172 | 3,6*1012 -5,1*1012 | 3,9*1012 -5,6*1012 |
| 60-65 | 114-154 | 122-168 | 3,5*1012 -5,2*1012 | 3,9*1012 -5,3*1012 |
| Over 65 | 110-156 | 122-168 | 3,4*1012 -5,2*1012 | 3,1*1012 -5,7*1012 |
Features of changes in blood counts during pregnancy:
- By increasing the total volume of blood, its viscosity decreases. As a result, pregnant women have a decrease in hemoglobin and a decrease in the number of platelets.
- The leukocyte formula changes: the concentration of leukocytes increases to 10*109/l, the numerical value of band neutrophils increases, and the content of lymphocytes decreases.
- The ESR value during pregnancy can be increased to 45 mm/h.
Reasons for ordering an analysis for ASLO is normal
With proper timely treatment, any streptococcal infections can be cured.
If such diseases have been severely neglected, then there is a high probability of severe complications:
- nervous system;
- joints;
- heart muscle;
- renal nephrons.
Most often, such complications can appear several months after the onset of recovery. Therefore, streptococcal infections should be treated with great responsibility and if any of their manifestations you should immediately visit a doctor. If the diagnosis confirms your fears, you should begin treatment as soon as possible.
An ASLO test helps diagnose streptococcal infections. Only such an examination is recommended not to be carried out in the first days of damage to the body, but after a few weeks. This feature helps to more accurately identify the connection between the pathology present in the body and streptococcal pathogens.
Many foreign medical institutions prescribe ASLO examinations to children who suffer from diseases of the nervous system, joints, heart and kidneys caused by streptococcus. Such examinations are prescribed even for children who had this infection about a year ago. This method helps in making a more accurate diagnosis.
If an increased ASLO titer is detected, the doctor assumes the influence of a recent streptococcal disease on the condition of the kidneys and heart. Such cases require the use of a specific treatment regimen.
Doctors in many countries have come to the conclusion that they have adopted a single norm for the titer value, on the basis of which one can judge its increase. Analysis of ASLO, the norm of which is determined in advance, is considered elevated when the value exceeds 200 units. This value should be present in women and men examined in this way.
For children's bodies, this indicator has a lower value. The norm for antistreptolysin O in a child’s body is the range from zero to one hundred and forty units per milliliter.
Elevated ASL-O during pregnancy
According to doctors, increasing the level of antistreptolysin does not affect pregnancy in any way and cannot harm the unborn child. If a pregnant woman is found to have elevated levels of ASLO, and there are no signs of any complications after suffering streptococcal infections, treatment is not carried out.
Doctors take a very responsible approach to the diagnosis and treatment of streptococcal infections and insist on taking antibiotics even with a slight increase in temperature and not too pronounced manifestations. In most cases, they are not life-threatening, are easily cured and result in a complete recovery.
But you should know that after diseases caused by streptococci, severe complications can develop in the heart, kidneys, joints, and nervous system. Their signs usually appear several weeks or months after recovery. At the same time, the level of ASL-O increases only one to three weeks after infection, so in the first days it is impossible to determine whether the disease is caused by streptococci. This analysis is relevant mainly for children, since studies have shown that ASLO is not as strongly associated with streptococcal infections in adults.
How is the analysis done?
If the doctor has prescribed such a test for the patient, it should definitely be done. The reason for this is the corresponding state of the body, which indicates the presence of a certain kind of infection in it.
Before donating blood for this examination, you should prepare a little. Although this preparation is quite simple, it helps to obtain the most accurate results from the examination.
Before performing the analysis, it is recommended:
do not eat food for twelve hours;
- take a disposable syringe with you (usually the doctor warns you about this);
- the day before, stop taking all prescribed medications;
- the day before the test, avoid salty, spicy, fatty and spicy foods. You should also not eat sweets, meat and flour products.
- one week before donating blood, do not drink drinks containing any amount of alcohol.
In the morning, on an empty stomach, having arrived at the appropriate laboratory or hospital, you, having taken all the necessary documents, go to the office to submit your biomaterial.
The algorithm for this procedure is very simple:
- Prepare the hand on which the veins are best visible. If the veins lie quite deep, the doctor recommends using your fist to make these vessels more visible.
- A laboratory specialist, using a disposable syringe with a volume of no more than ten milliliters, will take the required amount of blood from a vein.
- The technician will give you a small amount of damp cotton wool to stop the bleeding. It is recommended to keep your arm in a bent position so that the bleeding stops as quickly as possible.
Blood sampling for this analysis is carried out according to standard methods. The main condition is maintaining sterility.
Consequences of streptococcal infections
Streptococcal infection has pronounced symptoms and is therefore easily identified. Treatment is carried out with antibiotics. If therapy is ineffective or the infection proceeds atypically, there is a possibility that complications characteristic of streptococcal infections may develop - glomerulonephritis or rheumatic fever.
More often they occur in children after scarlet fever or tonsillitis. ALSO testing is done to determine the relationship between symptoms of complications and recent streptococcal infections.
Rheumatic fever is characterized by fever, shortness of breath, heart pain, redness of the skin and swelling around the joints. This disease can lead to heart defects.
Complications after streptococcal infections most often develop in children, for example, after a sore throat
With glomerulonephritis, lower back pain and fever are observed, the amount of urine excreted decreases, and blood appears in it. Arterial hypertension and renal failure may develop against the background of the disease.
The ALS-O test can help determine whether these symptoms are caused by a streptococcal infection, since these symptoms can occur with other conditions.
Proper preparation for analysis
You need to donate blood for antistreptolysin in the morning (before 11 o’clock). For the study, blood is drawn from a vein. The procedure is performed using a disposable syringe. The following factors may influence the results of the examination:
- Physical exercise;
- Bad habits;
- Certain medications;
- Liver dysfunction;
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Hemolysis is the decomposition of red blood cells, with the release of hemoglobin;
- Nephrotic syndrome.
The following recommendations should be followed to exclude falsely elevated ASLO levels in the test results:
- Blood donation is done on an empty stomach. Dinner should be 8-12 hours in advance;
- Consumption of alcoholic beverages is prohibited per day;
- The last cigarette should be smoked at least one hour before visiting the laboratory;
- It is necessary to stop taking “accidental” medications that may affect the result, and the doctor who ordered the study must be notified of all prescribed drugs;
- The day before, you need to take care of yourself, avoid strength exercises and physical activity.
Basic rules for preparing to take the UAC
It is recommended to donate blood early in the morning, after 12 hours of fasting. In exceptional cases, you can drink unsweetened tea. In addition you should:
- in agreement with the doctor, stop taking medications the day before the test
- do not donate blood after physiotherapy or x-ray examination
- do not donate blood directly after mental and physical stress
- 1 hour before the procedure, refrain from smoking
- Avoid fatty and spicy foods and alcohol 48 hours before the procedure
- go to bed at your usual time, get up no later than one hour before blood sampling
Repeated examinations should be carried out at the same hours, since the morphological composition of the blood is prone to daily fluctuations. I suggest watching a video of how a general blood test is done:
Do not neglect the rules of preparation for the research procedure, and you will not be afraid of false results!
So, now the reader knows what a general blood test shows, the purpose of its use, what indicators the general analysis includes. How to prepare for the test procedure, and what factors influence the results. We learned about normal values and how they change under various conditions and diseases of the body.
Specifics of the study
To understand what an ASLO analysis is, you need to understand the specifics of infections caused by streptococci.
When a dangerous microorganism enters the systemic bloodstream, it begins to secrete streptolysin. This substance has a toxic nature, due to which it is capable of destroying red blood cells, causing damage to the main “pump” of a person - the heart.
As the disease progresses, toxic substances become more and more numerous, so the immune system begins to repel their attack with the help of antistreptolysins. These are antibodies aimed at neutralizing the action of streptococci. The more antibodies are formed in the bloodstream, the easier it is for the body to win the fight against infections. In this case, an increase in antistreptolysin is observed 1-2 weeks after infection. Its concentration reaches peak values after a month. Then there is a gradual decrease in antibodies, although their presence may remain in the blood for another six months.
Carrying out a biochemical blood test allows you to determine the number of protective bodies. Thanks to this indicator, doctors diagnose the stage of streptococcal disease and its severity. The lack of qualified assistance leads to pathological changes in the heart and joints. Damage to the kidneys and nervous system is observed.
Despite the high diagnostic performance of the analysis, it should be noted that in 15% of patients experiencing an infection of streptococcal origin, the levels of antigens in the blood do not exceed the norm.
Rules for blood sampling
The procedure for collecting blood for biochemical analysis:
- Blood sampling takes place in a specialized institution (hospital, clinic, private medical clinic); in some cases, it is also possible at home.
- Blood is collected using disposable consumables, which are opened in front of the patient.
- The procedure is performed on an empty stomach, preferably early in the morning. For drinking, regular water is allowed.
- In cases where the patient is taking various medications, it is necessary to draw blood before taking it.
- After blood sampling, the patient needs to remain in the field of view of medical personnel for some time.
A biochemical blood test in children is carried out at any age, however, in infants, blood is taken from the heel.
Pathological causes of increased ASLO in adults
The concentration of Antistreptolysin-O increases in many diseases involving streptococcus or complications of streptococcal infection.
In what diseases are ASLO levels elevated?
| Character pathologists | Name of the disease |
| Specific diseases - the cause of development is exclusively streptococcus | Scarlet fever Sore throat (acute streptococcal tonsillitis) Erysipelas Rheumatism* |
| Nonspecific diseases - can develop against the background of various types of viral and/or bacterial infections, including those involving streptococcus | Acute respiratory infection Pyoderma (purulent skin lesion) Osteomyelitis Pharyngitis Sinusitis Otitis Endocarditis Myocarditis Pericarditis Meningitis SepsisRheumatoid arthritis |
| Infectious and allergic complications of streptococcal infection | Rheumatic fever Acute glomerulonephritis Rheumatic polyarthritis Rheumatic carditis Rheumatic encephalopathies, encephalitis Minor chorea Rheumopleuritis |
*Rheumatism is a dangerous complication of streptococcal infection. Develops 10-14 or more days after suffering a streptococcal disease (more often after scarlet fever, tonsillitis, pharyngitis). It is expressed in systemic inflammation of various connective tissues, mainly cardiac and periarticular.
The onset of the disease can be acute or latent, with periodic exacerbations.
Forms of rheumatism: - acute rheumatic fever - rheumatic carditis (heart damage) - rheumatic polyarthritis, - rheumatic nephritis, - rheumatic damage to blood vessels, nervous system, muscles, skin, lungs, etc.
Variants of results in dynamics
This laboratory test is suitable for monitoring the course of a pathological process, but I would like to draw the reader’s attention to the fact that a single test of antibody concentration will not be particularly informative in terms of diagnosis and prognosis, so tests should be carried out serially with an interval of one week (7 days).
And here there are various options:
The titer of antistreptolysin-O begins to increase approximately a week after the pathogen enters. The peak occurs at 3-5 weeks and, if everything goes well (the body can handle it), the ASLO level will begin to decrease and reach normal values by six months to a year.
A persistent increase in the concentration of antibodies to the beta-hemolytic streptococcus antigen gives reason to suspect a later complication of the infection - the rheumatic process. The development of the rheumatic process can be assumed after a sore throat (with a long-term, not changing towards a decrease in the activity of antistreptolysin-O).
A favorable course of the rheumatic process (without involving the heart in the process) is indicated (and encouraging in terms of prognosis) by a decrease in the ASLO titer to normal by the end of the first or second month of the disease. With adequate treatment, these periods can be significantly reduced.
On the contrary, the absence of changes in ASLO titers towards a decrease (they continue to remain high six months after the onset of the disease) complicates the prognosis and makes one think about the onset of a relapse.
Despite the great diagnostic value of this laboratory test (ASLO), it should still be borne in mind that in the blood of individual patients, who can account for up to 15% of those with rheumatism, an increase in the titer of antibodies to streptolysin is not detected. And, conversely, relatively high levels are sometimes observed in carriers of the pathogen who do not have any signs of the disease. Elevated ASLO titers can also be expected in the blood of people with chronic tonsillitis, rheumatoid arthritis, or in carriers of streptococcal infection who consider themselves healthy because it is in a state of “hibernation” (albeit for a certain time).
graph: example of the dynamics of ASLO levels during streptococcal infection
It is known that the main reason for increased ASO activity is sensitization of the body with streptococcal antigen after penetration of streptococcal infection (in particular, Streptococcus pyogenes - GABHS). There is not much hope for post-infectious immunity in the event of infection - it does not differ in severity or duration, but it does allow for a high risk of complications. Streptococcal infection often leads to the development of a rheumatic process and the formation of acquired heart defects in children, therefore, after a sore throat or other infections in a child, it is very important to find out the values of this indicator (was the disease caused by streptococcus?).
Meanwhile, an analysis such as ASLO is often offered to an adult. This test, along with other tests (RF-rhematoid factor and CRP - acute phase reactive protein) helps establish the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis, although in RA the activity of ASLO is significantly lower than in rheumatism.
Antistreptolysin-O increased
Sometimes the results of indicators can be overestimated, even in the absence of streptococcal infection.
ASLO in the blood is elevated in the following cases:
- for liver pathologies;
- when a patient is diagnosed with nephrotic syndrome;
- when taking glucocorticosteroids or antibacterial drugs;
- if the patient has not properly prepared for the test;
- with hemolysis of erythrocytes.
Antistreptolysin-O is elevated - reasons
There are a number of factors that influence the value of this indicator.
An increase in ASLO in the blood often has the following causes:
- erysipelas;
- rheumatic fever;
- pyoderma;
- diffuse glomerulonephritis;
- tonsillitis;
- sinusitis;
- otitis.
If antistreptolysin-O is elevated, only a doctor can say for sure what this means. However, this indicator more often indicates the development of streptococcal infection, which can be provoked as follows:
- contact with a carrier of this pathogenic microorganism;
- visiting places with large crowds of people;
- using common hygiene items.
ASLO is elevated in the blood - what to do?
If the number of antibodies is recorded at high levels, additional research is required. All prescriptions must be made by a doctor. When antistreptolysin-O is elevated - what does this even mean, he will explain in detail to the patient and answer all questions that arise. To obtain reliable information, all studies must be completed on time.
In most cases, when antistreptolysin is elevated in the blood, the following tests are prescribed:
- detection of uric acid levels in plasma;
- determination of blood saturation with C-reactive protein;
- immunological tests.
Antistreptolysin-O – treatment
All appointments must be made by a doctor. He knows what antistreptolysin is, what this analysis says, and what to do if the level is significantly higher than normal. Therapy for each patient is selected individually. More often it involves taking the following medications:
- antibiotics (Augmentin, Ampicillin);
- immunostimulants (Immunal);
- antihistamines (Suprastin).
If a high level of antistreptolysin is detected, in order not to aggravate the condition, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
Do not self-medicate! Be wary of alternative medicine, since some herbal remedies are incompatible with antibiotics. If folk remedies are taken during therapy, they must be agreed with the doctor.. https://www.youtube.com/embed/LzKjnKHeOVE
Purpose of the study
When an antigen meets an antibody, a reaction occurs. The interaction occurs in 2 stages:
- The first phase is the identification of the antigen and its combination with antistreptolysin O;
- The second phase proceeds similarly to the gluing of particles (agglutination)
The first phase involves insoluble particles, that is, the bacteria themselves. The second stage is the reaction for soluble toxins. The goal of the whole thing is to neutralize and remove antigens out. In the process of interaction of ASLO with streptolysin (an enzyme secreted by streptococci), a third party also appears - complement proteins (globulins).
ASLO analysis helps determine the amount of antibodies and deviations from generally accepted standards. Based on the results obtained, you can not only identify the presence of infection, but also find out how long a person has been a carrier of streptococcal infection. The study allows us to answer the questions:
- Whether the person is currently sick or not;
- Assume the limitation period for infection.
For this purpose, a latex test is used in medical practice. It does not require expensive equipment and is carried out quickly. It shows what concentration and titer of antibodies is present in the body.
A more expensive alternative to latex analysis is the turbidimetric titration method. It is carried out using measuring instruments: a photometer and a spectrophotometer.
This approach to research helps to make quantitative measurements of ASLO in the blood.
You can learn more about ASLO in our article “Antistreptolysin O (ASLO) in the blood: what it is, the norm by age, interpretation of results, therapy.”
Checking the sample helps to determine the presence of autoimmune and rheumatic diseases and assess the existing inflammatory process.
When conducting a complex of immunological studies, the following indicators are checked:
- Total protein;
- C-reactive protein;
- Uric acid;
- Circulating immune complexes (CIC)
- Antistreptolysin O.
Antistreptolysin-O norm
There are several methods for conducting this research:
- The most popular way to get tested for antistreptolysin-O is the latex test. It is considered less expensive, and diagnosis takes little time. To perform this test, frozen blood samples and reagents are warmed to room temperature. Then take 2 glasses and place a drop of biological material on each of them. One will be for the positive control and the other will be for the negative control. Place the reagent on each glass and mix the samples. After this, they are sent to a mechanical rotor.
- Another common technique is turbidimetric titration. When detecting antibodies, a spectrophotometer and a photometer are used.
Normal ASLO levels in the blood of adults
This figure is the same for women and men. ASLO in the blood - the norm in the adult population is 200 U/ml
. A lower level of antibodies in the blood is also considered normal. To ensure the correctness of the result obtained, a repeat study is often prescribed. It is carried out one week after the initial blood donation.
Norm of ASLO in the blood of children
The maximum permissible value of this indicator is somewhat different from what it is in adulthood.
If antistreptolysin-O is determined in blood serum, the norm for children is as follows:
- up to 7 years – 100 U/ml;
- 7-14 years – 150 U/ml;
- over 14 years old – 200 U/ml.
Interpretation of results
ASLO in the blood is a marker of streptococcal damage. Decoding the analysis helps:
- identify the acute phase of the disease if the antibody titer is higher than normal, approximately 2-4 times; the higher the amount of streptococcal toxins, the more severe the pathological process;
- if the antibody titer is increased by two times or less, this is evidence of a past infection, the body is currently recovering, but in order to reliably confirm this fact, additional measures are needed: bacterial culture on nutrient media, a throat smear, and so on;
- if the level of antibodies remains at a level of 1.5 - 4 times higher than normal for several weeks, we are talking about an autoimmune process: rheumatoid arthritis, glomerulonephritis, which requires consultation with a specialist;
- a permanent increase in antibodies in the blood up to 1.5-2 times indicates carriage: the person is dangerous to others, preventive treatment is needed, but for accurate diagnosis a bacterial culture is needed;
- normal ASLO values with prolonged low-grade fever exclude the diagnosis of active rheumatism.
The ASLO indicator decreases gradually during therapy; full recovery occurs after six months to a year. During this period, fluctuations in the ASLO are likely. The dynamics of the study involves analysis - once every few weeks.
It is important to consider that an ASLO indicator at the normal level is not a complete guarantee of health: perhaps antibodies simply have not yet begun to be produced.
About 15% of cases of rheumatism, 20% of severe streptococcal infections, up to half of cases of glomerulonephritis of streptococcal origin, and more than 70% of streptococcal dermatoses occur without an increase in ASLO.
Explanation of the analysis for Antistreptolysin-O
/what does Antistreptolysin-O say in a blood test - interpretation of results/
To monitor changes in serum ASLO levels, blood tests are performed at least 2 times with an interval of 1-2 weeks.
| ASLO concentration in blood | Decoding |
| ASLO level exceeds the norm by 4 or more times | a sign of a recent streptococcal infection |
| There is no tendency to decrease ASLO more than 6-8 months after a streptococcal infection | sign of the development of rheumatism Recommendations: - consultation with a rheumatologist |
| The level of ASLO for a long time exceeds the norm by approximately 1.5 -2 times | a sign of carriage of streptococcus or persistent streptococcal infection (for example, with chronic tonsillitis) Recommendations: - throat culture for flora with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics - consultation with an ENT doctor, rheumatologist |
| Normal ASLO levels with prolonged low-grade fever | exclude the diagnosis of active rheumatism |
| Normal ASLO values for suspected rheumatism | do not exclude the diagnosis of rheumatism |
Do normal ASLO values always exclude the disease?
No not always.
Without an increase in ASLO, the following occur: - about 10-15% of cases of rheumatism - up to 20% of severe streptococcal infections - up to 50% of cases of post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis - approximately 60-70% of cases of cutaneous forms of streptococcal infection
What influences/distorts the analysis results?
Reasons for false underestimation of ASL-O
- Early use of antibiotics to treat disease
- Treatment with corticosteroid hormones
- Treatment with immunosuppressants
- Kidney pathology (nephrotic syndrome)
- Hemolysis is the destruction of red blood cells in a blood sample (in this case, the test results are invalid)
Causes of false overestimation of ASL-O
- Hypercholesterolemia (high blood cholesterol)
- Liver diseases
- Tuberculosis
Treatment and reduction of elevated Antistreptolysin-O
ASLO is just an immune “trace” of the body’s recent contact with streptococcus. A high level of this indicator is not dangerous in itself and does not require special treatment or reduction.
Treatment of acute or chronic streptococcal infection is carried out with antibiotics - mainly penicillins.
To relieve pain and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis, NSAIDs are used - mainly Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid).
Effect of ASL-O levels on pregnancy
By themselves, high ASLO levels in pregnant women are safe - they do not in any way affect pregnancy or fetal development.
But if a woman suffers from rheumatism, this complicates the course of pregnancy and childbirth.
With an exacerbation of rheumatism in a pregnant woman: - in the early stages, a miscarriage or disruption of fetal formation may occur; - in the second and third trimester there is a high risk of developing fetal hypoxia, malnutrition and even intrauterine death of the fetus.
Active rheumatic carditis in a pregnant woman is dangerous both for herself and for the unborn child.
Additional examinations
A disorder involving high levels of antistreptolysin-O cannot be detected by this test. It allows you to state the existence of a problem, partially assess its stage, but nothing more.
It is necessary to assign a system of measures as early as possible to obtain complete information.
Among the methods, in addition to our own analysis for ASLO, we can name the following:
- Throat swab. Plays a key role, especially in the detection of acute pathological processes. The task is to assess the flora and its sensitivity to antibiotics of specific species.
Several issues are being addressed at once. The first concerns the statement of the existence of a problem, the detection of streptococcus in a smear. The second is determining treatment tactics. Early selection of medications to combat the disorder.
- General blood test. Used to indirectly confirm the presence of a pathological process. The level of leukocytes and ESR increases, and some other indicators may change. This is not so significant. Especially if the patient has already received any treatment before the start of a comprehensive diagnosis.
- Visual assessment of the condition of the pharynx, structures of the upper respiratory tract. It is carried out as part of an initial examination by an ENT doctor. It’s a routine technique, but that doesn’t make it any less important.
- Biochemical blood test.
In addition to those mentioned, those methods are also shown that can specify the condition of the heart and kidneys. To assess complications and immediate possible causes of changes in ASLO levels. ECG, ECHO, ultrasound of internal organs.
What it is
ASLO (also: ASL O, ASL-O, ASLO) stands for “antistreptolysin-O”. Let's break it down into components.
Streptolysin is a streptococcal exotoxin.
Streptococci are a group of bacteria that, when multiplied in the body, cause extremely unpleasant diseases: scarlet fever, purulent tonsillitis, erysipelas, otitis media, and other purulent inflammations. The word “exotoxin” means that streptolysin, after being produced in the body of the bacterium, is immediately sent out into the human body. Because of this feature, diseases caused by streptococci have an acute onset and develop quickly.
The "O" at the end means that this type of streptolysin is destroyed when exposed to oxygen. There is also streptolysin-S, which is resistant to oxygen, but it is rare.
“Anti” – opposition. Indicates a molecule that fights streptolysin.
Putting it all together, antistreptolysin-O is an immune molecule that destroys streptolysin-O: an oxygen-sensitive exotoxin produced by streptococci.
Research results and their possible dynamics
Let us recall that the study is of diagnostic value if it monitors the dynamics of changes in antibody levels. For this purpose, they are carried out several times.
Let's look at how to decipher the results of laboratory tests as they are carried out.
- The peak of elevated rates is recorded a month after infection. Then it begins a slow and steady decline, which indicates that the body is coping with the pathology.
- A persistent increase in antigen levels is classified as a course of the rheumatic process. A similar complication can also be diagnosed after a sore throat.
- The success of rheumatism treatment is indicated by even a slight decrease in titers 2 months after the onset of the disease.
- The absence of downward dynamics within six months indicates the presence of a relapse.
What to do if abnormalities in the blood test for ASLO are detected? Inflated digital indicators of this laboratory study record the past pathology associated with streptococci. However, high titre values do not pose a danger to human life and health. Therefore, measures aimed at normalizing ASLO are not being taken, while continuing to monitor the dynamics of possible changes.
In adults
Age (years) Level (in IU per milliliter)
| 14-21 | 0-200 |
| 22-25 | 0-220 |
| 26-30 | 0-210 |
| 31-45 | 0-230 |
| 45-60 | 0-240 |
| Over 60 | 0-250 |
ASLO standards are the same for women and men. With age, there is a tendency for the upper level of the reference value (normal range) to increase.
In older people, the adequate level of antistreptolysin O is somewhat higher, which is associated with the accumulated burden of diseases and natural aging processes in the body.
It should be taken into account that there may be some individual deviations regardless of age.
Also, finding a result between the lower and upper bars does not guarantee the absence of streptococcal damage. Everything is extremely conditional and requires verification.
Norm of ASLO in the blood of children of different ages
Antistreptolysin-O may be elevated due to the presence of other hidden infections. If an abnormal indicator is detected, it is recommended to undergo a series of examinations to identify some other pathogens:
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- cytomegalovirus;
- herpes type 6.
They are well determined by a blood test for igg antibodies. Their activity causes damage to the respiratory tract, against the background of which the growth of other infections begins. Treatment in this case is based on the use of antiviral drugs, since antibiotics do not act on viruses.
Only when bacterial complications begin can the doctor recommend another drug to avoid serious consequences and quickly suppress the associated infection. Parents should examine their child if he often suffers from colds. It is these symptoms that mask a streptococcal infection.
| Child's age | Norm, IU/ml |
| Children under 7 years old | Up to 100 |
| 7-14 years | 150-200 |
| Over 14 years old | Up to 250 |
Normal levels of antistreptolysin-O for boys and girls are at the same level.
ASLO during pregnancy
A biochemical blood test during pregnancy is a mandatory laboratory test. At the same time, a slight increase in ASLO indicators in this case does not pose any threat to either the expectant mother or her baby, so treatment is not prescribed. However, the doctor makes such conclusions if the streptococcal infection suffered did not leave behind complications.
Laboratory testing to determine the level of ASLO is more informative in children. This is due to the correct determination of the nature of the disease. Thus, identifying the streptococcal nature of a sore throat requires the use of antibiotics, while other types do not require their use. Incorrect therapy will cause dangerous complications associated with disruption of the functioning of vital internal organs. Such a diagnosis will help determine the advisability of prescribing a specific treatment.
It should be remembered that it makes no sense to decipher the results of the research on your own. This issue is resolved by qualified doctors.
Is treatment necessary?
It should be noted that treatment if ASLO is elevated is not always appropriate.
In each specific case, the doctor must understand the situation in detail and outline ways out of it. The patient should understand this, but if necessary, remind the doctor. If chronic carriage is detected without signs of an acute inflammatory process, the prescription of antibacterial therapy is inappropriate. However, it is necessary to consult with an ENT doctor and dentist to exclude and sanitize the source of chronic infection (carious teeth, chronic tonsillitis, etc.).
If the diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis is confirmed, annual courses of bicillin prophylaxis may be recommended to reduce the risk of rheumatic complications. If tonsillitis occurs in a decompensated form, the question of removing the tonsils is raised.
Patients with reduced immunity are prescribed a course of immunomodulatory therapy and multivitamin preparations (2 times a year) to increase the body's natural resistance to infections.
However, if the disease occurs in the acute phase (acute lacunar tonsillitis, erysipelas, streptococcal pyoderma, etc.), systemic antibacterial therapy is mandatory. The choice of drug and dose depends on the location of the source of infection and the severity of the patient’s condition.
Preference is given to penicillins (aminopenicillins and inhibitor-protected drugs), cephalosporins and macrolides. The duration of taking antibiotics for severe streptococcal infections should be at least 10 days. The rest of the treatment is systematic.
ASLO is higher than normal
If antistreptolysin O is elevated, what does this mean? First of all, this indicates the presence of streptococcal infection in the body. This indicator is also checked for the following diseases:
- Rheumatism,
- Sore throat,
- Myocarditis,
- Scarlet fever,
- Osteomyelitis,
- Otitis,
- Glomerulonephritis.
Unfortunately, it is not practical to use this indicator for emergency diagnosis of infections. This is because after contracting a streptococcal infection, the level of ASLO remains within normal limits for another week. Only on the 8th day the number of antibodies begins to increase, reaching a maximum value a month later. After the patient recovers, the blood condition returns to normal after 6-12 months.
You need to take the test at least 2 times to track the dynamics of the disease and evaluate the effectiveness of the chosen treatment method. The interval between blood donations should be 1.5-2 weeks.
An increased value of ASLO indicators is, for example, a consequence of rheumatoid arthritis and streptococcal rheumatism. This is very important when selecting a course of therapy.
Antistreptolysin analysis is also important in confirming streptolysin in the serum, that is, the presence of bacteria in the body. The course of treatment is based on taking antibiotics. If the moment is missed, then the recovery process will be accompanied by relapses and complications (rheumatic fever, glamerulonephritis).